-
摘要:
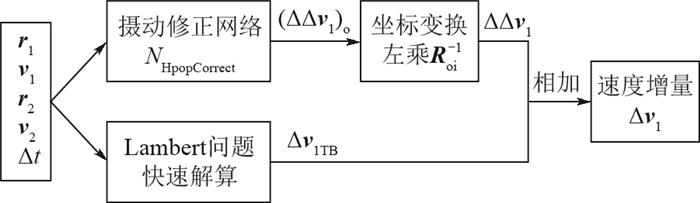
为保证在轨机动实时性和高精度的要求,提出了一种基于机器学习的在轨实时机动决策方法。通过优化算法离线获得摄动下的精确解,减去二体解得到速度增量差,将其投影到轨道坐标系获得速度增量摄动修正项,以此作为神经网络输出,设计网络参数并训练得到摄动修正网络、组合应用摄动修正网络和二体解实现高精度的在轨实时轨道机动决策。仿真结果表明:卫星按照该决策机动完成后的终端位置偏差与按照优化算法给出的决策机动完成后终端位置偏差精度一致,且前者决策耗时仅为后者决策耗时的0.01%左右。所提轨道机动决策方法兼顾了精度与实时性,适用于星上决策。
Abstract:In order to ensure the real-time maneuverability and high-precision requirements of orbital maneuver, a real-time maneuver decision-making method based on machine learning is proposed. The optimal solution under perturbation is obtained offline through the optimization algorithm. The two-body solution is subtracted to obtain the speed increment difference, which is projected onto the orbital system to obtain the speed increment perturbation correction term, which is used as the output of the neural network. The network parameters are designed and trained to obtain perturbation correction network. The combination of perturbation correction network and two-body solution is used to achieve high-precision real-time orbital maneuver decision. The simulation results show that the terminal position deviation after the completion of the maneuver according to the decision is consistent with the accuracy of the terminal position deviation after the completion of the decision maneuver according to the optimization algorithm, and the former decision time is only about 0.01% of the latter decision time. The orbital maneuver decision-making method proposed in this paper takes into account both accuracy and real-time performance, and is suitable for on-board decision-making.
-
Key words:
- orbital maneuver /
- neural networks /
- machine learning /
- Lambert maneuver /
- perturbation correction
-
表 1 样本点到样本中心点最远距离
Table 1. The farthest distance from sample point to sample center point
参数 数值 δr1x/m 1 000 δr1y/m 1 000 δr1z/m 1 000 δv1x/(m·s-1) 1 δv1y/(m·s-1) 1 δv1z/(m·s-1) 1 δr2x/m 1 000 δr2y/m 1 000 δr2z/m 1 000 δv2x/(m·s-1) 1 δv2y/(m·s-1) 1 δv2z/(m·s-1) 1 表 2 网络结构参数取值
Table 2. Parameter value of network structure
神经网络参数 数值 网络隐层数 1,2,3,4 隐层节点数 8,16,32,64,128 表 3 不同层数、节点数和激活函数的速度增量网络的性能
Table 3. Performance of speed increment networks with different layers, units and activation functions
隐层层数/节点数 MSE logsig softmax poslin purelin tansig 1/8 9.95×10-6 8.38×10-5 8.23×10-9 2.06×10-9 5.76×10-6 1/16 3.05×10-6 1.81×10-5 5.42×10-6 2.02×10-9 1.45×10-6 1/32 6.40×10-6 2.20×10-6 2.17×10-9 2.02×10-9 3.83×10-6 1/64 6.41×10-6 7.47×10-6 2.73×10-7 2.01×10-9 4.27×10-6 1/128 2.46×10-4 2.62×10-6 7.91×10-6 2.02×10-9 2.97×10-6 2/8 2.26×10-5 5.98×10-5 2.86×10-5 2.02×10-9 3.10×10-5 2/16 5.66×10-6 2.69×10-5 3.86×10-6 2.02×10-9 3.70×10-6 2/32 2.60×10-6 4.37×10-6 6.06×10-5 2.02×10-9 8.53×10-6 2/64 3.33×10-4 1.54×10-6 5.09×10-4 2.02×10-9 6.34×10-5 2/128 1.89×10-3 2.91×10-6 5.29×10-3 2.02×10-9 9.91×10-4 3/8 2.94×10-5 1.18×10-4 2.96×10-1 2.02×10-9 8.34×10-6 3/16 3.23×10-6 1.60×10-5 4.88×10-5 2.01×10-9 4.08×10-6 3/32 5.15×10-6 1.64×10-5 2.43×10-3 2.03×10-9 3.28×10-6 3/64 4.24×10-4 9.36×10-6 5.23×10-3 2.02×10-9 1.25×10-4 3/128 2.90×10-3 2.93×10-6 9.91×10-2 2.02×10-9 3.13×10-3 4/8 4.02×10-5 2.98×10-1 2.96×10-1 2.02×10-9 2.57×10-5 4/16 2.45×10-6 3.03×10-1 1.05×10-2 2.02×10-9 8.95×10-6 4/32 5.82×10-6 1.31×10-5 7.84×10-3 2.03×10-9 9.21×10-6 4/64 4.66×10-4 1.13×10-5 1.35×10-1 2.02×10-9 2.91×10-4 4/128 2.65×10-3 2.98×10-1 1.50 2.02×10-9 2.94×10-3 表 4 不同层数、节点数和激活函数的摄动偏差网络的性能
Table 4. Performance of perturbation deviation networks with different layers, units and activation functions
隐层层数/节点数 MSE logsig softmax poslin purelin tansig 1/8 2.80×10-6 1.04×10-6 1.91×10-6 6.11×10-6 5.50×10-6 1/16 1.62×10-6 1.04×10-6 2.24×10-6 5.87×10-6 4.11×10-6 1/32 3.60×10-6 1.34×10-6 8.77×10-6 1.87×10-6 4.86×10-6 1/64 3.27×10-6 1.19×10-6 7.61×10-6 2.58×10-6 3.04×10-6 1/128 8.65×10-6 2.26×10-6 8.98×10-6 7.81×10-7 7.07×10-6 2/8 2.08×10-6 1.30×10-6 3.33×10-6 3.96×10-6 4.73×10-6 2/16 3.13×10-6 2.07×10-6 4.83×10-6 8.44×10-7 4.59×10-6 2/32 3.20×10-6 1.78×10-6 4.35×10-6 3.59×10-7 3.19×10-6 2/64 1.86×10-6 8.88×10-7 5.48×10-6 1.09×10-7 2.16×10-6 2/128 5.23×10-6 5.71×10-7 3.04×10-6 1.52×10-8 2.02×10-6 3/8 6.12×10-6 5.85×10-7 1.61×10-6 9.80×10-7 2.06×10-6 3/16 5.45×10-6 8.64×10-7 2.22×10-6 4.71×10-7 2.32×10-6 3/32 2.44×10-6 7.58×10-7 3.87×10-6 8.09×10-8 2.74×10-6 3/64 2.49×10-6 2.02×10-6 3.55×10-6 2.98×10-9 2.52×10-6 3/128 2.43×10-6 7.33×10-7 9.31×10-7 4.11×10-10 2.98×10-6 4/8 7.63×10-7 1.52×10-6 9.29×10-7 1.03×10-6 9.74×10-7 4/16 9.66×10-7 8.19×10-7 3.84×10-6 4.16×10-7 2.02×10-6 4/32 1.99×10-6 1.24×10-6 3.53×10-6 6.47×10-9 1.12×10-6 4/64 1.84×10-6 1.51×10-6 3.57×10-7 1.06×10-10 1.57×10-6 4/128 1.87×10-6 3.99×10-7 6.99×10-7 8.84×10-12 1.18×10-6 表 5 不同层数, 节点数和激活函数的摄动修正网络的性能
Table 5. Performance of perturbation correction networks with different layers, units and activation functions
隐层层数/节点数 MSE logsig softmax poslin purelin tansig 1/8 9.44×10-7 3.87×10-7 3.16×10-6 2.70×10-6 5.14×10-6 1/16 2.29×10-6 9.71×10-7 6.09×10-6 3.01×10-6 1.83×10-6 1/32 1.64×10-6 1.36×10-6 7.63×10-6 3.61×10-6 4.02×10-6 1/64 2.87×10-6 7.55×10-7 4.58×10-6 3.67×10-6 9.22×10-6 1/128 7.44×10-6 2.81×10-7 6.37×10-6 5.56×10-7 7.38×10-6 2/8 1.24×10-6 2.06×10-6 2.71×10-6 2.29×10-6 1.21×10-6 2/16 9.09×10-7 6.05×10-7 4.78×10-6 2.10×10-6 1.84×10-6 2/32 2.73×10-6 1.26×10-6 1.99×10-6 1.02×10-6 4.42×10-6 2/64 1.89×10-6 1.08×10-6 5.50×10-6 6.50×10-8 2.95×10-6 2/128 4.18×10-6 9.30×10-7 5.67×10-6 2.20×10-8 3.87×10-6 3/8 3.00×10-7 2.51×10-6 1.52×10-6 1.51×10-6 1.16×10-6 3/16 2.18×10-6 1.81×10-6 4.38×10-6 1.00×10-6 1.05×10-6 3/32 1.65×10-6 1.10×10-6 5.48×10-6 1.01×10-7 2.51×10-6 3/64 2.15×10-6 1.40×10-6 4.15×10-6 4.33×10-9 1.95×10-6 3/128 2.95×10-6 9.17×10-7 2.87×10-6 5.72×10-10 2.33×10-6 4/8 4.20×10-6 7.73×10-7 1.46×10-6 1.55×10-6 1.26×10-6 4/16 7.32×10-7 1.25×10-6 2.00×10-6 3.41×10-7 1.65×10-6 4/32 8.72×10-7 1.00×10-6 1.85×10-6 5.47×10-9 2.16×10-6 4/64 2.11×10-6 1.54×10-6 1.93×10-6 1.14×10-10 1.54×10-6 4/128 2.63×10-6 1.00×10-6 3.29×10-7 7.28×10-12 2.03×10-6 表 6 终端位置偏差统计
Table 6. Statistics of terminal position deviation
方法 dmax/m dmin/m dmean/m 优化算法(样本) 3.864 0×10-3 2.340 0×10-4 2.008 0×10-3 最优速度增量网络 2.892 5×10-1 3.076 0×10-3 7.396 2×10-2 最优摄动偏差网络 1.192 3×10-2 6.240 0×10-4 4.751 9×10-3 最优摄动修正网络 1.117 8×10-2 3.150 0×10-4 4.175 8×10-3 -
[1] 夏红伟, 李莉, 曲耀斌, 等. 卫星编队构型设计与轨道机动算法优化[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2013, 21(2): 186-191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6734.2013.02.012XIA H W, LI L, QU Y B, et al. Satellites formation configuration design and orbit maneuver algorithm optimization[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2013, 21(2): 186-191(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6734.2013.02.012 [2] 于瀚. 航天器轨道机动可达区域研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.YU H. The study of reachable domain for spacecraft maneuver[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [3] 谭丽芬. 赤道椭圆交会轨道规划与制导方法[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2011.TAN L F. Rendezvous trajectory planning and guidance approach for equatorial elliptical orbit[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2011(in Chinese). [4] 张守玉, 姜振东. 基于STK的卫星轨道机动模型设计与仿真[J]. 计算机仿真, 2004, 21(10): 25-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJZ200410008.htmZHANG S Y, JIANG Z D. Design and simulation of satellite orbital maneuver model on STK[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2004, 21(10): 25-27(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJZ200410008.htm [5] BATE R R. 航天动力学基础[M]. 吴鹤鸣, 李肇杰, 译. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 1990.BATE R R. Fundamentals of astrodynamics[M]. WU H M, LI Z J, translated. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 1990(in Chinese). [6] 李栋林, 黄福铭. 基于Lambert问题的精确拦截与交会策略研究[J]. 飞行力学, 2008, 26(2): 57-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FHLX200802016.htmLI D L, HUANG F M. Research into accurate interception and rendezvous scheme based on Lambert problem[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2008, 26(2): 57-59(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FHLX200802016.htm [7] 桑艳, 周进. 基于Lambert算法的脉冲精确变轨策略[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2009, 31(3): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GFKJ200903008.htmSANG Y, ZHOU J. An approach of accurate impulse transfer based on Lambert algorithm[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2009, 31(3): 29-32(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GFKJ200903008.htm [8] JEZEWSKI D J. Optimal rendezvous trajectories subject to arbitrary perturbations and constraints[C]//AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Confernce. Reston: AIAA Press, 1992: 4507. [9] CHANG Y, ZHOU J. Orbital correction method for two-impulse rendezvous between non-coplanner elliptic orbits considering the J2 perturbation[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2008, 29(4): 1172-1176. http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_journal-astronautics_thesis/0201220260288.html [10] 周须峰, 唐硕. 固定时间拦截变轨段制导的摄动修正方法[J]. 飞行力学, 2006, 24(4): 46-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FHLX200604011.htmZHOU X F, TANG S. Disturbed modify method of fixed-time interception's guidance in orbit-change stage[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2006, 24(4): 46-49(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FHLX200604011.htm [11] 裴忠才, 尹丽, 王占林. 基于神经网络的仿真转台控制系统[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2005, 31(9): 1045-1048. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2005.09.024PEI Z C, YIN L, WANG Z L. Simulating turntable control system with neural network[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2005, 31(9): 1045-1048(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2005.09.024 [12] CHENG L, WANG Z, JIANG F, et al. Real-time optimal control for spacecraft orbit transfer via multiscale deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 55(5): 2436-2450. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8587201/ [13] ZHONG R, XU S. Neural-network-based terminal sliding-mode control for thrust regulation of a tethered space-tug[J]. Astrodynamics, 2018, 2(10): 175-185. doi: 10.1007/s42064-017-0019-0 [14] SÁNCHEZ-SÁNCHEZ C, IZZO D. Real-time optimal control via deep neural networks: Study on landing problems[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2018, 41(5): 1122-1135. doi: 10.2514/1.G002357 [15] IZZO D, SPRAGUE C I, TAILOR D V. Machine learning and evolutionary techniques in interplanetary trajectory design[M]//FASANO G, PINIER J. Modeling and optimization in space engineering. Berlin: Springer, 2019: 191-210. [16] FURFARO R, BLOISE I, ORLANDELLI M, et al. Deep learning for autonomous lunar landing[C]//AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2018: 18-363. [17] 董云峰, 陈士明, 苏建敏, 等. 卫星姿态控制动态模拟技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 300-301.DONG Y F, CHEN S M, SU J M, et al. Dynamic simulation technology of satellite attitude control[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010: 300-301(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: