-
摘要:
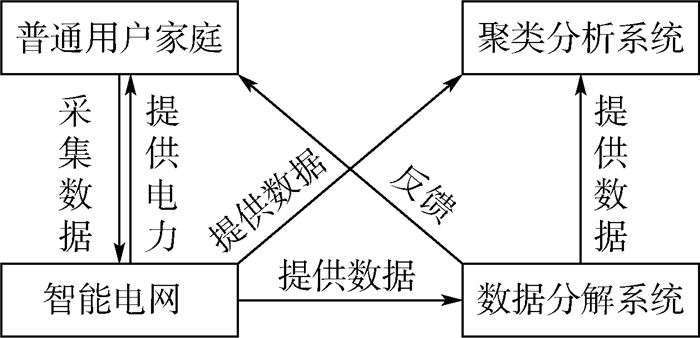
随着智能电网的普及和大数据技术的发展,利用用电数据分析用户的用电行为越来越受到关注,现存的能源分解方法无法满足实际应用中对分辨率和分解准确率的高要求,以及聚类分析方法过于粗糙没有充分挖掘每类电器的用电特点。提出了基于能源分解的用户用电行为分析方法。在判别式稀疏编码算法模型的基础上,针对
L 0正则项不易求解、L 1正则项稀疏约束效果不理想的问题,提出用L 1/2正则项稀疏约束进行能源分解,并且把用户之间的同质性作为正则项加入基础模型来修正模型的性能。基于能源分解的结果,使用用户单类电器的用电特征代替总用电特征精细化分析用户的用电行为,并改进传统的K-Mean聚类算法进行实验验证。实验结果表明:所提出的基于L 1/2正则项稀疏约束和同质性约束的能源分解方法相比于传统判别式稀疏编码算法,能够有效提升能源分解的准确率。同时,基于能源分解的用户用电行为聚类分析效果也有明显提升。Abstract:With the popularization of smart grids and the development of big data technology, more and more attention has been paid to the analysis of users' electricity consumption behavior through electricity consumption data. The existing energy decomposition methods cannot meet the high requirements for resolution and decomposition accuracy in practical applications, and the cluster analysis method is too rough and does not fully show the electricity consumption characteristics of each type of electrical appliances. In view of this, this paper proposes an analysis method of users' electricity consumption behavior based on energy decomposition. Based on the discriminative sparse coding algorithm model, firstly, to solve the problem that the regular term of
L 0 is not easy to solve and the effect of the sparse constraint ofL 1 regular term is not ideal, we propose to use the sparse constraint ofL 1/2 regular term to perform energy decomposition, and add the homogeneity between users as a regular term to the basic model to modify the performance of the model. Secondly, based on the results of energy decomposition, we use the electricity consumption characteristics of a user's single-type electrical appliances instead of the total electricity consumption characteristics to refine the analysis of user's electricity consumption behavior, and improve the traditional K-Mean clustering algorithm for experimental verification. The experimental results show that the energy decomposition method based on the sparse constraint ofL 1/2 regular term and the constraint of homogeneity can effectively improve the accuracy of energy decomposition compared with the traditional discriminative sparse coding method. At the same time, the result of cluster analysis of users' electricity consumption behavior based on energy decomposition is also significantly improved. -
表 1 实验结果
Table 1. Experimental results
方法 分解准确率/% 训练集 测试集 NMF 56.20 36.66 NMF+ L1 85.60 66.95 NMF+ L1/2 75.93 70.41 本文方法 77.79 73.16 表 2 参数Ef对比结果
Table 2. Parameter Ef contrast results
Ef 0.000 1 0.001 0.01 0.1 0.5 1 Acc/% 69.42 69.72 66.74 59.22 58.74 58.77 -
[1] DIECJMANN J, COOPERMAN A, BRODRICK J. Efficiency energy. Buildings energy data book[M]. Washington, D.C. : US Department of Energy, 2009. [2] 辛苗苗, 张延迟, 解大. 基于电力大数据的用户用电行为分析研究综述[J]. 电气自动化, 2019, 41(1): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3886.2019.01.001XIN M M, ZHANG Y C, XIE D. Summary of researches on consumer behavior analysis based on big power data[J]. Electrical Automation, 2019, 41(1): 1-4(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3886.2019.01.001 [3] HART G W. Nonintrusive appliance load monitoring[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1992, 80(12): 1870-1891. doi: 10.1109/5.192069 [4] LAUGHMAN C, LEE K, COX R, et al. Power signature analysis[J]. IEEE Power and Energy Magazine, 2003, 1(2): 56-63. doi: 10.1109/MPAE.2003.1192027 [5] SHAW S R, ABLER C B, LEPARD R F, et al. Instrumentation for high performance nonintrusive electrical load monitoring[J]. Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, 1998, 120(3): 224-229. doi: 10.1115/1.2888073 [6] BERGES M, GOLDMAN E, MATTHEWS H S, et al. Learning systems for electric consumption of buildings[C]//International Workshop on Computing in Civil Engineering 2009. Reston: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2009: 1-10. [7] PATEL S N, ROBERTSON T, KIENTZ J A, et al. At the flick of a switch: Detecting and classifying unique electrical events on the residential power line (nominated for the best paper award)[C]//International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing. Berlin: Springer, 2007: 271-288. [8] ZEIFMAN M, ROTH K. Nonintrusive appliance load monitoring: Review and outlook[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2011, 57(1): 76-84. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2011.5735484 [9] KOLTER J, BATRA S, NG A. Energy disaggregation via discriminative sparse coding[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2010, 23: 1153-1161. [10] KIM H, MARWAH M, ARLITT M, et al. Unsupervised disaggregation of low frequency power measurements[C]//Proceedings of the 2011 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, 2011: 747-758. [11] PARSON O, GHOSH S, WEAL M, et al. An unsupervised training method for non-intrusive appliance load monitoring[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 2014, 217: 1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.artint.2014.07.010 [12] KOLTER J Z, JAAKKOLA T. Approximate inference in additive factorial hmms with application to energy disaggregation[C]//Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, 2012: 1472-1482. [13] KELLY J, KNOTTENBELT W. Neural NILM: Deep neural networks applied to energy disaggregation[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd ACM International Conference on Embedded Systems for Energy-Efficient Built Environments. New York: ACM, 2015: 55-64. [14] SIROJAN T, PHUNG B T, AMBIKAIRAJAH E. Deep neural network based energy disaggregation[C]//2018 IEEE International Conference on Smart Energy Grid Engineering (SEGE). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 73-77. [15] GAO Y, SCHAY A, HOU D Q, et al. Home appliance energy disaggregation using low frequency data and machine learning classifiers[C]//201716th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 76-83. [16] BATRA N, SINGH A, WHITEHOUSE K. Gemello: Creating a detailed energy breakdown from just the monthly electricity bill[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2016: 431-440. [17] 李培强, 李欣然, 陈辉华, 等. 基于模糊聚类的电力负荷特性的分类与综合[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2005, 25(24): 73-78. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2005.24.013LI P Q, LI X R, CHEN H H, et al. The characteristics classification and synthesis of power load based on fuzzy clustering[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2005, 25(24): 73-78(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2005.24.013 [18] 王璨, 冯勤超. 基于价值评价的电力用户分类研究[J]. 价值工程, 2009, 28(5): 64-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4311.2009.05.022WANG C, FENG Q C. The research of power customers classification based on value assessment[J]. Value Engineering, 2009, 28(5): 64-67(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4311.2009.05.022 [19] 李欣然, 姜学皎, 钱军, 等. 基于用户日负荷曲线的用电行业分类与综合方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2010, 34(10): 56-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXT201010012.htmLI X R, JIANG X J, QIAN J, et al. A classifying and synthesizing method of power consumer industry based on the daily load profile[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2010, 34(10): 56-61(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXT201010012.htm [20] ZHONG C L, SHAO J, ZHENG F, et al. Research on electricity consumption behavior of electric power users based on tag technology and clustering algorithm[C]//20185th International Conference on Information Science and Control Engineering (ICISCE). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 459-462. [21] NORDAHL C, BOEVA V, GRAHN H, et al. Profiling of household residents' electricity consumption behavior using clustering analysis[C]//International Conference on Computational Science. Berlin: Springer, 2019: 779-786. [22] LEE D D, SEUNG H S. Learning the parts of objects by non-negative matrix factorization[J]. Nature, 1999, 401(6755): 788-791. doi: 10.1038/44565 [23] OLSHAUSEN B A, FIELD D J. Emergence of simple-cell receptive field properties by learning a sparse code for natural images[J]. Nature, 1996, 381(6583): 607-609. doi: 10.1038/381607a0 [24] RAHIMPOUR A, QI H R, FUGATE D, et al. Non-intrusive energy disaggregation using non-negative matrix factorization with sum-to-k constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2017, 32(6): 4430-4441. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2017.2660246 [25] TANG J, GAO H, HU X, et al. Exploiting homophily effect for trust prediction[C]//Proceedings of the 6th ACM Interhational Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2013: 53-62. -







 下载:
下载: