-
摘要:
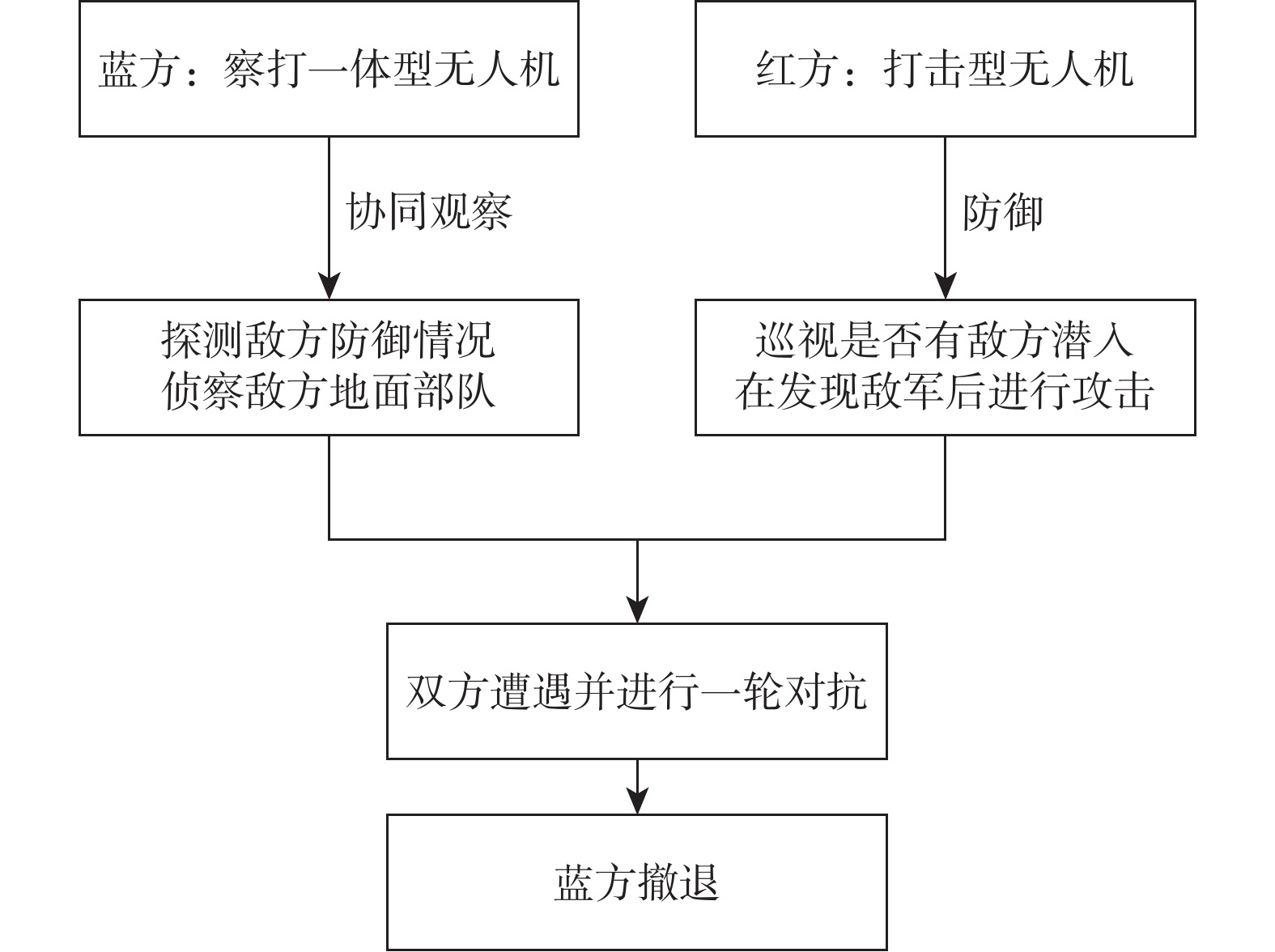
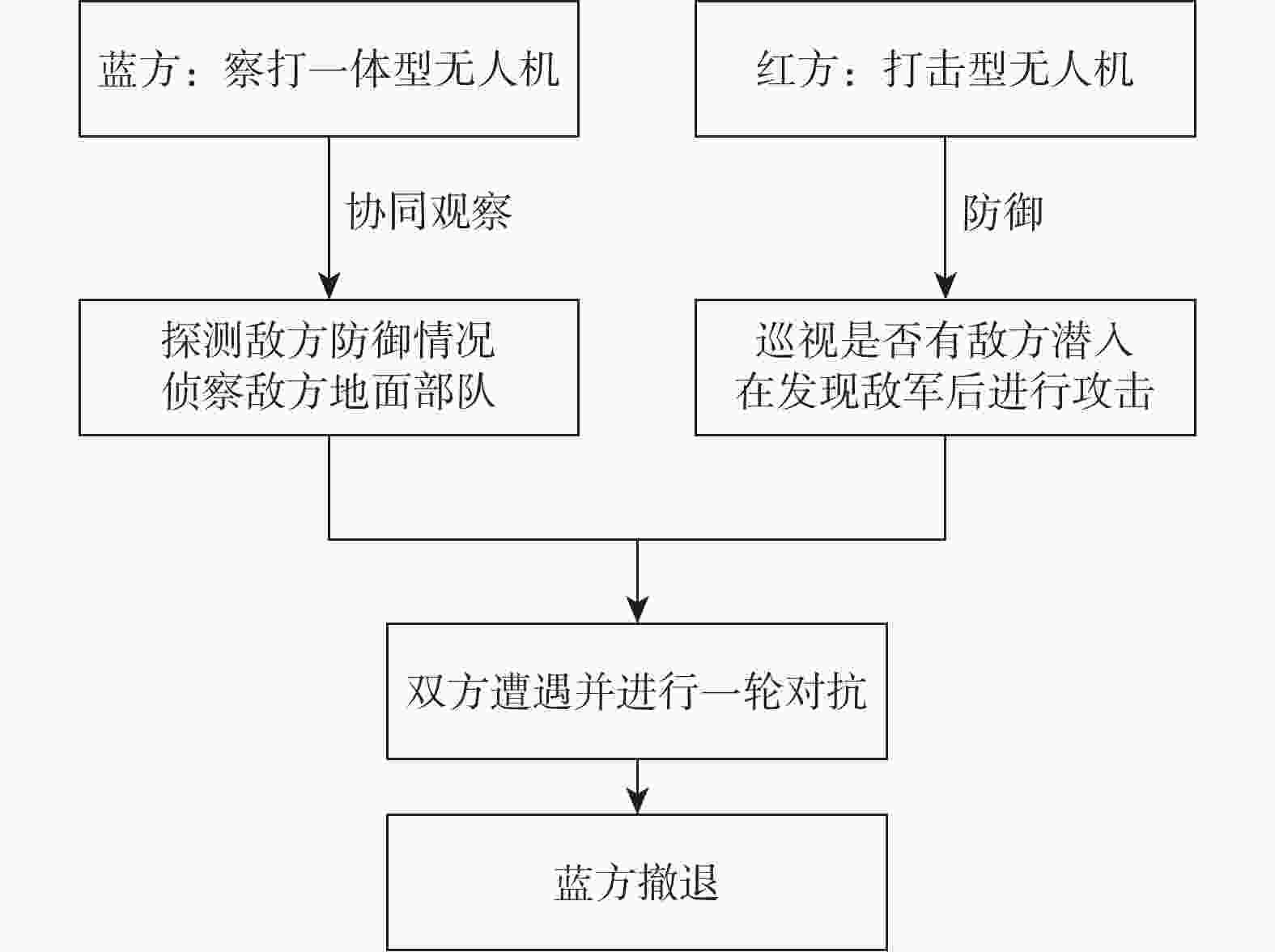
无人机集群协同对抗是未来作战的发展方向,为了突出集群强进攻、难防御、高灵活的优势,对高维度、强动态、非线性无人机集群的协同对抗的复杂系统进行有效建模是一个重要的研究方向。应用复杂空间网络理论构建了对抗双方的协同网络、对抗网络及协同对抗网络,模拟无人机集群的协同侦察场景,分别在二维和三维空间中建立了无人机集群协同对抗模型;分析了影响杀伤率的因素,提出了杀伤率与空间距离的解析式;通过网络级联效应分析了无人机集群协同网络的鲁棒性,验证了所提无人机集群协同对抗模型的有效性,为无人机集群协同对抗的建模提供了一种新思路。
Abstract:UAV swarm cooperative confrontation is a development direction for future war. In order to highlight the advantages of the swarm such as strong attack, difficult defense and high flexibility, it is an important research direction to effectively model the complex system of high-dimensional, strong dynamic and nonlinear UAV cluster cooperative confrontation. In this paper, we apply the complex spatial network theory to construct a cooperative confrontation network, a cooperative network and a confrontation network between two UAV swarms. Meanwhile, we establish a UAV swarm cooperative confrontation model in 2D and 3D based on the cooperative reconnaissance scene of UAV swarm. Then, we analyze the impact of the spatial distance between opponent UAVs on the hit rate, and put forward the formula of hit rate with spatial distance. We analyze the robustness of the cooperative network of UAV swarm through cascading effects and verify the effectiveness and practicality of the UAV swarm cooperative confrontation model. Our work will provide new insight for the modeling of UAV swarm cooperative confrontation.
-
Key words:
- UAV swarm /
- cooperative confrontation /
- random spatial network /
- complex network /
- cascading effects
-
表 1 不同红方杀伤率下的级联效果
Table 1. Cascading effects under different hit rates of red UAVs
红方
杀伤率三维场景 二维场景 被击落
无人机架数网络
最终S值被击落
无人机架数网络
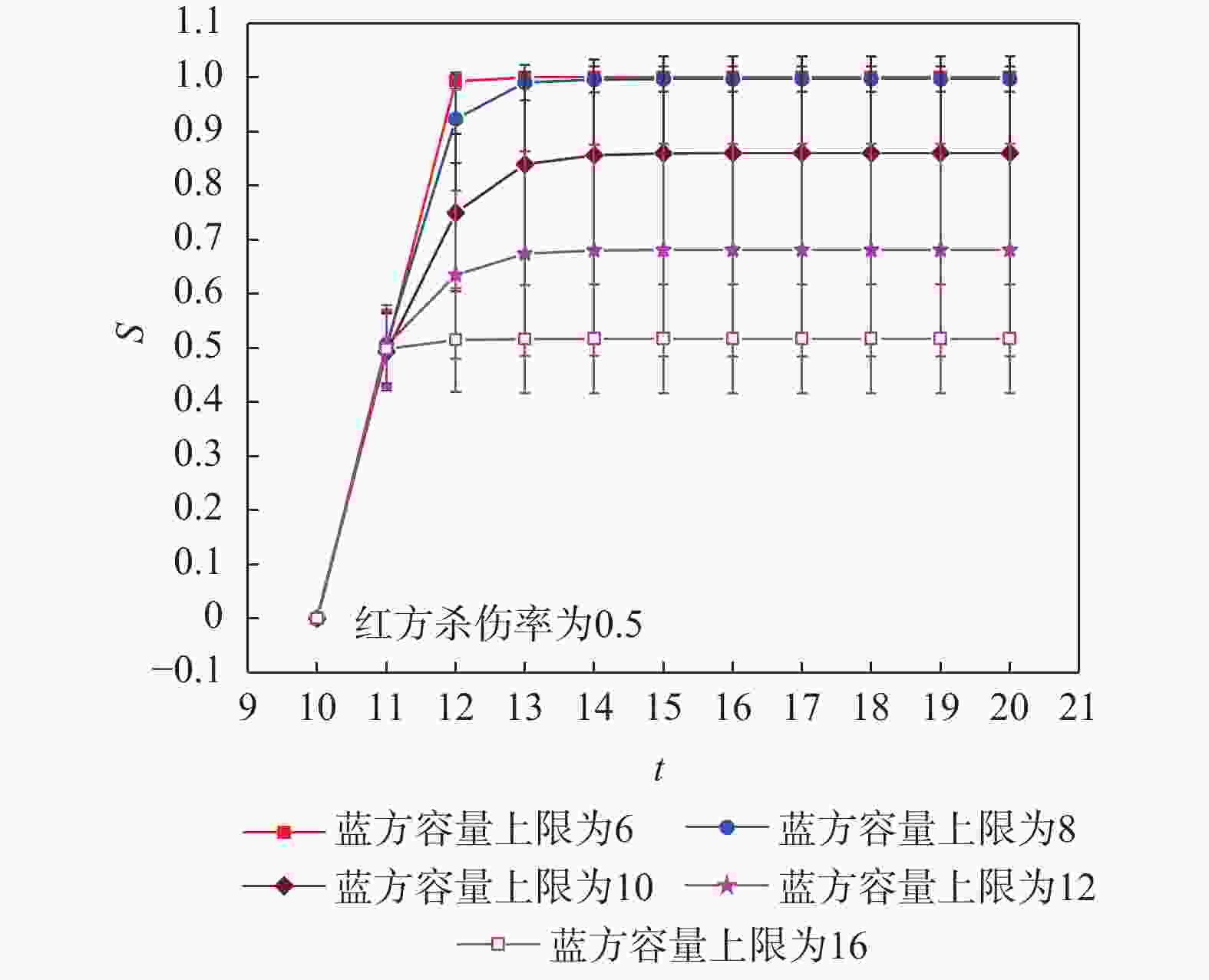
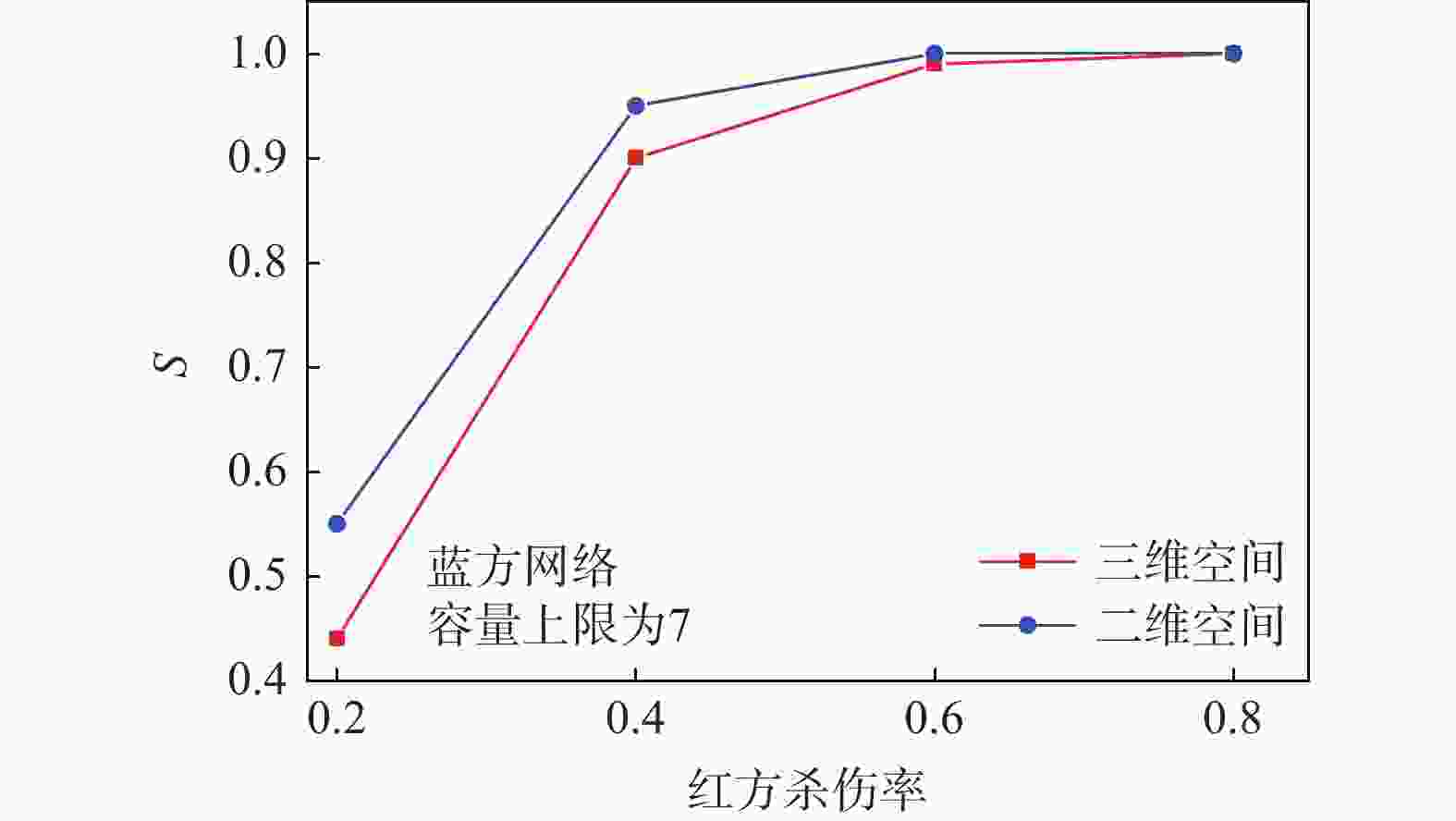
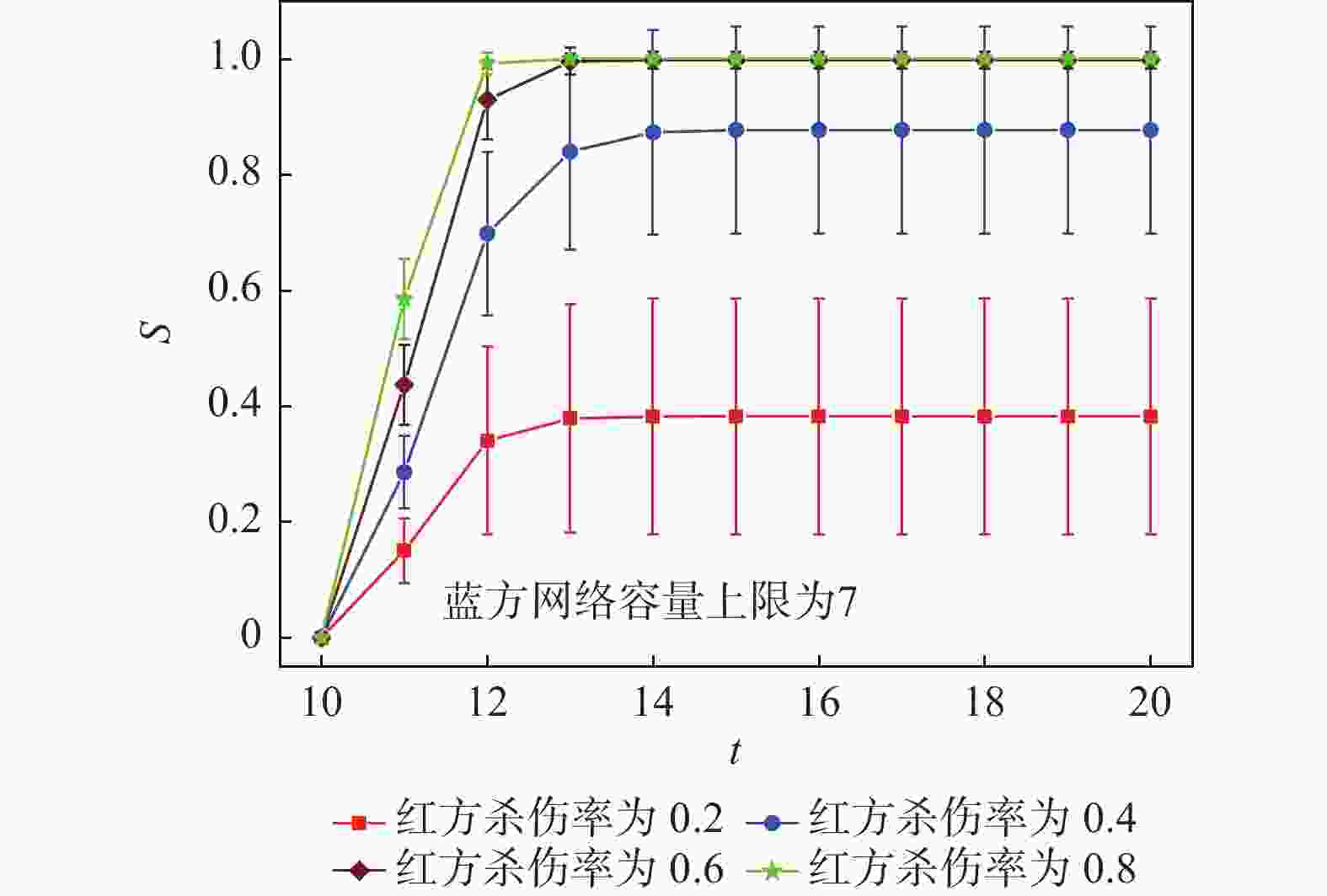
最终S值0.2 8.04 0.44 9.80 0.546 0.4 14.56 0.90 20.04 0.95 0.6 21.68 0.99 30.64 1.00 0.8 29.48 1.00 39.32 1.00 表 2 不同蓝方容量上限下的级联效果
Table 2. Cascading effects under different capacity-limitation of blue UAVs
蓝方容量上限 三维场景 二维场景 被击落
无人机架数网络
最终S值被击落
无人机架数网络
最终S值6 19.68 1.00 25.04 1.00 8 18.20 0.83 26.68 1.00 10 18.60 0.54 24.56 0.86 12 19.48 0.42 25.16 0.64 -
[1] ALISTAIR D. Modeling robot swarms using agent-based simulation[D]. Monterey: Naval Postgraduate School, 2002. [2] GRASSÉ P P. Nest reconstruction and interindividual coordination in bellicositermes natalensis and cubitermes sp. the theory of stigmergy: An attempt to interpret the behaviour of builder termites[J]. Insectes Sociaux, 1956, 6: 41-80. [3] LIN Z J, HONG-TAO L H. Consensus based on learning game theory with a UAV rendezvous application[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2015, 28(1): 191-199. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2014.12.009 [4] 刘鑫, 杨宵鹏, 刘雨帆, 等. 基于GA-OCPA学习系统的无人机路径规划方法[J]. 航空学报, 2017, 38(11): 287-297. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2017.321275LIU X, YANG X P, LIU Y F, et al. UAV path planning method based on GA-OCPA learning system[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2017, 38(11): 287-297(in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2017.321275 [5] 朱黔, 许诺, 黄蓓, 等. 基于角色切换策略的多无人机协同区域搜索[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(5): 928-938. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0070ZHU Q, XU N, HUANG B, et al. Multi-UAV collaborative area search based on role-switching strategies[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(5): 928-938(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0070 [6] 曾佳, 申功璋, 杨凌宇. 无人机在线协同航迹规划时序问题[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2009, 41(3): 334-338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2615.2009.03.010ZENG J, SHEN G Z, YANG L Y. Unmanned online collaborative flight path planning timing issues[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2009, 41(3): 334-338(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2615.2009.03.010 [7] LI H, LONG T, XU G T, et al. Coupling-degree-based heuristic prioritized planning method for UAV swarm path generation[C]// 2019 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3636-3641. [8] 蒋进. 无人机集群动态避撞算法研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2019.JIANG J. UAV swarm dynamic collision avoidance algorithm research[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019 (in Chinese). [9] 牛轶峰, 凌黎华. 无人机规避或跟踪空中目标的自适应运动导引方法[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2017, 39(4): 116-124. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201704018NIU Y F, LIN L H. Adaptive motion guidance methods for UAV evasion or tracking of aerial targets[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2017, 39(4): 116-124(in Chinese). doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201704018 [10] WANG Y, BAI P, LIANG X, et al. Reconnaissance mission conducted by UAV swarms based on distributed PSO path planning algorithms[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 105086-105099. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2932008 [11] MANJUNATHA K A, HU F. Deep Q-learning-based node positioning for throughput-optimal communications in dynamic UAV swarm network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2019, 5(3): 554-566. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2019.2907520 [12] LAKAS A, BELKACEM A N, HASSANI S A. An adaptive multi-clustered scheme for autonomous UAV swarms[C]//2020 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 19855085. [13] 谢剑. 基于微分博弈论的多无人机追逃协同机动技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2015.XIE J. Differential game theory for multi-UAV pursuit maneuvers technology based on collaborative research[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2015(in Chinese). [14] 王晓光, 章卫国, 陈伟. 无人机编队超视距空战决策及作战仿真[J]. 控制与决策, 2015, 30(2): 328-334. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2013.1751WANG X G, ZHANG W G, CHEN W. BVR air combat decision making and simulation for UAV formation[J]. Control and Decision, 2015, 30(2): 328-334(in Chinese). doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2013.1751 [15] 周文卿, 朱纪洪, 匡敏驰. 一种基于群体智能的无人空战系统[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2020, 50(3): 363-374. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2019-0196ZHOU W Q, ZHU J H, KUANG M C. An unmanned air combat system based on swarm intelligence[J]. Scientia Sinica: Informationis, 2020, 50(3): 363-374(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/SSI-2019-0196 [16] 冉惟之. 基于群体智能的无人机集群协同对抗系统的设计与实现[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2020.RAN W Z. Design and implementation of cooperative adversarial system based on swarm intelligence for unmanned aerial vehicles[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020(in Chinese). [17] 陈灿, 莫雳, 郑多, 等. 非对称机动能力多无人机智能协同攻防对抗[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(12): 342-354. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.24152CHEN C, MO L, ZHENG D, et al. Cooperative attack-defense game of multiple UAVs with asymmetric maneuverability[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(12): 342-354(in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.24152 [18] CRUCITTI P, LATORA V, PORTA S. Centrality measures in spatial networks of urban streets[J]. Physical Review E, 2006, 73(3): 036125. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.73.036125 [19] BARTHELEMY M. Morphogenesis of spatial network[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 177-196. [20] CRUZ J B, SIMAAN M A, GACIC A, et al. Game-theoretic modeling and control of a military air operation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2001, 37(4): 1393-1405. doi: 10.1109/7.976974 [21] COBB B J. Adaptive discrete event simulation for analysis of harpy swarm attack[D]. Monterey: Naval Postgraduate School, 2011: 1-59. [22] ALBERT R, ALBERT I, NAKARADO G L. Structural vulnerability of the North American power grid[J]. Physical Review E, 2004, 69(2): 025103. -






 下载:
下载: