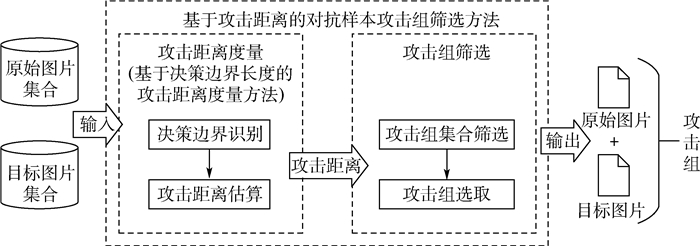
A method for filtering the attack pairs of adversarial examples based on attack distance
-
摘要:
黑盒对抗样本生成过程中通常会指定1个攻击组,包括1个原始样本和1个目标样本,使得生成的对抗样本与原始样本范数差别不大,但被分类器识别为目标样本的分类。针对攻击组的攻击难度不同导致攻击不稳定的问题,以图像识别领域为例,设计了基于决策边界长度的攻击距离度量方法,为攻击组的攻击难易程度提供了度量方法。在此基础上,设计了基于攻击距离的对抗样本攻击组筛选方法,在攻击开始前就筛去难以攻击的攻击组,从而实现在不修改攻击算法的前提下,提升攻击效果。实验表明:相比于筛选前的攻击组,筛选后的攻击组的总体效果提升了42.07%,攻击效率提升了24.99%,方差降低了76.23%。利用攻击组的对抗样本生成方法在攻击前先进行攻击组筛选,可以稳定并提高攻击效果。
Abstract:During the generation of black-box adversarial examples, an attack pair is usually specified, including a source example and a target example. The purpose is to let the generated adversarial example only have little norm difference from the source example, but it is recognized by the classifier as the classification of the target sample. In order to solve the problem of the instability of adversarial attacks caused by different attack difficulty of attack pairs, taking the image recognition field as an example, this paper presented an attack distance measurement method based on the length of the decision boundary, which provided a measurement method for the attack difficulty of attack pairs. Then this paper designed a filtering method based on attack distance of the attack pairs, which filtered out attack pairs that were difficult to attack before the attack started, so this method can improve the attack performance without modifying the attack algorithm. Experiments show that, compared with the attack pairs before filtering, the filtered attack pairs improve the overall attack performance by 42.07%, improve the attack efficiency by 24.99%, and stabilize the variance by 76.23%. It is recommended that all methods of generating adversarial examples using attack pairs should filter attack pairs before attack to stabilize and improve the attack performance.
-
Key words:
- adversarial examples /
- black box /
- decision boundary /
- filtering /
- image recognition
-
表 1 筛选前后查询次数对比
Table 1. Comparison of query times before and after filtering
场景 指标 NES Attack Filtered NES CMA Attack Filtered CMA 平均提升效果/% 场景1 平均值 1.01×105 7.87×104 5.81×104 2.88×104 36.25 中位数 9.64×104 7.22×104 4.74×104 2.74×104 33.65 方差 1.51×109 1.16×109 1.32×109 9.36×107 58.04 场景2 平均值 9.79×104 9.66×104 4.75×104 4.26×104 5.82 中位数 9.63×104 9.66×104 4.33×104 4.26×104 0.65 方差 1.00×109 4.20×108 2.99×108 1.14×107 77.09 场景3 平均值 9.76×104 6.64×104 5.92×104 3.05×104 40.22 中位数 8.98×104 6.64×104 5.14×104 3.05×104 33.36 方差 9.52×108 3.59×106 6.22×108 7.79×107 93.55 -
[1] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. doi: 10.1145/3065386 [2] SZEGEDY C, LIU W, JIA Y Q, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]//2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-9. [3] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2015-04-10)[2020-09-21]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556. [4] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [5] HUANG G, LIU Z, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2261-2269. [6] SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, et al. Intriguing properties of neural networks[EB/OL]. (2014-02-19)[2020-09-21]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6199. [7] GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, SZEGEDY C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples[EB/OL]. (2015-05-20)[2020-09-21]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6572. [8] KURAKIN A, GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO S. Adversarial machine learning at scale[EB/OL]. (2017-02-11)[2020-09-21]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.01236. [9] MADRY A, MAKELOV A, SCHMIDT L, et al. Towards deep learning models resistant to adversarial attacks[EB/OL]. (2019-09-04)[2020-09-21]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.06083. [10] DONG Y P, LIAO F Z, PANG T, et al. Boosting adversarial attacks with momentum[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 9185-9193. [11] CARLINI N, WAGNER D. Towards evaluating the robustness of neural networks[C]//2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 39-57. [12] PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, JHA S, et al. The limitations of deep learning in adversarial settings[C]//2016 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 372-387. [13] MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, FAWZI A, FROSSARD P. DeepFool: A simple and accurate method to fool deep neural networks[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 2574-2582. [14] PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, GOODFELLOW I, et al. Practical black-box attacks against deep learning systems using adversarial examples[EB/OL]. (2017-05-19)[2020-09-21]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.02697. [15] XIE C H, ZHANG Z S, ZHOU Y Y, et al. Improving transferability of adversarial examples with input diversity[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 2725-2734. [16] TRAMER F, KURAKIN A, PAPERNOT N, et al. Ensemble adversarial training: Attacks and defenses[EB/OL]. (2020-04-26)[2020-09-21]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.07204. [17] ILYAS A, ENGSTROM L, ATHALYE A, et al. Black-box adversarial attacks with limited queries and information[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning, 2018: 2137-2146. [18] KUANG X H, LIU H Y, WANG Y, et al. A CMA-ES-based adversarial attack on black-box deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 172938-172947. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2956553 [19] DONG Y P, SU H, WU B Y, et al. Efficient decision-based black-box adversarial attacks on face recognition[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 7706-7714. [20] BRENDEL W, RAUBER J, BETHGE M. Decision-based adversarial attacks: Reliable attacks against black-box machine learning models[EB/OL]. (2018-02-16)[2020-09-21]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.04248. [21] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436-444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539 [22] HELMSTAEDTER M, BRIGGMAN K L, TURAGA S C, et al. Connectomic reconstruction of the inner plexiform layer in the mouse retina[J]. Nature, 2013, 500(7461): 168-174. doi: 10.1038/nature12346 [23] XIONG H Y, ALIPANAHI B, LEE L J, et al. The human splicing code reveals new insights into the genetic determinants of disease[J]. Science, 2015, 347(6218): 1254806. doi: 10.1126/science.1254806 [24] HINTON G, DENG L, YU D, et al. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: The shared views of four research groups[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2012, 29(6): 82-97. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2012.2205597 [25] SUTSKEVER I, VINYALS O, LE Q V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks[C]//Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS). Cambridge: MIT Press, 2014: 3104-3112. [26] MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529-533. doi: 10.1038/nature14236 [27] GIUSTI A, GUZZI J, CIRŞAN D C, et al. A machine learning approach to visual perception of forest trails for mobile robots[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2016, 1(2): 661-667. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2015.2509024 [28] MIDDLEHURST C. China unveils world's first facial recognition atm[EB/OL]. (2015-01-01)[2020-09-01]. https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/asia/china/11643314/China-unveils-worlds-first-facial-recognition-ATM.html. [29] 刘恒, 吴德鑫, 徐剑. 基于生成式对抗网络的通用性对抗扰动生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(5): 57-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXAQ202005008.htmLIU H, WU D X, XU J. Generating universal adversarial perturbations with generative adversarial networks[J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(5): 57-64(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXAQ202005008.htm [30] HUANG Q, KATSMAN I, GU Z Q, et al. Enhancing adversarial example transferability with an intermediate level attack[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4732-4741. [31] WIERSTRA D, SCHAUL T, PETERS J, et al. Natural evolution strategies[C]//2008 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2008: 3381-3387. [32] HANSEN N. The CMA evolution strategy: A tutorial[EB/OL]. (2016-04-04)[2020-09-21]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1604.00772. [33] 侯留洋, 罗森林, 潘丽敏, 等. 融合多特征的Android恶意软件检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(1): 67-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXAQ202001012.htmHOU L Y, LUO S L, PAN L M, et al. Multi-feature Android malware detection method[J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(1): 67-74(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXAQ202001012.htm -







 下载:
下载: