Analysis and optimization of temperature field uniformity of proton exchange furnace
-
摘要:
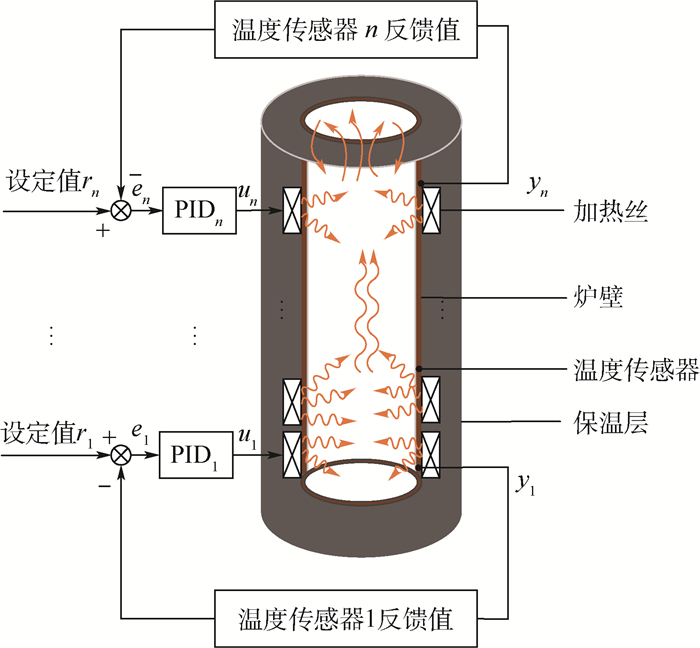
针对质子交换炉的温度场均匀性问题,结合质子交换炉的结构特点,基于FLUENT用户自定义函数(UDF)开发了质子交换炉炉温控制算法,并在此基础上提出了多种加热控温方案;利用FLUENT软件对不同方案下的质子交换炉温度场进行仿真,分析不同控温方式下炉内温度场均匀性与传感器位置布置、加热丝布置高度的关系,找到最佳方案。结果表明:采用三段控温、3个传感器位置分别布置在3段加热丝中间、加热丝布置高度4倍于均匀温区长度时炉内温度场均匀性最好,均匀温区内最大偏差为0.03℃;对于既定结构的立式炉体,增加加热丝布置高度、优化设计传感器布置方案和炉体控温方式可以提高温度场均匀性。该方法为同类电加热炉温度场均匀性的优化设计提供了思路。
Abstract:Aimed at the problem of temperature field uniformity of proton exchange furnace, combined with the structural characteristic of the furnace, temperature control algorithm was developed based on FLUENT user-defined function (UDF). Based on this, various heating and temperature control schemes were proposed. The FLUENT software was used to simulate temperature field of the furnace under different schemes. The relationship between the temperature field uniformity and the placement of the sensor and the height of the heating wire under different temperature control methods was analyzed to find the best scheme. The results show that the temperature field uniformity is best when three temperature controllers are used, the positions of three sensors are respectively arranged in the middle of three heating wires, and the height of heating wire is arranged 4 times the length of the uniform temperature zone. The maximum temperature deviation in the uniform temperature zone is 0.03℃. For a given structure of the vertical furnace, increasing the height of the heating wire and optimizing the design of the sensor layout and temperature control method of the furnace body can improve the temperature field uniformity. This method provides ideas for optimizing temperature field uniformity of the same type of electric heating furnace.
-
Key words:
- LiNbO3 waveguides /
- proton exchange furnace /
- temperature field /
- uniformity /
- numerical simulation
-
表 1 边界条件的设置
Table 1. Boundary condition setting
边界名称 边界类型 边界条件 参数 炉顶 壁面 对流 传热系数=10W/(m2·K)自由流体温度为300K 炉壁 壁面 热流量 没有加热丝覆盖的壁面:热流量=0;有加热丝覆盖的壁面:热流量=UDF flux 炉底 壁面 热流量 热流量=0 表 2 18种设计方案
Table 2. 18 kinds of design schemes
序号 控温方式 传感器位置布置 加热丝布置高度/m 1 整段控温 z=0 h=2Δh=0.4 2 h=3Δh=0.6 3 h=4Δh=0.8 4 z=0.2m h=2Δh=0.4 5 h=3Δh=0.6 6 h=4Δh=0.8 7 两段控温 组合方式1 h=2Δh=0.4 8 h=3Δh=0.6 9 h=4Δh=0.8 10 组合方式2 h=2Δh=0.4 11 h=3Δh=0.6 12 h=4Δh=0.8 13 三段控温 组合方式1 h=2Δh=0.4 14 h=3Δh=0.6 15 h=4Δh=0.8 16 组合方式2 h=2Δh=0.4 17 h=3Δh=0.6 18 h=4Δh=0.8 表 3 3种控温方式下的最佳方案对比
Table 3. Comparison of the best solutions under three temperature control methods
序号 最佳方案 最大偏差ΔTmax/℃ 3 整段控温,传感器位置布置在z=0,加热丝布置高度h=4Δh 1.73 12 两段控温,传感器位置布置组合方式2,加热丝布置高度h=4Δh 0.95 18 三段控温,传感器位置布置组合方式2,加热丝布置高度h=4Δh 0.03 -
[1] FAKHRI M A, AL-DOURI Y, HASHIM U, et al.Optical investigation of nanophotonic lithium niobate-based optical waveguide[J].Applied Physics B, 2015, 121(1):107-116. doi: 10.1007/s00340-015-6206-x [2] CAO L, ABOKETAF A, WANG Z H, et al.Hybrid amorphous silicon(a-Si:H)-LiNbO3 electro-optic modulator[J].Optics Communications, 2014, 330:40-44. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2014.05.021 [3] FAKHRI M A, AL-DOURI Y, HASHIM U, et al.Annealing temperature effects on morphological and optical studies of nano and micro photonics lithium niobate using for optical waveguide applications[J].Australian Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences, 2015, 9(12):128-133. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8ec99da3-de94-48c8-ba62-8d5d41c7af2b [4] SHEN L, HE J J, YANG C H, et al.Temperature uniformity control of large-scale vertical quench furnaces for aluminum alloy thermal treatment[J].IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2015, 24(1):24-39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d5919295987cd122ec120cb60ed4bcad [5] EMADI A, SABOONCHI A, TAHERI M, et al.Heating characteristics of billet in a walking hearth type reheating furnace[J].Applied Thermal Engineering, 2014, 63(1):396-405. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2013.11.003 [6] LING Z, CHEN J, FANG X, et al.Experimental and numerical investigation of the application of phase change materials in a simulative power batteries thermal management system[J].Applied Energy, 2014, 121:104-113. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.01.075 [7] PANG L, WANG M, WANG W, et al.Optimal thermal design of a stacked mini-channel heat sink cooled by a low flow rate coolant[J].Entropy, 2013, 15(11):4716-4731. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_c495d6c38835bc326683c2d3acccfe16 [8] 唐家鹏.ANSYS FLUENT 16.0超级学习手册[M].北京:人民邮电出版社, 2016:502-507.TANG J P.ANSYS FLUENT 16.0 super study manual[M].Beijing:People's Posts and Telecommunications Press, 2016:502-507(in Chinese). [9] CHICATELLI A, HARTLEY T T, COLE G, et al.Interdisciplinary modeling using computational fluid dynamics and control theory[C]//American Control Conference.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 1994, 3: 3438-3443. [10] YANG Y, REUTER M A, HARMAN D T M.CFD modelling for control of hazardous waste incinerator[J].Control Engineering Practice, 2003, 11(1):93-101. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5f690df21c8c3996f7012fc132f3ce9f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [11] GAO X J, WANG S Y, WANG P.The evaluation method of PID controller parameter tuning based on FLUENT[C]//Control and Decision Conference.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 4850-4854. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7162784 [12] 李友荣, 吴双应, 石万元, 等.传热分析与计算[M].北京:中国电力出版社, 2013:3-15.LI Y R, WU S Y, SHI W Y, et al.Heat transfer analysis and calculation[M].Beijing:China Electric Power Press, 2013:3-15(in Chinese). [13] 王福军.计算流体动力学分析:CFD软件原理与应用[M].北京:清华大学出版社, 2004:7-11.WANG F J.Computational fluid dynamics analysis:Principles and applications of CFD software[M].Beijing:Tsinghua University Press, 2004:7-11(in Chinese). [14] 朱能伟, 方晓东.基于FLUENT的准分子激光器气体流场数值仿真[J].中国激光, 2016, 43(9):44-49. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgjg201609007ZHU N W, FANG X D.Numerical simulation of gas flow field in excimer laser based on FLUENT[J].Chinese Laser, 2016, 43(9):44-49(in Chinese). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgjg201609007 [15] 胡坤, 李振北.ANSYS ICEM CFD工程实例详解[M].北京:人民邮电出版社, 2014:34-39.HU K, LI Z B.Detailed explanation of ANSYS ICEM CFD project[M].Beijing:People's Posts and Telecommunications Press, 2014:34-39(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: