圆柱绕流是一个典型的流动问题,广泛存在于航空航天、船舶以及风工程[1-2]等实际工程问题中。其流动尾流区域存在卡门涡街、流动分离和层流湍流的转捩等复杂的流动现象[3-4]。长久以来围绕圆柱绕流的流动、减阻等难题进行了深入细致的研究,而对于圆柱绕流噪声的研究却是从1878年Strouhal[5]开始的,接下来也有众多的学者研究了圆柱绕流气动噪声的基本理论和传播机理(例如文献[6-10])。圆柱绕流的噪声现象是基本声源的叠加,即单极子声源、偶极子声源和四极子声源。上述3类噪声源的综合作用严重影响着流场内噪声及远场监测点接收的噪声,其中最主要的是由于流体与圆柱表面相互作用产生的不稳定压力而导致的偶极子声源[11]。Revell等[12]对雷诺数为4.5×104~4.5×105和马赫数为0.1~0.5的表面光滑和粗糙的圆柱绕流气动噪声进行了实验性研究,发现声压级(Sound Pressure Level,SPL)很大程度上受到阻力系数的影响,由此掀起了气动噪声研究热潮,圆柱绕流气动噪声的研究又一次成为气动噪声研究的主角。
目前,国内的气动噪声研究大部分基于数值模拟(例如文献[11, 13-14]),而气动声学实验研究还处在起步阶段,尚亟待开展。因此,在北京航空航天大学D5气动声学风洞进行了圆柱绕流气动声学测量实验,实验段的风速范围在30~80 m/s,雷诺数Re为4.1×104~1.1×105,在亚临界区范围内(300≤Re<3×105),此时,附面层仍为层流分离,而尾迹已转变为湍流涡街。对测量点的声压进行快速傅里叶变换(FFT)可以得到频域下的声压规律、监测点声压级和总声压级(Overall Sound Pressure Level,OASPL)。进而对不同的圆柱绕流流动状态下的声场进行定性与定量的分析,探讨圆柱绕流在亚临界区雷诺数范围内的周期性流动现象的声学特性和圆柱绕流的噪声产生及辐射机理,为进一步研究圆柱等钝体绕流的流动控制和降噪技术做铺垫。
1 实验设备为了研究气动噪声问题,在北京航空航天大学国家流体力学教育部重点实验室建造的1 m×1 m的D5气动声学风洞中进行圆柱绕流气动声学测量实验。风洞的实验设备介绍如下:风扇直径为2.26 m,轮毂比为0.6,转速为750 r/min,风速为100 m/s,电机功率为210 kW,桨叶16片,压增1 600 Pa,效率为83.8%。风洞的总体结构如图 1所示,图中:Ⅰ为喷口(收缩比9∶1);Ⅱ为开口实验段(宽1 m×高1 m×长2 m);Ⅲ为集气口;Ⅳ为闭口实验段;围绕实验段建造了一个6 m×6 m×7 m封闭的全消声室,吸声结构采用平板吸声体,消声室自由场的低频截止频率为200 Hz。
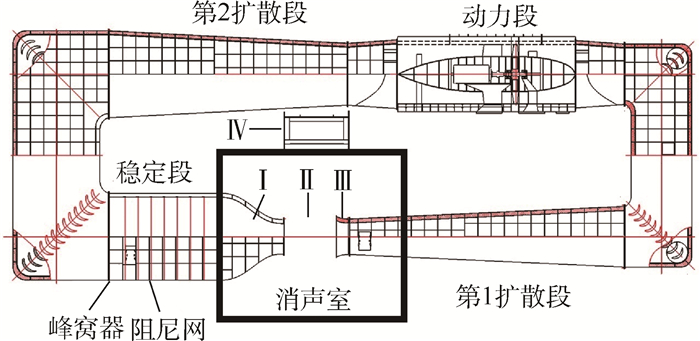
|
| 图 1 D5气动声学风洞总体结构 Fig. 1 Layout of D5 aeroacoustic wind tunnel |
圆柱绕流气动噪声实验是在风洞开口实验段的消声室中进行的,圆柱尺寸为直径0.02 m,位于风洞喷口下游0.8 m的位置上。
实验中,来流速度U范围为30~80 m/s,通过分布在不同监测点位置的传声器的使用,测量得到不同风速下的声压信号,处理得到不同监测点的声压级频谱及其A声级,再通过积分计算得到监测点的总声压级。实验多次测量圆柱噪声,进行重复性检验和修正以消除操作误差。
针对60 m/s来流速度下2.0 m监测点进行了5次噪声实验测量,声压级频谱图和A声级频谱图结果的重复性检验如图 2所示,从图中可以看出偏差基本上在±1 dB范围内,因此说明在相同的条件下实验风洞流场和声场在不同时刻具有良好的稳定性。

|
| 图 2 实验重复性检验 Fig. 2 Experimental repeatability test |
在U=30~80 m/s条件下,监测点分别位于圆柱轴线距离2.0 m和2.5 m的垂直位置上,测得的圆柱绕流气动噪声的频谱图与对应来流速度下风洞的背景噪声进行对比,结果如图 3和图 4所示。
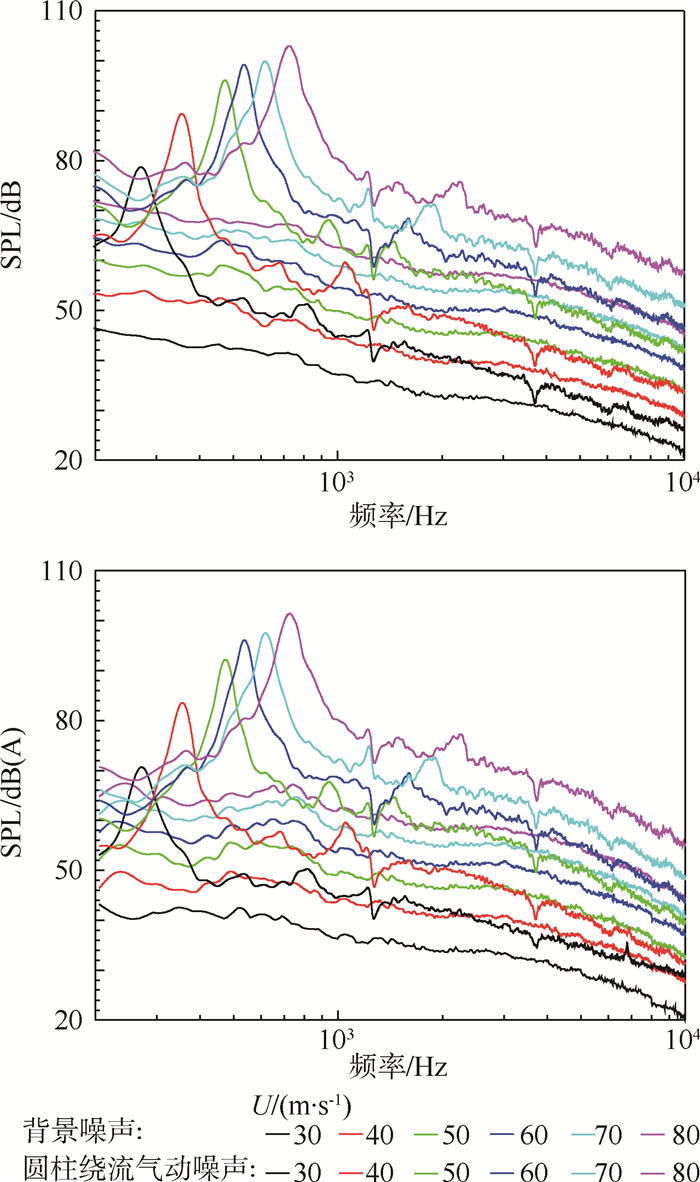
|
| 图 3 2.0 m处不同来流速度下的声压级频谱 Fig. 3 SPL spectrum of 2.0 m at different speeds |
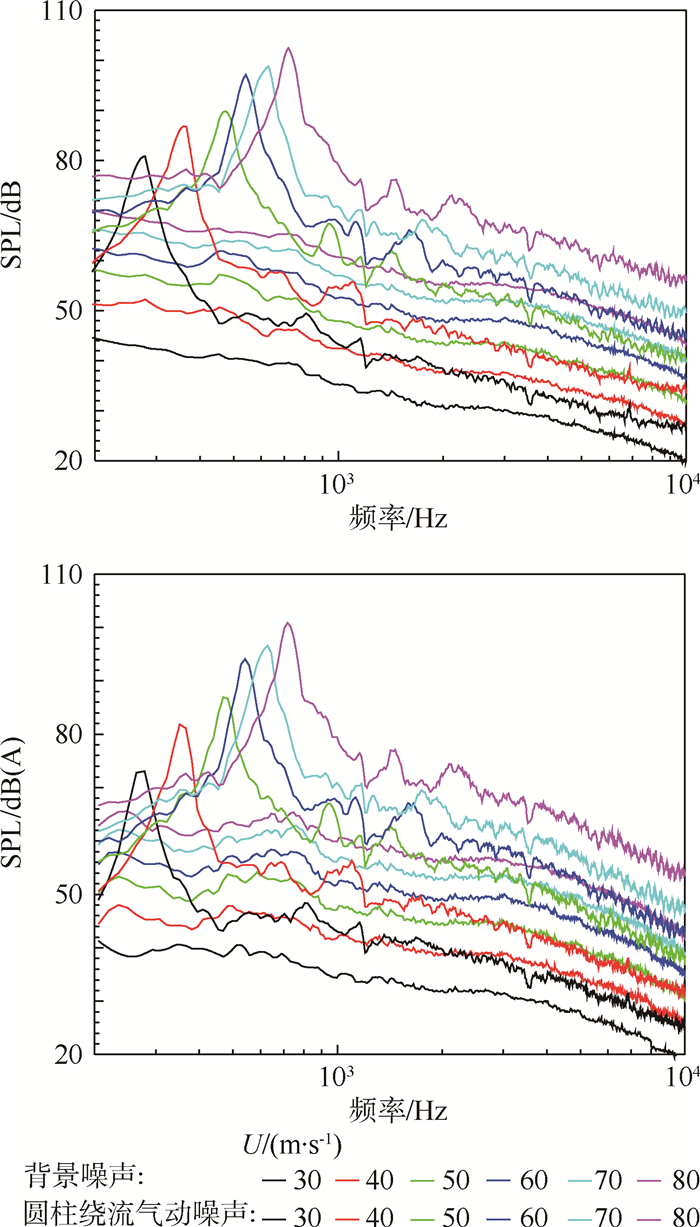
|
| 图 4 2.5 m处不同来流速度下的声压级频谱 Fig. 4 SPL spectrum of 2.5 m at different speeds |
通过图 3和图 4可以看出圆柱绕流气动噪声的声压级高于风洞背景噪声的声压级曲线,而且都大于5 dB,尤其圆柱主频下的声压级尖峰值要高于背景噪声30 dB以上,说明风洞能很好地测量圆柱噪声和捕捉圆柱的主频及尖峰。
同时从图 3和图 4中还可以看出,随着来流速度的增加,圆柱绕流气动及背景噪声的声压级都在逐渐递增,圆柱绕流气动噪声与背景噪声的间距也越来越大,圆柱绕流气动噪声的主频在逐渐递增。对于圆柱这种典型的钝体而言,其尾迹流动常用量纲分析后获得的周期性流动特征的相似准数——斯特劳哈尔数(St)进行描述[15]。
通过St=fD/U(f为频率,D为圆柱直径)和圆柱绕流气动噪声声压级与U6成正比这2个数学关系式,将频率和声压级进行无量纲化处理,参考速度Uref=10 m/s,得到2.0 m和2.5 m监测点的无量纲声压级SPL-60lg(U/Uref)随St的频谱图,如图 5所示。
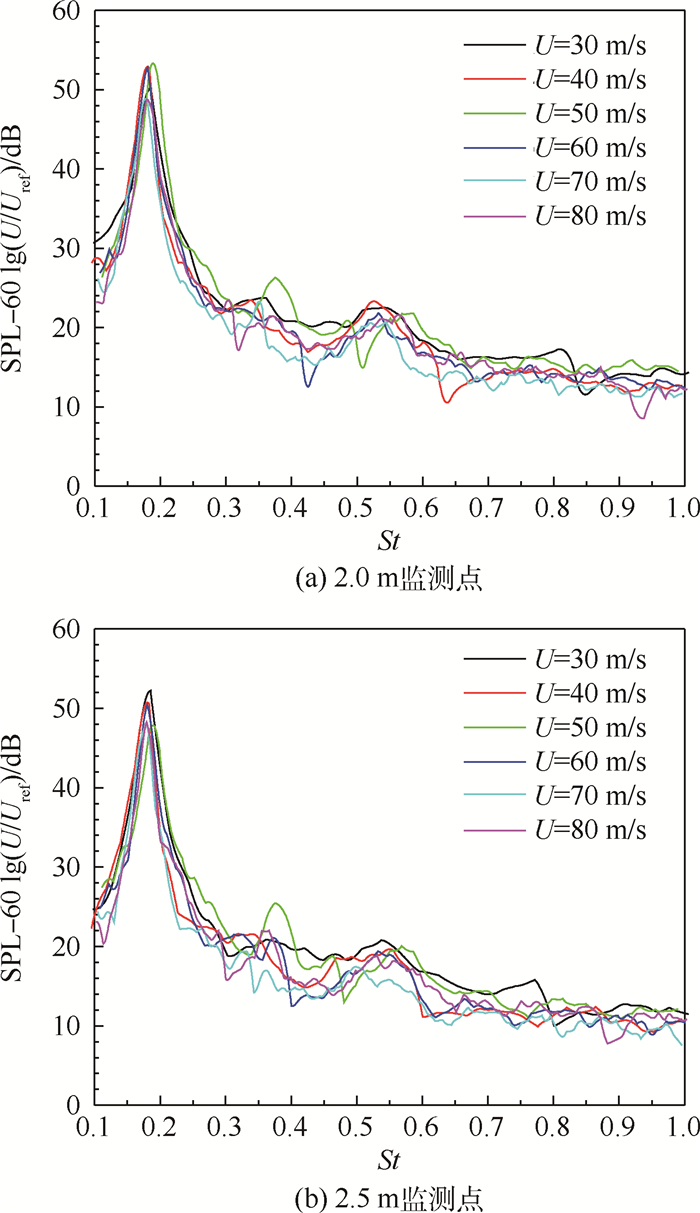
|
| 图 5 2.0 m和2.5 m处无量纲声压级频谱 Fig. 5 Non-dimensional SPL spectrum of 2.0 m and 2.5 m |
通过图 5可以看出,圆柱绕流的监测点噪声近似与U6成正比,St在一个很小的范围内波动。由于本实验的来流速度范围为30~80 m/s,相应Re=4.1×104~1.1×105,在亚临界雷诺数范围内。亚临界雷诺数范围内Revell等[12]实验得到St=0.195~0.200,Norberg[16]实验得到St=0.180~0.191;在Re=1.6×103~1.5×105,St的经验公式为St=0.185 3+0.026 1e-0.9x2.3,x=lg(Re/1 600)。将圆柱监测点声压级的主频进行整理,与经验公式求得的对应雷诺数下的St进行对比,其结果见表 1和表 2。
| U/(m·s-1) | Re | St | St参考值 | 误差/% |
| 30 | 4.1×104 | 0.176 | 0.188 9 | 6.7 |
| 40 | 5.5×104 | 0.176 | 0.187 6 | 6.1 |
| 50 | 6.8×104 | 0.188 | 0.186 8 | 0.6 |
| 60 | 8.2×104 | 0.181 | 0.186 5 | 2.9 |
| 70 | 9.6×104 | 0.176 | 0.186 2 | 5.4 |
| 80 | 1.1×105 | 0.180 | 0.186 0 | 3.2 |
| U/(m·s-1) | Re | St | St参考值 | 误差/% |
| 30 | 4.1×104 | 0.176 | 0.188 9 | 6.7 |
| 40 | 5.5×104 | 0.176 | 0.187 6 | 6.1 |
| 50 | 6.8×104 | 0.188 | 0.186 8 | 0.6 |
| 60 | 8.2×104 | 0.181 | 0.186 5 | 2.9 |
| 70 | 9.6×104 | 0.180 | 0.186 2 | 3.3 |
| 80 | 1.1×105 | 0.180 | 0.186 0 | 3.2 |
通过表 1和表 2中可以看出,此次实验的结果与Revell等[12]和Norberg[16]的实验与经验公式得到的涡脱落频率基本上相差不大,除个别来流速度条件下实验结果存在6%的误差,其他情况与已有结果吻合良好,说明实验误差在可以接受的范围之内,进一步说明在D5气动声学风洞内进行的圆柱绕流气动噪声实验是确信可靠的。
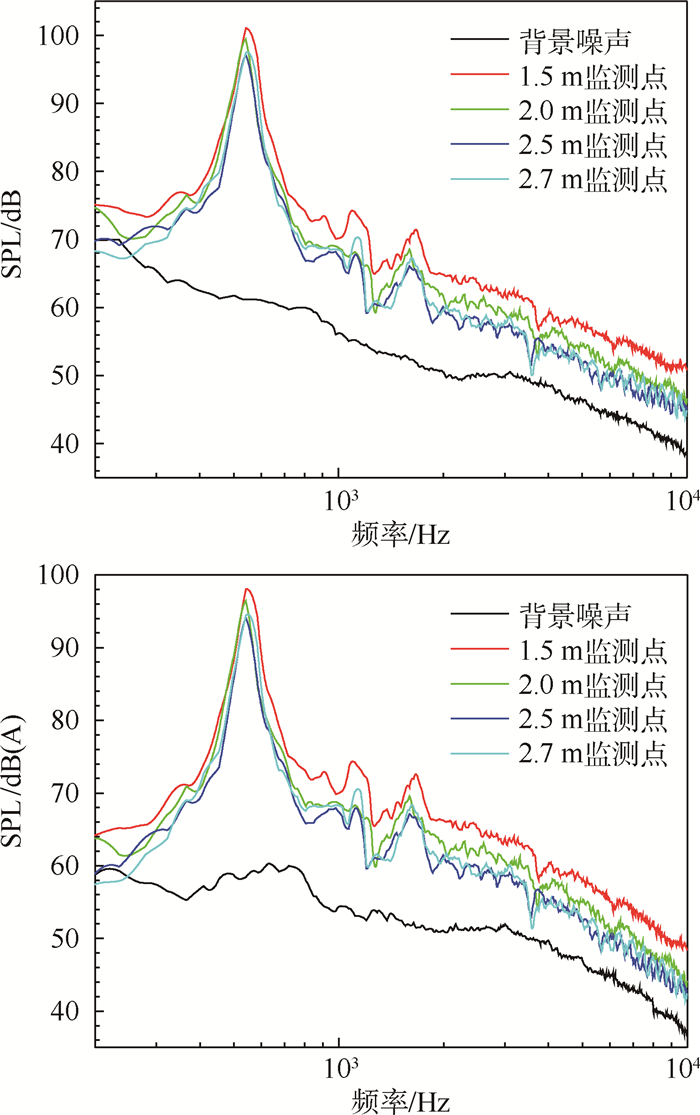
3.2 不同距离圆柱绕流气动噪声在60 m/s来流速度条件下测量圆柱绕流气动噪声,监测点位于喷口下游0.8 m的位置,同时距离圆柱轴线1.5、2.0、2.5、2.7 m,测量得到圆柱绕流声压级频谱和A声级频谱,如图 6所示。
|
| 图 6 U=60 m/s不同距离的声压级频谱 Fig. 6 SPL spectrum of different distances at U=60 m/s |
从图 6可以看出,距离圆柱轴线不同位置的监测点的声压级基本上满足其距离越远声压级越低的关系,而且声压级的曲线基本上是平移的关系,1.5 m监测点要高出2.0 m监测点4 dB左右,2.0 m监测点噪声比2.5 m监测点噪声要大2 dB左右,2.5 m和2.7 m由于距离间隔较小,基本上是重合的2条曲线。
同时从图 6可以看出,尽管监测点的距离有所不同,但是频谱图的尖峰值对应的主频基本上是相同的,也就说明捕捉到的圆柱尾缘的涡脱落周期是一致的。
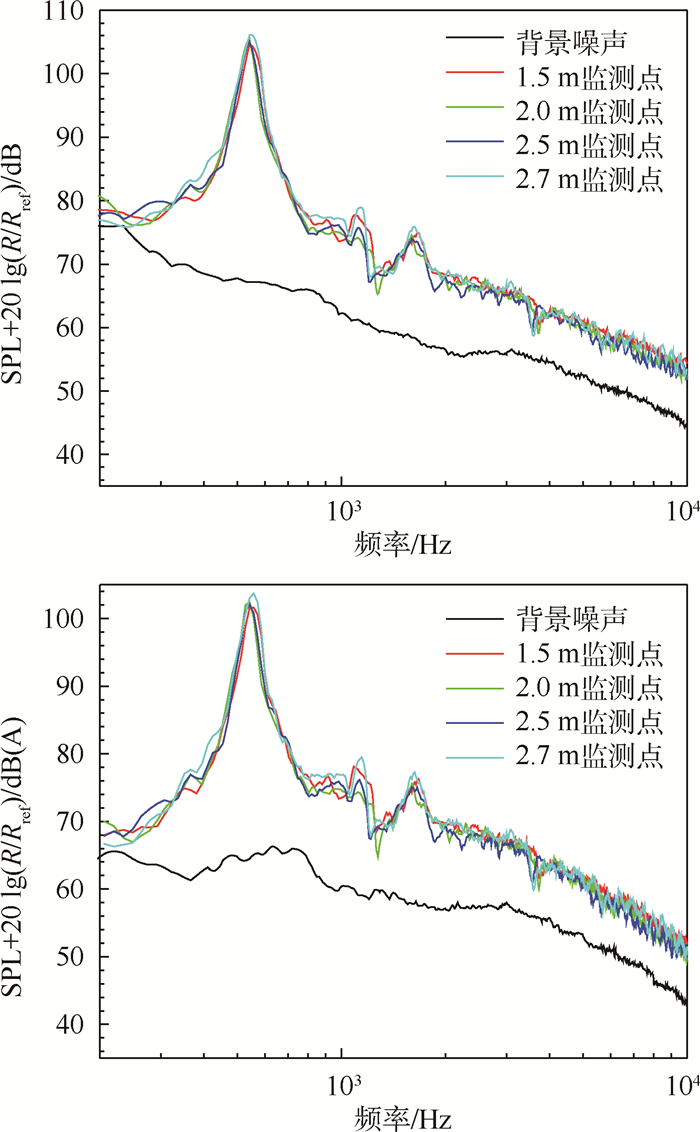
为了进一步观察圆柱绕流监测点声压级与监测点到声源的距离的关系,取参考距离Rref=1 m,对监测点到声源的距离进行了声压级无量纲化SPL+20lg(R/Rref)处理,得到声压级频谱和A声级频谱,如图 7所示。
|
| 图 7 不同距离无量纲后的声压级频谱 Fig. 7 Non-dimensional SPL spectrum of different distances |
通过图 7可以看出,对监测点到声源的距离进行无量纲化之后,不同声传播距离的声压级频谱图基本上重合为一条曲线,显著地表明其声压级的尖峰值对应着相同的尾缘涡脱落频率,同时也验证了该圆柱绕流气动噪声的声压级基本上满足与声传播距离的2次方成反比的数值关系。
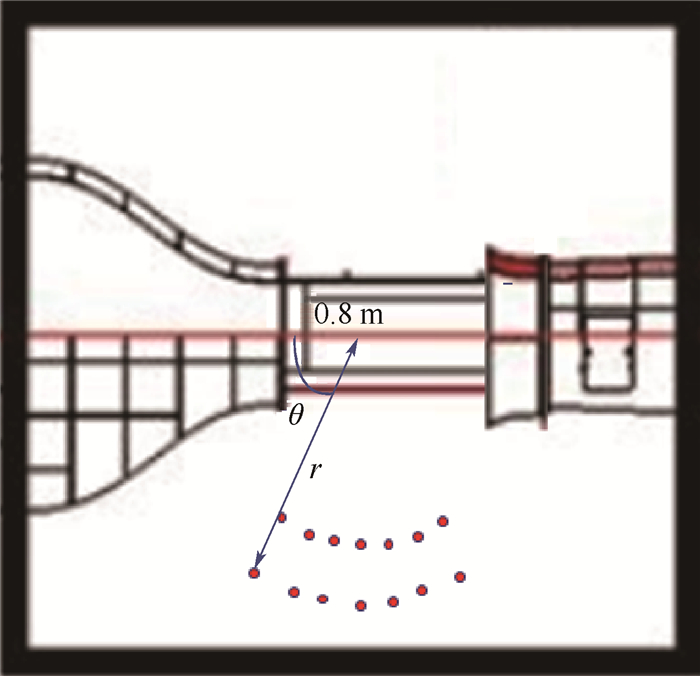
3.3 圆柱绕流气动噪声指向性为研究圆柱绕流气动噪声问题的指向性,将监测点如图 8所示布置:监测点在距离圆柱轴线2.0 m和2.5 m的圆周半径r上,偏角θ变化范围是60°~120°,间隔是10°,一共布置14个监测点进行声压级指向性的测量。
|
| 图 8 指向性监测点分布示意图 Fig. 8 Schematic of directivity arrangement of monitors |
传感器测量的声压,经过快速傅里叶变换得到声压级,通过积分可以得到不同速度下不同监测点的总声压级。2.0 m和2.5 m监测点在不同来流速度下的总声压级的指向性曲线如图 9所示。总声压-A声级的指向性曲线如图 10所示。

|
| 图 9 不同来流速度下总声压级的指向性曲线 Fig. 9 Directivity curves of OASPL at different speeds |

|
| 图 10 不同来流速度下总声压-A声级的指向性曲线 Fig. 10 Directivity curves of A-weighted OASPL at different speeds |
从图 9和图 10可以看出,随着来流速度的增加,监测点总声压级逐渐升高。同时还可以看出,圆柱绕流的噪声特性基本上是与来流方向成90°的监测点总声压级最大,向喷口和集气口方向偏移的监测点的总声压级都逐渐递减,大体上满足偶极子噪声源的噪声特性。
但是在r=2 m的指向性圆周上,当θ=120°,即越靠近集气口的监测点声压级没有如预测似的下降反而却有所增加,这可能是由于r=2 m圆周上,偏转120°的监测点距离风洞轴线较近,而风洞喷收口边缘到风洞中心轴线的距离是0.5 m,布置较近的监测点可能会受到一定程度的风场的干扰。同时也可能是由于监测点布置的距离及角度在测量上存在操作误差。
4 结 论通过在北京航空航天大学D5气动声学风洞进行的圆柱绕流气动声学实验,得到了圆柱绕流在亚临界区雷诺数范围内的声学特性和圆柱绕流的噪声产生及辐射机理。
1) 圆柱表面交替涡脱落产生的非定常脉动力是产生噪声的主要原因,远场噪声指向性在垂直气流方向最大,随着偏离垂直方向角度的增大噪声逐渐减小,属于典型的偶极子噪声源辐射特性。
2) 随着来流速度的增加,接收点到声源距离的减小,监测点的声压级增大;而且圆柱绕流气动噪声与来流速度的6次方成正比,与接收点到声源距离的2次方成反比,进一步说明偶极子类型的噪声源是圆柱绕流的主要噪声源。
| [1] | BECKER S,KALTENBACHER M,ALI I.Aeroacoustic investigation of the flow around cylinder geometries:A benchmark test case[C]//13th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference (28th AIAA Aeroacoustics Conference).Reston:AIAA,2007:1-14. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [2] | CATALALANO P, WANG M, IACCARINO G. Numerical simulation of the flow around a circular cylinder at high Reynolds numbers[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow,2003, 24 (4) : 463 –469. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [3] | 夏雪湔, 邓学蓥. 工程分离流动力学[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 1991 : 157 -211. XIA X J, DENG X Y. Flow separation engineering mechanics[M]. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 1991 : 157 -211. (in Chinese). |
| Cited By in Cnki (0) | Click to display the text | |
| [4] | 邢国清. 流体力学泵与风机[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2009 : 14 -98. XING G Q. Fluid mechanics pump and fan[M]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2009 : 14 -98. (in Chinese). |
| Cited By in Cnki (0) | Click to display the text | |
| [5] | STROUHAL V. Ueber eine besondere art der tonerregung[J]. Annalen Der Physik,1878, 241 (10) : 216 –251. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [6] | GERRARD J H. Measurements of the sound from circular cylinders in an air stream[J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society,1955, 68 : 453 –461. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [7] | CURLE N. The influence of solid boundaries upon aerodynamic sound[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A,1955, 231 (1187) : 505 –514. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [8] | PHILLIPS O M. The intensity of Aeolian tones[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics,1956, 1 (6) : 607 –624. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [9] | ETKIN B, KORBACHER G K, KEEFE R T. Acoustic radiation from a stationary cylinder in a fluid stream (Aeolian tones)[J]. Acoustical Society of America Journal,1957, 29 (1) : 30 –36. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [10] | GERRARD J H. An experimental investigation of the oscillating lift and drag of a circular cylinder shedding turbulent vortices[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics,1961, 11 (2) : 244 –256. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [11] | 龙双丽, 聂宏, 许鑫. 不同雷诺数下圆柱绕流气动噪声数值模拟[J]. 声学技术,2011, 30 (2) : 111 –116. LONG S L, NIE H, XU X. Numerical simulation of noise induced by flow around a cylinder at different Reynolds number[J]. Technical Acoustics,2011, 30 (2) : 111 –116. (in Chinese). |
| Cited By in Cnki (0) | Click to display the text | |
| [12] | REVELL J D, PRYDZ R A, HAYS A P. Experimental study of aerodynamic noise vs drag relationships for circular cylinders[J]. AIAA Journal,1978, 16 (9) : 889 –897. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [13] | 唐科范, FRANKEJ. 用解NS方程和FW-H积分的混合方法计算圆柱绕流噪声[J]. 水动力学研究与进展,2009, 24 (2) : 190 –199. TANG K F, FRANKE J. Numerical simulation of noise induced by flow around cylinder using the hybrid method with the solutions of NS equation and FW-H integration[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics,2009, 24 (2) : 190 –199. (in Chinese). |
| Cited By in Cnki (0) | Click to display the text | |
| [14] | 陈宗广, 郭鹏. 圆柱绕流空气动力噪声数值模拟[J]. 声学技术,2013, 32 (4) : 65 –68. CHEN Z G, GUO P. Numerical simulation of aerodynamics noise induced by flow around a circular cylinder[J]. Technical Acoustics,2013, 32 (4) : 65 –68. (in Chinese). |
| Cited By in Cnki (0) | Click to display the text | |
| [15] | ORSELLI R M,MENEGHINI J R,SALTAR F.Two and three dimensional simulation of sound generated by flow around a circular cylinder[C]//15th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference (30th AIAA Aeroacoustics Conference).Reston:AIAA,2009:11-13. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [16] | NORBERG C. Fluctuating lift on a circular cylinder:Review and new measurements[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures,2003, 17 (1) : 57 –96. |
| Click to display the text | |



