Quantitative method of influence of thermal runaway gas combustion on thermal runaway propagation of lithium-ion battery
-
摘要:
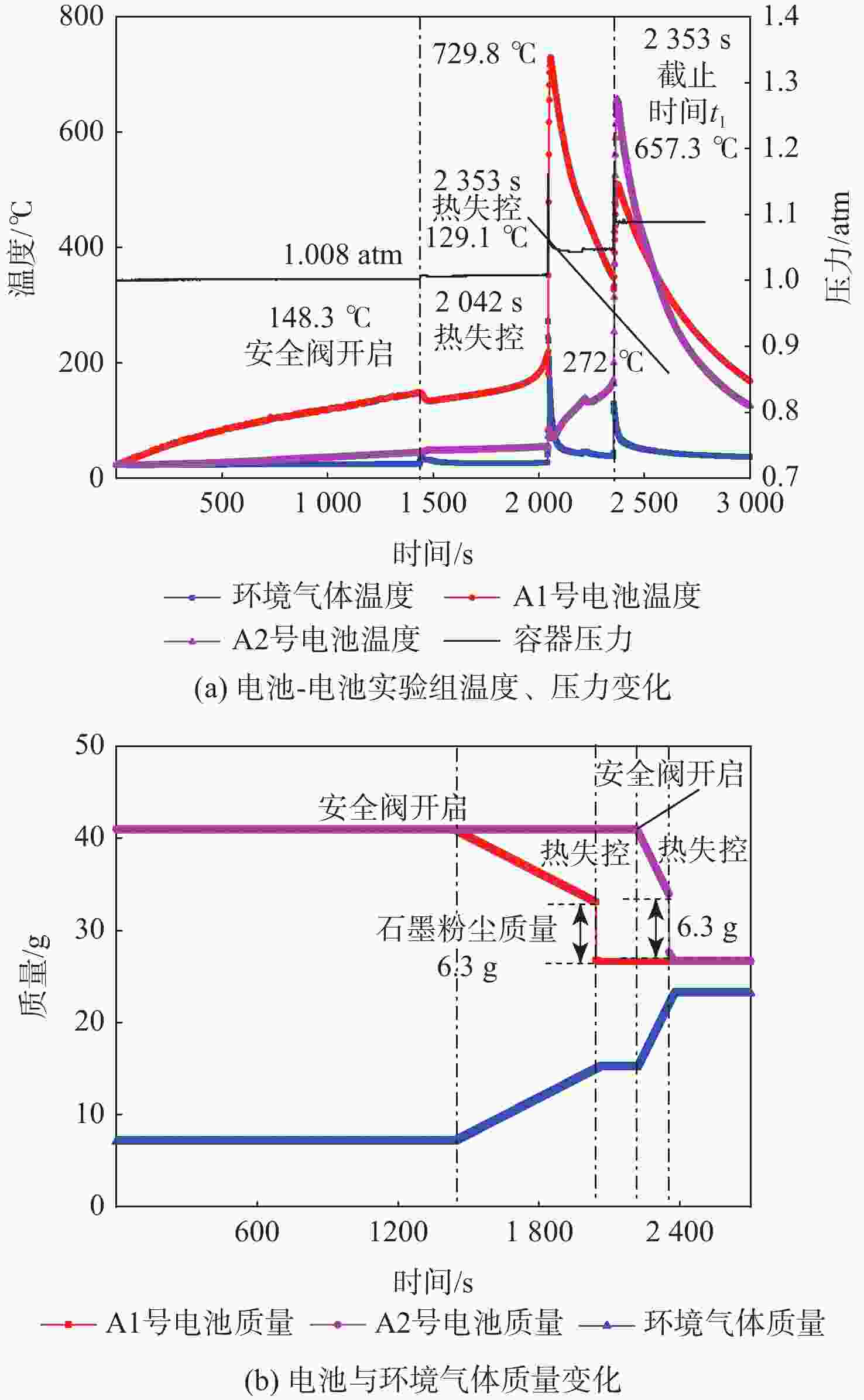
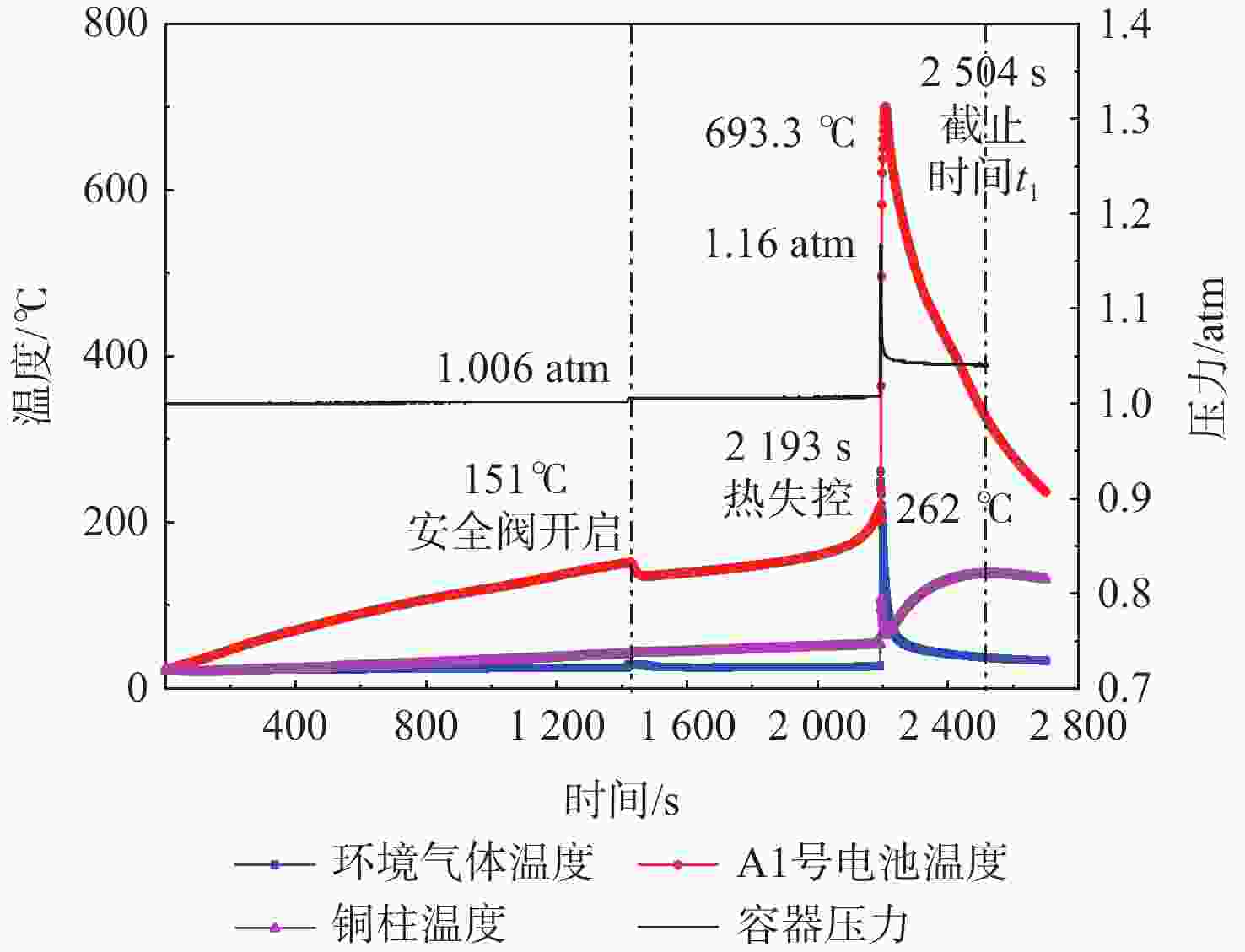
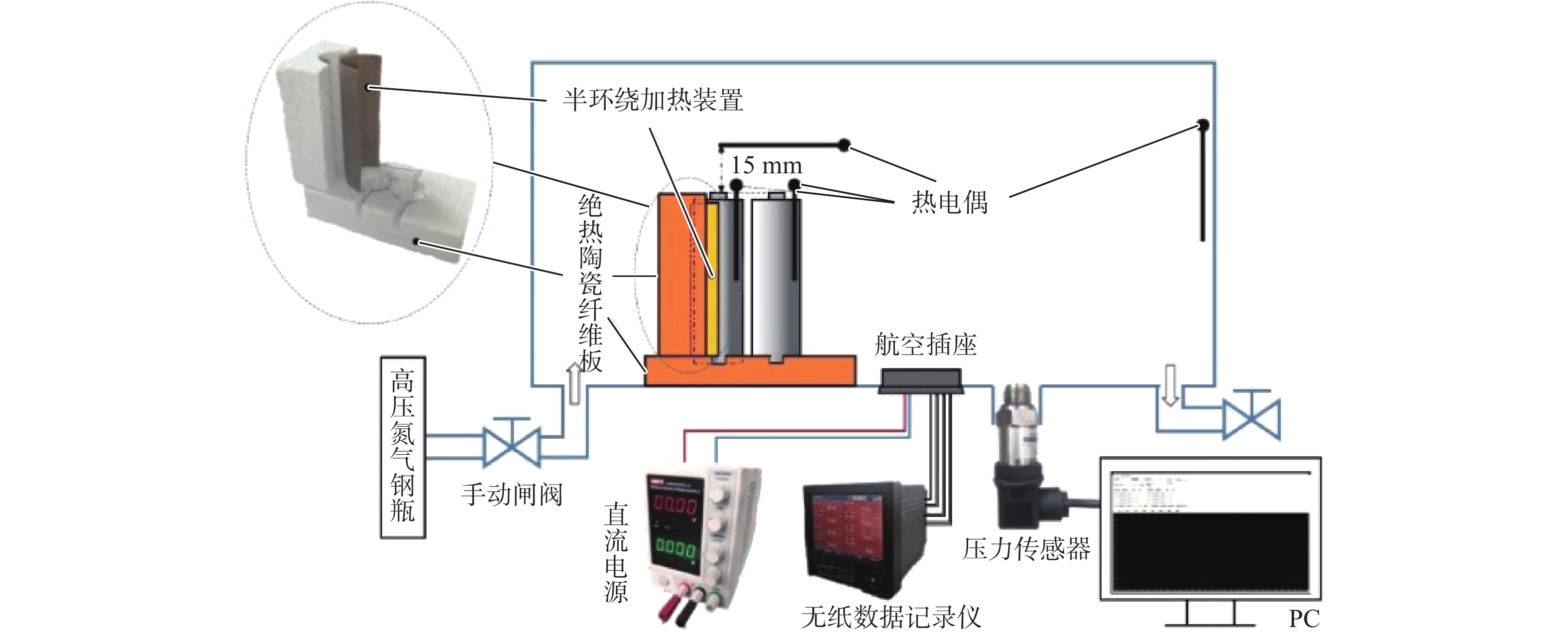
为量化锂离子电池热失控过程产生热失控气体对热失控传播的影响,基于能量守恒方程和铜基电池量热法,提出了一种计算热失控气体燃烧对热失控传播贡献占比的方法。选取商用18650型电池,利用自主设计搭建的热失控气体释能测算实验平台获取计算所需参数。实验结果表明:第1节电池热失控气体燃烧释放的能量在第2节电池热失控所需能量中占比达到5.42%,使第2节电池自产热增加了42%,热失控时间提前了29%。研究结果有助于进一步探索热失控传播过程中的能量传递效率,为单元层级和系统层级的电池安全设计提供理论支持。
Abstract:In order to quantify the effect of thermal runaway gas produced in the thermal runaway process of lithium-ionbattery on thermal runaway propagation, based on the energy conservation equation and the equivalent substitution method, this paper presents a method to calculate the contribution of thermal runaway gas combustion to thermal runaway propagation. The self-designed experimental platform of thermal runaway gas energy release calculation was used to pick the commercial 18650 battery and collect the parameters required for the calculation. According to the experiment results, the energy released during the combustion of the first cell’s thermal runaway gas accounts for 5.42% of the energy needed by the second cell’s thermal runaway, resulting in a 42% increase in the second cell’s self-heat production and a 29% reduction in thermal runaway time. The research results are helpful to further explore the energy transfer efficiency in the process of runaway heat transfer, and provide theoretical support for cell level and system level battery safety design.
-
Key words:
- lithium-ion batteries /
- gas /
- thermal runaway propagation /
- combustion /
- energy transfer
-
表 1 锂离子电池参数
Table 1. Parameters of lithium-ion battery
参数 额定容量/mAh 电压/V 内阻/mΩ 荷电状态SOC/% 初始质量/g 数值 2200 4.17±0.01 30±5 100 41±0.5 表 2 空气环境下传递能量测量和计算结果
Table 2. Measurement and calculation results of energy transfer in air environment
实验类型 t1
/smB,1 (t1)/g mB,2 (t1)/g $\displaystyle\int_{ {t_1} }^{ {t_2} } \left({P_{ {\text{B,} }1} } + {P_{ {\text{B,} }2} }\right){\text{d} }t$/J $\displaystyle\int_{{t_1}}^{{t_2}} {{P_{{\text{B,1}}}}{\text{d}}t} $/J 电池-电池 2353 26.629 26.740 19134.6 电池-铜柱 2504 26.617 17854.5 表 3 氮气环境下传递能量测量和计算结果
Table 3. Measurement and calculation results of transfer energy in nitrogen environment
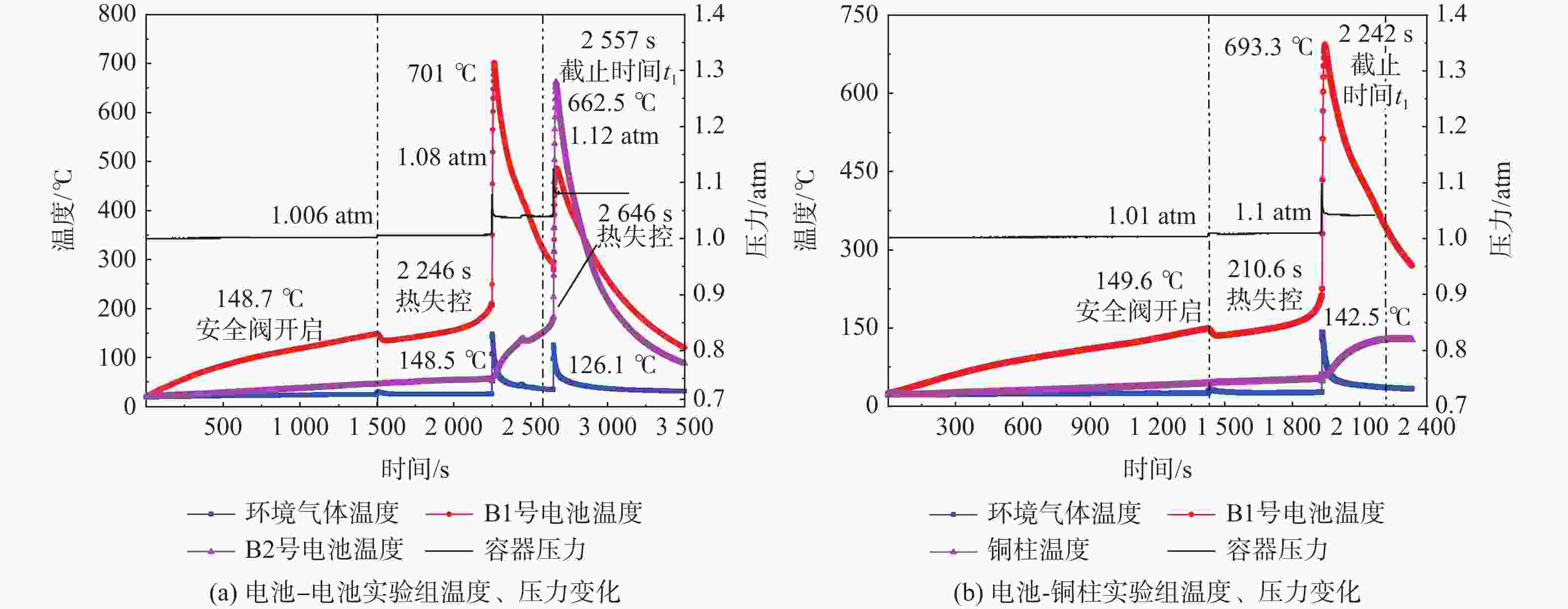
实验类型 t1
/smB,1 (t1)/g mB,2 (t1)/g $\displaystyle\int_{ {t_1} }^{ {t_2} } \left( {P'_{ {\text{B,1} } } } + {P'_{ {\text{B,2} } } }\right){\text{d} }t$/J $\displaystyle\int_{ {t_1} }^{ {t_2} } { {P'_{ {\text{B,1} } } }{\text{d} }t}$/J 电池-电池 2557 26.525 26.730 17556.3 电池-铜柱 2242 26.502 16657.2 表 4 2号电池自产热及接收能量计算
Table 4. Calculation of self generated heat and received energy of No.2 battery
实验
条件2号电池
自产热/J2号电池升温
所需热量/J2号电池接收
外界热量/J传递到2号电池的热
失控气体释能大小/J空气环境 1280.1 6384.5 5104.4 346.1 氮气环境 899.1 5657.4 4758.3 -
[1] 芮新宇, 冯旭宁, 韩雪冰, 等. 锂离子电池热失控蔓延问题研究综述[J]. 电池工业, 2020, 24(4): 193-201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7923.2020.04.005RUI X Y, FENG X N, HAN X B, et al. Review on the thermal runaway propagation of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Chinese Battery Industry, 2020, 24(4): 193-201(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7923.2020.04.005 [2] 张青松, 罗星娜, 程相静, 等. 基于锂离子电池温降指数的细水雾添加剂筛选方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(6): 1073-1079. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0362ZHANG Q S, LUO X N, CHENG X J, et al. Method for screening fine water mist additive based on temperature drop index of lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(6): 1073-1079(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0362 [3] 张磊, 张春颖, 黄昊, 等. 三元锂电池过充诱导燃烧特性的试验研究[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2021, 40(2): 157-159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2021.02.001ZHANG L, ZHANG C Y, HUANG H, et al. Experimental study on the combustion characteristics of ternary lithium battery by overcharge[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2021, 40(2): 157-159(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2021.02.001 [4] 张磊, 黄昊, 张永丰, 等. 锂电池穿刺燃烧特性及其抑制技术研究[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2020, 39(4): 526-528. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2020.04.028ZHANG L, HUANG H, ZHANG Y F, et al. Study on combustion characteristics and suppression technology of lithium batteries by puncture[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 526-528(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2020.04.028 [5] 张青松, 曹文杰, 罗星娜, 等. 基于多米诺效应的锂离子电池热释放速率分析方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(5): 902-907. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0383ZHANG Q S, CAO W J, LUO X N, et al. Analysis method of heat release rate of lithium-ion battery based on Domino effect[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(5): 902-907(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0383 [6] FENG X N, REN D S, HE X M, et al. Mitigating thermal runaway of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Joule, 2020, 4(4): 743-770. doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2020.02.010 [7] ROTH E P, DOUGHTY D H, FRANKLIN J, et al. DSC investigation of exothermic reactions occurring at elevated temperatures in lithium-ion anodes containing PVDF-based binders[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2004, 134(2): 222-234. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.03.074 [8] JHU C Y, WANG Y W, SHU C M, et al. Thermal explosion hazards on 18650 lithium-ion batteries with a VSP2 adiabatic calorimeter[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 192(1): 99-107. [9] JHU C Y, WANG Y W, WEN C Y, et al. Self-reactive rating of thermal runaway hazards on 18650 lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2011, 106(1): 159-163. doi: 10.1007/s10973-011-1452-6 [10] JHU C Y, WANG Y W, WEN C Y, et al. Thermal runaway potential of LiCoO2 and Li (Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3) O2 batteries determined with adiabatic calorimetry methodology[J]. Applied Energy, 2012, 100: 127-131. [11] WEN C Y, JHU C Y, WANG Y W, et al. Thermal runaway features of 18650 lithium-ion batteries for LiFePO4 cathode material by DSC and VSP2[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2012, 109(3): 1297-1302. doi: 10.1007/s10973-012-2573-2 [12] LIU X, STOLIAROV S I, DENLINGER M, et al. Comprehensive calorimetry of the thermally-induced failure of a lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 280: 516-525. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.01.125 [13] LIU X, WU Z, STOLIAROV S I, et al. Heat release during thermally-induced failure of a lithium-ion battery: Impact of cathode composition[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2016, 85: 10-22. doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2016.08.001 [14] SAID A O, LEE C, STOLIAROV S I, et al. Comprehensive analysis of dynamics and hazards associated with cascading failure in 18650 lithium-ion cell arrays[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 248: 415-428. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.04.141 [15] SAID A O, LEE C, STOLIAROV S I, et al. Experimental investigation of cascading failure in 18650 lithium-ion cell arrays: Impact of cathode chemistry[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 446: 227347. [16] FENG X N, SUN J, OUYANG M G, et al. Characterization of penetration induced thermal runaway propagation process within a large format lithium-ion battery module[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 275: 261-273. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.11.017 -






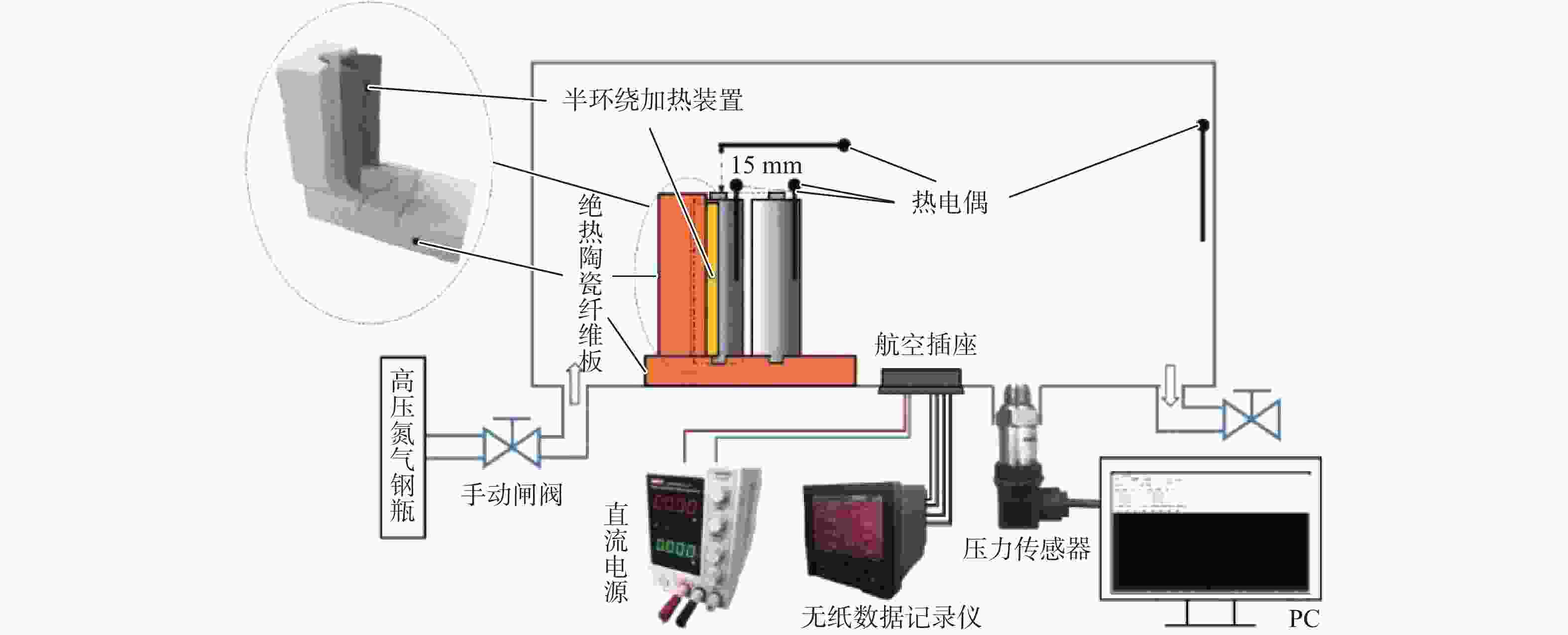
 下载:
下载: