Shape optimization of isogeometric boundary element method using flower pollination algorithm
-
摘要:
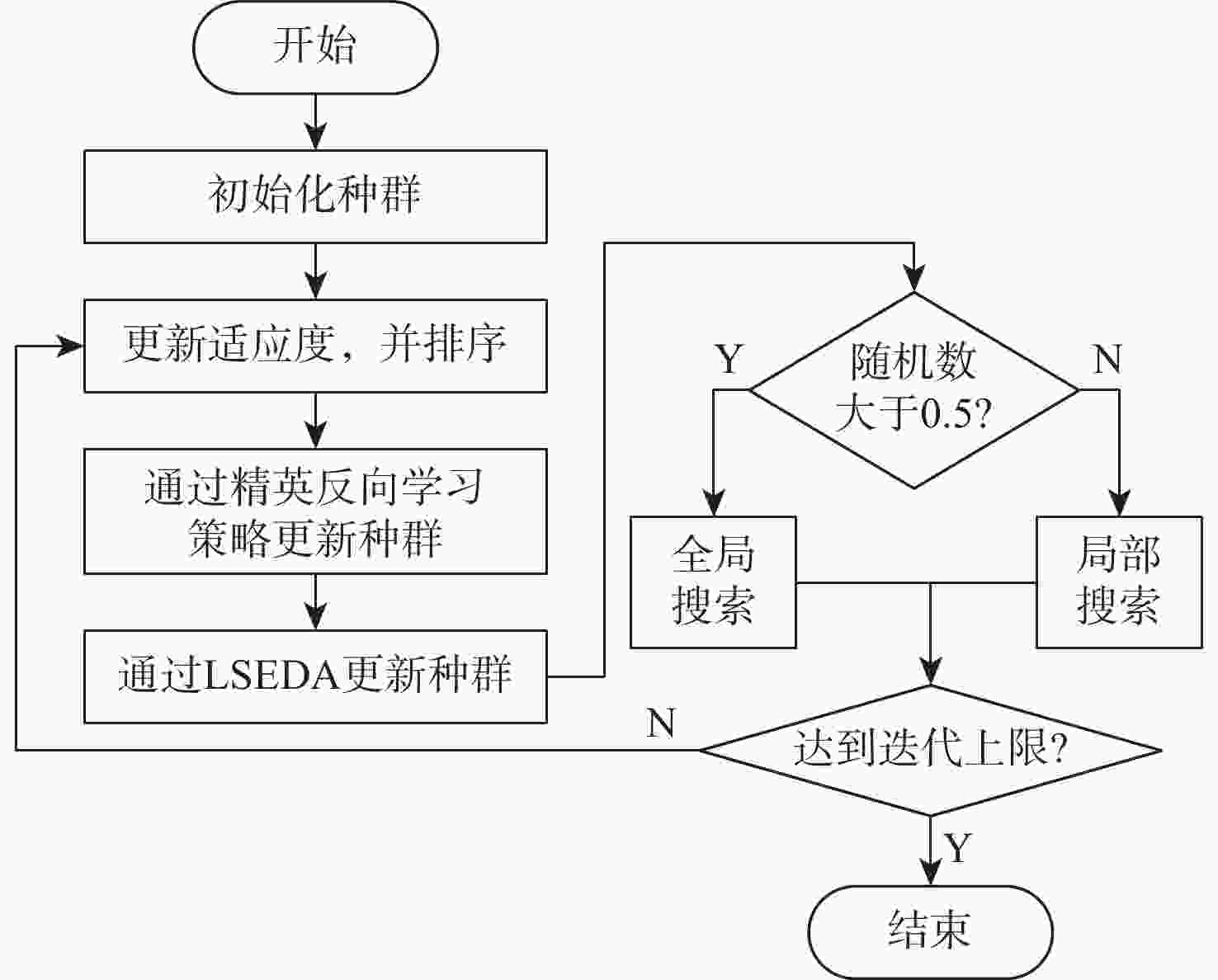
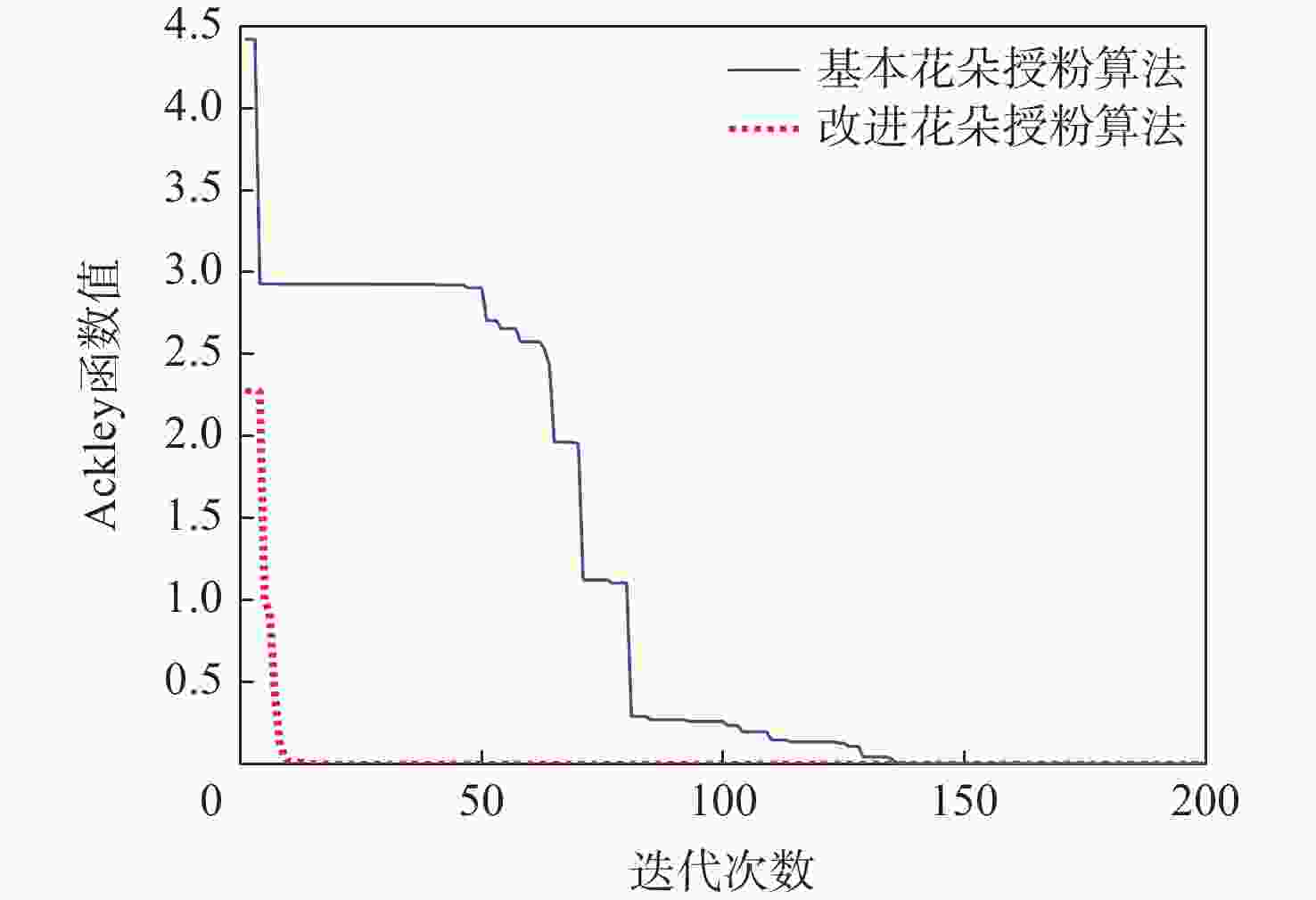
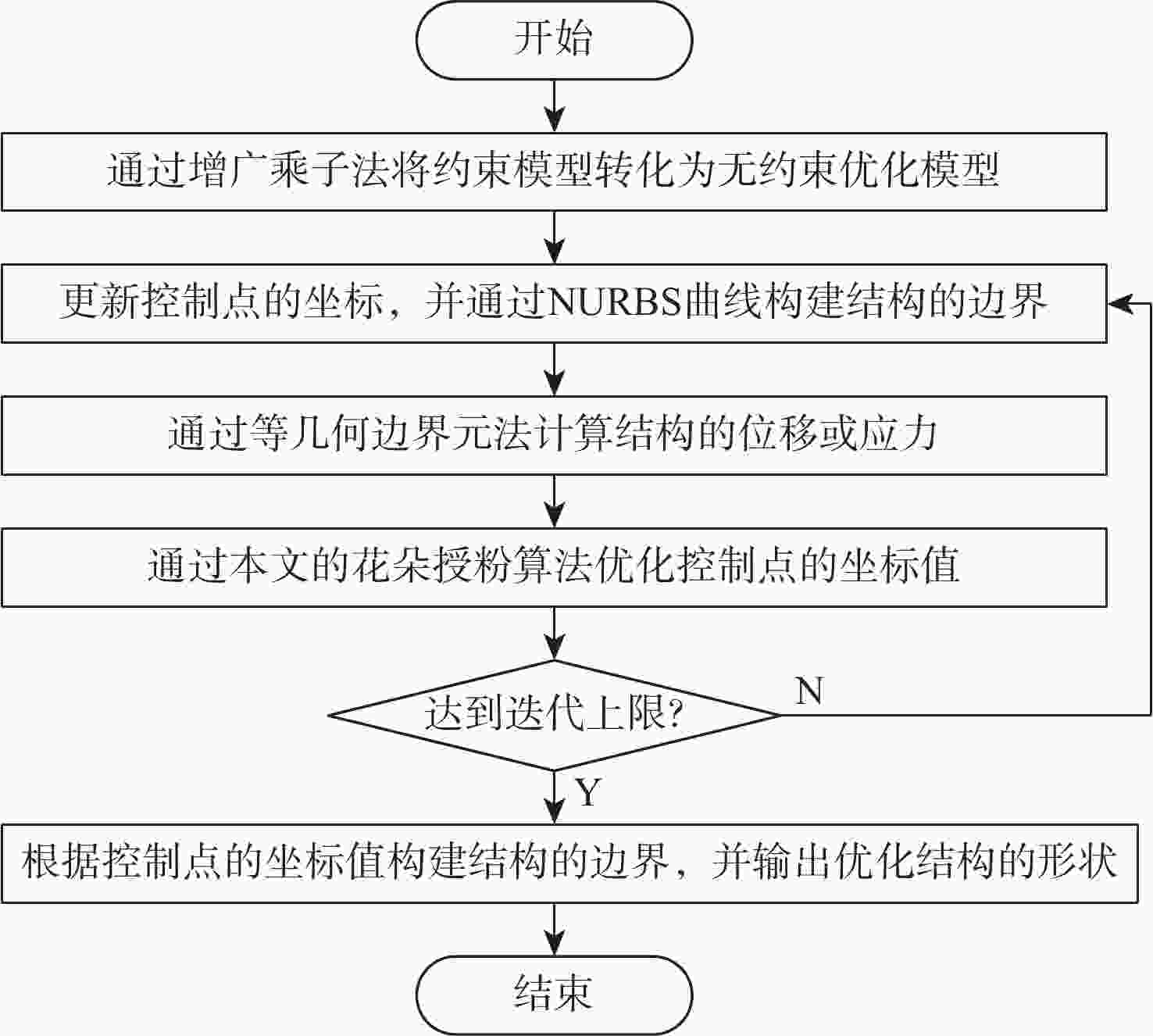
为了避免离散整个结构,以及减少几何模型与离散模型之间的误差,提出一种改进的花朵授粉算法优化等几何边界元模型的形状优化算法。采用的边界元法仅需离散结构边界,简化了离散过程,且加入的等几何分析可提高计算精度。以最小化位移或应力为目标函数,以结构面积等于指定面积为约束条件,采用增广乘子法将约束优化模型转化为无约束优化模型;通过等几何边界元法对结构的受力情况进行分析;采用精英反向学习策略及大规模分布估计算法(LSEDA)改进花朵授粉算法,通过花朵授粉算法优化控制点的坐标值,并通过非均匀有理 B 样条(NURBS)基函数构建结构的边界,输出最优结构的形状。Ackley函数的测试结果表明:改进的花朵授粉算法14步收敛,而原始花朵授粉算法136步收敛,且所得最小值为8.881 8×10−16,小于0.001 4,改进的花朵授粉算法寻优能力更强。形状优化的计算结果表明:所提算法可有效求解二维等几何边界元形状优化问题。
Abstract:In order to avoid discretizing the whole structure and reduce the error between the geometric model and the discrete model, a shape optimization method based on the flower pollination algorithm and isogeometric boundary element method is proposed. The boundary element method only needs to discretize the structure boundary, and this simplifies the discretization process. The boundary element method only needs to discretize the structure boundary, and this simplifies the discretization process. Furthermore, the isogeometric analysis is exploited to improve the accuracy. Firstly, the objective function is to minimize the displacement or stress, and the constraint condition is that the structural area is equal to the specified area; secondly, the constrained optimization model is transformed into an unconstrained optimization model by using the augmented lagrange multiplier method; Then, the bearing condition of the structure is analyzed by the isogeometric boundary elementmethod (IGABEM); finally, the elite opposite-based learning strategy and large scale estimation of distribution algorithms (LSEDA) are used to improve the flower pollination algorithm, and the coordinates of control points are optimized by the improved flower pollination algorithm. After that, the boundary of structure is constructed by the non-uniform rational B-splines (NURBS) basis function, and the optimal structure shape is drawn. According to the test findings for the Ackley function, the enhanced flower pollination algorithm converges in 14 steps as opposed to 136 steps for the original flower pollination algorithm, and its minimum value is 8.881 8×10−16 less than 0.0014, demonstrating that it is more capable of optimization. The computational results of shape optimization show that the proposed algorithm can effectively solve two-dimensional shape optimization problem based on isogeometric boundary element method.
-
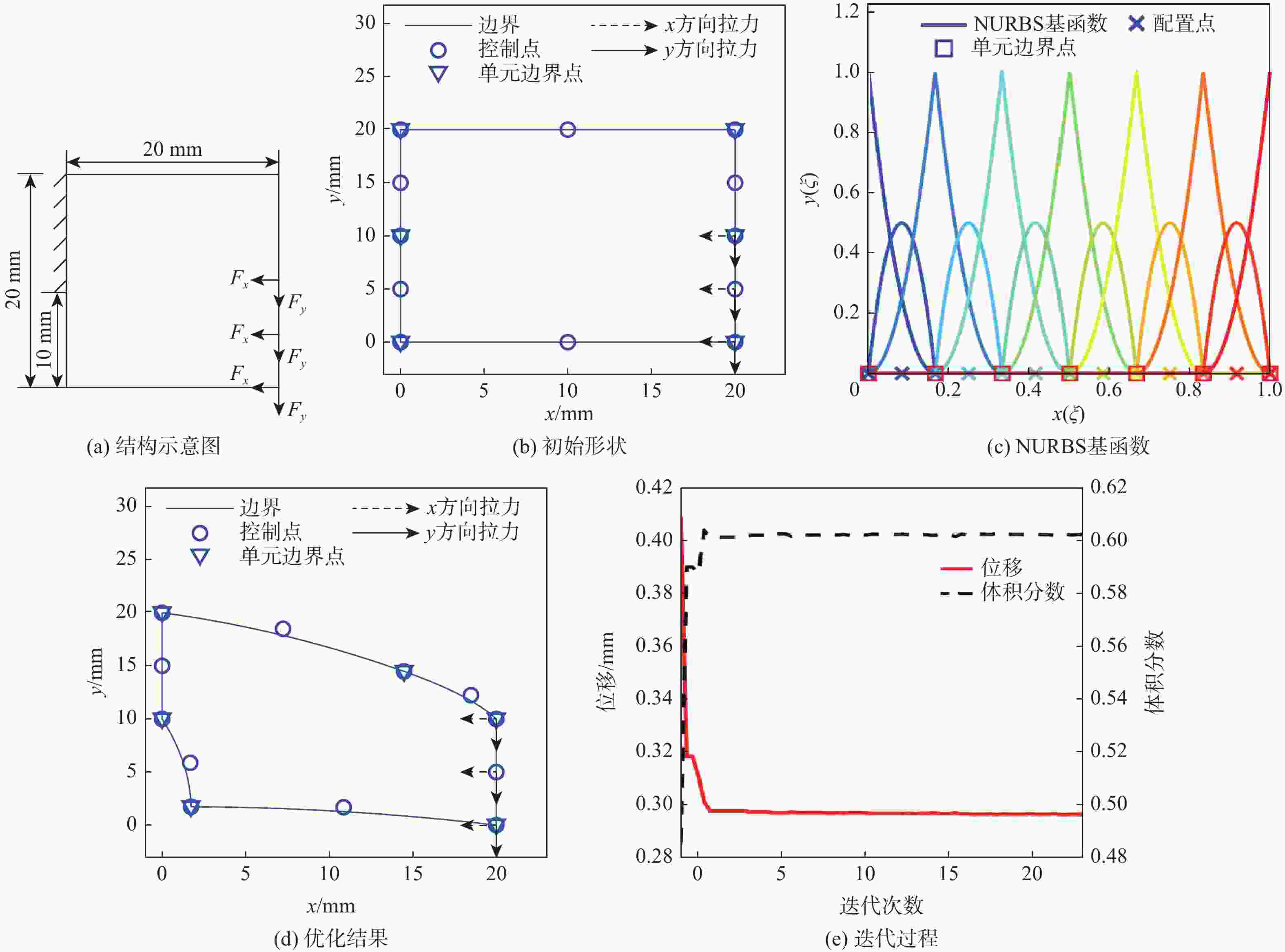
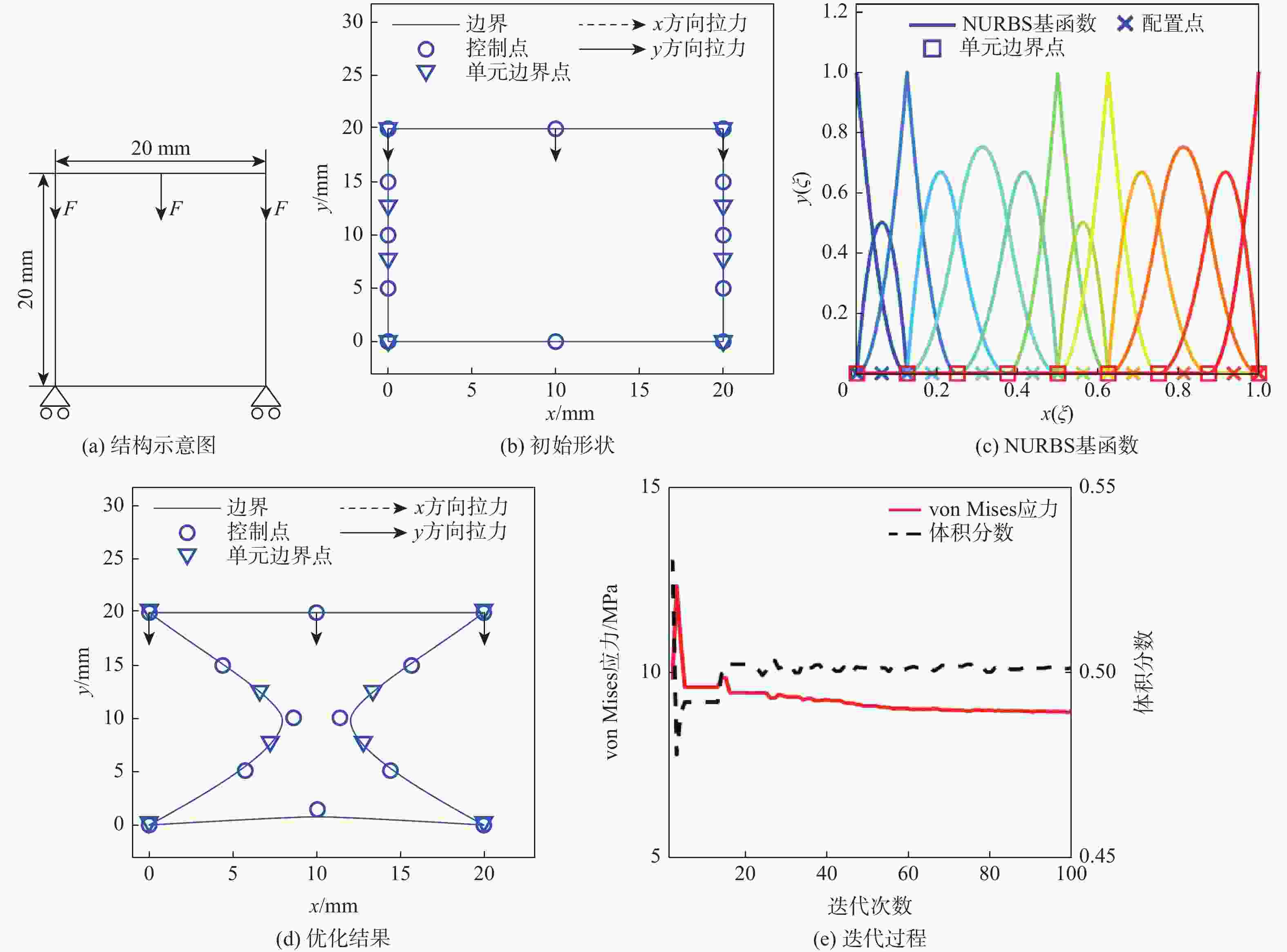
表 1 位移算例的控制点及节点向量
Table 1. Control points and knot vectors for displacement example
参数 数值 ${\boldsymbol{P}}$ [0, 0; 10, 0; 20, 0; 20, 5; 20, 10; 20, 15; 20, 20;
10, 20; 0, 20; 0, 15; 0, 10; 0, 5; 0, 0]${\boldsymbol{\varXi } }$
[0, 0, 0, 1/6, 1/6, 2/6, 2/6, 3/6, 3/6, 4/6, 4/6, 5/6, 5/6, 1, 1, 1]表 2 应力算力的控制点及节点向量
Table 2. Control points and knot vectors for stress example
参数 数值 ${\boldsymbol{P}}$ [0, 0; 10, 0; 20, 0; 20, 5; 20, 10; 20, 15; 20, 20;
10, 20; 0, 20; 0, 15; 0, 10; 0, 5; 0, 0]${\boldsymbol{\varXi } }$
[0, 0, 0, 1/8, 1/8, 2/8, 3/8, 4/8, 4/8, 5/8, 5/8, 6/8, 7/8, 1, 1, 1] -
[1] 彭一江, 刘应华. 基面力单元法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017.PENG Y J, LIU Y H. Base force element method[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017(in Chinese). [2] 吴紫俊, 黄正东, 左兵权, 等. 等几何分析研究概述[J]. 机械工程学报, 2015, 51(5): 114-129. doi: 10.3901/JME.2015.05.114WU Z J, HUANG Z D, ZUO B Q, et al. Perspectives on isogeometric analysis[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(5): 114-129(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2015.05.114 [3] SIMPSON R N, BORDAS S P A, LIAN H, et al. An isogeometric boundary element method for elastostatic analysis: 2D implementation aspects[J]. Computers & Structures, 2013, 118: 2-12. [4] HAO P, WANG Y T, MA R, et al. A new reliability-based design optimization framework using isogeometric analysis[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 345: 476-501 . doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2018.11.008 [5] LIAN H, KERFRIDEN P, BORDAS S P A. Shape optimization directly from CAD: An isogeometric boundary element approach using T-splines[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 317: 1-41. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2016.11.012 [6] YOON M, CHO S. Isogeometric shape design sensitivity analysis of elasticity problems using boundary integral equations[J]. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 2016, 66: 119-128. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2016.01.010 [7] LEE S W, YOON M, CHO S. Isogeometric topological shape optimization using dual evolution with boundary integral equation and level sets[J]. Computer-Aided Design, 2017, 82: 88-99. doi: 10.1016/j.cad.2016.08.004 [8] CHOI M J, CHO S. A mesh regularization scheme to update internal control points for isogeometric shape design optimization[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 285: 694-713. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2014.11.045 [9] LÜDEKER J K, SIGMUND O, KRIEGESMANN B. Inverse homogenization using isogeometric shape optimization[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 368: 113170. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113170 [10] KANG P, YOUN S K. Isogeometric shape optimization of trimmed shell structures[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2016, 53(4): 825-845. doi: 10.1007/s00158-015-1361-6 [11] SUN S H, YU T T, NGUYEN T T, et al. Structural shape optimization by IGABEM and particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 2018, 88: 26-40. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2017.12.007 [12] 张永恒. 工程优化设计与MATLAB实现[M]. 修订版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2011: 162-164.ZHANG Y H. Engineering optimization design and MATLAB implementation[M]. Revised ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2011:162-164 (in Chinese). [13] 薛晗, 邵哲平, 潘家财, 等. 基于文化萤火虫算法-广义回归神经网络的船舶交通流量预测[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2020, 54(4): 421-429. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2020.04.011XUE H, SHAO Z P, PAN J C, et al. Vessel traffic flow prediction based on CFA-GRNN algorithm[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2020, 54(4): 421-429(in Chinese). doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2020.04.011 [14] HE Q, HU X, REN H, et al. A novel artificial fish swarm algorithm for solving large-scale reliability-redundancy application problem[J]. ISA Transactions, 2015, 59: 105-113. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2015.09.015 [15] 王丽芳. 基于copula理论的分布估计算法研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2011.WANG L F. The research on estimation of distribution algorithm based on copula theory[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2011(in Chinese). [16] 王振. 融合Copula分布估计的AEA算法及其在约束优化问题中的应用[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2014.WANG Z. The AEA combined with Copula estimation of distribution algorithm and its application on constrained optimization problems[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2014 (in Chinese). [17] 韩江, 闵杰. 基于精英反向学习的烟花爆炸式免疫遗传算法[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 43(4): 433-437.HAN J, MIN J. A fireworks explosive immune genetic algorithm based on elite opposition-based learning[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2020, 43(4): 433-437(in Chinese). [18] 石彤, 李盼池. 量子教学优化算法及在函数优化中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(信息科学版), 2020, 38(5): 578-587. doi: 10.19292/j.cnki.jdxxp.2020.05.008SHI T, LI P C. Quantum teaching-learning-based optimization algorithm and its application in function optimization[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Information Science Edition), 2020, 38(5): 578-587(in Chinese). doi: 10.19292/j.cnki.jdxxp.2020.05.008 [19] 李士勇, 李研. 智能优化算法原理与应用[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2012.LI S Y, LI Y. Intelligent optimization algorithm theory and applications[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2012(in Chinese). [20] 梁田, 曹德欣. 基于莱维飞行的改进简化粒子群算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(20): 188-196.LIANG T, CAO D X. An improved and simplified particle swarm optimization algorithm based on Levy flight[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2021, 57(20): 188-196(in Chinese). [21] GUPTA S, DEEP K. Random walk grey wolf optimizer for constrained engineering optimization problems[J]. Computational Intelligence, 2018, 34(4): 1025-1045. doi: 10.1111/coin.12160 [22] WANG Y, LI B. A restart univariate estimation of distribution algorithm: sampling under mixed Gaussian and Lévy probability distribution[C]//2008 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2008: 3917-3924. [23] GAN B. Condensed isogeometric analysis for plate and shell structures [M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2019: 1-40. [24] PIEGL L A, TILLER W. The NURBS book[M]. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer, 1997. [25] COTTRELL J A, HUGHES T J R, BAZILEVS Y. Isogeometric analysis[M]. Hoboken: Wiley, 2009. [26] PROVATIDIS C G. Precursors of isogeometric analysis: Finite elements, boundary elements, and collocation methods[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2019. [27] DE FALCO C, REALI A, VÁZQUEZ R. GeoPDEs: A research tool for isogeometric analysis of PDEs[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2011, 42(12): 1020-1034. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2011.06.010 [28] VÁZQUEZ R. A new design for the implementation of isogeometric analysis in Octave and Matlab: GeoPDEs 3.0[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2016, 72(3): 523-554. [29] 高效伟, 彭海峰, 杨恺, 等. 高等边界元法——理论与程序[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 227-250.GAO X W, PENG H F, YANG K, et al. Advanced boundary element method: Theory and procedure[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015: 227-250(in Chinese). [30] 杨德全, 赵忠生. 边界元理论及应用[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2002.YANG D Q, ZHAO Z S. Boundary element theory and its application[M]. Beijing: Beijing Insititute of Technology Press, 2002(in Chinese). [31] OLIVEIRA H L, ANDRADE H C, LEONEL E D. An isogeometric boundary element approach for topology optimization using the level set method[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2020, 84: 536-553. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2020.03.047 [32] 姚振汉, 王海涛. 边界元法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2010.YAO Z H, WANG H T. Boundary element methods[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2010(in Chinese). [33] BIYIKLI E, TO A C. Proportional topology optimization: A new non-sensitivity method for solving stress constrained and minimum compliance problems and its implementation in MATLAB[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(12): e0145041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145041 [34] YANG X S. Nature-inspired optimization algorithms[M]. Asmsterdam: Elsevier, 2014: 155-173. -







 下载:
下载: