-
摘要:
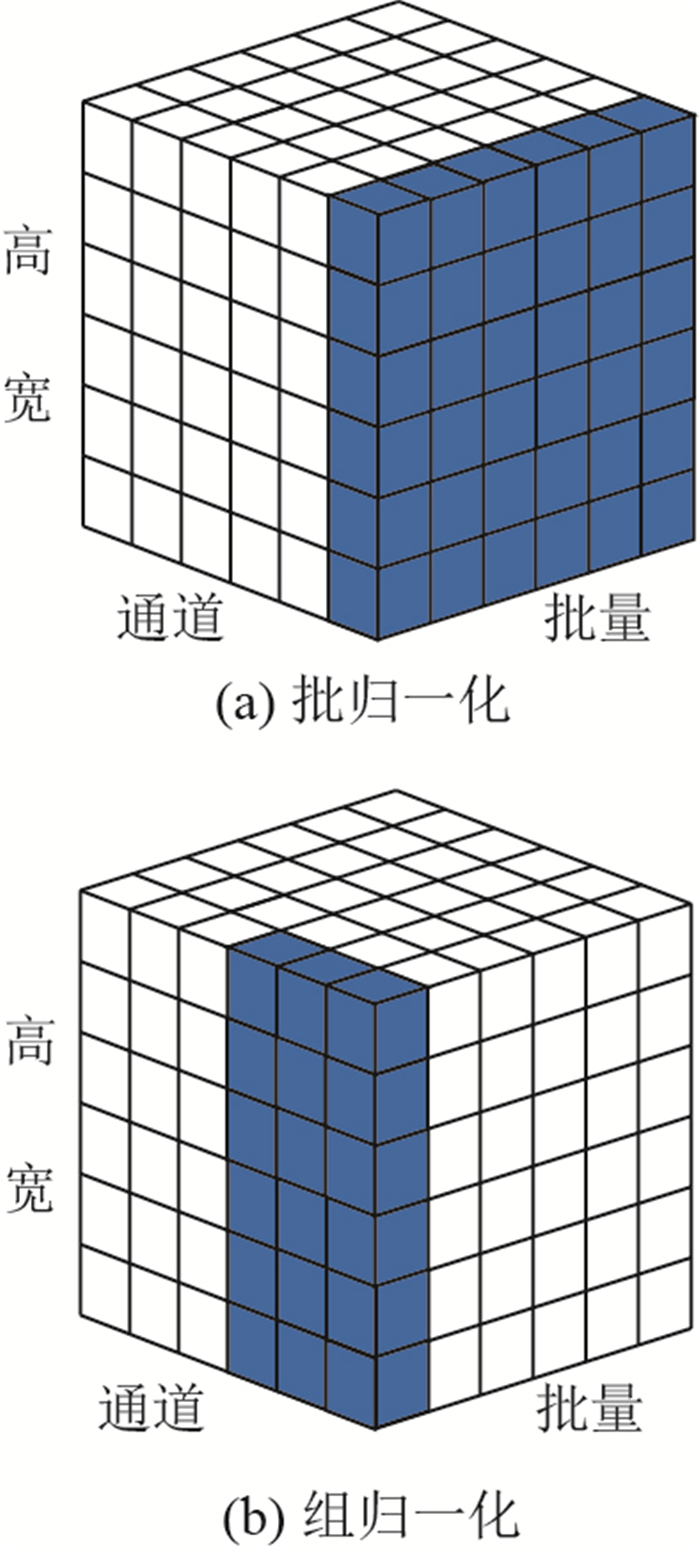
针对多尺度、多场景的合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像船舶检测问题,提出了一种基于EfficientDet的无预训练目标检测器。现有的基于卷积神经网络的SAR图像船舶检测器并没有表现出其应有的出色性能。重要原因之一是依赖分类任务的预训练模型,没有有效的方法来解决SAR图像与自然场景图像之间存在的差异性;另一个重要原因是没有充分利用卷积神经网络各层的信息,特征融合能力不够强,难以处理包括海上和近海在内的多场景船舶检测,尤其是无法排除近海复杂背景的干扰。SED就这2个方面改进方法,在公开SAR船舶检测数据集上进行实验,检测精度指标平均准确率(AP)达到94.2%,与经典的深度学习检测器对比,超过最优的RetineNet模型1.3%,在模型大小、算力消耗和检测速度之间达到平衡,验证了所提模型在多场景条件下多尺度SAR图像船舶检测具有优异的性能。
-
关键词:
- 船舶检测 /
- 合成孔径雷达(SAR) /
- 深度学习 /
- 卷积神经网络 /
- 目标检测
Abstract:Aiming at the problem of multi-scale and multi-scene Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) ship detection, an object detector without pre-training based on EfficientDet is proposed. The existing SAR image ship detectors based on convolutional neural networks do not show excellent performance that it should have. One of the important reasons is that they depend on the pre-training model of the classification tasks, and there is no effective method to solve the difference between the SAR image and the natural scene image. Another important reason is that the information of each layer of the convolutional network is not fully utilized, the feature fusion ability is not strong enough to deal with the detection of ships in multiple scenes including sea and offshore, and especially the interference of complex offshore background cannot be ruled out. SED improves the method in these two aspects, and conducts experiments on the public SAR ship detection data set. The detection accuracy index AP of SED reaches 94.2%, which, compared with the classic deep learning detector, has exceeded the best RetineNet model by 1.3%, and achieved a balance among model size, computing power consumption and detection speed. This verifies that the model can achieve excellent performance in multi-scale SAR image ship detection in multiple scenes.
-
表 1 消融实验
Table 1. Ablation experiment
条件 组成 预训练 √ BN √ √ √ GN √ √ BiFPN √ √ √ √ 改进BiFPN √ √ AP0.5/% 92.3 93.4 93.5 93.7 94.2 Nan AP0.5∶0.95/% 60.0 59.9 60.6 63.3 64.7 Nan 表 2 不同模型结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of results among different models
指标 SSD300 SSD512 Faster R-CNN
(R50)RetinaNet
(R50)EfficientDet-D0
(预训练)EfficientDet-D4
(预训练)SED AP0.5/% 88.5 89.6 91.8 92.9 92.3 93.4 94.2 AP0.5∶0.95/% 49.1 51.4 54.9 57.1 60.0 62.7 64.7 训练时长/min 10 43 23 15 14 195 19 测试时长/s 77 126 114 115 144 326 227 图像处理速度/(fp·s-1) 56.6 36.3 38.6 38.0 30.5 13.5 19.3 模型大小/MB 190.0 195.0 247.6 303.2 15.7 83.2 15.4 -
[1] KANJIR U, GREIDANUS H, KRIS ˇTOF O. Vessel detection and classification from spaceborne optical images: A literature survey[J]. Remote Sensing of Envioronment, 2018, 207: 1-26. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5877374/ [2] WANG Y, WANG C, ZHANG H, et al. Automatic ship detection based on retinanet using multi-resolution gaofen-3 imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(5): 531. doi: 10.3390/rs11050531 [3] EL-DARYMLI K, GILL E W, MCGUIRE P, et al. Automatic target recognition in synthetic aperture tadar imagery: A state-of-the-art review[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 6014-6058. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2611492 [4] YANG C S, PARK J H, RASHID A. An improved method of land masking for synthetic aperture radar-based ship detection[J]. Journal of Navigation, 2018, 71(4): 788-804. doi: 10.1017/S037346331800005X [5] MOLINA D E, GLEICH D, DATCU M, et al. Gibbs random field models for model-based despeckling of SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 7(1): 73-77. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5071276 [6] QIN X X, ZHOU S L, ZOU H X, et al. A CFAR detection algorithm for generalized gamma distributed background in high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(4): 806-810. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2224317 [7] ZHAO J, ZHANG Z, YU W, et al. A cascade coupled convolutional neural network guided visual attention method for ship detection from SAR images[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 50693-50708. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2869289 [8] LI J, QU C, SHAO J. Ship detection in SAR images based on an improved faster R-CNN[C]//2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-6. [9] WANG Y, WANG C, ZHANG H, et al. A SAR dataset of ship detection for deep learning under complex backgrounds[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(7): 765. doi: 10.3390/rs11070765 [10] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multiBox detector[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 21-37. [11] REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015: 91-99. [12] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2999-3007. [13] NOGUEIRA K, PENATTI O A, DOS SANTOS J A. Towards better exploiting convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 61: 539-556. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.07.001 [14] SHEN Z, LIU Z, LI J, et al. DSOD: Learning deeply supervised object detectors from scratch[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1919-1927. [15] ZHU R, ZHANG S, WANG X, et al. ScratchDet: Training single-shot object detectors from scratch[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 2268-2277. [16] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2117-2125. [17] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [18] TAN M, PANG R, LE Q V. EfficientDet: Scalable and efficient object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 10781-10790. [19] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1440-1448. [20] HE K, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2961-2969. [21] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[EB/OL]. [2020-05-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02767. [22] TIAN Z, SHEN C, CHEN H, et al. FCOS: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection[C]//2019 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 9627-9636. [23] LIU S, QI L, QIN H, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8759-8768. [24] GHIASI G, LIN TY, LE Q V. NAS-FPN: Learning scalable feature pyramid architecture for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 7036-7045. [25] IOFFE S, SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM Press, 2015: 448-456. [26] WU Y, HE K. Group normalization[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 3-19. [27] HOWARD A G, ZHU M, CHEN B, et al. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[EB/OL]. [2020-05-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861. [28] SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU M, et al. MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 4510-4520. [29] CHEN X, FANG H, LIN T, et al. Microsoft COCO captions: Data collection and evaluation server[J]. (2015-04-03)[2020-05-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1504.00325. [30] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[EB/OL]. (2017-01-30)[2020-05-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980v9. -







 下载:
下载: