-
摘要:
由于轨道机动燃料消耗,科学载荷加载、分离,以及伴飞小卫星在轨释放等原因引起天宫二号空间站质心(COM)发生位移,从而影响天宫二号的动力学质心定轨精度。针对这一问题,提出了基于全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)测量数据的简化动力学质心估计方法。燃料消耗是引起天宫二号质心发生位移的主要原因,质心在本体坐标系
X 轴方向位移最为显著。利用GNSS测量数据对天宫二号进行质心估计和精密定轨,在三轴对地稳定姿态下,本体坐标系X 轴方向与轨道切向重合,定轨结果对本体坐标系X 轴方向的质心位移并不敏感。但在连续偏航模式下,本体坐标系X 轴在轨道法向上有较大分量,X 轴方向的质心位移对基于GNSS测量计算的精密定轨结果有较大影响。定性和定量分析结果表明:偏航姿态模式下天宫二号本体坐标系X 轴方向质心位移估计具有可行性。天宫二号实测数据计算结果表明:与未做质心估计的定轨结果进行对比,质心估计后表征轨道动力学建模误差的经验加速度补偿水平在轨道径向、切向和法向上分别降低62%、50%和65%;载波相位后验残差标准差降低0.04 cm;精密轨道与全球激光测距数据比较精度提高0.86 cm。所提方法可以应用于大型低轨航天器在轨质心估计。Abstract:Due to fuel consumption of orbital maneuvers, payloads' load and separation, and the release of small satellite, the Center of Mass(COM) of Tiangong-2 space laboratory moves. To solve this problem, a reduced orbit dynamic determination and COM estimation method is given based on Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) measurement data in this paper. Fuel consumption is the main reason for the COM of Tiangong-2 moves. The COM mainly moves along the
X -axis of Tiangong-2 body-fixed coordinate system. The COM estimation and precise orbit determination of Tiangong-2 are performed using GNSS measurement data. And in a three-axis earth-pointing stabilization attitude mode, the orbit determination results are not sensitive to the displacement of COM in theX -axis of Tiangong-2 body-fixed coordinate system since theX -axis of Tiangong-2 body-fixed coordinate system coincides with the tangential direction of the orbit. However, in a yaw-steering mode, theX -axis of Tiangong-2 body-fixed coordinate system has a large projection on the orbital normal direction, which makes the displacement of COM in theX -axis of Tiangong-2 body-fixed coordinate system have a greater impact on the precision orbit determination results based on GNSS measurement calculation. And the qualitative and the quantitative analysis results show that the COM estimation is feasible in a yaw-steering attitude mode. Compared with the results without considering COM estimation, the Tiangong-2 measurement data calculation results considering COM estimation show that the empirical accelerations which represent orbital dynamics modeling error in the radial, tangential and normal directions are reduced by 62%, 50% and 65%, respectively, and the standard deviation of post-residuals of the carrier phase is reduced by 0.04 cm. Besides, the comparison accuracy of precision orbit data and the global laser ranging improves by 0.86 cm. The method proposed in this paper can be applied to COM estimation of the large-scale low-earth-orbit spacecraft. -
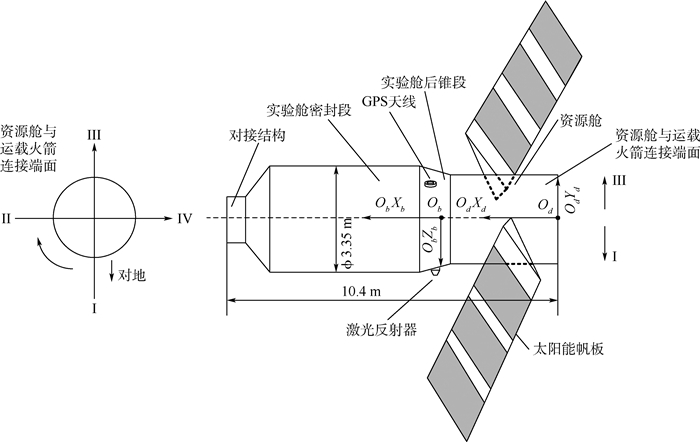
表 1 测量载荷与发射前参考质心的位置
Table 1. Positions of measured loads and reference COM before launch
位置 Xd/cm Yd/cm Zd/cm 天线相位中心 428.66 158.5 -101.31 激光角反射镜 414.88 -159.57 -0.09 发射前参考质心 416.03 0.63 0.53 表 2 本体坐标系Xb方向10 cm的质心位移变化对定轨结果的影响分析
Table 2. Analysis of influence of 10 cm COM offset in Xb-axis direction on orbit determination results
日期 Rx/cm Ry/cm Rz/cm 2018-01-08 6.39 6.81 2.58 2018-01-09 5.69 7.28 1.67 2018-01-10 5.42 7.63 1.85 平均值 5.83 7.24 2.03 表 3 本体坐标系Yb方向10 cm的质心位移变化对定轨结果的影响分析
Table 3. Analysis of influence of 10 cm COM offset in Yb-axis direction on orbit determination results
日期 Rx/cm Ry/cm Rz/cm 2018-01-08 7.8 6.3 1.00 2018-01-09 7.49 6.52 0.85 2018-01-10 7.83 6.58 1.04 平均值 7.71 6.47 0.96 表 4 本体坐标系Zb方向10 cm的质心偏移变化对定轨结果的影响分析
Table 4. Analysis of influence of 10 cm COM offset in Zb-axis direction on orbit determination results
日期 Rx/cm Ry/cm Rz/cm 2018-01-08 3.18 0.61 8.14 2018-01-09 2.75 0.53 8.86 2018-01-10 3.08 0.44 8.65 平均值 3.00 0.53 8.55 表 5 根据燃料消耗推算的天宫二号质心位置和天线相位中心位置
Table 5. Position of COM and antenna phase center of Tiangong-2 computed by fuel consumption
阶段 发生时间(UTC) 质量/kg 质心位置(整体坐标系)/cm 天线相位中心位置(本体坐标系)/cm 天宫二号整器 剩余燃料 轨控 2016-09-16 08:58:55 8 406.4 692.4 (416.03, 0.63, 0.53) (12.63, -101.84, -157.87) 阶段A~阶段C 2018-01-01 00:00:00 8 488.97 889.88 (393.29, 1.55, 0.53) (35.37, -101.84, -156.95) 表 6 所选实验时段的具体说明
Table 6. Specific instructions for selected experimental period
时段名称 时段 时段内天宫二号姿态模式 时段内是否有激光观测数据 具体实验方法 阶段A 2018-01-01—2018-01-10 连续偏航 无 对本体坐标系Xb、Yb、Zb 3个方向同时进行质心位移估计,给出质心位移,并对比质心估计前后的定轨结果 阶段B 2018-08-20—2018-08-24 三轴对地稳定 有 利用阶段A估计的质心位移进行质心校正后,完成精密定轨,并对轨道进行激光外符合校验 阶段C 2018-08-27—2018-08-30 连续偏航 有 利用阶段A估计的质心位移进行质心校正后,完成精密定轨,并对轨道进行激光外符合校验 表 7 偏航姿态模式下,本体坐标系3个方向的质心位移估计值及不确定度
Table 7. Estimates and uncertainties of COM offset in three directions in satellite-body-fixed coordinate system in attitude mode of yaw steering
日期 Xb/cm Yb/cm Zb/cm 2018-01-01 -16.54±0.35 -7.49±0.74 1.20±0.13 2018-01-02 -16.09±0.36 -5.68±0.86 1.21±0.13 2018-01-03 -16.26±0.41 -4.69±1.07 1.04±0.11 2018-01-04 -16.02±0.43 -6.76±1.38 1.11±0.14 2018-01-05 -15.74±0.41 -6.53±1.34 1.29±0.16 2018-01-06 -16.13±0.44 -9.57±2.19 1.02±0.13 2018-01-07 -15.30±0.48 -7.19±3.03 0.94±0.14 2018-01-08 -15.54±0.47 -3.84±3.36 0.80±0.14 2018-01-09 -15.79±0.53 -11.25±5.09 0.87±0.16 2018-01-10 -15.03±0.43 -10.87±3.27 0.88±0.19 平均值 -15.84 -7.39 1.04 标准差 0.46 2.49 0.16 表 8 三轴对地稳定姿态下,卫星激光测距比对结果
Table 8. SLR comparison results in attitude mode of three-axis Earth-pointing stabilization
日期 未应用质心位移量的定轨结果与激光测距比较残差/cm 应用质心位移量的定轨结果与激光测距比较残差/cm 2018-08-20 3.14 3.01 2018-08-21 3.29 3.17 2018-08-22 2.96 2.76 2018-08-23 3.03 2.95 2018-08-24 3.27 3.08 平均值 3.14 2.99 表 9 连续偏航姿态下,卫星激光测距比对结果
Table 9. SLR comparison results in attitude mode of yaw steering
日期 未应用质心位移量的定轨结果与激光测距比较残差/cm 应用质心位移量的定轨结果与激光测距比较残差/cm 2018-08-27 3.45 2.73 2018-08-28 3.12 2.12 2018-08-29 2.93 2.15 2018-08-30 2.82 1.87 平均值 3.08 2.22 -
[1] MONTENBRUCK O, VAN H T, KROES R, et al. Reduced dynamic orbit determination using GPS code and carrier measurements[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2005, 9(3): 261-271. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2005.01.003 [2] 秦建, 郭金运, 孔巧丽, 等. Jason-2卫星星载GPS数据cm级精密定轨[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2014, 39(2): 137-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201402003.htmQIN J, GUO J Y, KONG Q L, et al. Precise orbit determination of Jason-2 with precision of centimeters based on satellite-borne GPS technique[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2014, 39(2): 137-141(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201402003.htm [3] LI K, ZHOU X, WANG W, et al. Centimeter-level orbit determination for TG02 spacelab using onboard GNSS data[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(8): 2671. doi: 10.3390/s18082671 [4] 张强. 采用GPS与北斗的低轨卫星及其编队精密定轨关键技术研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2018: 22-35.ZHANG Q. Research on the key technologies of precise orbit determination for low earth orbit satellites and their formation using GPS and BDS[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2018: 22-35(in Chinese). [5] 秦显平. 星载GPS低轨卫星定轨理论及方法研究[J]. 测绘科学与工程, 2010, 30(1): 77-78. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90008-1011057310.htmQIN X P. Research on precision orbit determination theory and method of low earth orbiter based on GPS technique[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2010, 30(1): 77-78(in Chinese). https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90008-1011057310.htm [6] BRUINSMA S, TAMAGNAN D, BIANCALE R. Atmospheric densities derived from CHAMP/STAR accelerometer observations[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2004, 52(4): 297-312. doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2003.11.004 [7] 戴小蕾. 基于平方根信息滤波的GNSS导航卫星实时精密定轨理论与方法[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2016: 18-20.DAI X L. Real-time precise GNSS satellite orbit determination using the SRIF method: Theory and implementation[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2016: 18-20(in Chinese). [8] 刘伟, 俞洁, 杨立峰, 等. GEO卫星在轨横向质心快速估算方法[J]. 航天器工程, 2016, 25(5): 39-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2016.05.006LIU W, YU J, YANG L F, et al. Method of in-orbit lateral centroid fast estimation of GEO satellite[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2016, 25(5): 39-44(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2016.05.006 [9] TANYGIN S, WILLIAMS T. Mass property estimation using coasting maneuvers[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 1997, 20(4): 625-632. doi: 10.2514/2.4099 [10] 郭正勇, 张增安, 汪礼成, 等. 一种基于推力器控制的卫星质心在轨估算方法研究[J]. 上海航天, 2017, 34(5): 76-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHHT201705012.htmGUO Z Y, ZHANG Z A, WANG L C, et al. Study of on-orbit estimation method of satellite'centroid based on thrust control[J]. Aerospace Shanghai, 2017, 34(5): 76-82(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHHT201705012.htm [11] 谭沧海, 梁翠娜, 薛宏伟. 伪距定位算法中天线相位中心偏差的修正及误差分析[J]. 现代导航, 2017, 8(5): 328-333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDH201705004.htmTAN C H, LIANG C N, XUE H W. Analysis and correction of antenna phase center offsets on pseudo-range positioning algorithm[J]. Modern Navigation, 2017, 8(5): 328-333(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDH201705004.htm [12] 辛宁, 邱乐德, 张立华, 等. 一种重力卫星质心在轨标定算法[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2013, 33(4): 9-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKJ201304004.htmXIN N, QIU L D, ZHANG L H, et al. Study on on-orbit calibration of center of mass for gravity satellite[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2013, 33(4): 9-15(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKJ201304004.htm [13] 李洪银, 屈少波, 白彦峥, 等. 静电悬浮加速度计在轨质心位置的最小二乘估计[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(3): 897-902. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201703005.htmLI H Y, QU S B, BAI Y Z, et al. Least squares estimation of in-orbit mass center position of the electrostatic accelerometer[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(3): 897-902(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201703005.htm [14] 陈光锋, 唐富荣, 薛大同. 重力卫星在轨质心修正原理[J]. 宇航学报, 2005, 26(5): 567-570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHXB200505007.htmCHEN G F, TANG F R, XUE D T. The trim principle of center of mass of gravity satellite during orbit flight[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2005, 26(5): 567-570(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHXB200505007.htm [15] WANG W, LIU J, SHUA L, et al. Precise orbit determination of large-scale spacecraft in low earth orbit: Preliminary results[C]//Proceedings of the 68th International Astronautical Congress (IAC), 2017: 3-12. [16] SHAO K, GU D, JU B, et al. Analysis of Tiangong-2 orbit determination and prediction using onboard dual-frequency GNSS data[J]. GPS Solutions, 2020, 24(1): 11. doi: 10.1007/s10291-019-0927-y [17] KROES R. Precise relative positioning of formation flying spacecraft using GPS[D]. The Netherland: Delft University of Technology, 2006: 56-63. [18] WANG W, GAO Y. Effective empirical acceleration modeling and its application to enhanced-accuracy orbit prediction[J]. Transactions of the Japan Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, Aerospace Technology Japan, 2016, 14(30): 39-45. doi: 10.2322/tastj.14.pd_39 [19] JIA T U, GU D F, YI W U, et al. Phase residual estimations for PCVs of spaceborne GPS receiver antenna and their impacts on precise orbit determination of GRACE satellites[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2012, 25(4): 631-639. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HKXS201204017.htm [20] RIM H J, YOON S, SCHUTZ B, et al. Effect of center of mass position error on icesat precision orbit determination[C]//AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2010: 77-79. [21] CHOI K R. Jason-1 precision orbit determination using GPS combined with SLR and DORIS tracking data[D]. Austin: The University of Texas at Austin, 2003: 43-47. -







 下载:
下载: