-
摘要:
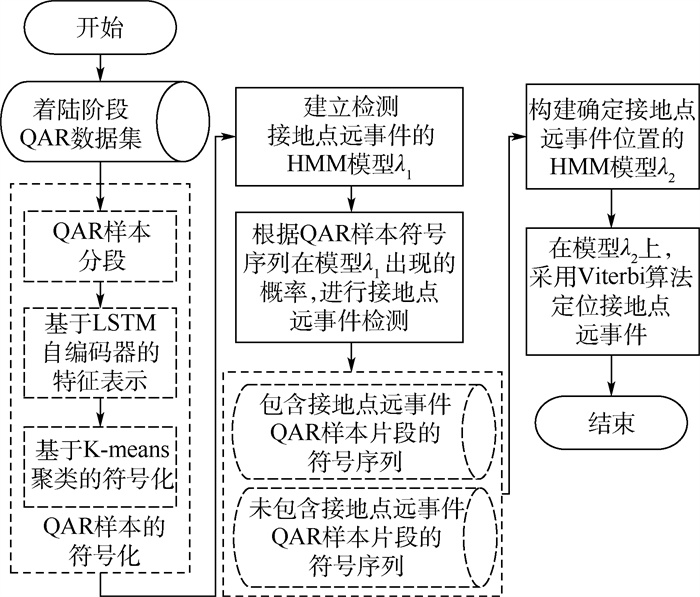
已有的飞行品质监控(FOQA)标准仅由地速的积分距离判定接地点远事件(LTE)的发生,无法结合多个快速存取记录器(QAR)参数检测并解释发生该事件的原因。通过滑动窗口对包含多个参数的QAR样本进行分段,按照分段位置形成若干分段样本集。由长短时记忆网络(LSTM)自编码器得到QAR样本分段及分段内向量的特征表示,采用K-means分别对这些表示向量进行聚类处理,实现QAR样本及其分段的符号化。使用正常航班QAR样本集的符号序列建立隐马尔可夫模型(HMM),以检测包含接地点远事件的航班。由发生及未发生接地点远事件的QAR样本各个分段的符号序列构建HMM后,采用Viterbi算法确定接地点远事件在QAR样本分段内的具体位置。在真实QAR数据集上的实验结果表明,与其他多维时间序列异常检测方法相比,所提方法不仅能有效检测接地点远事件,而且可以获得多个QAR参数的异常值,辅助领域专家分析发生该事件的原因。
-
关键词:
- 异常检测 /
- 接地点远事件(LTE) /
- 自编码器 /
- 隐马尔可夫模型(HMM) /
- 快速存取记录器(QAR)
Abstract:The existing flight operation quality assurance (FOQA) standard only uses the integral distance of the ground speed to define the long touchdown exceedance (LTE), which cannot detect and explain the exceedance using multiple quick access recorder (QAR) parameters. The QAR samples with multiple parameters were segmented by the sliding window, and the segmented sample sets were generated according to the segmentation position. The representation of the QAR sample segmentation and the vector within each QAR segment was obtained by the long short-term memory (LSTM) networks autoencoder, and the representation vectors were clustered by K-means to realize the symbolization of the QAR samples and the QAR segments. The hidden Markov model (HMM) model was built by using the symbolic sequence of the QAR sample set of the normal flights, which was used to detect the flights with the LTE. The second HMM model was constructed from the symbolic sequences of the segment of the normal QAR samples and the QAR samples including the LTE. Then the Viterbi algorithm was used to determine the specific positon of the LTE in the QAR sample segment. Experimental results on real QAR data sets show that, compared with other multi-dimensional time series anomaly detection methods, the proposed method can not only effectively detect the LTE, but also obtain the outliers of multiple QAR parameters, which can assist domain experts to analyze the cause of the exceedance.
-
表 1 参数说明
Table 1. Parameter description
参数 意义 标准气压高度 飞机与标准气压平面之间的距离 无线电高度 飞机距离地面的真实高度 N11、N21 1、2号发动机低压压气机转子负荷百分比 N12、N22 1、2号发动机高压压气机转子负荷百分比 EGT1、EGT2 1、2号发动机排气温度 左、右迎角 左、右机翼弦线与空气流速的夹角 俯仰角 机身纵轴线与水平面的夹角 倾侧角 飞机在横滚轴上的倾斜角度 方向舵偏角 方向舵左右偏转角度 空速 根据标准大气压下空速与动压关系测定的空速 垂直加速度 飞机在垂线上的加速度 纵向加速度 飞机在纵轴上的加速度 横向加速度 飞机在横轴上的加速度 下降率 飞机的垂直速度 FLAP1、FLAP2 飞机左右两边襟翼角度 表 2 异常航班数据检测的对比实验
Table 2. Comparison experiment of abnormal flight data detection
检测方法 准确率 召回率 F1 PCA+HMM 0.43 0.89 0.609 FCM+HMM 0.432 0.708 0.611 AHMM-AD 0.493 0.682 0.570 LTED-LSTM-HMM 0.600 0.968 0.741 -
[1] 孙瑞山, 韩文律. 基于差异检验的飞行超限事件参数特征分析[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2011, 7(2): 22-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDBK201102003.htmSUN R S, HAN W L. Anaylysis on parameters characteristics of flight exceedance events based on distinction test[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2011, 7(2): 22-27(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDBK201102003.htm [2] 郑磊, 池宏, 邵雪焱. 基于QAR数据的飞行操作模式及其风险分析[J]. 中国管理科学, 2017, 25(10): 109-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGK201710012.htmZHENG L, CHI H, SHAO X Y. Pattern recognition and risk analysis for flight operations[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2017, 25(10): 109-118(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGK201710012.htm [3] WANG L, REN Y, WU C X. Effects of flare operation on landing safety: A study based on ANOVA of real flight data[J]. Safety Science, 2018, 102: 14-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2017.09.027 [4] 汪磊, 郭世广, 任勇. 基于飞行数据正态云的着陆操作风险评价方法[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2019, 19(5): 1555-1561. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201905010.htmWANG L, GUO S G, REN Y. Landing operation risk evaluation based on the normal cloud of the flight data[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2019, 19(5): 1555-1561(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201905010.htm [5] LI L, DAS S, HANSMAN R J, et al. Analysis of flight data using clustering techniques for detecting abnormal operations[J]. Journal of Aerospace Information Systems, 2015, 12(9): 587-598. doi: 10.2514/1.I010329 [6] SHERIDAN K, PURANIK T G, MANGORTEY E, et al. An application of DBSCAN clustering for flight anomaly detection during the approach phase[C]//AIAA SciTech Forum. Reston: AIAA, 2020, 1851: 1-20. [7] EUGENE M, DYLAN M, JAMEY A, et al. Application of machine learning techniques to parameter selection for flight risk identification[C]//AIAA SciTech Forum. Reston: AIAA, 2020, 1850: 1-39. [8] LI L, HANSMAN R J, PALACIOS R, et al. Anomaly detection via a Gaussian mixture model for flight operation and safety monitoring[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2016, 64: 4557. [9] MELNYK I, MATTHEWS B, VALIZADEGAN H, et al. Vector autoregressive model-based anomaly detection in aviation systems[J]. Journal of Aerospace Information Systems, 2016, 13(4): 161-173. doi: 10.2514/1.I010394 [10] MELNYK I, BANERJEE A, MATTHEWS B, et al. Semi-Markov switching vector autoregressive model-based anomaly detection in aviation systems[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2016: 1065-1074. [11] KEYGHOBADI H, SEYEDIN A. Abnormality detection in a landing operation using hidden Markov model[J]. Journal of Computer & Robotics, 2017, 10(1): 31-37. [12] LI J, PEDRYCZ W, JAMAL I. Multivariate time series anomaly detection: A framework of hidden Markov models[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2017, 60: 229-240. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2017.06.035 [13] JIA Y Z, XU M Q, WANG R X. Symbolic important point perceptually and hidden Markov model based hydraulic pump fault diagnosis method[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(12): 4460. doi: 10.3390/s18124460 [14] 霍纬纲, 王慧芳. 基于自编码器和隐马尔可夫模型的时间序列异常检测方法[J]. 计算机应用, 2020, 40(5): 1329-1334. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJY202005015.htmHUO W G, WANG H F. Time series anomaly detection method based on autoencoder and HMM[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2020, 40(5): 1329-1334(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJY202005015.htm [15] MALHOTRA P, RAMAKRISHNAN A, ANAND G, et al. LSTM-based encoder-decoder for multi-sensor anomaly detection[C]//Anomaly Detection Workshop at 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, 2016. [16] 李航. 统计学习方法[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2019: 193-201.LI H. Statistical learning method[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2019: 193-201(in Chinese). [17] SRIVASTAVA N, MANSIMOV E, SALAKHUDINOV R. Unsupervised learning of video representations using LSTMs[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, 2015, 37: 843-852. [18] 占欣. 基于QAR数据的冲/偏出跑道风险评估研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2019: 15-20.ZHAN X. Research on risk evaluation of runway excursion based on QAR data[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2019: 15-20(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: