-
摘要:
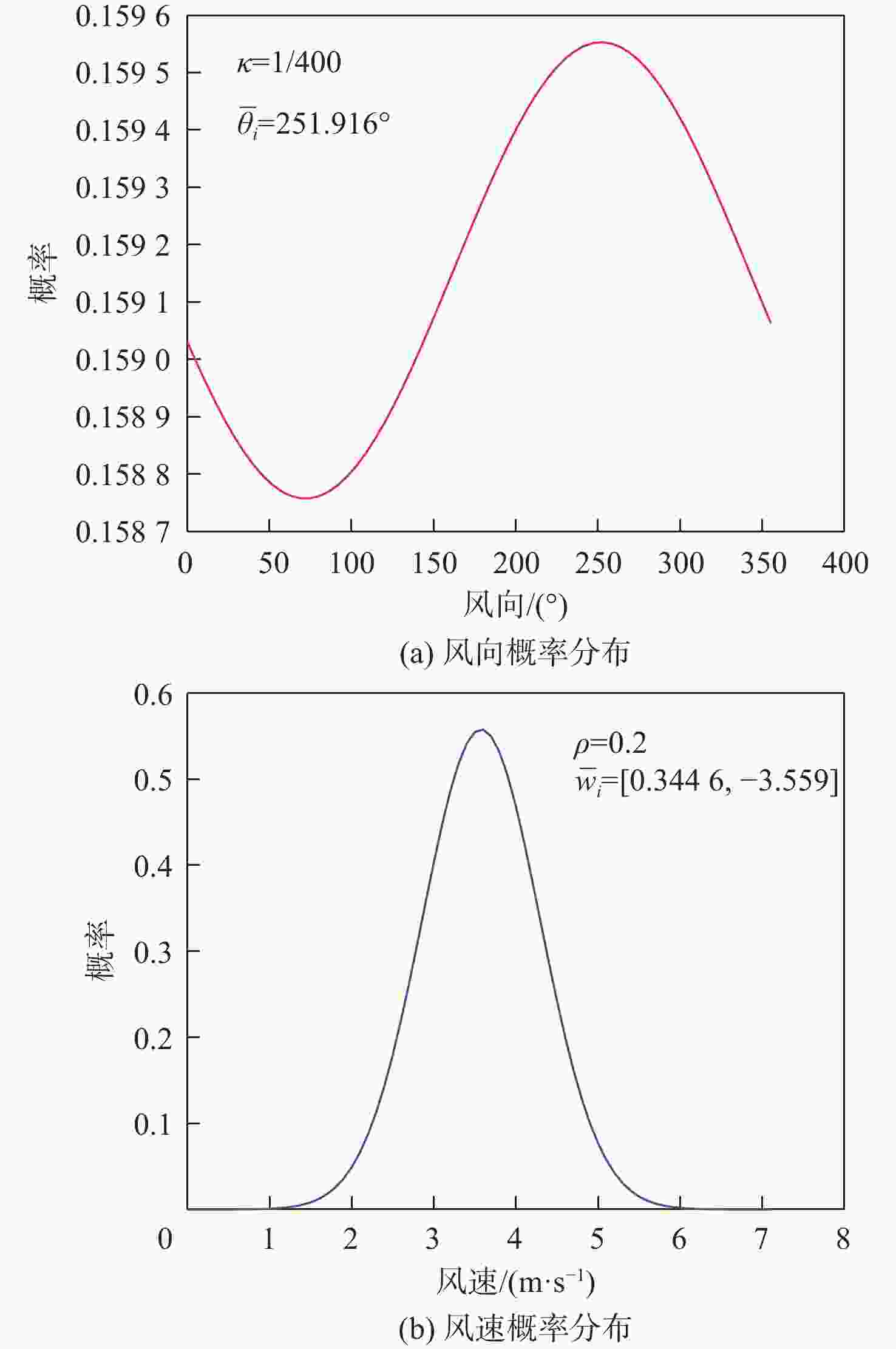
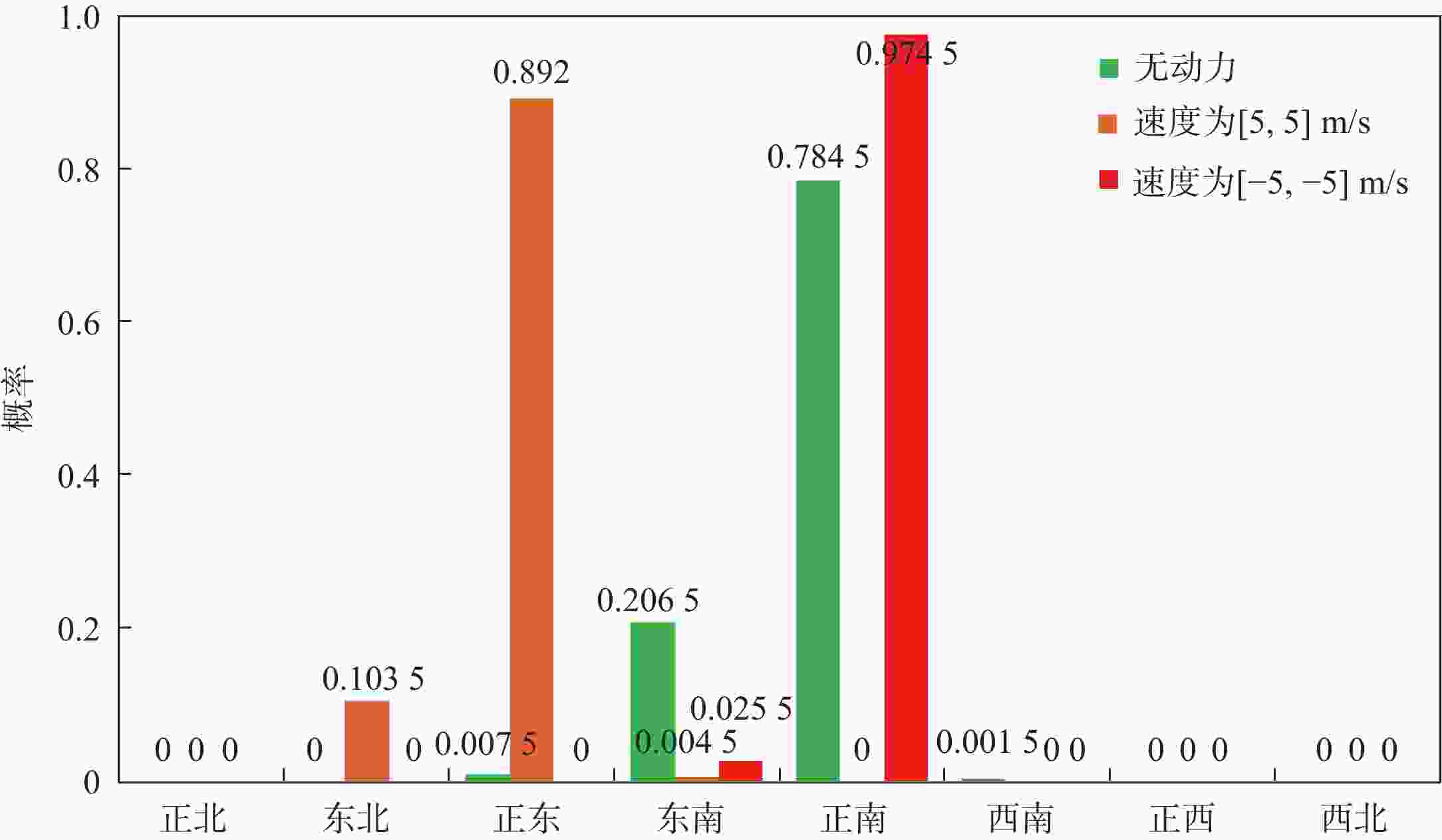
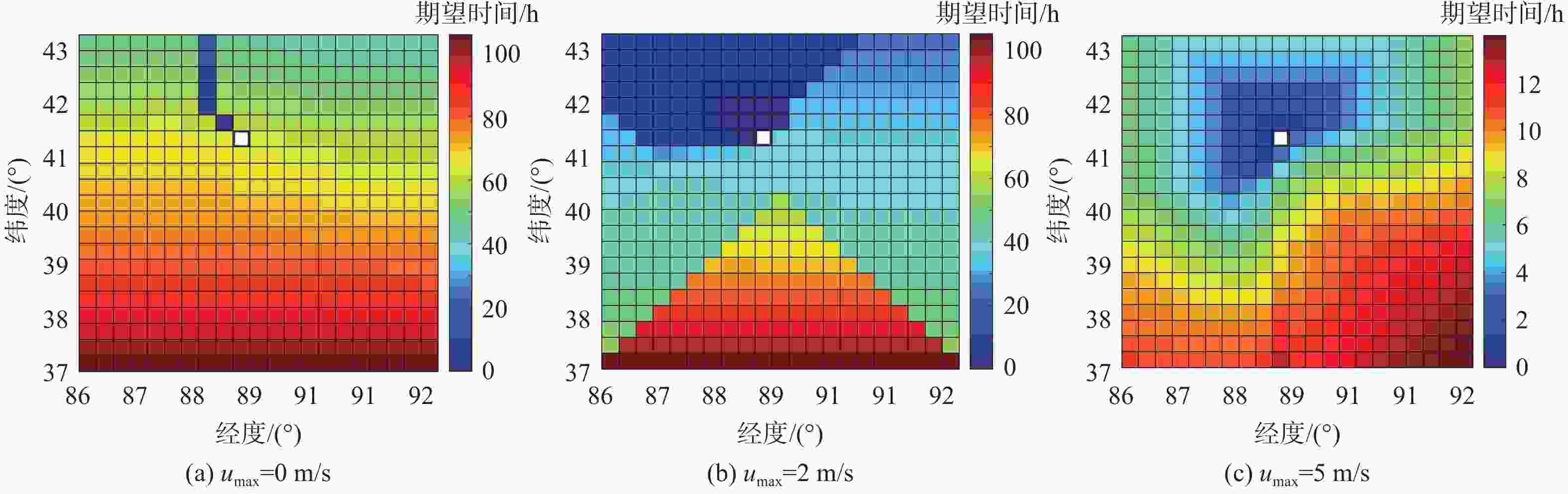
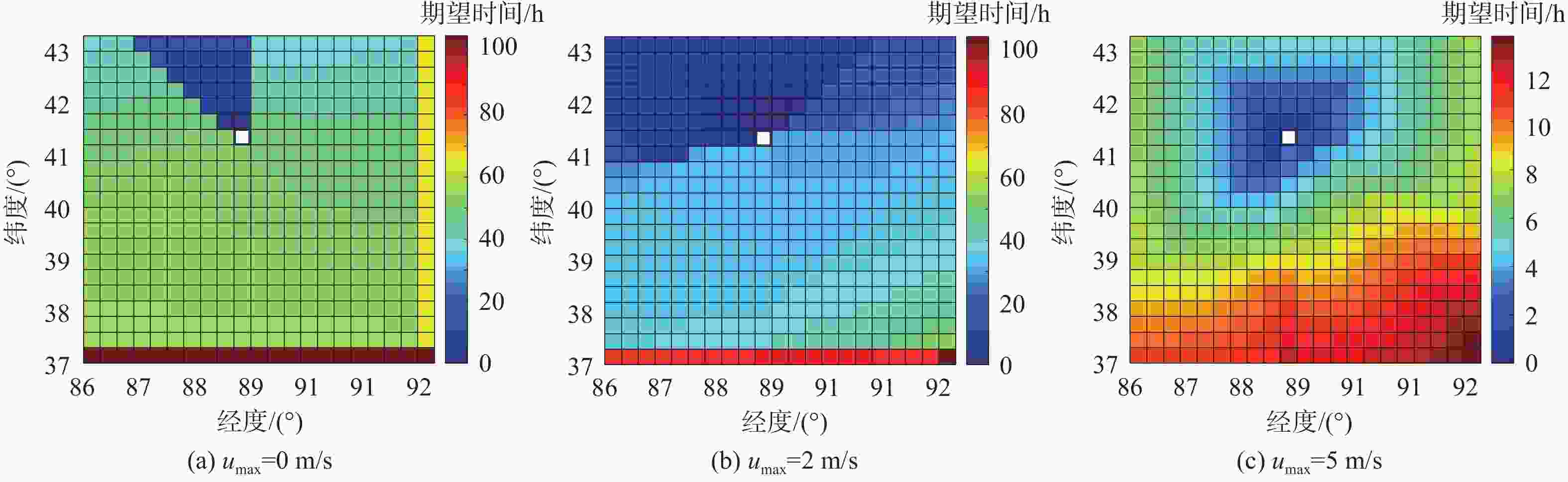
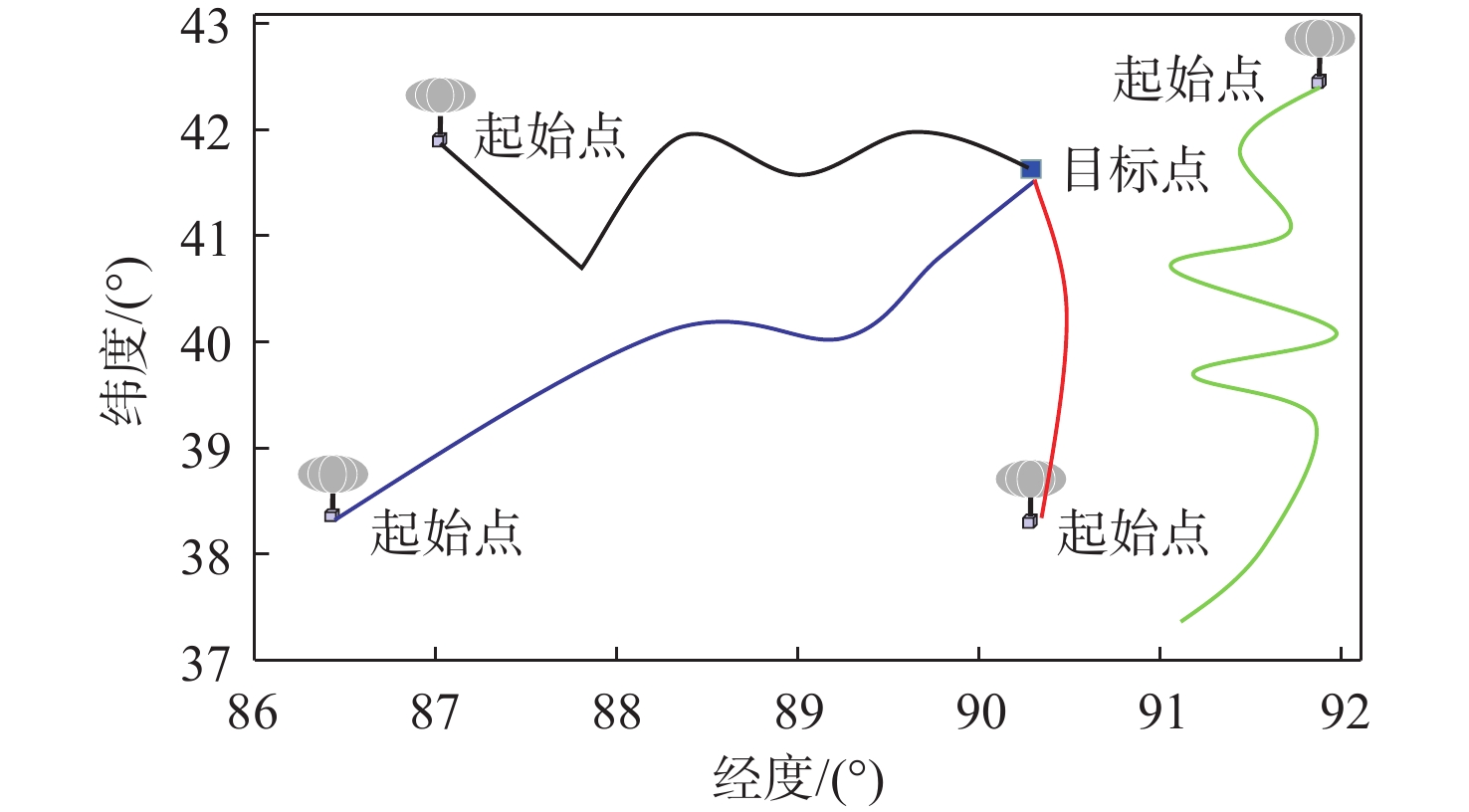
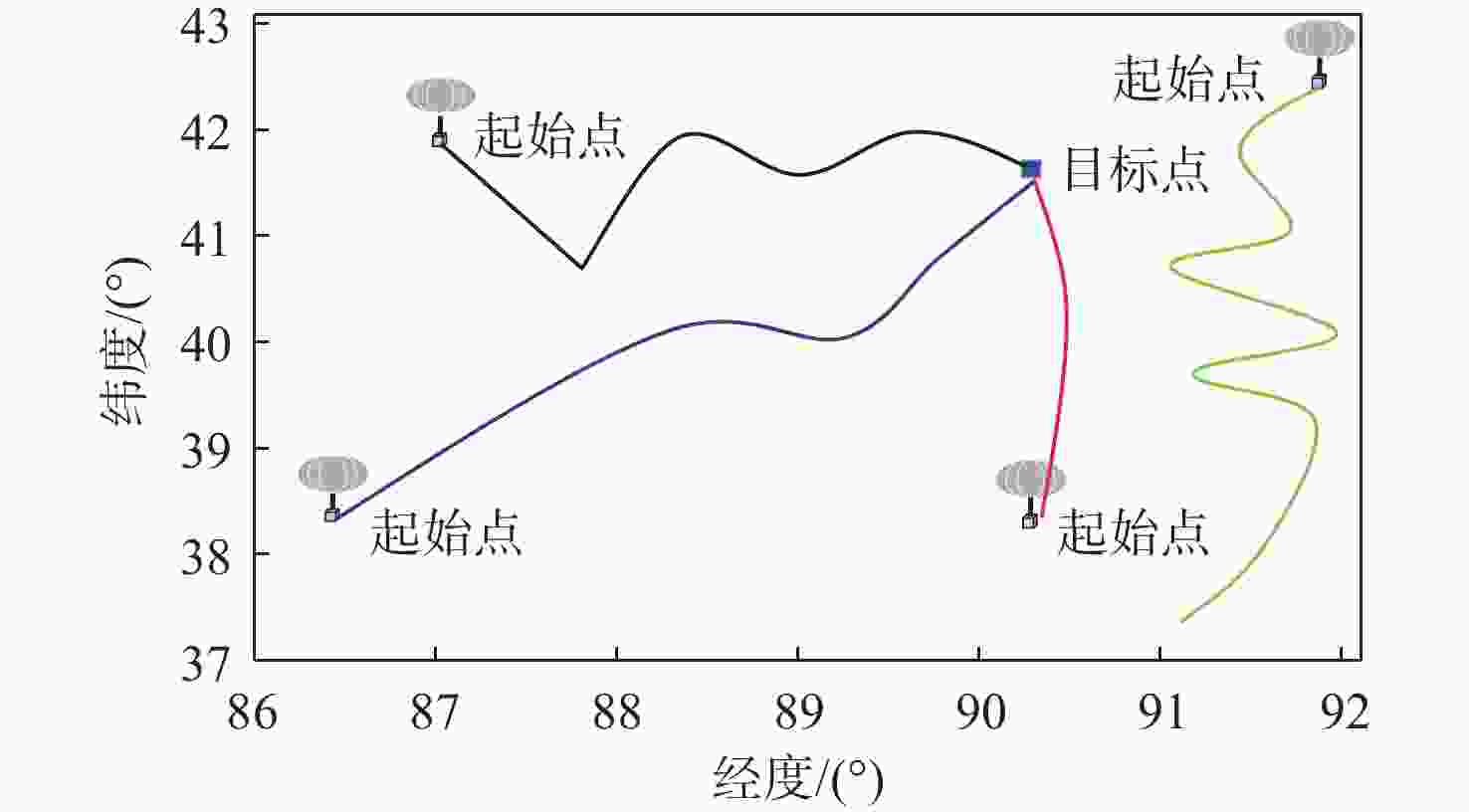
平流层浮空器是开展临近空间应用的重要平台,其在不确定风场中的路径规划是开展应用的关键。研究对象是具有一定水平驱动能力的平流层浮空器,针对其低动态、大尺寸及易受风场影响等特点,基于马尔可夫决策过程(MDP)提出一种浮空器在不确定风场作用下的二维全局路径规划方法,寻找由当前位置快速部署到目标区域所需时间最短的最优路径。由于风场中可能存在误差,将风场不确定性引入MDP模型中,设计相关模型参数,建立确定风场和不确定风场2种环境模型。通过仿真,分析具有不同驱动能力的浮空器在2种风场模型下的区域可达性、最优路径和最优动作序列的选择,结果表明:最优路径和最优动作会根据起始点/目标点位置、浮空器水平驱动能力及风场模型的不同发生比较大的变化;浮空器的水平驱动能力越强,区域可达性越高,2种风场模型对浮空器的二维全局路径规划影响的差异也随之减弱。
Abstract:The path planning in an unknown wind field is the main application challenge for stratospheric aerostats, which are a crucial platform for exploring the region of near space. The research object of this paper is stratospheric aerostat with certain horizontal actuation which are encountered with low dynamic, huge structural scale and the flight performance significantly affected by environmental wind field. An approach of two-dimensional global path planning based on the Markov decision process (MDP) in the wind field is presented, in which the problem of path planning is regarded as looking for the optimal path with the shortest time required for rapid deployment from the current location to the target. The actual wind vector field is not known exactly and may deviate significantly from the wind velocities estimated by the model. Since the exact wind vector field is unknown, it is possible that it will differ greatly from the model's predicted wind velocities. To address this issue, our technique explicitly incorporates wind uncertainty into the path planning algorithm, and designs the related parameters of approach in order to establish the determined wind field model and the uncertain wind field model . To solve this problem, we developed a method that explicitly accounts for wind uncertainty in the path planning algorithm and designs the relevant approach parameters to create both a determined wind field model and an uncertain wind field model. The reachability of aerostat with horizontal actuation in a given region relative to the target under different wind field models is compared, in addition, the shortest flight time path and the optimal action sequences are planned. The numerical simulations show that the optional path and actions sequence change with difference of the positions of start/target, the horizontal actuations and wind field models. The numerical simulations also show that the regional accessibility enlarges and the difference of the influence between two wind field models on the two-dimensional global path planning of the aerostat decreases with increase of the horizontal actuation of the aerostat.
-
-
[1] BELMONT A D, DARTT D G, NASTROM G D. Variations of stratospheric zonal winds, 20-65km, 1961-1971[J]. Journal of Applied Meterology, 2010, 14(4): 585-594. [2] 洪延姬. 临近空间飞行器技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业大学出版社, 2012: 9-12.HONG Y J. Aircraft technology of near space[M]. Beijing: National University of Defense Technology Press, 2012: 9-12 (in Chinese). [3] 黄宛宁, 李颖思, 周书宇, 等. 现代浮空器军事应用[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(15): 20-27.HUANG W N, LI Y S, ZHOU S Y, et al. Military applications of modern lighter-than-air vehicles[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2017, 35(15): 20-27(in Chinese). [4] 杨希祥, 杨晓伟, 邓小龙. 反步法与神经网络融合的平流层飞艇轨迹鲁棒控制方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2021, 42(3): 351-358. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.03.010YANG X X, YANG X W, DENG X L. Robust trajectory control method for stratospheric airships with combination of backstepping and neural network[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2021, 42(3): 351-358(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.03.010 [5] 邓小龙, 丛伟轩, 李魁, 等. 风场综合利用的新型平流层浮空器轨迹设计[J]. 宇航学报, 2019, 40(7): 748-757.DENG X L, CONG W X, LI K, et al. Trajectory design of a novel stratospheric aerostat based on comprehensive utilization of wind fields[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2019, 40(7): 748-757(in Chinese). [6] JIANG Y, LV M, QU Z, et al. Performance evaluation for scientific balloon station-keeping strategies considering energy management strategy[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 156: 290-302. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2020.04.011 [7] 林康, 马云鹏, 郑泽伟, 等. 基于副气囊的平流层浮空器高度控制研究[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(7): 1-13.LIN K, MA Y P, ZHENG Z W, et al. Height control of stratospheric aerostat based on secondary airbag[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(7): 1-13(in Chinese). [8] JIANG Y, LV M, LI J. Station-keeping control design of double bal loon system based on horizontal region constraints[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 100: 105792. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.105792 [9] 李智斌, 黄宛宁, 张钊, 等. 2020年临近空间科技热点回眸[J]. 科技导报, 2021, 39(1): 54-68.LI Z B, HUANG W N, ZHANG Z, et al. Summary of the hot spots of near space science and technology in 2020[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2021, 39(1): 54-68 (in Chinese). [10] BELLEMARE M G, CANDIDO S, CASTRO P S, et al. Autonomous navigation of stratospheric balloons using reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2020, 588(7836): 77-82. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2939-8 [11] 孙玉山, 王力锋, 吴菁, 等. 智能水下机器人路径规划方法综述[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2020, 4(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2020.01.001SUN Y S, WANG L F, WU J, et al. A general overview of path planning methods for autonomous underwater vehicle[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2020, 4(1): 1-7(in Chinese). doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2020.01.001 [12] SUN J, TANG J, LAO J. Collision avoidance for cooperative UAVs with optimized artificial potential field algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 18382-18390. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2746752 [13] 黄东晋, 蒋晨凤, 韩凯丽. 基于深度强化学习的三维路径规划算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2020, 56(15): 30-36.HUANG D J, JIANG C F, HAN K L. 3D path planning algorithm based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2020, 56(15): 30-36(in Chinese). [14] TAI L, LIU M. Towards cognitive exploration through deep reinforcement learning for mobile robots[J]. IEEE IROS, 2016: 465-488. [15] WOLF M T, BLACKMORE L, KUWATA Y, et al. Probabilistic motion planning of balloons in strong, uncertain wind fields[C]//2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 1123-1129. [16] 陈魁. 基于马尔可夫决策过程的码垛机器人路径规划研究 [D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2012.CHEN K. Research on path planning based on Markov decision processes for palletizing robot [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2012 (in Chinese). [17] YU X, ZHOU X, ZHANG Y. Collision-free trajectory generation and tracking for UAVs using Markov decision process in a cluttered environment[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2019, 93(1): 17-32. [18] KULARATNE D, HAJIEGHRARY H, HSIEH M A. Optimal path planning in time-varying flows with forecasting uncertainties[C]//2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 4857-4864. [19] NANAZ F, LARS B, YOSHIAKI K, et al. Feasibility studies on guidance and global path planning for wind-assisted montgolfière in titan[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2013, 8(4): 1112-1125. [20] PASHENKOVA E, RISH I, DECHTER R. Value iteration and policy iteration algorithms for Markov decision problem[C]//Department of Information and Computer Science. Irvine: University of Salifornia, 1996. [21] SUTTON R S, BARTO A G. Reinforcement learning: An introduction [M]. Cambridge: The MIT Press, 2018: 33-35. -






 下载:
下载: