-
摘要:
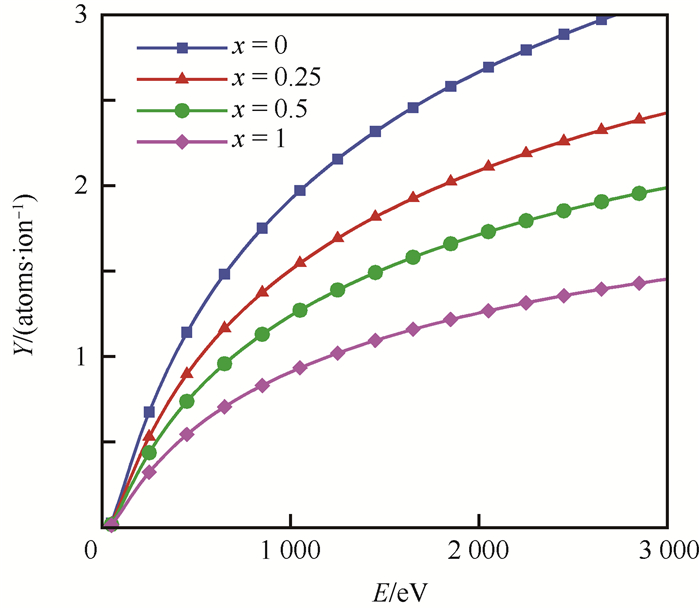
为了得到在低能条件下更为精确的Ar+和Xe+轰击SiO2的溅射模型,对已有化合物溅射模型进行调研分析,总结了3种溅射模型,分别为Pencil模型、Bach模型和Seah模型,并对其不足之处加以分析。在Seah模型基础上,对溅射阈值采用新的计算方法,并利用等效原子法改进溅射参数和表面键能的计算方法,形成改进后的新模型。结合已有的关于Ar+和Xe+法向轰击SiO2的实验数据,对4种模型的计算结果进行对比分析。对于Ar+和Xe+法向轰击SiO2,改进后的溅射模型的均方根误差最小,拟合优度最高,均优于其他3种模型。说明在低能状态下,采用改进后的模型可以更为精确地计算Ar+和Xe+轰击SiO2的溅射率。
Abstract:In order to obtain the more accurate sputtering model of SiO2 for bombardment with low energy Ar+ and Xe+, three existing models, Pencil model, Bach model and Seah model, were investigated and the deficiencies were analyzed. On the basis of Seah model, the sputtering parameters and surface binding energy were calculated by equivalent atomic method. Meanwhile, a new calculation method of sputtering threshold was applied to form a new advanced model. Combined with the experimental data of SiO2 for bombardment at normal incidence with Ar+ and Xe+, the calculation results of the four models were contrastively analyzed. The results show that, for both Ar+ and Xe+ bombardment, the root mean square error of the new advanced model is the smallest and the goodness of fit is the largest, which means the new advanced model is better than other three models. Under the low energy condition, the new advanced model can calculate the sputtering yield of SiO2 bombarded by Ar+ and Xe+ more accurately.
-
Key words:
- argon ion /
- xenon ion /
- silicon dioxide /
- sputtering /
- improvement
-
表 1 Seah模型中计算Q的相关系数
Table 1. Correlation coefficients for calculation of Q in Seah model
离子 a b c d e f Ar+ 0.020 6 15.483 19.83 0.022 1 16 50 Xe+ 0.029 6 9.729 29.52 0.018 8 30 50 表 2 不同模型对于Ar+法向轰击SiO2实验数据的拟合
Table 2. Fitting of experimental data of SiO2 bombarded at normal incidence by Ar+ using different models
拟合结果 Pencil模型 Seah模型 本文改进模型 RMSE 0.040 0 0.037 3 0.036 9 R 0.764 3 0.798 7 0.803 7 表 3 不同模型对于Xe+法向轰击SiO2实验数据的拟合
Table 3. Fitting of experimental data of SiO2 bombarded at normal incidence by Xe+ using different models
拟合结果 Pencil模型 Seah模型 本文改进模型 RMSE 0.029 1 0.034 3 0.023 2 R 0.635 5 0.410 9 0.788 2 -
[1] SIGMUND P.Theory of sputtering.I:Sputtering yield of amorphous and polycrystalline targets[J].Physical Review, 1969, 184(2):383-416. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.184.383 [2] 计京津. 稀薄等离子体羽流的溅射效应研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2011: 3-9. https://wuxizazhi.cnki.net/lunwen-1011268095.htmlJI J J.Study of rarefied plasma plume sputtering effect[D].Shanghai:Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2011:3-9(in Chinese). https://wuxizazhi.cnki.net/lunwen-1011268095.html [3] BOYD I D, FALK M L.A review of spacecraft material sputtering by Hall thruster plumes:AIAA-2001-3353[R].Reston:AIAA, 2001. [4] SEAH M P, NUNNEY T S.Sputtering yields of compounds using argon ions[J].Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics, 2010, 43(25):253001. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/43/25/253001 [5] BOHDANSKY J, ROTH J, BAY H L.An analytical formula and important parameters for low-energy ion sputtering[J].Journal of Applied Physics, 1980, 51(5):2861-2865. doi: 10.1063/1.327954 [6] KELLY R, LAM N Q.The sputtering of oxides.Part I:A survey of the experimental results[J].Radiation Effects, 1973, 19(1):39-48. doi: 10.1080/00337577308232213 [7] PENCIL E J, RANDOLPH T, MANZELLA D H.End-of-life stationary plasma thruster far-field plume characterization:AIAA-1996-2709[R].Reston:AIAA, 1996. [8] YAMAMURA Y, TAWARA H.Energy dependence of ion-induced sputtering yields from monatomic solids at normal incidence[J].Atomic Data and Nuclear Data Tables, 1996, 62(2):149-253. doi: 10.1006/adnd.1996.0005 [9] ROSENBERG D, WEHNER G K.Sputtering yields for low energy He+, Kr+, and Xe+ ion bombardment[J].Journal of Applied Physics, 1962, 33(5):1842-1845. doi: 10.1063/1.1728843 [10] BACH H.Ion beam sputtering of silicate glasses and oxides[J].Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1988, 102(1):36-42. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/002230938890110X [11] SEAH M P, CLIFFORD C A, GREEN F M, et al.An accurate semi-empirical equation for sputtering yields.I:For argon ions[J].Surface and Interface Analysis, 2005, 37(5):444-458. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-9918 [12] MATSUNAMI N, YAMAMURA Y, ITIKAWA Y, et al.Energy dependence of the ion-induced sputtering yields of monatomic solids[J].Atomic Data and Nuclear Data Tables, 1984, 31(1):1-80. doi: 10.1016/0092-640X(84)90016-0 [13] SEAH M P.An accurate semi-empirical equation for sputtering yields.Ⅱ:For neon, argon and xenon ions[J].Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B:Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2005, 229(3):348-358. [14] YAMAMURA Y.Contribution of anisotropic velocity distribution of recoil atoms to sputtering yields and angular distributions of sputtered atoms[J].Radiation Effects, 1981, 55(1-2):49-55. doi: 10.1080/00337578108225465 [15] MALHERBE J B.Sputtering of compound semiconductor surfaces.I.Ion-solid interactions and sputtering yields[J].Critical Reviews in Solid State and Material Sciences, 1994, 19(2):55-127. doi: 10.1080/10408439408244588 [16] DAVIDSE P D, MAISSEL L I.Equivalent dc sputtering yields of insulators[J].Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 1967, 4(1):33-36. doi: 10.1116/1.1492514 [17] JORGENSON G V, WEHNER G K.Sputtering studies of insulators by means of Langmuir probes[J].Journal of Applied Physics, 1965, 36(9):2672-2674. doi: 10.1063/1.1714558 [18] CANTAGREL M, MARCHAL M.Argon ion etching in a reactive gas[J].Journal of Materials Science, 1973, 8(12):1711-1716. doi: 10.1007/BF02403521 [19] TU Y Y, CHUANG T J, WINTERS H F.Chemical sputtering of fluorinated silicon[J].Physical Review B, 1981, 23(2):823-835. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.23.823 [20] MOGI K, OGIWARA T, SUZUKI M.Sputter etching rate ratio of Si to SiO2 using Mesh-Replica method[J].Journal of Surface Analysis, 2002, 9(4):514-523. doi: 10.1384/jsa.9.514 [21] TARTZ M, HEYN T, BUNDESMANN C, et al.Measuring sputter yields of ceramic materials[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Electric Propulsion Conference.Fairview Park:ERPS, 2009:IEPC-2009-240. [22] YALIN A P, SURLA V, FARNELL C, et al.Sputtering studies of multi-component materials by weight loss and cavity ring-down spectroscopy:AIAA-2006-4338[R].Reston:AIAA, 2006. http://www.engr.colostate.edu/lpdl/publications.html [23] YALIN A P, RUBIN B, DOMINGUE S R, et al.Differential sputter yields of boron nitride, quartz, and kapton due to low energy Xe bombardment:AIAA-2007-5314[J].Reston:AIAA, 2007. http://www.engr.colostate.edu/ionstand/publications/papers/AIAA-2007-5314.pdf [24] TONDU T, CHARDON J P, ZURBACH S.Sputtering yield of potential ceramics for Hall effect thruster discharge channel[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Electric Propulsion Conference.Fairview Park:ERPS, 2011:IEPC-2011-106. -







 下载:
下载: