-
摘要:
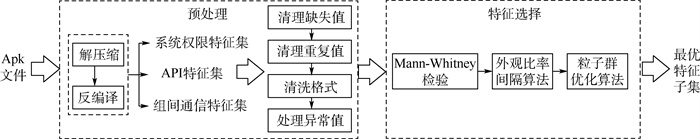
针对Android恶意软件检测特征选择中,对类间具有相同频率分布的特征过度关注而导致特征冗余问题,提出了一种Android恶意软件检测低冗余特征选择方法。利用Mann-Whitney检验方法选择出存在频率分布偏差的特征;通过外观比率间隔算法量化偏差程度和特征出现频率剔除低偏差和整体软件中低频使用的特征;结合粒子群优化算法和分类器检测效果得到最优特征子集。使用公开数据集DREBIN和AMD进行实验,实验结果显示,在AMD数据集上选择出了294维特征,进行特征选择后6种分类器的检测准确率提高了1%~5%,在DREBIN数据集上选择出了295维特征,少于4种对比方法,且进行特征选择后6种分类器的检测准确率提高了1.7%~5%。实验结果表明,所提方法能够降低Android恶意软件检测中特征的冗余性,提升恶意软件的检测准确率。
-
关键词:
- Android恶意软件检测 /
- 特征选择 /
- Mann-Whitney检验 /
- 粒子群优化算法 /
- 外观比率间隔算法
Abstract:A low redundancy feature selection method for Android malware detection is proposed to solve the problem of feature redundancy caused by excessive attention to features with the same frequency distribution between classes. First, the method selects features with frequency distribution bias by Mann-Whitney test, and then quantifies the degree of bias and feature appearance frequency by the appearance ratio interval algorithm to reject features with low bias and low use frequency in the overall software. Finally, the particle swarm optimization algorithm is combined with model detection effect to obtain the optimal feature subset. Experiments were conducted using public datasets DREBIN and AMD. The experimental results show that 294-dimensional features were selected on the AMD dataset, and the detection accuracy of the six classifiers is improved by 1%-5%, 295-dimensional features were selected on the DREBIN dataset less than 4 comparison methods, and the detection accuracy of the six classifiers is improved by 1.7%-5%. The experimental results illustrate that the proposed method can reduce the redundancy of features in Android malware detection and improve the malware detection accuracy.
-
表 1 初始特征信息
Table 1. Initial feature information
特征类型 数目 特征 系统权限 24 READ CALENDAR WRITE CALENDAR CAMERA READ CONTACTS WRITE CONTACTS …… API 620 android/net/ConnectivityManager;
startUsingNetworkFeatureandroid/net/wifi/WifiManager;
enableNetworkandroid/net/wifi/WifiManager;
disconnectandroid/net/wifi/WifiManager;
setWifiEnabled…… 组间通信Intent 45 Android.intent.action.MAIN Android.intent.action.VIEW Android.intent.action.ATTACH DATA Android.intent.action.EDIT Android.intent.action.PICK …… 表 2 Mann-Whitney检验输入矩阵
Table 2. Mann-Whitney test input matrix
数据集 特征fi 数据集 特征fi 恶意软件1 0 良性软件1 0 恶意软件2 0 良性软件2 0 恶意软件3 0 良性软件3 1 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ 恶意软件n Bf 良性软件m Mf 表 3 实验所用软件资源
Table 3. Software resources used in experiment
软件名称 来源 Python 3.7.3 https://www.python.org/(开源) Anaconda 4.3.3 https://www.anaconda.com/(开源) 表 4 实验所用硬件资源
Table 4. Hardware resources used in experiment
名称 描述 实验计算机 Mac 操作系统 MacOS High Sierra 网络配置 3.1 GHz Intel Core i5处理器,8 GB 2 133 MHz内存 表 5 数据集概况
Table 5. Description of dataset
数据集 软件总数量 恶意软件数量 良性软件数量 类别 DREBIN 11 120 5 560 5 560 2 AMD 49 300 24 650 24 650 2 表 6 AMD数据集的最优特征子集
Table 6. Optimal feature subset of AMD dataset
特征类型 数目 特征(AMD数据集) 系统权限 14 ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE ACCESS_WIFI_STATE BROADCAST_STICKY CAMERA GET_TASKS …… API 262 android/net/wifi/WifiManager; enableNetwork android/net/wifi/WifiManager; setWifiEnabled Dex Class Loader …… 组间通信Intent 18 android.intent.action.ACTION_SHUTDOWN android.intent.action.AIRPLANE_MODE android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED android.intent.action.MEDIA_MOUNTED android.intent.action.SEARCH …… 表 7 特征选择实验结果(AMD数据集)
Table 7. Experimental results of feature selection (AMD dataset)
方法 原始特征集(689维) 最优特征集(294维) Accuracy/% Precision/% Recall/% F1 Accuracy/% Precision/% Recall/% F1 GBDT 95.0 94.9 95.2 0.950 95.6 96.2 95.1 0.956 MLP 96.0 96.1 96.1 0.961 96.4 96.0 97.4 0.970 LR 92.9 90.2 95.5 0.927 94.6 95.2 95.2 0.947 AdaBoost 93.2 92.3 94.2 0.932 93.8 94.3 93.5 0.939 NB 86.4 85.3 87.5 0.864 85.0 94.5 88.9 0.864 RF 97.6 96.7 98.5 0.974 98.2 98.1 98.4 0.983 表 8 特征选择实验结果(DREBIN数据集)
Table 8. Experimental results of feature selection (DREBIN dataset)
方法 原始特征集(689维) 最优特征集(295维) Accuracy/% Precision/% Recall/% F1 Accuracy/% Precision/% Recall/% F1 GBDT 96.8 90.4 94.3 0.924 96.9 92.0 94.5 0.935 MLP 97.0 93.3 92.7 0.930 98.4 95.0 94.0 0.944 LR 96.3 88.8 93.3 0.924 96.1 89.0 93.1 0.924 AdaBoost 96.0 90.0 91.3 0.903 96.8 89.9 92.2 0.916 NB 94.6 82.1 91.4 0.865 95.3 86.7 91.9 0.871 RF 98.1 93.2 98.2 0.956 98.9 94.9 98.9 0.967 表 9 特征选择方法实验结果对比
Table 9. Comparison of experimental results among feature selection methods
-
[1] 中国互联网络信息中心. 第44次中国互联网络发展现状统计报告[R]. 北京: 中国互联网络信息中心, 2019.China Internet Network Information Center. The 44th China statistical reports on internet development[R]. Beijing: China Internet Network Information Center, 2019(in Chinese). [2] International Data Corporation. Worldwide smartphone market shares[R]. New York: International Data Corporation, 2019. [3] YERIMA S Y, SEZER S, MCWILLIAMS G. Analysis of Bayesian classification-based approaches for Android malware detection[J]. IET Information Security, 2014, 8(1): 25-26. doi: 10.1049/iet-ifs.2013.0095 [4] PEHLIVAN U, BALTACI N, ACARTURK C, et al. The analysis of feature selection methods and classification algorithms in permission based Android malware detection[C]//Computational Intelligence in Cyber Security. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 1-8. [5] WANG W, WANG X, FENG D, et al. Exploring permission-induced risk in Android applications for malicious application detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2014, 9(11): 1869-1882. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2014.2353996 [6] CEN L, GATES C S, SI L, el al. A probabilistic discriminative model for Android malware detection with decompiled source code[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2015, 12(4): 400-412. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2014.2355839 [7] ZHAO K, ZHANG D, SU X, et al. Fest: A feature extraction and selection tool for Android malware detection[C]//Computers and Communication. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 714-720. [8] TAO G, ZHENG Z, GUO Z, et al. MalPat: Mining patterns of malicious and benign Android apps via permission-related APIs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2018, 67(1): 355-369. doi: 10.1109/TR.2017.2778147 [9] LI J, SUN L, YAN Q, et al. Significant permission identification for machine learning based Android malware detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 14(7): 3216-3225. [10] DESNOS A, GUEGUEN G, BACHMANN S. Androguard package[EB/OL]. (2020-04-30)[2021-09-01]. https://github.com/androguard. [11] MANN H B, WHITNEY D R. On a test whether one of two random variables is statistically larger than the other[J]. Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1947, 18(1): 50-60. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177730491 [12] FRIEDMAN J H. Stochastic gradient boosting[J]. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2002, 38(4): 367-378. [13] FREUND Y, SCHAPIRE R E. A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting[J]. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 1997, 55(1): 119-139. doi: 10.1006/jcss.1997.1504 [14] HANSEN L K, SALAMON P. Neural network ensembles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1990, 12(10): 993-1001. doi: 10.1109/34.58871 [15] RUCZINSKI I, KOOPERBERG C, LEBLANC M. Logic regression[J]. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 2003, 12(3): 475-511. doi: 10.1198/1061860032238 [16] FRIEDMAN N, GEIGER D, GOLDSZMIDT M. Bayesian network classifiers[J]. Machine Learning, 1997, 29: 131-163. doi: 10.1023/A:1007465528199 [17] BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45: 5-32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 [18] MORALES O S, ESCAMILLA A P J, RODRGUEZ M A, et al. Native malware detection in smartphones with Android OS using static analysis, feature selection and ensemble classifiers[C]//International Conference on Malicious and Unwanted Software. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 67-74. [19] SEDANO J, GONZLEZ S, CHIRA C, et al. Key features for the characterization of Android malware families[J]. Logic Journal of the IGPL, 2017, 25(1): 54-66. doi: 10.1093/jigpal/jzw046 [20] RAI S, DHANESHA R, NAHATA S, et al. Malicious application detection on Android smartphones with enhanced static-dynamic analysis[C]//International Conference on Information Systems Security. Berlin: Springer, 2017: 194-208. [21] FATIMA A, MAURYA R, DUTTA M K, et al. Android malware detection using genetic algorithm based optimized feature selection and machine learning[C]//International Conference on Telecommunications & Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 220-223. [22] SUN L, LI Z, YAN Q, et al. SigPID: Significant permission identification for android malware detection[C]//International Conference on Malicious and Unwanted Software. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-8. -







 下载:
下载: