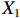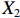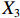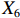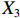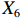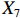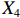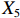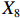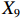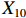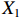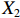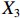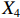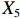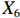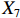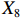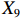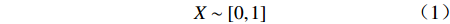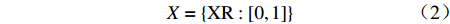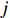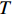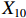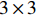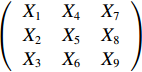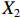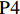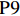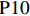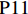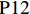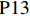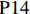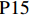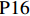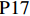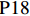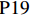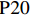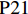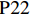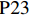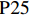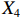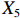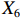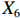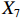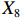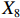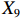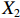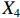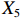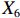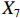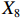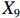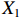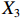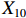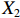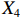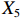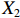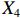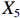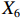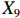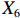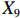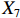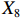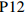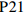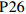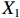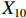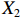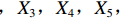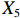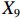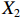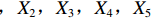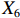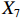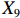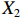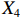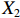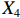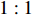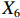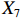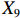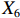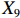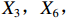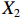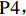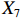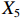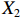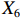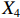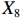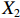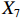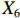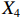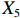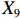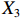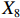Current Situation, Limitations and Optimization Paths of the Financing of Long-term Care Insurance in China: Empirical Analysis Based on 27 Pilot Policy Texts
-
摘要:
筹资是长期护理保险(LTCI)制度建设中的首要环节与核心问题。基于政策文本,以筹资机制为核心构建由10个一级变量和31个二级变量组成的LTCI筹资政策的政策一致性(PMC)指数模型,对全国两批共27份试点城市筹资政策进行量化评价,结果显示,扩大试点阶段中的完美和优秀等级政策占比之和达77.78%,LTCI试点质量显著提升。分析PMC曲面发现,试点城市政策的性质明确、功能完备、透明度高,仍存在时效偏短、级别较低、筹资机制不完善、筹资保障规范性不足等问题,进而提出两种优化策略。建议政府应以疏解当期困境与促成稳定预期为目标设计LTCI筹资机制,兼顾公平性、平等性和适当性标准,重视部门协同,从资金投入、法律法规等方面来强化支持。
-
关键词:
- 长期护理保险(LTCI) /
- 筹资机制 /
- 政策评价 /
- 政策一致性(PMC)指数模型 /
- 政策优化
Abstract:Financing is the first priority and core issue in the construction of long-term care insurance (LTCI) system. Based on the policy texts, the paper has constructed a LTCI financing policy PMC index model composed of 10 primary variables and 31 secondary variables with the financing mechanism as the core, to quantitatively evaluate the financing policies of 27 pilot cities in China. The results show that in the second pilot phase, the perfect and excellent policies accounted for 77.78% of all policies and the quality of LTCI pilot has been significantly improved. The analysis of the PMC surface reveals that the pilot policies are clear in nature, complete in function and high in transparency, but there are still problems such as short time limit, low level, imperfect financing mechanism and insufficient regulation of financing guarantee. Therefore, the paper proposes two optimization paths. The government should design the LTCI financing mechanism with the goal of relieving current difficulties and stabilizing expectations. In addition, it should take into account the criteria of fairness, equality and appropriateness, attach importance to the coordination among various departments, and strengthen support from the aspects of capital investment, laws and regulations.
-
一、 问题的提出
长期护理保险(long-term care insurance,LTCI)制度定型、发展与完善的首要环节是形成公平、合理、稳定的筹资机制,作为社会保险制度的物质保障环节,筹资机制是LTCI制度探索中的核心难题[1]。学者们将LTCI筹资机制概括为筹资对象、筹资渠道、筹资标准、筹资责任分担[2]、筹资模式[3]、费用给付[4]、制度财务模式[5]等方面。基于既有研究取得的共识性结论,笔者认为,LTCI筹资机制应包括参保人群、筹资来源、筹资标准、筹资方式、基金管理、筹资责任分担、给付水平7个方面,并依据政策文本来评价以筹资机制为核心的LTCI筹资政策,分析LTCI试点现状及局限,进而提出优化路径,以期能为推动LTCI试点进程,加快制度的完善与定型提供一定的参考和借鉴。
政策评价是公共政策实施中的必要环节,作为一种重要的分析工具,通过收集与政策相关的信息并进行评估,再将评估后的信息反馈给决策者[6],为政策废改立提供依据。政策评价方法的选择对评估结论具有重要影响[7]。西方的政策评价方法较多,且优劣各异[8],以20世纪70年代为界,前三代政策评价方法以实证主义本位为基本特征,强调数理分析和社会实验;第四代政策评价则采纳规范本位方法论,反映了对价值分析与判断的重视。政策评价方法于发展中相互融合,最终形成批判复合主义的方法论[9]。除方法论外,还可以根据被评价政策类型来选择政策评价方法,具体包括两类:第一类是对政策本身的评价,第二类是对政策效果的评价。文本分析、扎根理论、模糊评价、政策一致性(PMC)指数模型、数据包络分析法(DEA)、优劣解距离法(TOPSIS)等属于第一类;双重差分法(DID)、层次分析法(AHP)、处理效应模型、合成控制法(SCM)、灰色关联法、社会结构矩阵等则属于第二类。笔者所采用的LTCI筹资政策评价方法属于第一类。
综合考虑样本量、指标设置及权重确定的客观性等因素,笔者选择PMC指数模型来对LTCI筹资政策文本进行量化评价。Ruiz Estrada等基于Omnia Mobilis假设提出的PMC指数模型认为,世界万事万物均是运动且相互联系的,因此不应忽视任何一个变量,故而变量的选择应尽可能广泛全面,且需为每个变量赋予相同的权重[10]。PMC指数模型被广泛应用于“双创”政策[11]、“中国芯”扶持政策[12]、大数据发展政策[13]、养老服务政策[14]、农民工就业政策[15]71-83、托幼公共服务政策[16]124-136等的量化评价,为相关领域的政策优化提供了评价工具支持。
LTCI自2016年试点以来,各试点城市因地制宜地发布试点方案,有效解决了当地失能老人的长期护理需求,并取得了丰富的经验,但试点中的诸多局限也阻碍了制度定型,如资金来源独立性缺失,政策试点中以身份为依据的制度分立等问题既影响制度保障绩效,也不利于提升公平性,特别是试点至今尚未形成统一筹资机制,更是延缓了国家层面的制度实施进程。当前,有关LTCI筹资机制的研究多从定性的角度出发,通过比较分析归纳试点现状,来剖析局限并提出对策,量化研究则较少。随着2020年国家层面扩大LTCI试点,第二批试点城市陆续发布试点方案,中国LTCI筹资机制试点出现了新的变化,不乏值得肯定与借鉴之处。笔者拟基于国家层面LTCI两批试点城市中关涉筹资的政策文本,构建LTCI筹资政策PMC指数模型来进行量化评价,力求客观反映试点进展,并通过绘制代表性政策的PMC曲面,剖析其优势和局限,尝试提出优化路径,以期能为LTCI制度试点的深化、发展及完善提供一定的参考依据。
二、 LTCI筹资政策的PMC指数模型建构
(一) 样本选取
2016年,人力资源和社会保障部办公厅发布《关于开展长期护理保险制度试点的指导意见》(人社厅发〔2016〕80号),选择15个城市开始国家层面的LTCI试点[17];2020年,国家医保局会同财政部发布《关于扩大长期护理保险制度试点的指导意见》(医保发〔2020〕37号),增加14个LTCI试点城市,并进一步规定LTCI的资金来源[18]。截至2021年5月,除甘南藏族自治州外,已有28个试点城市公布或修改了LTCI试点办法。笔者遵循政策文本的权威性、严谨性、完整性和精确性原则[15]71-83,剔除宁波市,共得到27份政策文本,如表1所示。
表 1 27份LTCI试点政策文本汇总编号 政策名称 发文字号 发布日期 $ \mathrm{P}1 $ 《承德市城镇职工长期护理保险实施办法(试行)》 承人社发〔2016〕28号 2016年11月23日 $ \mathrm{P}2 $ 《吉林省深入推进长期护理保险制度试点工作实施方案》 吉医保联〔2021〕7号 2021年4月13日 $ \mathrm{P} 3$ 《齐齐哈尔市深化长期护理保险制度试点实施方案(试行)》 齐政办规〔2021〕1号 2021年2月19日 $ \mathrm{P}4 $ 《上海市长期护理保险试点办法》 沪府发〔2017〕97号 2017年12月30日 $ \mathrm{P}5 $ 《关于建立基本照护保险制度的意见(试行)》 通政发〔2015〕73号 2015年10月20日 $ \mathrm{P}6 $ 《关于开展长期护理保险试点第二阶段工作的实施意见》 苏府〔2020〕10号 2020年1月20日 $ \mathrm{P}7 $ 《安庆市城镇职工长期护理保险试点的实施意见》 宜政办秘〔2017〕5号 2017年1月20日 $ \mathrm{P}8 $ 《全面开展长期护理保险制度试点实施方案》 饶府字〔2019〕33号 2019年7月27日 $ \mathrm{P}9 $ 《青岛市长期护理保险办法》 青政发〔2021〕6号 2021年3月25日 $ \mathrm{P}10 $ 《荆门市长期护理保险办法(试行)》 荆政发〔2016〕43号 2016年11月22日 $ \mathrm{P}11 $ 《广州市长期护理保险试行办法》 穗医保规字〔2020〕10号 2020年12月30日 $ \mathrm{P}12 $ 《重庆市长期护理保险实施细则 (试行)》 渝医保发〔2018〕14号 2018年12月11日 $ \mathrm{P}13 $ 《深化长期照护保险制度试点的实施意见》 成府发〔2020〕16号 2020年5月12日 $ \mathrm{P}14 $ 《八师石河子市长期护理保险实施细则(试行)》 师市办发〔2017〕15号 2017年2月23日 $ \mathrm{P}15 $ 《北京市长期护理保险制度扩大试点方案》 京医保发〔2020〕30号 2020年10月28日 $ \mathrm{P}16 $ 《天津市长期护理保险制度试点实施方案》 津政办规〔2020〕24号 2020年12月17日 $ \mathrm{P} 17$ 《关于建立长期护理保险制度的实施意见》 晋市政发〔2020〕14号 2020年12月30日 $ \mathrm{P}18 $ 《呼和浩特市长期护理保险制度试点实施方案》 呼政办发〔2020〕31号 2021年1月22日 $ \mathrm{P}19 $ 《盘锦市开展全国长期护理保险制度试点工作实施方案》 盘政办发〔2020〕25号 2020年12月15日 $ \mathrm{P}20 $ 《关于开展长期护理保险制度试点的实施方案》 榕政综〔2020〕262号 2020年12月24日 $ \mathrm{P}21 $ 《开封市长期护理保险制度试行办法》 汴政〔2020〕36号 2020年12月30日 $ \mathrm{P}22 $ 《湘潭市长期护理保险制度试点实施方案》 潭政办发〔2020〕33号 2020年12月10日 $ \mathrm{P}23 $ 《南宁市人民政府关于南宁市长期护理保险制度试点的实施意见》 南府规〔2021〕3号 2021年1月11日 $ \mathrm{P} 24$ 《黔西南州长期护理保险制度试点实施方案》 黔西南府办发〔2020〕27号 2020年11月6日 $ \mathrm{P} 25$ 《昆明市人民政府关于全面开展长期护理保险制度试点工作方案》 昆政发〔2020〕39号 2020年12月29日 $ \mathrm{P} 26$ 《汉中市长期护理保险实施办法(试行)》 汉政办发〔2020〕25号 2020年11月5日 $ \mathrm{P} 27$ 《乌鲁木齐市长期护理保险办法(试行)》 乌政办〔2018〕254号 2018年11月2日 (二) PMC指数模型设置
Ruiz Estrada指出,PMC指数模型既可以评价政策的一致性水平,也可以识别政策的优势及局限[19]523-536。PMC指数构建主要包括四个基本步骤:一是变量分类与参数识别,二是构建多投入产出表,三是测量PMC指数,四是构造PMC曲面。PMC指数模型要求在变量选择时尽可能全面,基于LTCI政策特点与Ruiz Estrada提出的PMC指标模型[19]523-536,综合LTCI筹资机制的7个方面,调整并确定了由10个一级变量和31个二级变量组成的PMC指标体系及评价标准,如表2所示。
表 2 LTCI筹资机制的PMC指标体系及评价标准一级变量 二级变量 评价标准 政策性质(X1) 描述(X1-1) 说明LTCI的制度性质:是为1,否为0 建议(X1-2) 提出对LTCI筹资模式的指导意见:是为1,否为0 支持(X1-3) 从政策协调、组织管理等角度支持LTCI资金筹集工作:是为1,否为0 引导(X1-4) 从政策主体与政策受体的角度引导对LTCI筹资的重视与认同,旨在提高积极性与遵从度:是为1,否为0 政策时效(X2) 短期(X2-1) 有效期为2年(含)以内:是为1,否为0 中期(X2-2) 有效期为2~5年(含):是为1,否为0 长期(X2-3) 有效期为5年以上:是为1,否为0 政策功能(X3) 明确权责(X3-1) 明确各方权责:是为1,否为0 规范引导(X3-2) 政策引导规范:是为1,否为0 分类推进(X3-3) 体现分类推进思想:是为1,否为0 统筹协调(X3-4) 统筹推进试点:是为1,否为0 发布机构(X4) 省、自治区、直辖市(X4-1) 发布机构为省(自治区、直辖市)级政府机构:是为1,否为0 地级市(X4-2) 发布机构为地级市政府机构:是为1,否为0 参保对象(X5) 城镇职工(X5-1) 覆盖城镇职工:是为1,否为0 城乡居民(X5-2) 覆盖城乡居民:是为1,否为0 政策规范(X6) 筹资来源(X6-1) 独立筹资,无医保基金介入:是为1,否为0 筹资原则(X6-2) 采用“以支定收”的筹资原则:是为1,否为0 筹资标准(X6-3) 明确筹资标准:是为1,否为0 筹资方式(X6-4) 实行“比例缴费”:是为1,否为0 责任分担(X6-5) 同比例分担缴费责任:是为1,否为0 激励约束(X7) 给付方式(X7-1) 按比例支付:是为1,否为0 给付封顶线(X7-2) 设置封顶线:是为1,否为0 待遇与筹资关联机制(X7-3) 设置待遇与筹资关联机制:是为1,否为0 保障措施(X8) 资金保障(X8-1) 划转启动资金/建立调剂金/计提风险准备金等:是为1,否为0 法律法规(X8-2) 提供法律规范:是为1,否为0 组织领导(X8-3) 协调组织领导:是为1,否为0 基金管理(X8-4) 明确基金管理办法:是为1,否为0 政策评价(X9) 目标明确(X9-1) 筹资目标是否清晰:是为1,否为0 依据充分(X9-2) 筹资标准确定依据是否明确:是为1,否为0 方案公平(X9-3) 缴费方案设置是否满足公平性标准:是为1,否为0 权责清晰(X9-4) 各缴费主体权责是否明确:是为1,否为0 政策公开(X10) 政策公开发布:是为1,否为0 表2中,政策性质(
$ {X}_{1} $ )、政策时效($ {X}_{2} $ )、政策功能($ {X}_{3} $ )、政策规范($ {X}_{6} $ )的二级变量根据张文静等[20]的研究设定,并结合LTCI试点现状对$ {X}_{2} $ 和$ {X}_{3} $ 的二级变量进行调整,参照LTCI筹资机制的内涵重新定义了$ {X}_{6} $ 的所有二级变量;建立激励约束($ {X}_{7} $ )并设定相关二级变量;根据张永安和耿喆[21]、王霆和刘玉[15]71-83和祝西冰[16]124-136研究中二级变量的设定思路,来设定发布机构($ {X}_{4} $ )、参保对象($ {X}_{5} $ )、保障措施($ {X}_{8} $ )、政策评价($ {X}_{9} $ )对应的二级变量;政策公开($X_{10} $ )下不设二级变量。一级变量
$ {X}_{1} $ 用于反映LTCI试点文件是否具有描述、建议、支持、引导的功能。$ {X}_{2} $ 根据LTCI试点文件的政策文本与实际运行时间,分为短期、中期和长期。$ {X}_{3} $ 分为明确权责、规范引导、分类推进、统筹协调4个维度。结合LTCI试点城市政策发布机构级别,$ {X}_{4} $ 包括省(自治区、直辖市)和地级市两个级别。$ {X}_{5} $ 根据LTCI试点现状分为仅覆盖城镇职工和覆盖城乡所有居民两类。$ {X}_{6} $ 反映LTCI筹资机制,包括筹资来源、筹资原则、筹资标准、筹资方式、责任分担。待遇给付作为LTCI支出端影响筹资规模,$ {X}_{7} $ 反映与筹资密切相关的待遇给付参数,包括给付方式、给付封顶线、待遇与筹资关联机制。资金筹集是制度运行的物质基础,因此,与缴费率和征缴率相关的因素均纳入$ {X}_{8} $ ,包括资金保障、法律法规、组织领导、基金管理。$ {X}_{9} $ 是对LTCI筹资政策的评价,虽然政策评价从来都不是价值无涉的,但即便是多元的原则和标准也具有比想象中更多的相同点[22]。引入Gilbert和Terrell的社会福利政策的价值因素——整合“公平性”与“平等性”标准,即比例平等与数量平等构成政策评价的维度,包括制度目标是否明确、筹资标准的确定依据是否充分、筹资方案是否公平、各筹资主体权责规定是否清晰[23]。其中,筹资方案是否公平的判断标准如下:一是纵向公平表现在筹资方式设计上,要求缴费额随收入水平上升而提高;二是横向公平表现在筹资责任分担上,要求平等分担缴费责任。同时满足上述标准视为筹资方案公平,否则视为不公平。(三) PMC指数计算
PMC指数计算大致分为4个步骤:一是将参数代入多投入产出表,二是根据式(1)和式(2)计算二级变量的值,三是根据式(3)计算一级变量的值,四是根据式(4)计算PMC指数。
$$ X\sim\left[\mathrm{0,1}\right] $$ (1) $$ X=\left\{\mathrm{X}\mathrm{R}:\left[\mathrm{0,1}\right]\right\} $$ (2) $$ {X}_{t}=\left(\sum _{j=1}^{n}\frac{{X}_{tj}}{T\left({X}_{tj}\right)}\right)\text{,}t=\mathrm{1,2}, \cdots ,\infty $$ (3) $$\begin{split} \mathrm{P}\mathrm{M}\mathrm{C}=\;&{X}_{1}\left(\sum _{j=1}^{4}\frac{{X}_{1j}}{4}\right)+{X}_{2}\left(\sum _{j=1}^{3}\frac{{X}_{2j}}{3}\right)+{X}_{3}\left(\sum _{j=1}^{4}\frac{{X}_{3j}}{4}\right)+\\ & {X}_{4}\left(\sum _{j=1}^{2}\frac{{X}_{2j}}{2}\right)+{X}_{5}\left(\sum _{j=1}^{2}\frac{{X}_{5j}}{2}\right)+{X}_{6}\left(\sum _{j=1}^{5}\frac{{X}_{6j}}{5}\right)+\\ & {X}_{7}\left(\sum _{j=1}^{3}\frac{{X}_{7j}}{3}\right) + {X}_{8}\left(\sum _{j=1}^{4}\frac{{X}_{8j}}{4}\right) + {X}_{9}\left(\sum _{j=1}^{4}\frac{{X}_{9j}}{4}\right) + {X}_{10} \end{split}$$ (4) 式中:XR为X的取值范围;
$ t $ 为一级变量;$ j $ 为二级变量;$ T $ 为一级变量下辖二级变量的数量。PMC指数评价标准,如表3所示。
表 3 PMC指数评价标准PMC指数 [0,5) [5,7) [7,9) [9,10] 政策评价 不良 可接受 优秀 完美 为了更加直观地呈现政策得分及其优势和局限,根据PMC指数可以构建PMC曲面。LTCI筹资政策的PMC指数模型共包括10个一级变量,由于所有LTCI试点政策均公开发布,因此,剔除
$ {X}_{10} $ 后可构建一个$ 3\times 3 $ 矩阵为$ \left(\begin{array}{ccc}{X}_{1}& {X}_{4}& {X}_{7}\\ {X}_{2}& {X}_{5}& {X}_{8}\\ {X}_{3}& {X}_{6}& {X}_{9}\end{array}\right) $ 。此外,为分析现有政策与最优选择间的差异,进而提出优化路径,设置一个虚拟完美政策
① ,并与各试点政策相减来计算凹陷指数。三、 LTCI筹资政策实证分析:现状与局限
(一) LTCI筹资现状:基于PMC指数的分析
27个试点城市LTCI筹资政策的PMC指数,如表4所示
② 。1份政策达到完美等级,18份政策为优秀等级,其他8份政策为可接受等级,完美等级和优秀等级占比之和为70.37%。表 4 27项LTCI试点筹资政策的PMC指数编号 $ {X}_{1} $ $ {X}_{2} $ $ {X}_{3} $ $ {X}_{4} $ $ {X}_{5} $ $ {X}_{6} $ $ {X}_{7} $ $ {X}_{8} $ $ {X}_{9} $ $ {X}_{10} $ PMC指数 排名 等级 凹陷指数 $ \mathrm{P}1 $ 1.00 0.67 0.75 0.50 0.50 0.40 0.67 0.75 0.75 1.00 6.98 15 可接受 3.02 $ \mathrm{P}2 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.80 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 9.13 1 完美 0.87 $ \mathrm{P}3 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.40 0.67 0.75 0.75 1.00 6.90 16 可接受 3.10 $ \mathrm{P}4 $ 1.00 0.67 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.40 0.33 0.75 0.75 1.00 7.90 8 优秀 2.10 $ \mathrm{P}5 $ 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.20 0.67 1.00 0.75 1.00 8.12 4 优秀 1.88 $ \mathrm{P}6 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.20 0.33 0.75 0.50 1.00 6.62 19 可接受 3.38 $ \mathrm{P}7 $ 1.00 0.67 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.20 0.67 0.75 0.50 1.00 6.78 17 可接受 3.22 $ \mathrm{P}8 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.20 0.33 0.75 0.50 1.00 6.62 19 可接受 3.38 $ \mathrm{P}9 $ 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.60 0.33 1.00 0.75 1.00 8.68 2 优秀 1.32 $ \mathrm{P}10 $ 1.00 0.67 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.40 1.00 0.75 0.75 1.00 8.07 6 优秀 1.93 $ \mathrm{P}11 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.80 0.67 0.75 0.75 1.00 7.80 11 优秀 2.20 $ \mathrm{P}12 $ 1.00 0.67 1.00 1.00 0.50 0.40 0.33 0.75 0.50 1.00 7.15 13 优秀 2.85 $ \mathrm{P}13 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.80 0.33 1.00 1.00 1.00 8.47 3 优秀 1.53 $ \mathrm{P}14 $ 1.00 0.67 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.20 1.00 1.00 0.50 1.00 7.87 10 优秀 2.13 $ \mathrm{P}15 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.60 0.67 0.75 0.75 1.00 8.10 5 优秀 1.90 $ \mathrm{P} 16$ 1.00 0.33 1.00 1.00 0.50 0.60 0.67 1.00 1.00 1.00 8.10 5 优秀 1.90 $ \mathrm{P} 17$ 1.00 0.67 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.80 0.67 0.75 1.00 1.00 7.88 9 优秀 2.12 $ \mathrm{P}18 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.80 0.67 0.75 1.00 1.00 8.05 7 优秀 1.95 $ \mathrm{P}19 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.80 0.67 1.00 1.00 1.00 7.80 11 优秀 2.20 $ \mathrm{P}20 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.80 0.67 0.75 1.00 1.00 7.55 12 优秀 2.45 $ \mathrm{P}21 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.60 0.67 0.75 0.75 1.00 7.10 14 优秀 2.90 $ \mathrm{P}22 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.80 0.67 1.00 1.00 1.00 7.80 11 优秀 2.20 $ \mathrm{P}23 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.80 0.67 1.00 1.00 1.00 7.80 11 优秀 2.20 $ \mathrm{P} 24$ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.60 0.33 1.00 0.50 1.00 6.77 18 可接受 3.23 $ \mathrm{P}25 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.80 0.67 1.00 1.00 1.00 7.80 11 优秀 2.20 $ \mathrm{P} 26$ 1.00 0.33 0.75 0.50 0.50 0.40 0.33 0.75 0.50 1.00 6.07 20 可接受 3.93 $ \mathrm{P}27 $ 1.00 0.67 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.20 0.67 0.75 0.50 1.00 6.78 17 可接受 3.22 均值 1.00 0.48 0.98 0.63 0.72 0.54 0.61 0.85 0.77 1.00 7.58 2.42 $ {\mathrm{P}2}_{} $ 为完美等级政策,PMC指数为9.13,除了在$ {X}_{2} $ 方面因政策更新导致得分较低外,其他指标的得分均高于整体均值。${\mathrm{P}4}$ ,${\mathrm{P}5}$ ,${\mathrm{P}9}$ ,${\mathrm{P}10}$ ,${\mathrm{P}11}$ ,${\mathrm{P}12}$ ,${\mathrm{P}13}$ ,${\mathrm{P}14}$ ,${\mathrm{P}15}$ ,${\mathrm{P}16}$ ,${\mathrm{P}17}$ ,${\mathrm{P}18}$ ,${\mathrm{P}19}$ ,${\mathrm{P}20}$ ,${\mathrm{P}21}$ ,${\mathrm{P}22}$ ,${\mathrm{P}23}$ ,${\mathrm{P}25}$ 为优秀等级政策,PMC指数均值为7.89,高于整体PMC指数均值7.58。其中,P4,P10,P12,P14,P17的LTCI筹资政策有效期为2~5年,P5,P9则对LTCI筹资政策进行长期规划。在$ {X}_{4} $ 方面,共有7份政策的得分较高,除P2,P4,P9,P12,P15,P16属于重点联系省份(吉林省、山东省)和直辖市(上海市、重庆市、北京市、天津市)的政策外,P13除了作为成都市发布的试点政策外,还具有四川省的政策支持。在$ {X}_{5} $ 方面,优秀等级政策中,覆盖城镇职工和覆盖城乡所有居民的比例为1:1,由于PMC指数模型假定各一级变量的权重相同,因此,该变量的差异并不影响PMC指数结果。$ {X}_{6} $ 是对筹资机制设计的反映,P4,P5,P10,P12,P14在$ {X}_{6} $ 方面的得分均显著偏低,且均为第一批试点城市的政策,原因在于,这些城市的LTCI基金均依赖医保基金划拨,至今尚未形成独立、稳定的筹资渠道。其中,P5,P12,P14延续定额筹资,难以避免LTCI缴费累退性,且筹资责任分担方面均未能实现同比例划分,违背了LTCI“统一性原则”[24]和医保发〔2020〕37号文件对筹资责任分担的规定。在$ {X}_{7} $ 方面,除了P12实行定额支付外,其他城市皆采用按比例支付,但P4未设置封顶线,在人口老龄化背景下便增大LTCI基金的潜在风险;P5给付水平低于国家相关指导意见中的基本水平,可能难以有效疏解失能老人及其家庭的当期困境。$ {X}_{8} $ 方面的差异主要体现在资金保障上,P5,P9,P13,P14,P16,P19,P22,P23,P25为LTCI划转启动资金,或建立调剂金,或计提风险准备金,因此,这些政策的$ {X}_{8} $ 得分均为满分。在$ {X}_{9} $ 方面,P13,P16,P17,P18,P19,P20,P22,P23,P25均为满分,P4,P5,P9,P10,P11,P12由于筹资责任分担设置不符合公平性标准,P15,P21由于缺乏筹资标准确定的明确依据,P14则由于兼具上述两种局限,从而导致上述政策未能得到满分。P1,P3,P6,P7,P8,P24,P26,P27为可接受等级政策,PMC指数均值为6.69,低于整体PMC指数均值7.58。在
$ {X}_{2} $ 方面,P3,P6,P8,P24,P26低于平均水平,原因在于,这些均为第二批试点或2020年后更新试点方案的城市的政策,施行时间较短。在$ {X}_{3} $ 方面,除了P1,P26未体现“分类推进”导致得分低于平均水平外,其他试点城市的政策得分均为满分。由于可接受等级的城市政策的发布机构级别均停留在地级市层面,故而在$ {X}_{4} $ 方面的得分相同。在$ {X}_{5} $ 方面,P1,P3,P7,P24,P26,P27这6份政策仅覆盖职工群体,占比为75.00%。在$ {X}_{6} $ 方面,仅P24的得分高于该指标均值0.54,其余城市政策的该指标得分均显著低于均值0.54。在$ {X}_{7} $ 方面,P1,P3,P7,P27实行按比例支付,并设置最高限额控制LTCI支出,但该等级所有政策均未构建筹资与待遇关联机制。另外,除P24外,可接受等级政策中没有为LTCI设置划转启动资金、建立调剂金等“资金保障”,从而拉低了$ {X}_{8} $ 得分。而导致$ {X}_{9} $ 得分较低的原因有二:一是缺少筹资标准的确定依据,使“依据充分”赋值为0;二是筹资责任的非同比例分担使“方案公平”的值为0。其中,P1由于缴费责任分担比例不一,P3由于缺少确定筹资标准的依据,P6,P7,P8,P24,P26,P27则是既缺少筹资依据又未能实现同比例分担。下文将按试点时间来比较两批试点城市LTCI筹资政策均值的PMC指数,如表5所示。
表 5 两批试点城市LTCI筹资政策均值的PMC指数比较试点城市 $ {X}_{1} $ $ {X}_{2} $ $ {X}_{3} $ $ {X}_{4} $ $ {X}_{5} $ $ {X}_{6} $ $ {X}_{7} $ $ {X}_{8} $ $ {X}_{9} $ $ {X}_{10} $ PMC指数均值 第一批 1.00 0.57 0.98 0.68 0.86 0.43 0.60 0.84 0.70 1.00 7.65 第二批 1.00 0.38 0.98 0.58 0.58 0.66 0.62 0.87 0.85 1.00 7.51 比较上述两批试点城市的LTCI筹资政策发现:第一,两批城市的筹资政策在
$ {X}_{1} $ ,$ {X}_{3} $ ,$ {X}_{10} $ 上的得分相同,说明政策性质和功能明确、政策透明度高。第二,第一批试点城市的筹资政策在$ {X}_{2} $ ,$ {X}_{4} $ ,$ {X}_{5} $ 上的得分高于第二批城市。原因在于,第一批城市试点较早,如南通市LTCI试点政策至今已逾7年;而青岛市在2021年更新的试点政策中明确规定有效期为6年,提高了$ {X}_{2} $ 得分。第一批试点城市包括两个直辖市和两个重点联系省份,以及四川省也发布了省级LTCI试点指导意见,因此,$ {X}_{4} $ 得分较高。在$ {X}_{5} $ 方面,第一批试点城市筹资政策中实现覆盖城乡全体居民的占比为71.43%,而第二批试点城市筹资政策中纳入城乡全体居民的占比仅为15.38%。第三,第二批试点城市筹资政策在$ {X}_{6} $ 和$ {X}_{9} $ 方面的得分高于第一批城市。在$ {X}_{6} $ 方面,以医保发〔2020〕37号文件为指导的LTCI试点办法在筹资机制设置上有了质的提升,特别是实现了独立筹资和同比例分担缴费责任。此外,第二批试点城市筹资政策进一步明确了独立筹资来源,并规定了筹资标准的确定依据,这也提高了$ {X}_{9} $ 得分。第四,两批试点城市筹资政策在$ {X}_{7} $ 和$ {X}_{8} $ 上得分相近,大多采用按比例限额支付,但是普遍缺乏筹资与待遇关联机制,资金保障仍需完善。综上可知,第一批试点城市筹资政策的覆盖面较广、稳定性较强,第二批试点城市筹资政策机制设计更具公平性。随着第一批试点城市筹资政策的优化,如长春市在扩大试点阶段实现同比例分担缴费责任等,最终表现为2020年后发布或修改的LTCI试点方案中达到完美和优秀等级的比例为77.78%。(二) 基于PMC曲面的代表性政策分析
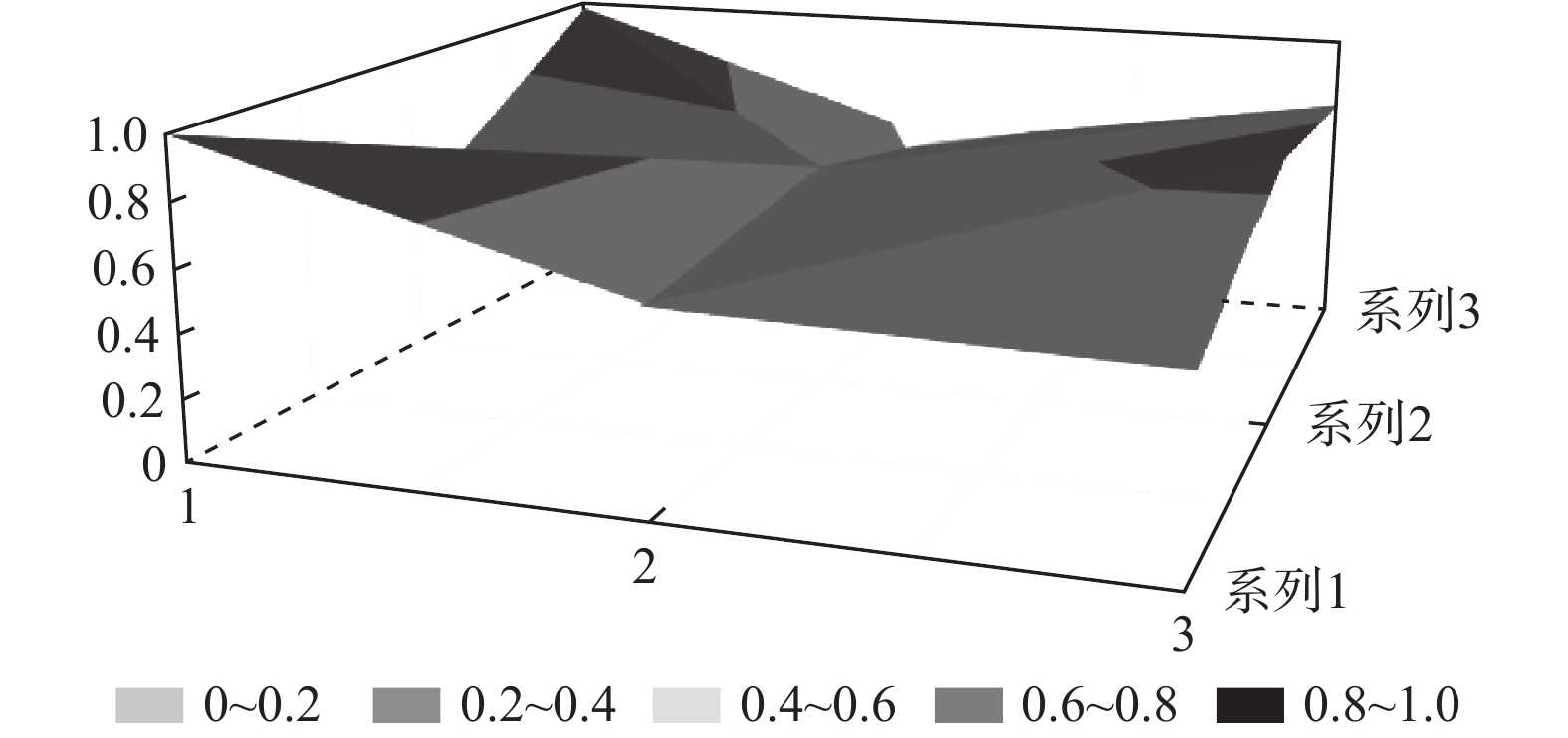
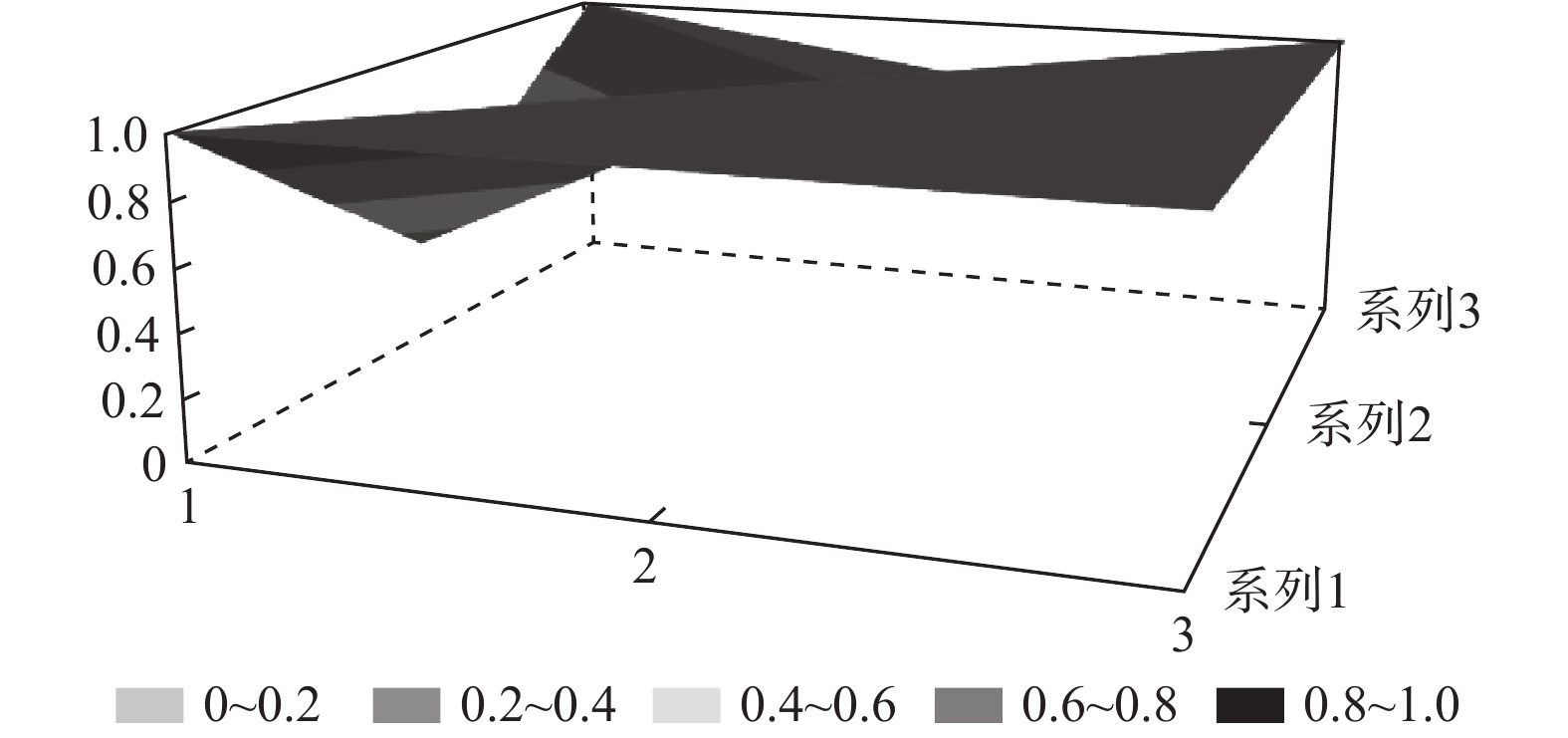
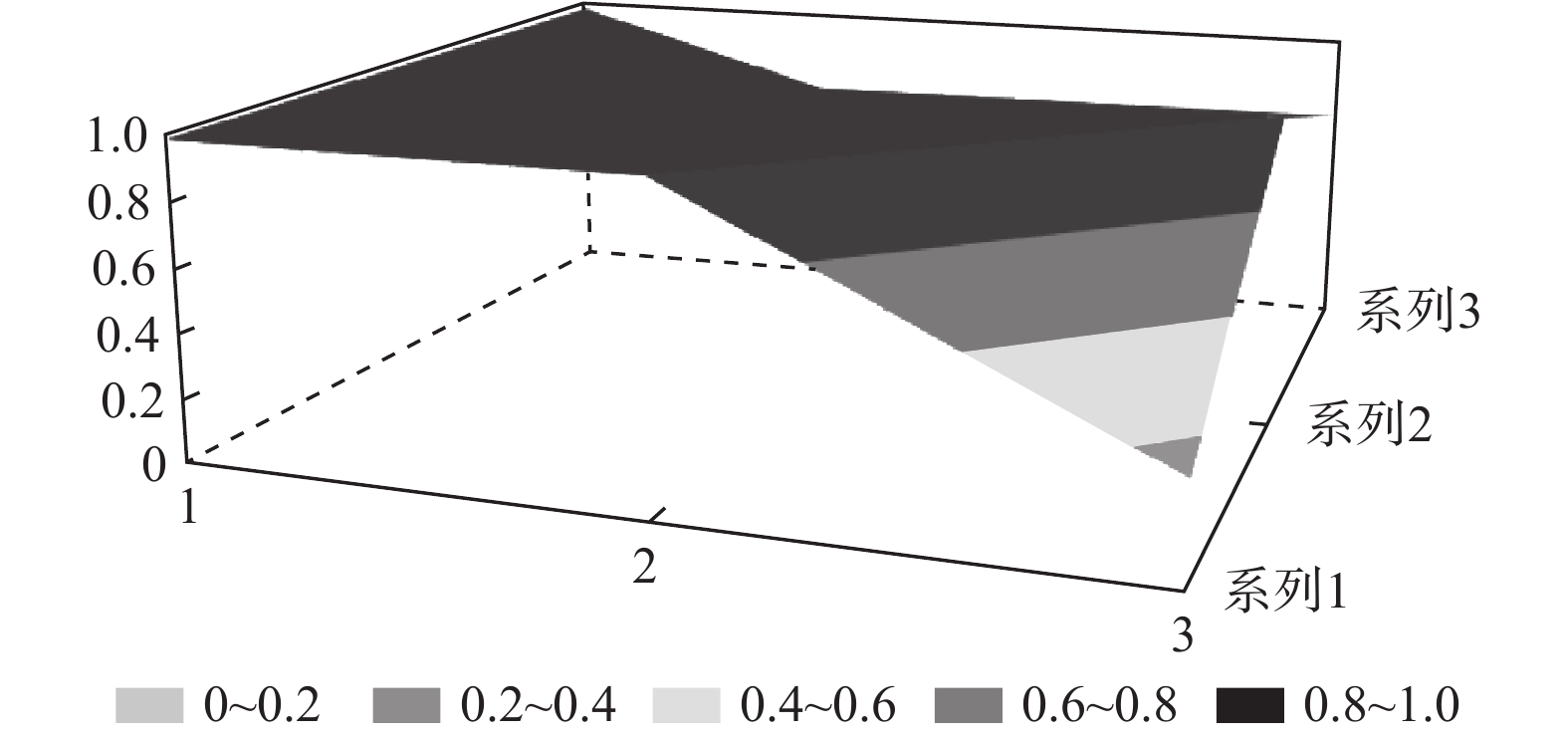
为了进一步直观地反映各试点筹资政策的优势和局限,笔者选择了一些代表性政策来绘制其PMC曲面。首先,为了方便进行比较,笔者选取27份政策一级变量的均值构建了虚拟政策P28;其次,代表性政策有三:一是完美等级政策P2,二是优秀等级政策中的得分首位P9、得分偏低的P12和得分末位的P21,三是可接受等级政策的末位
$ \mathrm{P}26 $ 。上述曲面图,如图1~图6所示,其中,凸起的部分表示该一级变量得分较高,凹陷的地方表示该一级变量得分较低。由图2可知,P2的
$ {X}_{1} $ 和$ {X}_{10} $ 与均值一致,X2~X9中除了$ {X}_{2} $ 因2021年更新LTCI试点政策导致得分低于均值外,其他一级变量均高于均值,其中$ ,{X}_{3},{X}_{4},{X}_{5}, {X}_{7},{X}_{8},{X}_{9} $ 均为满分。政策功能完善,且长春市作为LTCI第一批重点联系省份的城市,出台了省级LTCI试点意见。另外,2021年调整试点办法,将参保对象由“城镇职工+城镇居民”扩展至覆盖全民;形成了独立筹资渠道,实现了职工参保人的单位与个人同比例承担缴费责任;设置了按比例限额支付,并构建了待遇与筹资关联机制,体现了“多缴多得”“长缴多得”的参保激励;继续为制度划拨启动资金,提高了$ {X}_{5} $ ~$ {X}_{9} $ 的值。因此,仅为$ {X}_{2} $ 处存在明显凹陷,其他变量均高于平均水平,属于完美等级政策,具有较强的借鉴意义。P9位于优秀等级政策首位,青岛市作为第一批试点城市,于2021年更新了试点政策,对LTCI筹资进行了长期规划;政策功能完备,与作为重点联系省份政策的P2一致,政策发布机构级别较高,并实现了全民参保,因此
$ ,{X}_{2},{X}_{3},{X}_{4},{X}_{5} $ 均为满分;但在责任分担方面未能实现同比例划分。此外,未在试点办法中明确按比例给付的封顶线,筹资与待遇关联机制方面仅为不同缴费水平设置了差异化支付比例,未能体现“长缴多得”,因此,表现为$ {X}_{6} $ ,$ {X}_{7} $ ,$ {X}_{9} $ 处存在凹陷。P12和P21分别属于第一批和第二批试点城市的政策,前者在优秀等级政策中得分偏低,后者位于优秀等级政策最末位。P12为直辖市政策且试点时间较长,因此,表现为
$ {X}_{2} $ ,$ {X}_{4} $ 处凸起;P21则在$ {X}_{2} $ ,$ {X}_{4} $ 这两个指标上得分偏低,因此,也在相应位置存在凹陷。这两个城市的政策在参保对象方面都仅覆盖城镇职工,但P21作为第二批试点城市的政策实现了独立筹资,按$ 1:1 $ 划分筹资责任并实现按比例限额支付,参数设计相对完善,因此,表现为$ {X}_{6} $ ,$ {X}_{7} $ ,$ {X}_{9} $ 处凸起;而P12则由于依赖医保基金划拨,未能同比例划分缴费责任,以及定额给付存在一定程度的滞后性,可能无法有效满足当地失能老人的照护需求,因此,表现为$ {X}_{6} $ ,$ {X}_{7} $ ,$ {X}_{9} $ 处存在凹陷。P26的PMC指数位于整个样本最末位。原因在于,政策中未能体现“分类推进”思想,筹资机制设计规定采用定额筹资、筹资标准确定依据缺失、非同比例分担缴费责任、定额支付难以体现适当性标准,资金保障力度不足等,因此,表现为
$ {X}_{3},{X}_{6}, {X}_{7},{X}_{8}, {X}_{9} $ 处存在明显凹陷。(三) LTCI筹资政策的局限性
由图1可知,LTCI筹资政策明确了政策性质和政策功能,并实现政策公开,但仍存在以下局限:
第一,政策时效偏短。无论是从先后两批试点城市政策分别的均值,还是整体均值来看,
$ {X}_{2} $ 的得分明显偏低,且第二批试点城市政策尤甚,部分原因在于第二批试点城市公布政策的时间较短。但从客观上却说明,LTCI缺乏长期规划,特别是筹资政策的不稳定,难以保障制度独立、可持续发展。第二,LTCI筹资政策发布机构级别偏低。除了重点联系省份的政策(P2, P9)和直辖市的政策(
$ \mathrm{P}4, \mathrm{P}12,\mathrm{P}15,\mathrm{P}16 $ )外,仅P13(成都市)在试点中由四川省颁布,其他试点城市政策的发布机构均为地级市政府,发布级别较低不利于统筹资源,也在一定程度上加剧了政策碎片化。第三,LTCI覆盖范围受限。第二批试点城市政策中,除P15和P18外,其他都仅覆盖城镇职工。如果2016年试点初期考虑基金承受能力选择从职工群体开始参保,那么2020年扩大试点时仍集中于城镇职工便有延续路径依赖之嫌。以身份标准设置参保屏障,忽视城乡其他居民的公民社会权力,将会削弱制度公平性和基金抗风险能力,且会增加未来制度整合成本。
第四,作为筹资政策的核心维度,LTCI筹资机制仍需完善。试点中筹资机制的局限表现为:近半数试点城市依赖医保基金划拨;延续定额筹资方式虽便于操作,但具有累退性的缺陷;筹资标准确定依据缺失不利于形成科学动态的调整机制;各缴费主体之间责任划分不合理,财政或个人筹资比例失衡损害制度公平及可持续;“以收定支”的筹资原则从根本上未能尊重社会保险基本原理[25],存在用“预算平衡”替代“精算平衡”的风险;缺乏筹资与待遇关联机制,削弱缴费激励。
第五,LTCI启动资金划转的规范性缺失。人社厅发〔2016〕80号和医保发〔2020〕37号这两份国家级试点文件均未规定LTCI启动资金来源,试点中的承德市、上海市、苏州市、安庆市、上饶市等16个城市也缺乏有关启动资金来源的规定,占比近六成。实践中,LTCI基金主要来源于医保统筹基金结余,但缺乏规范化划转方式,难以明确医保基金于LTCI的责任,长期下去不仅会阻碍LTCI财务的平衡与独立发展,而且随着人口进一步老龄化还将会危及医保基金平稳运行。
四、 LTCI筹资政策优化路径:以P26为例
P26排名样本末位,作为第二批试点城市的政策,理应取得更好的表现,然而却事与愿违。鉴于此,笔者基于PMC指数的可追溯性,在此提出两种优化策略:一是比较各一级变量与整体政策均值的差异,二是通过比较凹陷指数与引入的完美虚拟政策间的差异,如表6所示。
表 6 P26的两种优化策略$ \mathrm{P}26 $ 与PMC指数整体均值的差 凹陷指数占比/% $ {X}_{1} $ 0 0 $ {X}_{2} $ −0.15 16.96 $ {X}_{3} $ −0.23 6.36 $ {X}_{4} $ −0.13 12.72 $ {X}_{5} $ −0.22 12.72 $ {X}_{6} $ −0.14 15.27 $ {X}_{7} $ −0.27 16.96 $ {X}_{8} $ −0.10 6.36 $ {X}_{9} $ −0.27 12.72 $ {X}_{10} $ 0 0 对表6中“与PMC指数整体均值的差”取绝对值可知,第一种策略下P26的优化路径为:
$ {X}_{7} $ ,$ {X}_{9} $ —$ {X}_{3} $ —$ {X}_{5} $ —$ {X}_{2} $ —$ {X}_{6} $ —$ {X}_{4} $ —$ {X}_{8} $ 。汉中市LTCI筹资政策优化,一是应完善待遇给付设计,采用按比例支付方式,并构建筹资与待遇关联机制,在确保有效减轻失能老人及其家庭面临的经济压力的同时强化参保激励,同时,明确筹资标准的确定依据,同比例划分缴费责任;二是重视政策分类推进的功能,适时将城乡居民纳入参保范围;三是重视政策连续性与稳定性,在制定LTCI政策时应考虑中期乃至长期方案以促成稳定性预期;四是按照社会保险原理确定“以支定收”的筹资原则,实行比例缴费,形成动态筹资机制,同时有效避免筹资的累退性;五是提升试点政策发布机构层级促进协同治理,并增加对LTCI的资金保障与支持,尽快使申请人受益,发挥示范作用。表6中的“凹陷指数占比”是第二种策略,按照由大到小排序,优化路径为:
$ {X}_{2} $ ,$ {X}_{7} $ —$ {X}_{6} $ —$ {X}_{4} $ ,$ {X}_{5} $ ,$ {X}_{9} $ —$ {X}_{3} $ ,$ {X}_{8} $ 。首先,重视政策有效期,避免“朝令夕改”;通过完善待遇给付的有关规定约束基金支出从而控制照护资金需求规模,引导参保人待遇预期。其次,优化筹资机制,强化制度科学性与经济可持续性,继而提高试点政策级别,提升规范力度和整合能力;尽快扩大覆盖面,保障公民权利。最后,完善政策功能,强化筹资制度保障措施。综上可知,LTCI筹资政策的优化路径并不唯一,无论是先从微观层面上完善筹资机制的各项参数,还是先从宏观层面上强调社会保险政策稳定预期的功能,均需要根据环境变化进行选择,而其中某个变量的改革会对其他变量取值产生联动影响。故而,应强化顶层设计,关注各政策变量间互动关系,以系统的视角优化LTCI筹资政策,设计科学、合理的筹资机制,并从资金划拨、法律规制等方面为LTCI基金提供支持,为LTCI制度发展提供物质保障。五、 结论与建议
基于政策文本和PMC指数模型构建针对LTCI筹资政策的量化评价体系,选择国家先后两批共27份政策文本分析筹资政策的一致性水平,对第一批与第二批试点政策差异,以及代表性政策进行比较,结果发现LTCI筹资政策兼具“描述”“建议”“支持”“引导”的性质,具备“明确权责”“规范引导”“分类推进”“统筹协调”的功能,政策目标明确,也均实现公开。最后,选择代表性政策绘制PMC曲面并进行分析,并为末位政策提供两种优化策略。
综合各城市LTCI筹资政策,为中国LTCI深化试点,促进制度定型与完善提出以下建议:
第一,以疏解当期困境与促成稳定预期为目标,优化LTCI筹资机制设计,兼顾公平性、平等性和适当性标准。筹资机制试点现状显示:受益对象仅覆盖城镇职工的占比为55.56%,过半城市试点政策未包含城乡居民;资金来源尚依赖医保基金的占比为40.74%,独立性较差;48.15%的城市政策采用定额筹资;筹资责任分担不均的城市政策近五成;苏州市等6个城市的政策实行定额支付。另外,九成的试点城市政策采用“以收定支”的筹资原则,与社会保险基本原理相违背,也不利于参保人稳定预期。因此,应扩大覆盖范围、实现独立筹资并基于“以支定收”的筹资原则确定筹资标准,筹资方式和责任分担遵循“公平性”与“平等性”,待遇给付体现“适当性”,形成科学的动态筹资机制。
第二,LTCI筹资政策诸环节与其他部门之间具有重要联系,如保障措施中划拨启动资金、独立筹资中的费用征缴、待遇给付中的经办管理与质量保障等均需要相关部门的协调配合。政策发布机构级别较低无疑增加了部门协同的难度,因此,应提升政策发布机构层级以强化政策的规范与指导力度。在政策时效方面,在科学构建LTCI筹资机制的基础上重视中长期规划,如青岛市和晋城市,提高政策稳定性有利于各方主体形成稳定预期,增进制度认同。
第三,从资金投入、法律法规等方面强化对LTCI筹资的支持。LTCI制度构建时要妥善处理好“隐性债务”问题,特别是在制度建立之初“老人”
③ 群体的权利保障,明确责任主体和资金来源于现收现付制的LTCI制度尤为重要。为了解决好制度初建时申请人的待遇支付问题,可划拨启动资金充实LTCI基金;通过完善法律法规提升LTCI遵缴率,平衡参保人的权利与义务,保障制度健康可持续发展。注释:
① 虚拟完美政策的各一级变量取值为1。② 27份政策的多投入产出表略。③ 借用养老保险中的概念,“老人”是指在LTCI制度建立时享受给付权利而未尽缴费义务的人群。 -
表 1 27份LTCI试点政策文本汇总
编号 政策名称 发文字号 发布日期 $ \mathrm{P}1 $ 《承德市城镇职工长期护理保险实施办法(试行)》 承人社发〔2016〕28号 2016年11月23日 $ \mathrm{P}2 $ 《吉林省深入推进长期护理保险制度试点工作实施方案》 吉医保联〔2021〕7号 2021年4月13日 $ \mathrm{P} 3$ 《齐齐哈尔市深化长期护理保险制度试点实施方案(试行)》 齐政办规〔2021〕1号 2021年2月19日 $ \mathrm{P}4 $ 《上海市长期护理保险试点办法》 沪府发〔2017〕97号 2017年12月30日 $ \mathrm{P}5 $ 《关于建立基本照护保险制度的意见(试行)》 通政发〔2015〕73号 2015年10月20日 $ \mathrm{P}6 $ 《关于开展长期护理保险试点第二阶段工作的实施意见》 苏府〔2020〕10号 2020年1月20日 $ \mathrm{P}7 $ 《安庆市城镇职工长期护理保险试点的实施意见》 宜政办秘〔2017〕5号 2017年1月20日 $ \mathrm{P}8 $ 《全面开展长期护理保险制度试点实施方案》 饶府字〔2019〕33号 2019年7月27日 $ \mathrm{P}9 $ 《青岛市长期护理保险办法》 青政发〔2021〕6号 2021年3月25日 $ \mathrm{P}10 $ 《荆门市长期护理保险办法(试行)》 荆政发〔2016〕43号 2016年11月22日 $ \mathrm{P}11 $ 《广州市长期护理保险试行办法》 穗医保规字〔2020〕10号 2020年12月30日 $ \mathrm{P}12 $ 《重庆市长期护理保险实施细则 (试行)》 渝医保发〔2018〕14号 2018年12月11日 $ \mathrm{P}13 $ 《深化长期照护保险制度试点的实施意见》 成府发〔2020〕16号 2020年5月12日 $ \mathrm{P}14 $ 《八师石河子市长期护理保险实施细则(试行)》 师市办发〔2017〕15号 2017年2月23日 $ \mathrm{P}15 $ 《北京市长期护理保险制度扩大试点方案》 京医保发〔2020〕30号 2020年10月28日 $ \mathrm{P}16 $ 《天津市长期护理保险制度试点实施方案》 津政办规〔2020〕24号 2020年12月17日 $ \mathrm{P} 17$ 《关于建立长期护理保险制度的实施意见》 晋市政发〔2020〕14号 2020年12月30日 $ \mathrm{P}18 $ 《呼和浩特市长期护理保险制度试点实施方案》 呼政办发〔2020〕31号 2021年1月22日 $ \mathrm{P}19 $ 《盘锦市开展全国长期护理保险制度试点工作实施方案》 盘政办发〔2020〕25号 2020年12月15日 $ \mathrm{P}20 $ 《关于开展长期护理保险制度试点的实施方案》 榕政综〔2020〕262号 2020年12月24日 $ \mathrm{P}21 $ 《开封市长期护理保险制度试行办法》 汴政〔2020〕36号 2020年12月30日 $ \mathrm{P}22 $ 《湘潭市长期护理保险制度试点实施方案》 潭政办发〔2020〕33号 2020年12月10日 $ \mathrm{P}23 $ 《南宁市人民政府关于南宁市长期护理保险制度试点的实施意见》 南府规〔2021〕3号 2021年1月11日 $ \mathrm{P} 24$ 《黔西南州长期护理保险制度试点实施方案》 黔西南府办发〔2020〕27号 2020年11月6日 $ \mathrm{P} 25$ 《昆明市人民政府关于全面开展长期护理保险制度试点工作方案》 昆政发〔2020〕39号 2020年12月29日 $ \mathrm{P} 26$ 《汉中市长期护理保险实施办法(试行)》 汉政办发〔2020〕25号 2020年11月5日 $ \mathrm{P} 27$ 《乌鲁木齐市长期护理保险办法(试行)》 乌政办〔2018〕254号 2018年11月2日 表 2 LTCI筹资机制的PMC指标体系及评价标准
一级变量 二级变量 评价标准 政策性质(X1) 描述(X1-1) 说明LTCI的制度性质:是为1,否为0 建议(X1-2) 提出对LTCI筹资模式的指导意见:是为1,否为0 支持(X1-3) 从政策协调、组织管理等角度支持LTCI资金筹集工作:是为1,否为0 引导(X1-4) 从政策主体与政策受体的角度引导对LTCI筹资的重视与认同,旨在提高积极性与遵从度:是为1,否为0 政策时效(X2) 短期(X2-1) 有效期为2年(含)以内:是为1,否为0 中期(X2-2) 有效期为2~5年(含):是为1,否为0 长期(X2-3) 有效期为5年以上:是为1,否为0 政策功能(X3) 明确权责(X3-1) 明确各方权责:是为1,否为0 规范引导(X3-2) 政策引导规范:是为1,否为0 分类推进(X3-3) 体现分类推进思想:是为1,否为0 统筹协调(X3-4) 统筹推进试点:是为1,否为0 发布机构(X4) 省、自治区、直辖市(X4-1) 发布机构为省(自治区、直辖市)级政府机构:是为1,否为0 地级市(X4-2) 发布机构为地级市政府机构:是为1,否为0 参保对象(X5) 城镇职工(X5-1) 覆盖城镇职工:是为1,否为0 城乡居民(X5-2) 覆盖城乡居民:是为1,否为0 政策规范(X6) 筹资来源(X6-1) 独立筹资,无医保基金介入:是为1,否为0 筹资原则(X6-2) 采用“以支定收”的筹资原则:是为1,否为0 筹资标准(X6-3) 明确筹资标准:是为1,否为0 筹资方式(X6-4) 实行“比例缴费”:是为1,否为0 责任分担(X6-5) 同比例分担缴费责任:是为1,否为0 激励约束(X7) 给付方式(X7-1) 按比例支付:是为1,否为0 给付封顶线(X7-2) 设置封顶线:是为1,否为0 待遇与筹资关联机制(X7-3) 设置待遇与筹资关联机制:是为1,否为0 保障措施(X8) 资金保障(X8-1) 划转启动资金/建立调剂金/计提风险准备金等:是为1,否为0 法律法规(X8-2) 提供法律规范:是为1,否为0 组织领导(X8-3) 协调组织领导:是为1,否为0 基金管理(X8-4) 明确基金管理办法:是为1,否为0 政策评价(X9) 目标明确(X9-1) 筹资目标是否清晰:是为1,否为0 依据充分(X9-2) 筹资标准确定依据是否明确:是为1,否为0 方案公平(X9-3) 缴费方案设置是否满足公平性标准:是为1,否为0 权责清晰(X9-4) 各缴费主体权责是否明确:是为1,否为0 政策公开(X10) 政策公开发布:是为1,否为0 表 3 PMC指数评价标准
PMC指数 [0,5) [5,7) [7,9) [9,10] 政策评价 不良 可接受 优秀 完美 表 4 27项LTCI试点筹资政策的PMC指数
编号 $ {X}_{1} $ $ {X}_{2} $ $ {X}_{3} $ $ {X}_{4} $ $ {X}_{5} $ $ {X}_{6} $ $ {X}_{7} $ $ {X}_{8} $ $ {X}_{9} $ $ {X}_{10} $ PMC指数 排名 等级 凹陷指数 $ \mathrm{P}1 $ 1.00 0.67 0.75 0.50 0.50 0.40 0.67 0.75 0.75 1.00 6.98 15 可接受 3.02 $ \mathrm{P}2 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.80 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 9.13 1 完美 0.87 $ \mathrm{P}3 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.40 0.67 0.75 0.75 1.00 6.90 16 可接受 3.10 $ \mathrm{P}4 $ 1.00 0.67 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.40 0.33 0.75 0.75 1.00 7.90 8 优秀 2.10 $ \mathrm{P}5 $ 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.20 0.67 1.00 0.75 1.00 8.12 4 优秀 1.88 $ \mathrm{P}6 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.20 0.33 0.75 0.50 1.00 6.62 19 可接受 3.38 $ \mathrm{P}7 $ 1.00 0.67 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.20 0.67 0.75 0.50 1.00 6.78 17 可接受 3.22 $ \mathrm{P}8 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.20 0.33 0.75 0.50 1.00 6.62 19 可接受 3.38 $ \mathrm{P}9 $ 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.60 0.33 1.00 0.75 1.00 8.68 2 优秀 1.32 $ \mathrm{P}10 $ 1.00 0.67 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.40 1.00 0.75 0.75 1.00 8.07 6 优秀 1.93 $ \mathrm{P}11 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.80 0.67 0.75 0.75 1.00 7.80 11 优秀 2.20 $ \mathrm{P}12 $ 1.00 0.67 1.00 1.00 0.50 0.40 0.33 0.75 0.50 1.00 7.15 13 优秀 2.85 $ \mathrm{P}13 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.80 0.33 1.00 1.00 1.00 8.47 3 优秀 1.53 $ \mathrm{P}14 $ 1.00 0.67 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.20 1.00 1.00 0.50 1.00 7.87 10 优秀 2.13 $ \mathrm{P}15 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.60 0.67 0.75 0.75 1.00 8.10 5 优秀 1.90 $ \mathrm{P} 16$ 1.00 0.33 1.00 1.00 0.50 0.60 0.67 1.00 1.00 1.00 8.10 5 优秀 1.90 $ \mathrm{P} 17$ 1.00 0.67 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.80 0.67 0.75 1.00 1.00 7.88 9 优秀 2.12 $ \mathrm{P}18 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.80 0.67 0.75 1.00 1.00 8.05 7 优秀 1.95 $ \mathrm{P}19 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.80 0.67 1.00 1.00 1.00 7.80 11 优秀 2.20 $ \mathrm{P}20 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.80 0.67 0.75 1.00 1.00 7.55 12 优秀 2.45 $ \mathrm{P}21 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.60 0.67 0.75 0.75 1.00 7.10 14 优秀 2.90 $ \mathrm{P}22 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.80 0.67 1.00 1.00 1.00 7.80 11 优秀 2.20 $ \mathrm{P}23 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.80 0.67 1.00 1.00 1.00 7.80 11 优秀 2.20 $ \mathrm{P} 24$ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.60 0.33 1.00 0.50 1.00 6.77 18 可接受 3.23 $ \mathrm{P}25 $ 1.00 0.33 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.80 0.67 1.00 1.00 1.00 7.80 11 优秀 2.20 $ \mathrm{P} 26$ 1.00 0.33 0.75 0.50 0.50 0.40 0.33 0.75 0.50 1.00 6.07 20 可接受 3.93 $ \mathrm{P}27 $ 1.00 0.67 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.20 0.67 0.75 0.50 1.00 6.78 17 可接受 3.22 均值 1.00 0.48 0.98 0.63 0.72 0.54 0.61 0.85 0.77 1.00 7.58 2.42 表 5 两批试点城市LTCI筹资政策均值的PMC指数比较
试点城市 $ {X}_{1} $ $ {X}_{2} $ $ {X}_{3} $ $ {X}_{4} $ $ {X}_{5} $ $ {X}_{6} $ $ {X}_{7} $ $ {X}_{8} $ $ {X}_{9} $ $ {X}_{10} $ PMC指数均值 第一批 1.00 0.57 0.98 0.68 0.86 0.43 0.60 0.84 0.70 1.00 7.65 第二批 1.00 0.38 0.98 0.58 0.58 0.66 0.62 0.87 0.85 1.00 7.51 表 6 P26的两种优化策略
$ \mathrm{P}26 $ 与PMC指数整体均值的差 凹陷指数占比/% $ {X}_{1} $ 0 0 $ {X}_{2} $ −0.15 16.96 $ {X}_{3} $ −0.23 6.36 $ {X}_{4} $ −0.13 12.72 $ {X}_{5} $ −0.22 12.72 $ {X}_{6} $ −0.14 15.27 $ {X}_{7} $ −0.27 16.96 $ {X}_{8} $ −0.10 6.36 $ {X}_{9} $ −0.27 12.72 $ {X}_{10} $ 0 0 -
[1] 胡宏伟,李延宇. 我国老年长期照护保险筹资、补偿水平优化设计研究−兼论老年照护保险框架设定[J]. 河北大学学报(哲学社会科学版),2017,42(5):117—128. [2] 尹海燕. 可持续的公共长期护理保险筹资机制:国外经验与中国方案[J]. 宏观经济研究,2020(5):166—175. [3] 许敏敏,段娜. 德国长期护理保险及其筹资机制经验对我国的启示[J]. 价格理论与实践,2019(7):99—103. [4] 景跃军,孟石,李元. 德美日长期护理保险资金筹集模式的特点及启示[J]. 延边大学学报(社会科学版),2018,51(2):101—107,143. [5] 孙洁,蒋悦竹. 社会长期护理保险筹资机制理论分析框架[J]. 江西财经大学学报,2018(1):59—68. [6] WOLLMANN H. Policy evaluation and evaluation research [M]// Handbook of public policy analysis. London: Routledge, 2017: 419—428.
[7] GREENE F J. Assessing the impact of policy interventions:The influence of evaluation methodology [J]. Environment and Planning C:Government and Policy,2009,27(2):216—229. doi: 10.1068/c07103b
[8] DANN C,NEUMANN G,PETERS J. Policy evaluation with temporal differences:A survey and comparison [J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research,2014,15:809—883.
[9] 高雪莲. 政策评价方法论的研究进展及其争论[J]. 理论探讨,2009(5):139—142. [10] RUIZ ESTRADA M A,YAP S F,NAGARAJ S. Beyond the ceteris paribus assumption:Modeling demand and supply assuming Omnia Mobilis [J]. International Journal of Economic Research,2008,5(2):185—194.
[11] 张永安,郄海拓. “大众创业、万众创新”政策量化评价研究−以2017的10项双创政策情报为例[J]. 情报杂志,2018(3):158—164,186. [12] 丁潇君,房雅婷. “中国芯”扶持政策挖掘与量化评价研究[J]. 软科学,2019(4):34—39. [13] 周海炜,陈青青. 大数据发展政策的量化评价及优化路径探究−基于PMC指数模型[J]. 管理现代化,2020(4):74—78. [14] 方永恒,刘佳敏. 国务院养老服务政策挖掘与量化评价−基于PMC指数模型分析[J]. 云南行政学院学报,2020,22(5):167—176. [15] 王霆,刘玉. 农民工就业政策量化评价[J]. 华南农业大学学报(社会科学版),2021,20(1):71—83. [16] 祝西冰. 托幼公共服务政策量化评价与优化建议−基于PMC指数模型分析[J]. 浙江工商大学学报,2020(3):124—136. [17] 人力资源和社会保障部办公厅. 人力资源社会保障部办公厅关于开展长期护理保险制度试点的指导意见[EB/OL]. (2016−06−27)[2021−08−11]. [18] 国家医保局, 财政部. 国家医保局 财政部关于扩大长期护理保险制度试点的指导意见[EB/OL]. (2020−09−16)[2021−08−11]. [19] RUIZ ESTRADA M A. Policy modeling:Definition,classification and evaluation [J]. Journal of Policy Modeling,2011,33(4):523—536. doi: 10.1016/j.jpolmod.2011.02.003
[20] 张文静,张丽,姚俊. 长期护理保险制度政策评价:基于PMC指数模型[J]. 中国卫生事业管理,2021(2):103—108. [21] 张永安,耿喆. 我国区域科技创新政策的量化评价−基于PMC指数模型[J]. 科技管理研究,2015(14):26—31. [22] DATTA L. Politics and evaluation:More than methodology [J]. American Journal of Evaluation,2011,32(2):273—294. doi: 10.1177/1098214011400060
[23] GILBERT N, TERRELL P. 社会福利政策引论 [M]. 沈黎, 译. 上海: 华东理工大学出版社, 2013: 94—95. [24] 贝弗里奇. 贝弗里奇报告: 社会保险和相关服务[M]. 劳动和社会保障部社会保险研究所, 译. 北京: 中国劳动社会保障出版社, 2004: 136. [25] 何文炯,杨一心. 社会医疗保险筹资若干问题辨析[J]. 中国医疗保险,2011(3):34—37. -
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 胡若晨,朱菊芳. 政策工具理论视角下国家体育消费试点城市政策供给特征与实践研究. 浙江体育科学. 2024(02): 40-45+53 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孙洁,黄艺飞. 构建长期护理保险保障体系的实证研究——以浙江省数据为例. 价格理论与实践. 2024(10): 53-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 胡乃军,古凤清. 长期护理资金需求与长期护理保险基金筹集研究——以北京市为例. 科技促进发展. 2024(Z2): 855-864 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李思成,张良文,方亚. 长期护理保险实施效果评价研究进展. 中国公共卫生. 2023(01): 122-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 陈泽霖,陈旻. 多元化筹资与“过渡治理”——基于福建省晋江市长护险筹资实践的考察. 社会建设. 2023(01): 57-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 胡芳,韦彦名,王宪妹. 保险科技赋能长期护理保险制度:内在机理、存在问题与实践路径. 西南金融. 2023(02): 57-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 胡若晨,朱菊芳,周铭扬. 中国式现代化进程中体育消费试点城市政策量化评价——基于PMC指数模型. 天津体育学院学报. 2023(04): 420-427 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 张治国,向晨. 基于PMC指数模型的我国医疗保障基金使用监管政策文本量化评价. 社会保障研究. 2023(04): 57-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 陈曦萌,兰代巧,陈燕. 基于PMC指数模型的产教融合政策量化评价研究. 广西职业技术学院学报. 2023(04): 68-81 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 陈显友,张瑞杰. 吉林省长期护理保险制度政策文本量化评价与优化研究. 社会建设. 2023(05): 37-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 王微,秦玲玲,张倩. 贵阳市长期护理保险筹资标准实证分析. 中国卫生经济. 2022(06): 26-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 穆井英,宋蕾. 人口老龄化背景下推行长期护理保险对护理教育的启示. 吉林广播电视大学学报. 2022(06): 124-126+130 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(10)



 下载:
下载: