-
摘要:
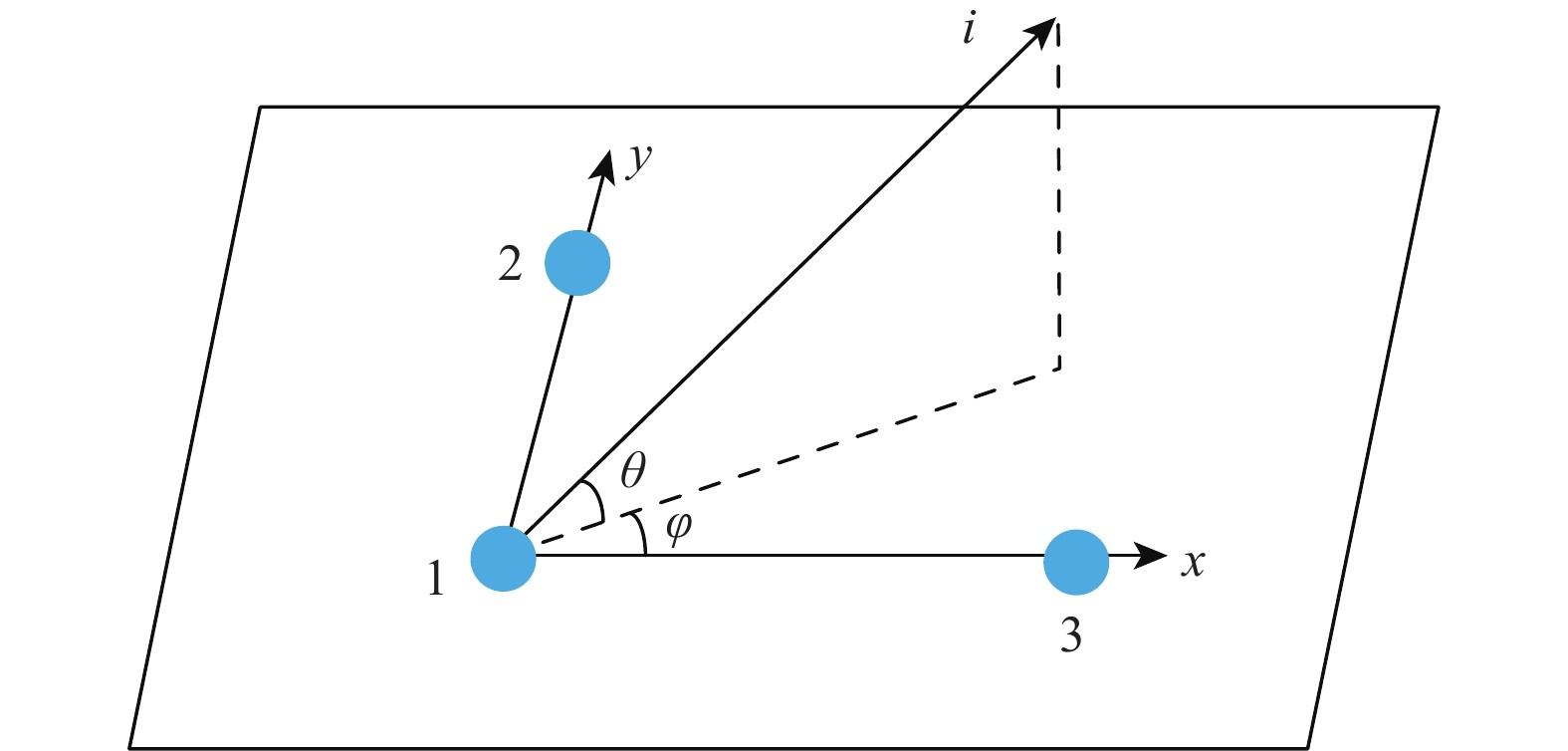
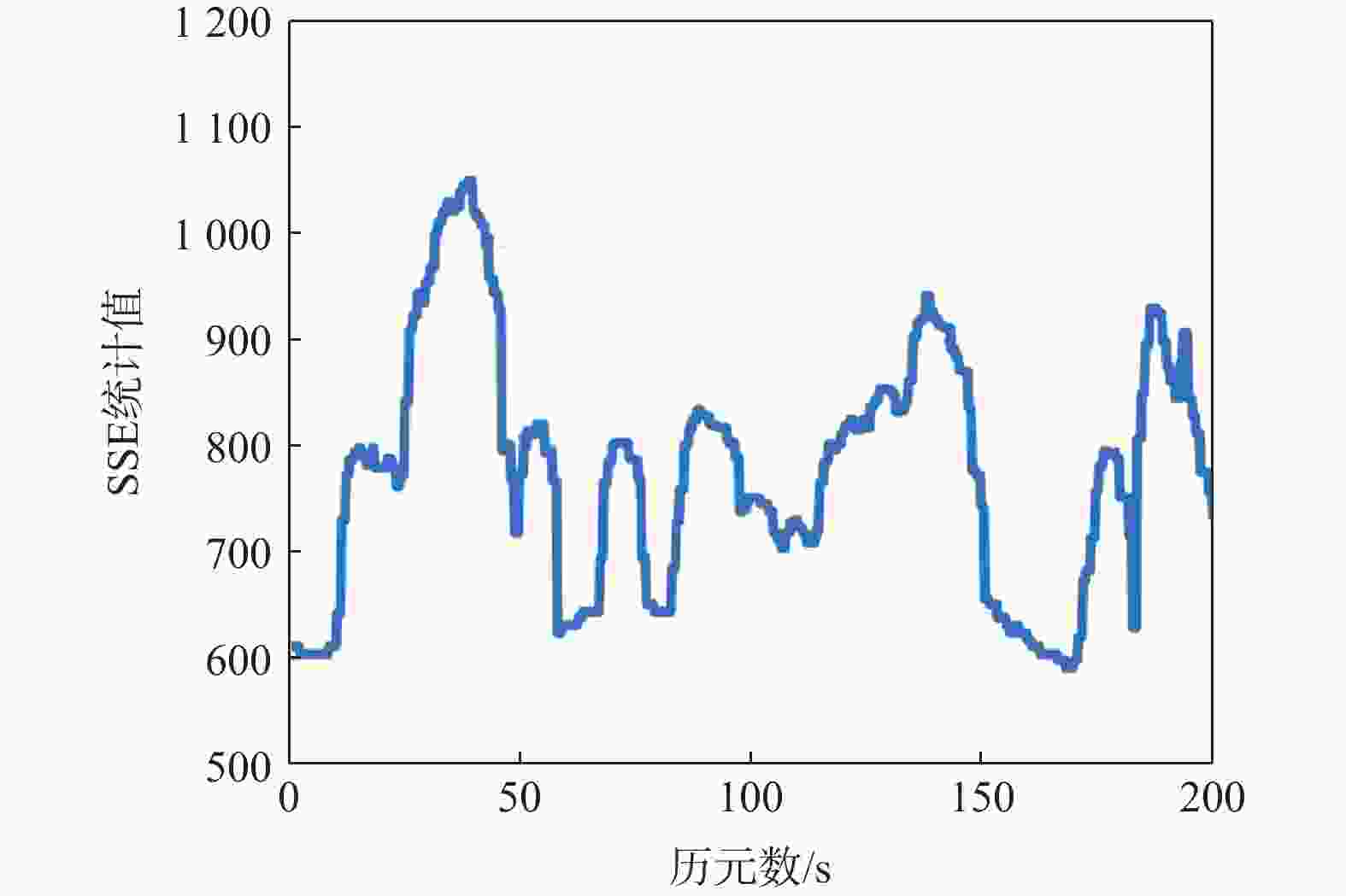
全球卫星导航系统(GNSS)的安全性已经引发了广泛关注。使用多天线的欺骗检测方法由于其独一无二的空间特性,已成为当前最有效的欺骗检测方法之一。提出一种使用三天线的联合定姿和欺骗检测方法,能够在确定天线载体姿态的同时检测出欺骗信号的存在。针对直接定姿法受限于基线向量精度的问题,使用长度约束的基线向量估计方法以获得高精度定姿结果。在姿态信息已知的前提下,根据星历信息、姿态变换矩阵及天线的几何关系可以获得载波相位单差的期望值。使用误差平方和(SSE)来评估载波相位单差观测值和期望值之间的偏差,并构建了欺骗信号的二元检验。结果表明:在无欺骗的情形下,所提方法能降低定姿的标准差76.1%以上;在有欺骗的情形,所提方法能够实现100%检测率,并降低定姿的标准差77.3%以上。
Abstract:The security of the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) has aroused widespread concern. The multiple-antennas method has become the most effective spoofing detection method due to its unique spatial characteristics. A joint attitude determination and spoofing detection method using three antennas is proposed, detecting spoofing signals and determining the attitude information. The baseline accuracy limits the traditional direct attitude determination method, so a length-constrained baseline vector estimation method is adopted to obtain high-precision attitude determination results. When attitude information is known, the carrier phase single-difference expected value can be obtained by the ephemeris, attitude transformation matrix, and the antennas’ geometric relationship. The sum of the squared error (SSE) is used to evaluate the deviation between the observed and expected value of carrier phase single-difference, and the spoofing signal binary detection is constructed. The results shows that this method can reduce the standard deviation of attitude determination by more than 76.1% when there is no spoofing signal, and achieve 100%. detection efficiency with a more than 77.3% reducation on standard deviation of attitude when spoofing signal involved.
-
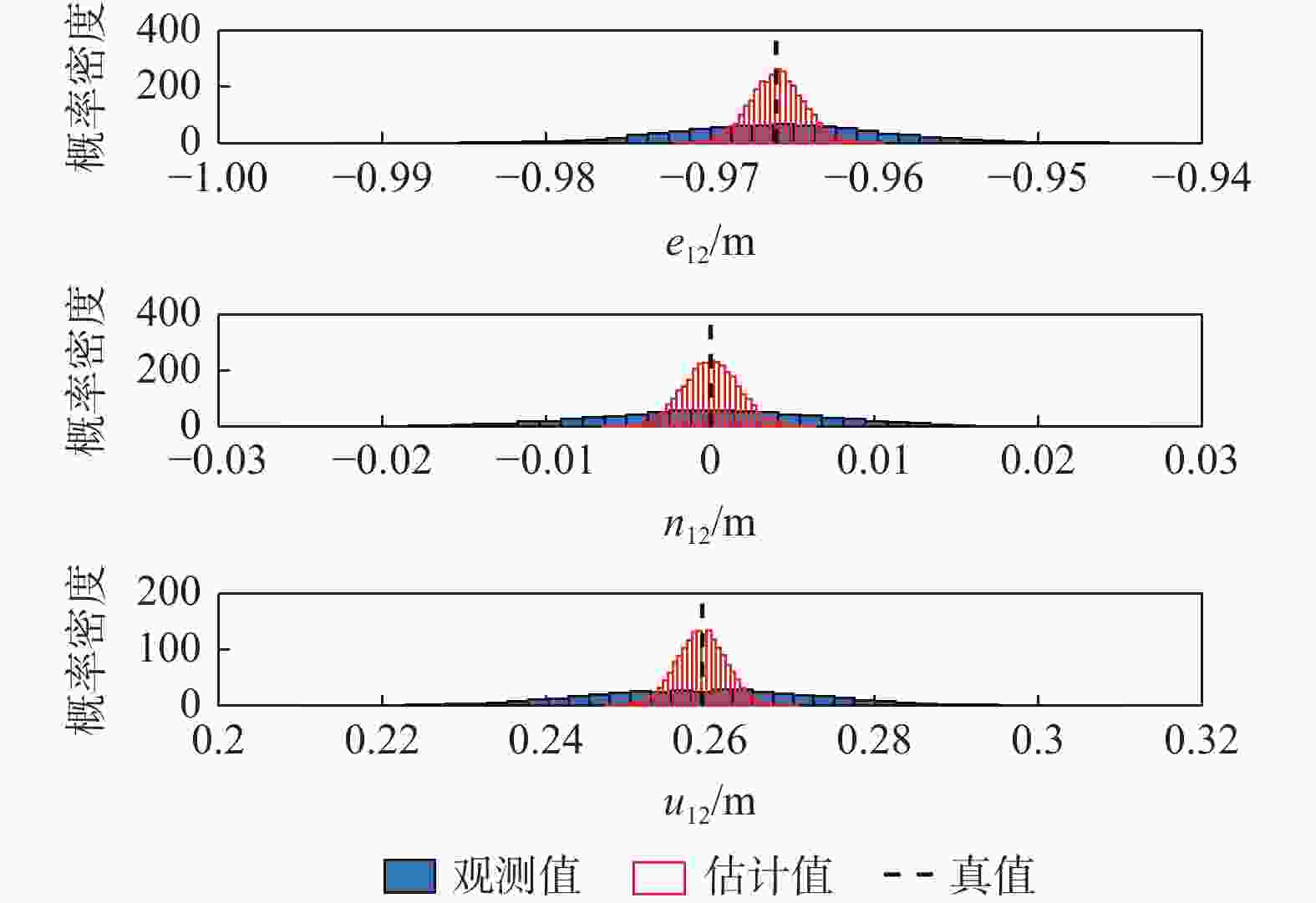
表 1 基线向量解算结果的统计量
Table 1. Statistics of baseline vector solution results
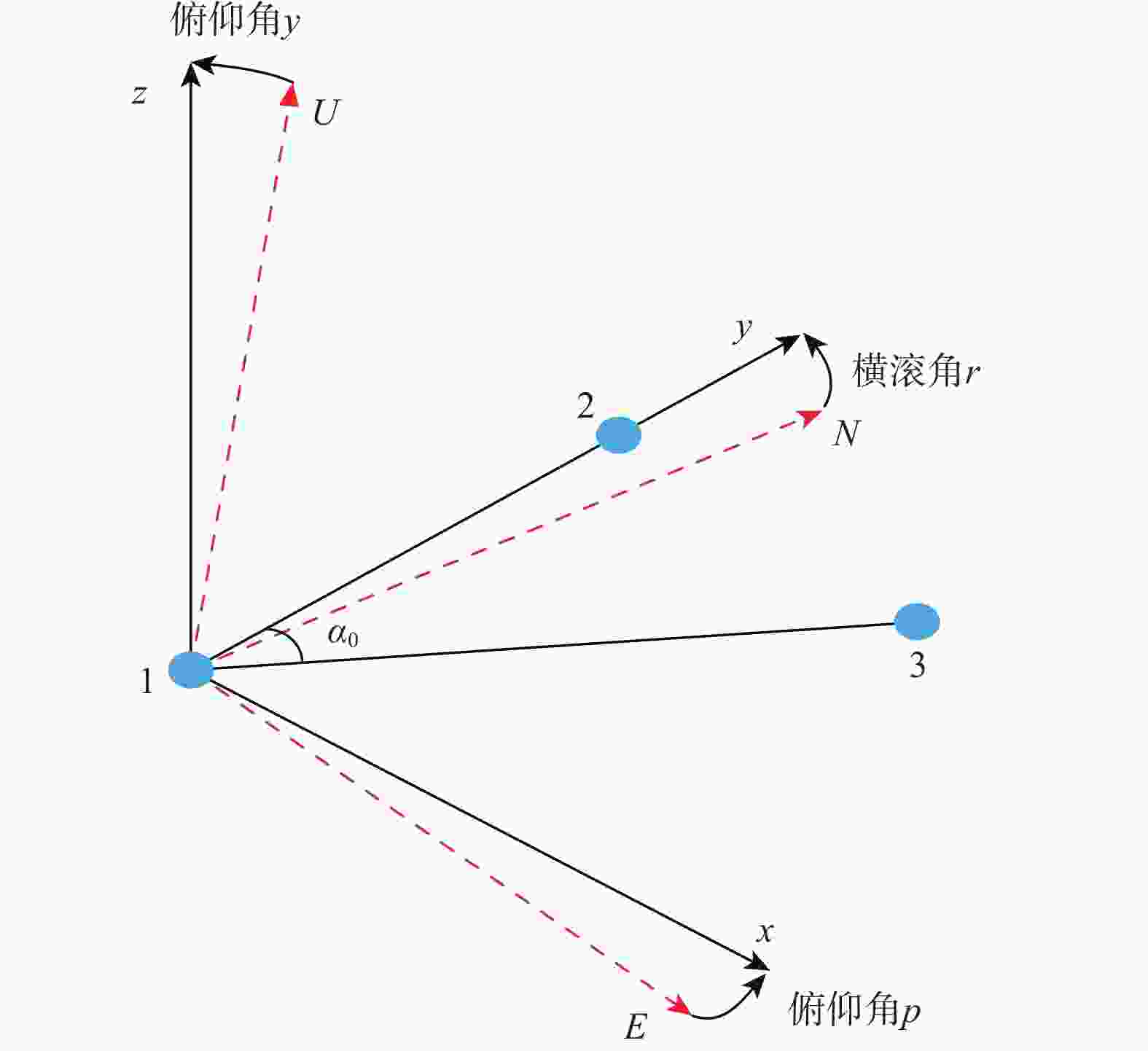
项目 时间/s 统计值 e12/m n12/m u12/m 观测值 均值 −0.966 0.000 0.259 标准差 0.0062 0.0071 0.0141 传统法 593.8 均值 −0.966 0.000 0.259 标准差 0.0017 0.0019 0.0029 线性化法 141.2 均值 −0.966 0.000 0.259 标准差 0.0016 0.0017 0.0030 表 2 姿态角误差的均值和标准差
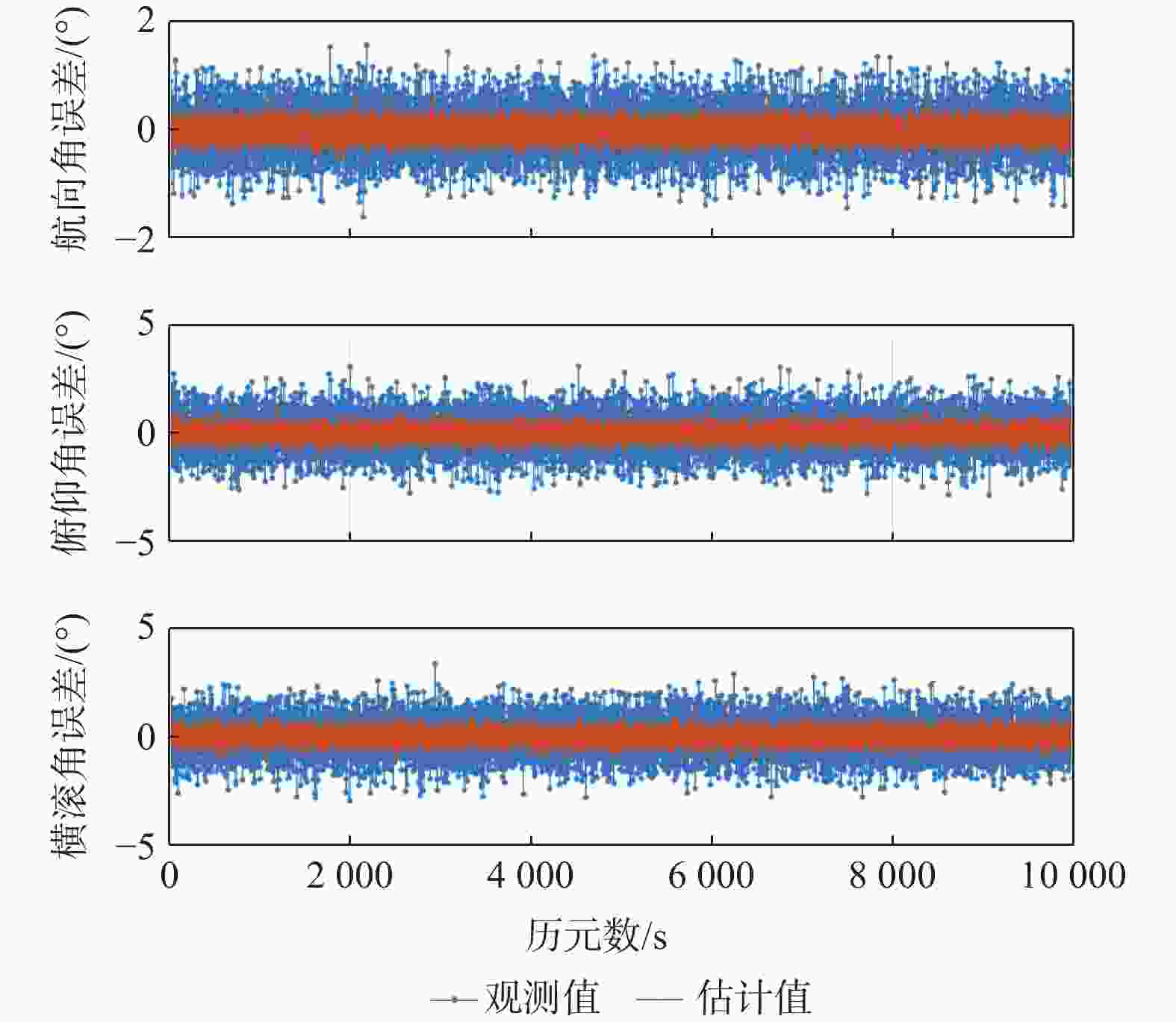
Table 2. Mean and standard deviation of attitude angle error
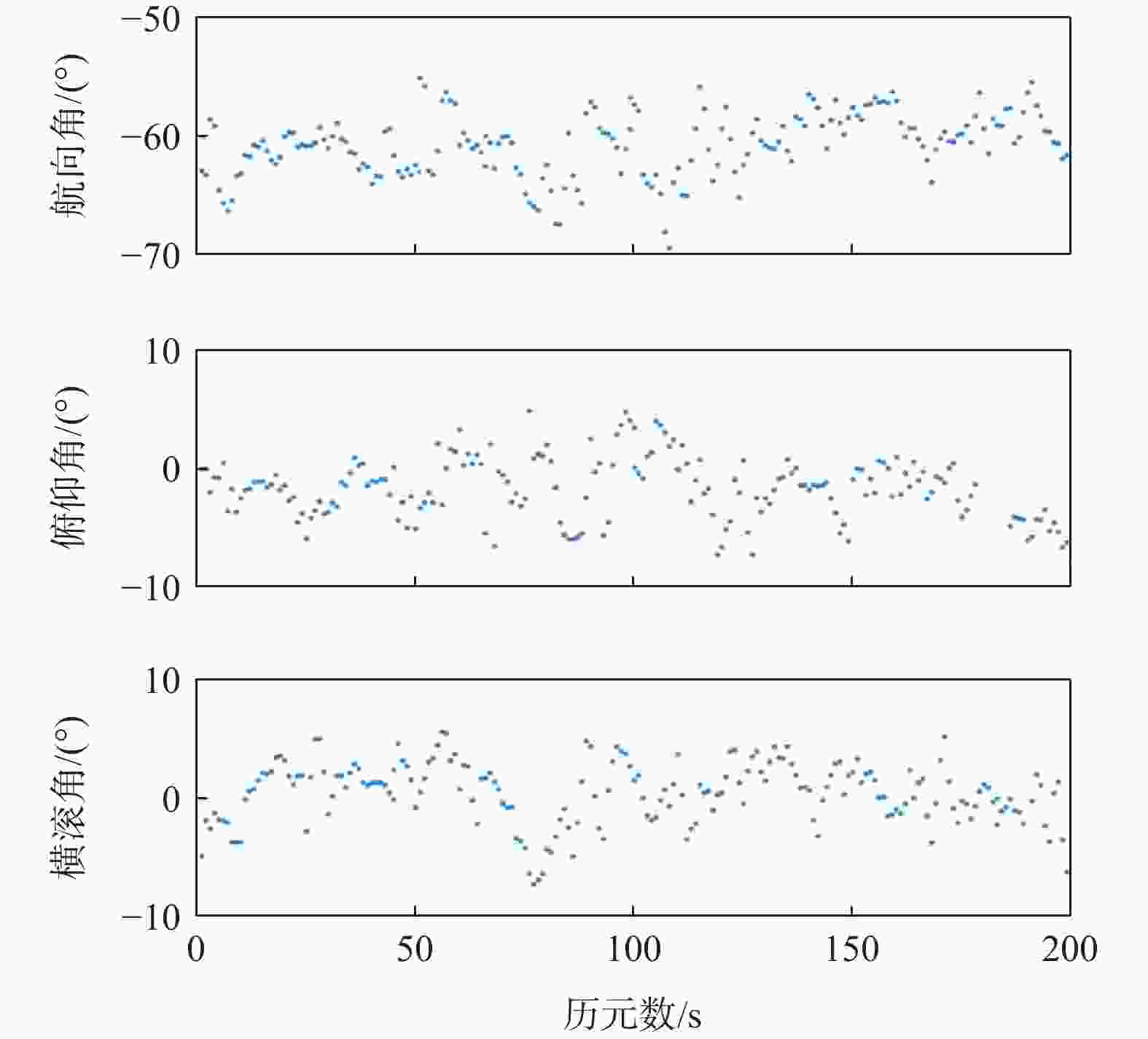
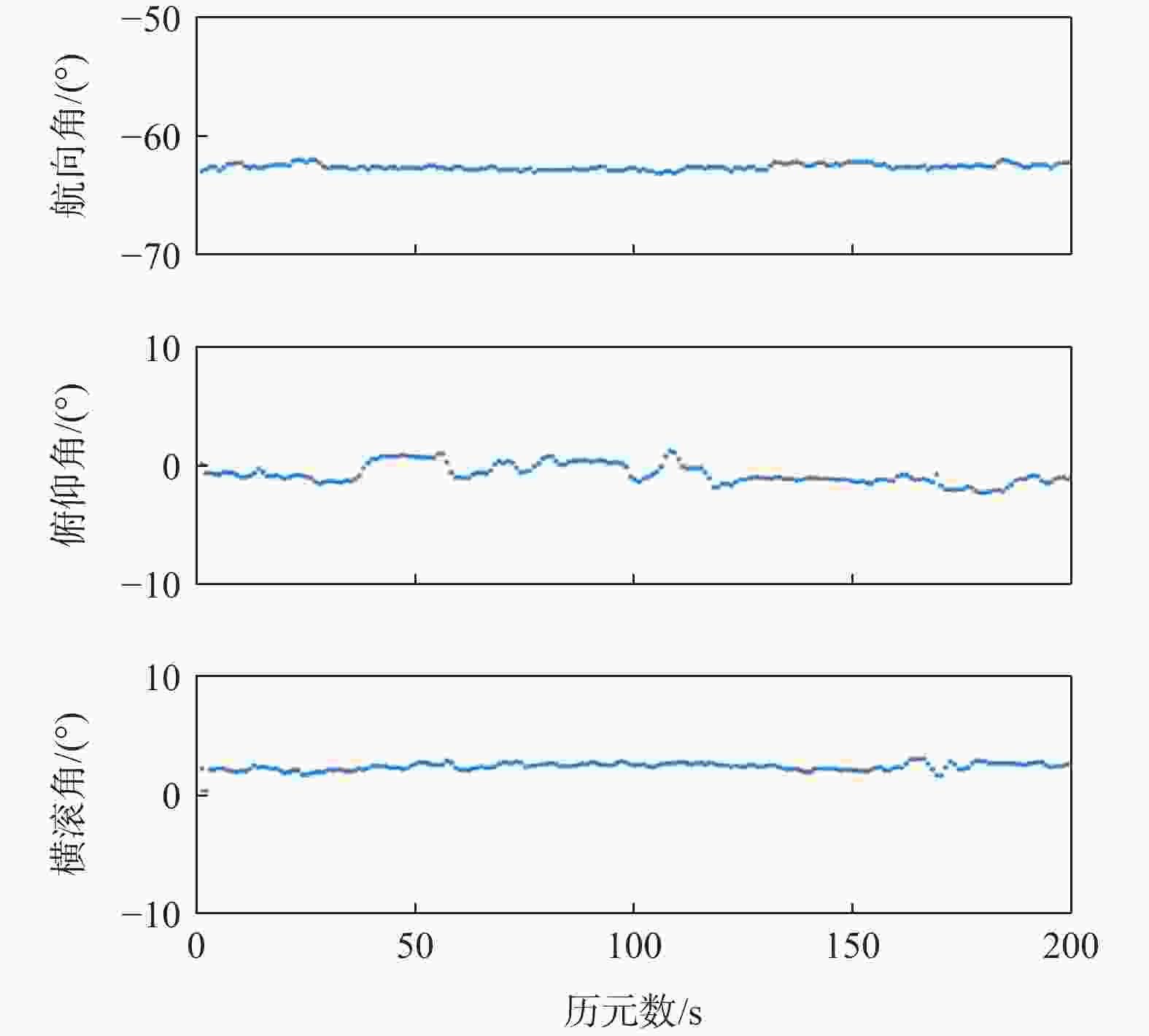
项目 统计值 航向角/(°) 俯仰角/(°) 横滚角/(°) 观测值 均值 −0.0049 0.0060 −0.0036 标准差 0.4227 0.8358 0.8251 估计值 均值 −0.0008 0.0004 −0.0003 标准差 0.1008 0.1742 0.1748 表 3 有欺骗信号时姿态角误差的统计值
Table 3. Statistical values of attitude angle error with spoofing signals
项目 统计值 航向角/(°) 俯仰角/(°) 横滚角/(°) 观测值 均值 7.478 0 −2.656 9 9.070 9 均方根 7.489 8 2.782 9 9.099 6 标准差 0.419 0 0.828 0 0.722 5 估计值 均值 −0.229 3 −0.353 3 −0.380 9 均方根 0.360 6 0.680 0 0.588 8 标准差 0.278 0 0.581 0 0.449 0 表 4 姿态角均值和标准差
Table 4. Mean and standard deviation of attitude angle
项目 统计值 航向角/(°) 俯仰角/(°) 横滚角/(°) 观测值 均值 −60.31 −2.21 −0.30 标准差 2.42 2.65 3.14 估计值 均值 −62.29 −1.08 1.86 标准差 0.32 0.60 0.37 -
[1] BROUMANDAN A, JAFARNIA-JAHROMI A, DANESHMAND S, et al. Overview of spatial processing approaches for GNSS structural interference detection and mitigation[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2016, 104(6): 1246-1257. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2016.2529600 [2] WANG F, LI H, LU M Q. GNSS spoofing detection based on unsynchronized double-antenna measurements[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 31203-31212. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2845365 [3] CHEN J J, XU Y, YUAN H, et al. A new GNSS spoofing detection method using two antennas[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 110738-110747. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3002804 [4] DANESHMAND S, JAFARNIA A, BROUMANDAN A, et al. Low-complexity spoofing mitigation[J]. GPS World Magazine, 2011, 22: 44-46. [5] 黄龙, 雍玲, 徐博, 等. 采用双天线载波相位差技术的卫星导航接收机抗欺骗方法[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2016, 38(4): 103-106. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201604016HUANG L, YONG L, XU B, et al. Analysis of carry phase difference detection for satellite navigation receivers anti-spoofing[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2016, 38(4): 103-106(in Chinese). doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201604016 [6] SWASZEK P F, HARTNETT R J. A multiple COTS receiver GNSS spoof detector-Extensions[C]//Proceedings of the International Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation. San Diego: Institute of Navigation, 2014: 1-12. [7] BORIO D, GIOIA C. A dual-antenna spoofing detection system using GNSS commercial receivers[C]//Proceedings of the 28th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation. Tampa: Institute of Navigation, 2015: 325-330. [8] PSIAKI M L, O’HANLON B W, POWELL S P, et al. GNSS spoofing detection using two-antenna differential carrier phase[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation. Tampa: Institute of Navigation, 2014: 2776-2800. [9] KONOVALTSEV A, CUNTZ M, HAETTICH C, et al. Autonomous spoofing detection and mitigation in a GNSS receiver with an adaptive antenna array[C]//Proceedings of the 26th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation. Nashville: Institute of Navigation, 2013: 2937-2948. [10] MEUER M, KONOVALTSEV A, CUNTZ M, et al. Robust joint multi-antenna spoofing detection and attitude estimation using direction assisted multiple hypotheses RAIM[C]//Proceedings of the 25th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation. Nashville: Institute of Navigation, 2012: 3007-3016. [11] XU H L, CUI X W, SHEN J N, et al. A two-step beam-forming method based on carrier phases for GNSS adaptive array anti-jamming[C]// The International Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation, Proceedings of the 2016 International Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation, Monterey: Institute of Navigation, 2016: 793-804. [12] SWASZEK P F, PRATZ S A, AROCHO B N, et al. GNSS spoof detection using shipboard IMU measurements[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation. Tampa: Institute of Navigation, 2014: 745-758. [13] APPEL M, KONOVALTSEV A, MEURER M. Joint antenna array attitude tracking and spoofing detection based on phase difference measurements[C]//Proceedings of the 29th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation. Portland: Institute of Navigation, 2016: 3018-3026. [14] 张鑫, 庞晶, 苏映雪, 等. 天线阵载波相位双差的欺骗干扰检测技术[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2014, 36(4): 55-60. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201404010ZHANG X, PANG J, SU Y X, et al. Spoofing detection technique on antenna array carrier phase double difference[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2014, 36(4): 55-60(in Chinese). doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201404010 [15] ZHANG P, ZHAO Y Z, LIN H, et al. A novel GNSS attitude determination method based on primary baseline switching for a multi-antenna platform[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(5): 747. doi: 10.3390/rs12050747 [16] HOFMANN-WELLENHOF B, LICHTENEGGER H, WASLE E. GNSS-global navigation satellite systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and more[M]. Vienna: Springer Vienna, 2007: 441-450. [17] BUIST P J, TEUNISSEN P J G, GIORGI G, et al. Multiplatform instantaneous GNSS ambiguity resolution for triple- and quadruple-antenna configurations with constraints[J]. International Journal of Navigation and Observation, 2009, 2009: 565426. [18] GONG A, ZHAO X B, PANG C L, et al. GNSS single frequency, single epoch reliable attitude determination method with baseline vector constraint[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(12): 30093-30103. doi: 10.3390/s151229774 [19] 舒宝, 刘晖, 张晋升, 等. 基于BDS/GPS组合定位的部分模糊度固定效果分析[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2017, 42(7): 989-994. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20150017SHU B, LIU H, ZHANG J S, et al. Performance assessment of partial ambiguity resolution based on BDS/GPS combined positioning[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2017, 42(7): 989-994(in Chinese). doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20150017 [20] GROVES P D. Principles of GNSS, inertial, and multisensor integrated navigation systems[M]. 2nd ed. Boston: Artech House, 2013: 288-289. [21] DEVORE J L. Probability and statistics for engineering and the sciences[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2005: 136-172. -






 下载:
下载: