Dynamic Change of Rural Information Consumption Differences in Different Areas of China
-
摘要:
信息消费成为拉动需求,促进经济增长的动力,但中国信息消费存在区域差异。利用泰尔指数对中国东、中、西三个区域2000—2015年农村信息消费进行研究,分析农村信息消费动态变化及区域差异的来源。研究结果表明,农村信息消费的差异主要来自区域间差异,东部地区的信息消费差异是农村信息消费总差异的主要来源。农村地区信息消费的区域间差异贡献率和区域内差异贡献率呈"此消彼长"的变化特征,且具有一定的周期性。据此可以看出,根据中国当前居民消费特征,制定刺激信息消费的政策可以有效缩短其发展周期,加速提高农村信息消费水平。
Abstract:Information consumption can boost demand and promote economic growth, but there are regional differences in information consumption in our country. This paper applies the Theil Index model to investigate the dynamic change process of regional development of rural information consumption, and carries out its spatial decomposition in three areas of China from 2000 to 2015, in order to determine the causes of regional differences in information consumption. The results indicate that the difference of information consumption in the three regions mainly results from interregional differences, and is less affected by regional differences, and that the difference of information consumption in the eastern region is the main source of information consumption differences in rural areas. The contribution rate of information consumption in rural areas of China is characterized by a "shift" between regional differences and interregional differences, and has a periodicity. According to the characteristics of information consumption and consumption characteristics of the stage current, it can be seen that the development of information policy can effectively shorten the information consumption development cycle and accelerate the improvement of rural information consumption level.
-
一、 引言
近年来,中国出台了许多与信息化、农业农村信息化相关的文件,刺激中国农村信息化的发展,从而带动农村信息消费。2006年国务院提出《关于推进社会主义新农村建设的若干意见》和《2006—2020年国家信息化发展战略》等有关文件,推动了部分区域的信息化发展,直到2012年中央1号文件强调农业农村信息化,将农业农村信息化政策从局部推进过渡到全局,同时随着网络“进村入户”工程和“宽带中国”政策,中国农村地区的信息化水平不断提高。2013年8月,国务院发布《国务院关于促进信息消费扩大内需的若干意见》,指出随着信息技术创新的不断加快,信息领域的新产品、新服务不断激发新的消费需求,信息消费成为有效拉动需求,促进经济增长的动力。
但是,已有研究表明由于中国东、中、西区域经济发展不平衡、农村信息基础设施的差距、信息产业发展及应用阶段不同,导致中国东、中、西区域之间信息化和信息消费存在着差距[1—3],即“区域鸿沟”。2000年东中西三个区域农村每年人均信息消费额分别为385.43元、244.96元、186.29元,到2015年上升到2 467.01元、2 026.78元、1 730.75元,从消费绝对额来看,东部地区一直保持领先地位,如表 1所示。中国东、中、西区域的居民信息消费存在显著差距,同样的城乡之间居民的信息消费也存在差距,并且这种差距在未来有不断扩大的发展趋势[4—6],因此,中国居民的信息消费尤其是农村居民的信息消费水平亟待提升,以缩小城乡差异,改善地区间的不平衡状态,促进区域经济协调发展。为实现此目标,首先要了解中国农村居民信息消费的区域差异的主要来源是什么,其次要明确信息化政策对农村居民信息消费是否起到促进作用。
表 1 中国三个区域人均信息消费水平①年份 /元 东部 中部 西部 2000 385.43 244.95 186.29 2001 414.33 264.98 203.09 2002 467.92 290.66 226.39 2003 546.29 339.07 269.05 2004 589.09 381.64 303.45 2005 737.04 465.10 363.34 2006 791.08 533.31 376.66 2007 832.52 567.00 409.33 2008 894.69 595.25 432.92 2009 986.32 638.65 495.85 2010 1 105.76 711.60 553.47 2011 1 257.83 824.03 676.87 2012 1 461.27 962.93 793.09 2013 1 685.93 1 112.27 961.30 2014 2 202.91 1 773.06 1 510.92 2015 2 467.00 2 062.78 1 730.75 为此,文章选取2000—2015年《中国农村统计年鉴》的数据,测算中国农村居民信息消费的泰尔指数,分析其动态变化及特征,揭示农村居民信息消费区域差异的来源,探索农村信息消费变化的规律,并验证以上信息化政策的有效性。为农村信息化的发展以及农村信息消费的提高提供理论依据,为制定相关政策提供建议。
二、 文献综述
虽然信息消费成为学者们研究的热点,但是学术界对信息消费的内涵的界定尚未统一。对信息消费的研究始于郑英隆,其在《信息消费论纲》中指出信息消费是社会各种类型决策者将现有的有关决策的信息进行消化吸收,并通过转化加工形成行动方案决策或思想决策的过程。[7]贺修铭从情报学的角度提出了信息消费的概念,确定了信息消费的基本过程。他认为信息消费是社会信息生产和交流过程的延续,是信息消费者获取信息、认知信息内容和再生信息等基本环节所构成的社会活动。他将信息消费划分为生活信息消费、学校信息消费、科研信息消费和决策信息消费四个层次。[8]随着信息消费领域的不断扩大,信息消费的内涵也在不断延伸。从最基本的信息的获取、加工、处理,到服务于生产、生活的信息消费行为(电子商务、社交等),从而带动相关产品的消费(信息终端的购买、网络接通费用、软件购买等)。信息消费的本质在于对消费主体有用的信息的消费,但是,由于信息具有无形性,且大小、价格、价值、度量等很难以一个固定标准去界定,所以信息必须以一定的载体形式或者过程形式出现。[9]总起来看,关于信息消费的内涵有两种主流观点,一种认为居民所有用于信息类商品和服务的支出均属于信息消费;另一种认为信息消费是基于互联网的新兴信息产品和新型信息服务的消费。
由于信息消费内涵未统一,所以信息消费的界定方法也不是惟一的。在相关研究中有以下两种界定方法:一种方法是将居民消费中扣除衣、食、住、行以外的其他费用的总额看作是居民信息消费总额。这种计算方法最早是用在对信息化水平测度的指标体系中,用来指代信息化指数。但是,这种方法包含了太多与信息消费无关的其他费用,对信息消费的界定范围过于宽泛。另一种方法是认为信息消费主要由医疗保健、交通与通讯、文化教育娱乐用品、服务等构成。[10—11]随着科技的进步,在这种计算方法中,信息消费所占的比重会越来越大,这样得出的信息消费额误差不会太大,而且数据可以从《中国统计年鉴》中获得,所以这种方法的可操作性也很强,故而这种方法在实证研究中应用最为广泛。
虽然,学者们对信息消费的内涵和界定方法没有达成统一,但是在中国城乡之间存在明显的“数字鸿沟”,不同地区之间也存在“数字鸿沟”,且“数字鸿沟”呈现日益扩大的趋势。[12]故而不同区域间的农村居民信息消费也存在差异。以往文献中主要从信息消费结构和信息消费量两个方面研究农村信息消费差异。陈立梅等运用ELES模型,根据恩格尔系数将中国划分为三个代表不同生活水平的组别,对中国农村居民信息消费水平和信息消费结构差异进行了深入分析,发现恩格尔系数越低,生活水平越高,信息消费水平越高,同时研究结果还表明信息消费对收入的敏感性较高,呈现出奢侈品的特性,不同收入群体的农民的信息消费倾向和需求弹性存在差异。[13]但是,该研究没有突出信息消费在空间地理上的集聚效应和扩散效应,信息消费有显著的空间集聚性和一致性。[14]有学者从空间地理视角研究某个省域内农村信息消费的差异,基于泰尔指数的测算,将信息消费差异进行空间分解,确定信息消费区域差异的来源。[15—16]研究表明,江苏省和浙江省的农村信息消费均存在差异,且差异主要原因是区域间信息消费的差异。
文章在以往文献研究的基础上,从以下几个方面有所突破。首先,基于上述对信息消费内涵的讨论,笔者认可将居民所有用于信息类商品和服务的支出划分为信息消费。考虑到统计年鉴中数据的可用性以及信息消费界定的准确性,文章将交通通信支出②和教育文化娱乐支出之和作为信息消费支出,缩小了信息消费的范围,使得数据尽可能接近真实的信息消费水平。已有大量文献表明,中国东、中、西区域之间存在着“数字鸿沟”,故而对中国东、中、西三大区域的信息消费进行空间分解,分析其信息消费的差异来源。文章根据中国统计年鉴的划分方法,将中国31个省市划分为东、中、西三大区域,利用泰尔指数分析中国农村信息消费的差异来源,为提高农村信息消费水平,缩小东、中、西区域信息消费差距提出政策建议。
三、 实证方法与数据收集
(一) 泰尔指数
目前国内在区域差异研究中使用最为普遍的测度方法主要有绝对差异指数和相对差异指数两种。绝对差异指数包括标准差、极差等;相对差异指数主要有基尼系数、泰尔指数、变异系数等。由于泰尔指数具有把整体差异划分为组内和组间差异的特性,被应用于区域整体差异以及区域间差异的实证研究。[17]该方法是泰尔在运用信息理论中熵的概念来计算收入不平等的过程中发现的[18],最早用来分析收入差距,后来被应用于区域差异的研究[19]。文章采用泰尔指数来测度中国农村信息消费的空间差异,并对东、中、西区域间差异和区域内差异对总差异的贡献率进行分解。泰尔指数分为T指标和L指标,其中T指标以GDP为加权变量,L指标以人口为加权变量[20],在衡量区域差异时更多地考虑了人口因素,以人口为加权变量下的泰尔指数表现出较好的稳健性。目前多数学者采用人口因素作为加权变量[21—22]。
借鉴以往文献,文章在权重指标的选取上,采用人口统计指标,对农村人口权重下的各省域信息消费的差异的动态变化特征进行考察和分析。为了测算的准确性,同时采用农林牧渔业总产值为权重,进一步测算该权重下的泰尔指数,并与以人口为权重下所测算出的指数进行比较。
文章按照中国统计局的划分方法,将中国31个省市分为东部(北京市、天津市、河北省、辽宁省、上海市、江苏省、浙江省、福建省、山东省、广东省、广西省、海南省)、中部(山西省、内蒙古自治区、吉林省、黑龙江省、安徽省、江西省、河南省、湖北省、湖南省)、西部(重庆市、四川省、贵州省、云南省、西藏自治区、陕西省、甘肃省、宁夏回族自治区、青海省、新疆维吾尔自治区)三大区域,各省市为基本单位,根据泰尔指数的理论及公式,分别计算以农村人口为权重的泰尔指数和以农林牧渔业总产值为权重的泰尔指数,泰尔指数的计算公式如下:

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
(5) 
(6) 其中:TE、TM、TW分别为中国东部、中部、西部地区农村信息消费差异的泰尔指数;TN、TB分别为区域内和区域间农村信息消费差异的泰尔指数;Yi为第i个省市的农村居民信息消费总额(人均信息消费支出×该省市的农村人口总数);Pi为第i个省市农村居民的人口数量;YE、YM、YW分别为中国东部、中部、西部地区农村居民信息消费总额;PE、PM、PW分别为中国东部、中部、西部地区农村居民人口总量;Y为中国农村信息消费总额;P为中国农村居民人口总量。其中用农林牧渔总值替换农村人口数量,即得到以农林牧渔总值为权重的中国农村信息消费差异的泰尔系数。
(二) 数据说明
文章通过《中国农村统计年鉴》《中国统计年鉴》《中国卫生统计年鉴》和《中国人口和就业统计年鉴》收集了中国2000—2015年全国以及各个省的农村信息消费、农村人口数量和农林牧渔业总产值数据。整理数据发现,2006年各个省的农村人口数量的数据缺失,故而根据2007年各个省的农村人口数量和2005年的农村人口数量,计算二者的均值作为2006年各个省的农村人口数量。
四、 实证结果
(一) 中国农村信息消费区域差异变化分析:基于农村人口数量作为权重
1.中国农村信息消费区域差异的总体泰尔指数分析
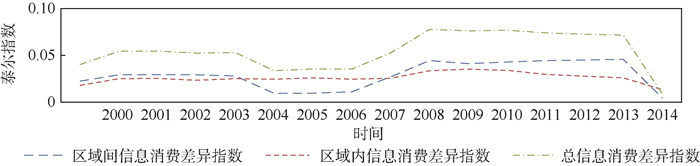
以中国农村人口数量作为权重指标,根据中国31个省市2000—2015年的数据,运用泰尔指数的计算式(4)~式(6)对中国农村信息消费的区域差异进行测算,并进一步计算分析区域间差异和区域内差异,计算结果如图 1所示。
从图 1可见,中国农村信息消费总差异呈现先上升后下降又快速上升的变化态势。21世纪初,中国信息产品及服务处于新兴和快速发展阶段,市场开拓迅速,普及率增长,之后区域间的差异不断缩小。2006年国务院提出《关于推进社会主义新农村建设的若干意见》和《2006—2020年国家信息化发展战略》等有关文件,为做好当前和今后农村信息消费和信息技术的应用指明了方向,经济较为发达的东部省份率先大力发展农村信息化,刺激农村信息消费,从而拉大区域间的差异。因此在图 1中体现为:2000—2002年间,区域差异的泰尔指数整体上升,当信息产品及服务的普及率增长到一定值后,区域差异的泰尔指数有所下降,2006年由于国家政策的出台,刺激东部省份农村信息化和农村信息消费的发展,东部地区农村互联网普及率比2005年增加1.9%,网民规模也在增加,信息传输、计算机服务和软件业的固定资产投资由2005年的1 581.8亿元增加到2006年的1 875.9亿元,增长率明显高于往年的投资,区域泰尔指数快速上升。
对总差异的泰尔指数和区域间差异的泰尔指数的比较发现,二者的变化趋势非常相近,并且随时间的变化也基本同步;而区域内差异的泰尔指数变化比较平稳。区域间差异是总体差异变化的重要组成部分,区域内差异对总体差异的变化影响较小。
区域间信息消费差异除了受信息化政策影响外,还受到居民人均可支配收入、居民信息化设施使用情况的影响。东部地区农村居民的人均可支配收入一直高于中西部地区,2015年东、中、西三大区域人均可支配收入分别为14 297.4元、10 919.0元、9 093.4元。人均可支配收入的差距造成移动电话支付能力和固定宽带支付能力的差距,从而造成信息消费水平的差距。同时东部地区移动电话、电脑和互联网的普及率高于中、西部地区。根据2016年中国信息社会发展报告中的数据,东部地区移动电话、电脑和互联网指数③分别为0.71、0.60、0.67,中部地区分别为0.50、0.34、0.46,西部地区分别为0.55、0.25、047。信息化基础设施持有量和普及率的差距,造成信息消费支出的区域差距。
由图 1还发现,2006年之后区域间信息消费差异一直大于区域内信息消费差异,表明中国东、中、西三大区域的信息消费相比全国区域内信息消费差异更明显。中国三大区域间经济发展水平、基础设施建设等方面存在很大差距,使得区域间农村信息消费的差距不断扩大,呈现出“马太效应”。较大的区域间农村信息消费的差距会加剧区域发展的不平衡,继而加大区域间的“数字鸿沟”。因此,在提高中国农村信息消费的同时重点考虑缩小区域间农村信息消费差异。
2.三大区域农村信息消费的泰尔指数分析
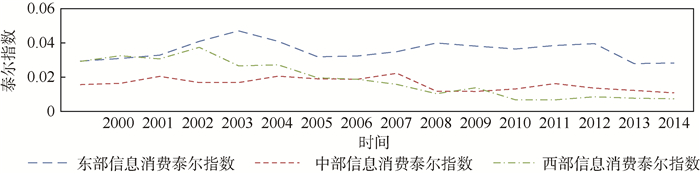
利用泰尔指数计算公式(1)~式(3),计算得到中国三大区域的农村信息消费差异的泰尔指数,其2000—2015年的动态变化如图 2所示。
东部地区的泰尔指数整体高于中部地区和西部地区,表明东部地区区域内农村居民信息消费的差异相比中部地区和西部地区的差异较为明显。虽然东部地区在中国三个区域内经济发展实力最强、信息化水平最高,但是东部区域内各省市之间的农村信息消费发展不平衡最为突出。2006年,由于国家相关信息化政策的出台,东部地区农村信息消费的区域差异呈现加大的趋势,与中部和西部地区的差异也在不断扩大。东部地区农业农村信息化发展在全国起到带头示范作用,例如:广东省农村卫生信息化“健康工程”;上海南汇区借助上海移动实现以手机为基础的信息通讯和生产协调系统,搭建“农信通”信息集合平台;天津在全市农村推广“电脑农业”,在30个农业生产领域开通专家决策咨询系统,并开始搭建农村电子商务平台。2006年东部地区各省份中,江浙沪、京津以及广东地区的人均信息消费额超过其他各省,这些项目在实施和发展的过程中有效带动了农村居民的信息消费,在一定程度上加大了东部地区各省市之间的信息消费差距,同时也加大了东部地区与中、西部地区的信息消费差距。直到2012年东部地区农村信息消费的区域差异急剧缩小,与中部和西部地区的差异也在缩小。这很大程度上是由于2012年中央1号文件强调农业农村信息化,将农业农村信息化政策从局部推进过渡到全局。2013年统计数据表明,中、西部地区的信息消费额快速增加,其信息消费额占比开始上升,而东部地区的信息消费额占比下降明显。中国农业农村信息化基础设施明显得到改善,“村村通电话工程”“广播电视村村通工程”“文化资源共享工程”等的开展,带动了全国农村居民信息消费,不仅缩小了东部地区各省市之间的信息消费差距,同时也缩小了东部地区与中、西部地区的信息消费差距。
中、西部地区信息消费泰尔指数比东部地区信息消费泰尔指数小的另一个原因是中、西部地区信息消费水平普遍偏低,各个省之间的信息消费水平差距很小,故而中、西部地区信息消费的泰尔指数小。但是东部地区信息消费水平较高,其中部分省市起到带头发展的作用,这就加大了省与省之间的差距,导致东部地区信息消费的泰尔指数较高。
三个区域内各省之间信息消费的差异也受到居民的支付能力和信息化基础设施普及程度的影响。根据2016年中国信息社会发展报告,全国31个省市信息化基础设施普及率和居民的信息支付能力④的排名情况来看,北京市、天津市和上海市遥遥领先,广东省和浙江省紧随其后,与东部其他省份差距非常大,而中、西部地区各省份的信息化基础设施普及率相差不大。这些因素也使得东部地区信息消费泰尔指数高于中、西部地区。
3.各区域差异贡献率的对比分析
为了进一步探讨中国东、中、西区域间的差异以及各区域内差异对总差异的影响程度,文章对各因素对总差异的贡献率进行测算,其计算公式如下:

(7) 两边同时除以T,得

(8) 其中:


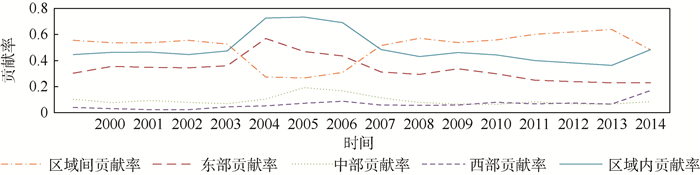
以农村人口为权重计算中国三大区域差异对总差异的贡献率,结果如图 3所示。
区域间差异对总差异的贡献率大体在30%和60%之间变化,相应的区域内差异对总差异的贡献率大体在40%和70%之间变化。由图 3可见,区域间差异的贡献率与区域内差异的贡献率的变化方向是相反的,即当区域间差异的贡献率上升时,区域内差异贡献率下降,反之亦然。2007年以前,区域内差异贡献率大于区域间差异贡献率,即区域内差异对总差异的影响程度大于区域间差异对总差异的影响程度,说明全国农村信息消费的差异主要来源于区域内差异;2007年以后,区域间差异对总差异的贡献率大于区域内差异对总差异的贡献率,说明全国农村信息消费的差异的主要来源于区域间差异。区域间差异的贡献率和区域内差异的贡献率呈现“此消彼长”的变化趋势,说明中国农村信息消费的增长方式是“扩散式”发展,首先是区域内少数省份的带头发展农村信息消费,然后带动整个区域农村信息消费的发展,最后扩散至全国农村信息消费的增长。
根据图 3可以明显发现,中国农村信息消费的发展规律带有一定的周期性,但是周期的长短不一致。中国,目前农村信息消费的发展趋势是区域间贡献率大于区域内贡献率,即三大区域之间农村信息消费的差异对总体差异的贡献较大。根据中国农村信息消费的发展规律,可以预测区域间差异的贡献率即将下降,而区域内差异的贡献率即将上升。
由图 3还可以看出,中国东部地区的差异贡献率明显高于中、西部地区的差异贡献率,表明中国三大区域中、东部地区对全国农村信息消费的差异的影响程度最大。故而,中国在未来缩小区域间农村信息消费差异的同时,应对东部地区各省市之间的农村信息消费差异给予足够的重视,平衡东部各省市之间信息消费的发展。
(二) 中国农村信息消费区域差异变化分析:基于农村农林牧渔业总产值作为权重
泰尔指数的测算方法体现了考察变量和权重变量的匹配程度,农村人口权重下的泰尔指数体现了信息消费与人口的匹配程度,农林牧渔业总产值权重下的泰尔指数体现了信息消费与农业GDP的匹配程度。为了检验泰尔指数的可靠性和稳健性,故而以中国农村农林牧渔业总产值作为权重进行泰尔指数的测算。
1.中国农村信息消费区域差异的总体泰尔指数分析
以农林牧渔业总产值为权重,计算信息消费总差异的泰尔指数、区域间信息消费差异的泰尔指数、区域内信息消费差异的泰尔指数,结果如图 4所示。比较图 4和图 1可以发现,人口权重下和农林牧渔业总产值权重下的中国农村信息消费总差异的泰尔指标变化趋势基本相同,但是以农林牧渔业总产值权重下的信息消费总差异的泰尔指数整体高于农村人口权重下的泰尔指数,这种差距在2006—2013年更为明显,具体表现为以人口为权重的总差异泰尔指数在这几年间在0.03~0.05的水平变化波动,而以农林牧渔业总产值为权重的总泰尔指数从2006年的0.035上升到2009年的0.078,之后变化幅度变小。两种权重下的区域间信息消费差异的泰尔指数和区域内信息消费差异的泰尔指数的变化趋势基本相同,变化的幅度虽然不同,但是没有总差异泰尔指数的变化幅度大。
以农林牧渔业总产值为权重计算的泰尔指数结构显示,2004年以前中国农村信息消费的区域间差异大于区域内差异,在2004年区域间信息消费泰尔指数下降,信息消费的区域内差异大于区域间差异,但是在2007年区域间差异开始超越区域内差异,并且在2009年之后两者之间的差距越来越大,区域间差异越来越接近总差异。近几年来,区域间差异是总差异的主要部分。
2.三大区域农村信息消费的泰尔指数分析
以农林牧渔业总产值为权重,计算中国东、中、西三大区域内农村信息消费差异的泰尔指数,计算结构如图 5所示。比较图 2和图 5发现,三大区域信息消费的泰尔指数整体变化趋势基本类似,但是以农林牧渔业总产值为权重计算的东部信息消费差异泰尔指数没用明显的高于中、西部的泰尔指数,这是与以人口为权重的计算结果的区别之一;以农林牧渔业总产值为权重计算的泰尔指数的变化幅度比以人口为权重计算的泰尔指数小,以东部信息消费泰尔指数为例,具体表现为:以农林牧渔业总产值为权重的泰尔指数的变化范围在0.03~0.047之间,而以人口为权重的泰尔指数的变化范围在0.017~0.037,尤其是2012年以后,以人口为权重的泰尔指数出现大幅度下降。东部地区信息消费的占比与人口权重变量的占比更加接近,而与农林牧渔业总产值权重变量的占比相距较大,同时中部和西部地区也存在类似的情况,因此,以农林牧渔业总产值为权重计算得到的泰尔指数显著高于以人口为权重的泰尔指数。农业总产值受到农村经济发展的影响较大,农林牧渔业总产值的波动变化放大了信息消费的区域差异。
3.各区域差异贡献率的对比分析
以农林牧渔业总产值为权重,计算三大区域信息消费以及区域间和区域内信息消费差异对信息消费总差异的贡献率,计算结果如图 6所示。比较图 3和图 6发现,中、西部地区信息消费差异的贡献率都很小,基本都在10%左右浮动。而且区域间贡献率和区域内贡献率都呈现出周期性,但是以农林牧渔业总产值为权重计算的贡献率的周期性没有以人口为权重计算的贡献率的周期性明显。
比较以农林牧渔业总产值为权重计算的贡献率发现,东部地区信息消费差异的贡献率与区域内信息消费差异的贡献率的变化趋势非常类似,而且区域内信息消费差异的贡献率与东部地区信息消费差异的贡献率非常接近,中、西部地区的贡献率非常小。
五、 结论
区域间信息消费的差异一直受到学者的关注,也是研究信息消费和区域经济发展的重点问题。文章选取农村人口和农林牧渔业总产值作为权重指标,运用泰尔指数的差异测度方法,对中国东、中、西三大区域农村信息消费的差异进行分析,并比较两种权重下的计算结果,计算结果表明:(1)中国农村信息消费的总差异主要受区域间差异影响,区域内差异影响较小。(2)中国东部地区农村信息消费的差异远远大于中、西部地区农村信息消费的差异。(3)区域间差异的贡献率和区域内差异的贡献率呈现“此消彼长”的变化趋势,说明中国农村信息消费的增长方式是“扩散式”发展,首先是区域内少数省份的带头发展农村信息消费,然后带动整个区域农村信息消费的发展,最后扩散至全国农村信息消费的增长。(4)中国农村信息消费的发展规律带有一定的周期性,但是周期的长短不一致。(5)中国东部地区的差异贡献率明显高于中、西部地区的差异贡献率,表明中国三大区域中、东部地区对全国农村信息消费的差异的影响程度最大。(6)农业农村信息化政策对中国农村信息消费的增加有一定的激励作用,即信息化相关政策能有效提高农村信息消费。
上述研究结论表明,解决中国农村信息消费的区域差异的关键是缩小区域间的信息消费差异,而不是东、中、西三大区域内的发展差距。区域内的信息消费差异会因经济政策、资源配置和使用行为等的影响日益趋同,信息消费高的地区带动周围信息消费低的地区,最后趋于消费水平的一致性。中国东、中、西三大区域之间由于地理环境、经济发展水平和产业基础等原因,三大区域之间存在较大差异,在信息技术高速发展时期出现信息消费水平差异属正常现象,而且在中国区域间信息消费差异的贡献率和区域内信息消费差异的贡献率呈“此消彼长”的特点,并且具有一定的周期性,目前中国区域间贡献率大于区域内贡献率的阶段,在未来几年内中国还将处于这个阶段,但是区域间贡献率会下降而区域内贡献率会上升。研究结果还表明,中国当前支持信息化相关政策的出台能够刺激农村信息消费,提高信息消费水平。故而,针对中、西部地区制定可行的政策,能够激励中、西部地区农村信息消费的发展,缩小与东部地区信息消费的差距,缩短区域间贡献率的下降周期;同时充分发挥东、中、西地区信息化示范基地以及信息化示范县的带头作用,鼓励其快速发展,拉大东、中、西区域内的信息消费差距,缩短区域内贡献率的上升周期,使得中国农村居民信息消费水平加速进入下一个发展周期,提高农村信息消费水平的上升速度。
注释:
① 数据来源于中国统计年鉴。
② 2001年及2001年以前农村统计年鉴的统计指标为交通运输和邮电支出,2001年以后的统计指标为交通通信支出。
③ 三个指数分别根据移动电话普及率、每百人平均电脑拥有量和互联网普及率计算得出。
④ 包括固定宽带支付能力指数和移动电话支付能力指数。前者反应的是人均GDP与宽带使用成本的关系,后者反应的是人均GDP与移动电话使用成本的关系。
-
表 1 中国三个区域人均信息消费水平①
年份 /元 东部 中部 西部 2000 385.43 244.95 186.29 2001 414.33 264.98 203.09 2002 467.92 290.66 226.39 2003 546.29 339.07 269.05 2004 589.09 381.64 303.45 2005 737.04 465.10 363.34 2006 791.08 533.31 376.66 2007 832.52 567.00 409.33 2008 894.69 595.25 432.92 2009 986.32 638.65 495.85 2010 1 105.76 711.60 553.47 2011 1 257.83 824.03 676.87 2012 1 461.27 962.93 793.09 2013 1 685.93 1 112.27 961.30 2014 2 202.91 1 773.06 1 510.92 2015 2 467.00 2 062.78 1 730.75 -
[1] 刘晓倩, 韩青.信息化对农村经济增长影响实证分析及展望——基于区域差异的比较[J].农业展望, 2016(8):47-52. [2] 丁疆辉, 刘卫东, 吴建民.中国农村信息化发展态势及其区域差异[J].经济地理, 2010(10):1693-1699. [3] 茶洪旺, 左鹏飞.中国区域信息化发展水平研究——基于动态多指标评价体系实证分析[J].财经科学, 2016(9):53-63. [4] 郑英隆, 王勇.我国城乡居民信息消费的结果差异增长[J].经济管理, 2009(1):152-159. [5] 肖婷婷.我国城乡居民信息消费比较——基于2000-2007年的实证[J].经济问题, 2010(2):46-48. [6] 王平, 陈启杰.基于ARMA模型的我国城乡居民信息消费差距分析[J].消费经济, 2009(5):3-6. [7] 郑英隆.信息消费论纲[J].上海社会科学院学术季刊, 1994(2):51-59. [8] 贺修铭.信息消费概念的确立及其理论基础[J].图书情报工作, 1996(4):45-51. [9] 王子敏, 黄卫东.江苏城乡居民信息消费关系实证研究[J].南京邮电大学学报(社会科学版), 2013(4):38-44. [10] 尹世杰.消费经济学[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2007:198-200. [11] 吴钢华, 杨京英, 闾海琪.信息消费系数及其测算方法研究[J].图书情报知识, 2007(2):69-71. [12] 孙根紧, 丁志帆.情绪波动、信息消费发散与福利分行效应——基于中国省际农村居民信息消费数据的数值模拟分析[J].财经科学, 2015(1):100-109. [13] 陈立梅, 刘冬辉, 胡星颖, 等.中国农村居民信息消费的差异分析[J].郑州航空工业管理学院学报, 2013(2):32-35. [14] 张红历, 梁银鹤.中国省域城镇居民信息消费差异分析[J].情报科学, 2016(2):9-14. [15] 陈立梅, 刘冬辉.江苏省农村信息消费差异的动态变化及空间分解——基于泰尔指数的实证分析[J].华东经济管理, 2016(2):21-26. [16] 于婧.浙江省区域信息消费差异的泰尔指数分析[J].区域经济, 2016(6):105-107. [17] ZHANG X P, KANBNR R.What difference do polarization measures make? An application to China[J].Journal of Development Studies, 2001(3):85-98.
[18] 苑林娅.中国收入差距不平等状况的泰尔指数分析[J].云南财经大学学报, 2008, 24(1):30-37. [19] 钱忠好, 牟燕.中国土地市场化水平:测度及分析[J].管理世界, 2012(7):67-75. [20] 胡望舒, 孙威.基于泰尔指数的北京市区域经济差异[J].中国科学院研究生学报, 2013, 30(3):353-360. [21] 胡志远, 欧向军.基于泰尔指数的江苏省区域差异多指标测度[J].经济地理, 2007, 27(5):719-724. [22] WANG S P, OUYANG Z G.The threshold effect of the urban-rural income disparity on real economic growth in China[J].Social Science in China, 2008(3):39-53.



 下载:
下载: