-
摘要:
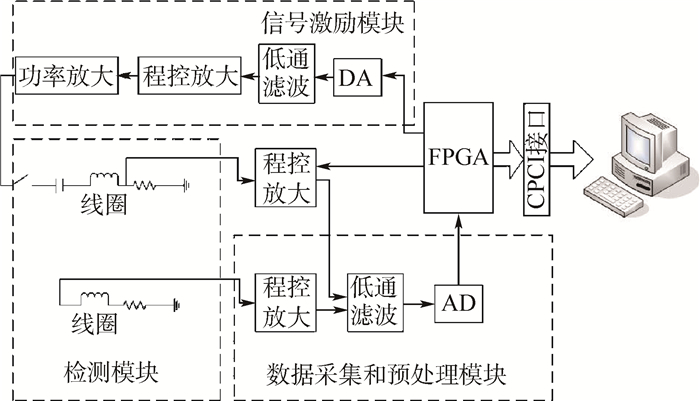
磁感应层析成像(MIT)技术在生物医学检查与诊断中有很好的应用前景。为了实现MIT对生物组织特性信息的获取,设计了具有多激励频率模式的磁感应层析成像系统。系统采用电压激励与测量的工作模式,可选择100 kHz~4 MHz范围内的单频、扫频和混频3种激励频率模式。系统包括激励源模块、传感器线圈阵列、数据采集和调理模块、数字解调模块,采用现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)控制多路复用器、程控放大器、模拟数字转换器等。经模拟实验测试,多激励频率模式系统所获得的测试数据具有较好的一致性,信噪比在46 dB以上,不同激励频率下采集的电压差数据可用于实现被测介质电导率分布的图像重建。
Abstract:Magnetic induction tomography (MIT) has promising applications in biomedical examination and diagnosis. In order to acquire biological tissue characteristic information, a magnetic induction tomography system with multi-excitation frequency mode is designed. The system operates under voltage excitation and voltage measurement mode, and it can select three excitation frequency modes of single frequency, sweep frequency and mixed frequency from 100 kHz to 4 MHz. The system includes excitation source module, sensor coil array, data acquisition and conditioning module, and digital demodulation module, and it uses field-programmable gate array(FPGA) to control multiplexer, programmable amplifier, analog-digital converter and so on. The simulation experiments show that the test data acquired by the system with multi-excitation frequency mode has good consistency, its signal to noise ratio is above 46 dB, and voltage difference acquired at different excitation frequencies can be used to realize the image reconstruction of measured object conductivity distribution.
-
[1] GRIFFITHS H.Magnetic induction tomography[J].Measurement Science & Technology, 2001, 12(8):1126-1131. [2] TARJAN P P, MCFEE R.Electrodeless measurements of the effective resistivity of the human torso and head by magnetic induction[J].IEEE Transactions on Bio-medical Engineering, 1968, 15(4):266-278. [3] 徐征, 何为, 何传红, 等.生物组织电导率磁感应测量原理及系统研究[J].仪器仪表学报, 2008, 29(9):1878-1882.XU Z, HE W, HE C H, et al.Study on the principles and system of measurement biological tissue conductivity with magnetic induction method[J].Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2008, 29(9):1878-1882(in Chinese). [4] KORJENEVSKY A, CHEREPENIN V, SAPETSKY S.Magnetic induction tomography:Experimental realization[J].Physiological Measurement, 2000, 21(1):89-94. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/21/1/311 [5] 王聪, 秦明新, 董秀珍, 等.磁感应方式电导率测量基础研究[J].中国医学物理学杂志, 2004, 21(3):182-185.WANG C, QIN M X, DONG X Z, et al.The basic research of the measurement of conductivity in a magnetic induction way[J].Chinese Journal of Medical Physics, 2004, 21(3):182-185(in Chinese). [6] NETZ J, FORNER E, HAAGEMANN S.Contactless impedance measurement by magnetic induction-A possible method for investigation of brain impedance[J].Physiological Measurement, 1993, 14(4):463-471. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/14/4/007 [7] 刘浩仟. 电磁层析成像系统的软硬件设计[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁大学, 2015.LIU H Q.Hardware and software design of electromagnetic tomography system[D].Shenyang:Liaoning University, 2015(in Chinese). [8] 刘泽, 何敏, 徐苓安, 等.多激励模式的电磁层析成像系统[J].仪器仪表学报, 2001, 22(6):614-617.LIU Z, HE M, XU L A, et al.Multi-mode excitation electromagnetic tomography system[J].Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2001, 22(6):614-617(in Chinese). [9] ROSELL-FERRER J, MERWA R, BRUNNER P, et al.A multifrequency magnetic induction tomography system using planar gradiometers:Data collection and calibration[J].Physiological Measurement, 2006, 27(5):S271-S280. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/27/5/S23 [10] WANG C, ZHANG J Q, LI F W, et al.Design of a non-magnetic shielded and integrated electromagnetic tomography system[J].Measurement Science and Technology, 2011, 22(10):1-10. [11] JIN G, SUN J, QIN M, et al.A new method for detecting cerebral hemorrhage in rabbits by magnetic inductive phase shift[J].Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2014, 52:374-378. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2013.09.019 [12] WATSON S, WILLIAMS R J, GOUGH W, et al.A magnetic induction tomography system for samples with conductivities below 10 Sm-1[J].Measurement Science & Technology, 2008, 19(4):88-91. [13] WEI H Y, SOLEIMANI M.Hardware and software design for a national instrument-based magnetic induction tomography system for prospective biomedical applications[J].Physiological Measurement, 2012, 33(5):863-879. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/33/5/863 [14] VAUHKONEN M, HAMSCH M, IGNEY C H.A measurement system and image reconstruction in magnetic induction tomography[J].Physiological Measurement, 2008, 29(6):S445-S454. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/29/6/S37 [15] SMITH R W M, FREESTON I L, BROWN B H.A real-time electrical impedance tomography system for clinical use-design and preliminary results[J].IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 1995, 43(2):133-140. [16] ZOLGHARNI M, GRIFFITHS H, LEDGER P D.Frequency-difference MIT imaging of cerebral haemorrhage with a hemispherical coil array:Numerical modelling[J].Physiological Measurement, 2010, 31(8):S111-S125. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/31/8/S09 -







 下载:
下载: