-
摘要:
针对传统态势评估方法权值确定困难、大规模数据处理和特征提取能力不足的问题,结合当前空战数据特征,将深度置信网络(DBN)应用于近距空战态势评估。通过密度峰值算法对空战特征数据进行聚类分析,并结合态势函数和专家判读进行修正,建立标准空战态势样本库;以重构误差和测试错误率为基础,建立网络拓扑结构和最优参数确定方法,提高模型的训练效率,并通过样本数据,对模型进行训练和验证。实验表明,模型态势分类正确率达到92.7%,模型运行时间满足应用需求,实例评估结果与客观态势一致性强。
-
关键词:
- 深度置信网络(DBN) /
- 态势评估 /
- 半监督学习 /
- 网络拓扑结构 /
- 密度峰值聚类
Abstract:Considering the difficulty in parameter setting, weakness of traditional situation assessment methods in processing and feature extraction of big data, feature of air combat data, applications of deep belief network (DBN) to close-range air combat situation assessment are discussed. A sample library of combat situation was constructed. The data were clustered using density peaks algorithm, and the results were revised by specialists of air combat and traditional functions. Then the model of deep belief network was constructed. According to the standard of test and reconstruction error, the network topology structure and optimal parameters were determined. The model was trained by the data from the sample library. Experimental results show that the model's situation classification accuracy reaches to 92.7%, and its running time meets the application requirements. Analysis of the practical example verified the feasibility of the DBN model.
-
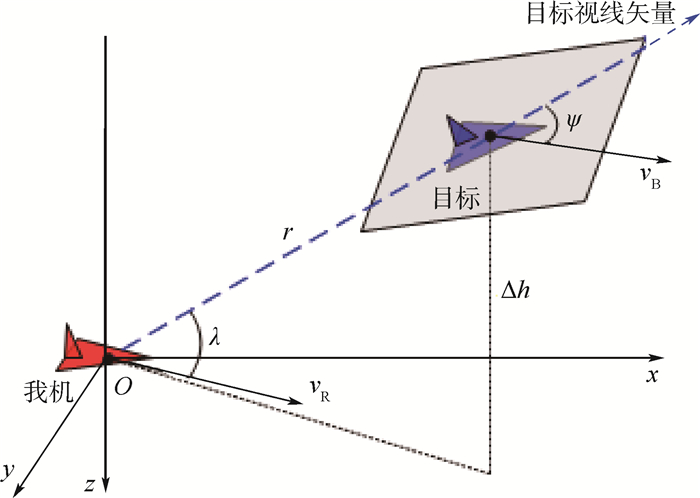
表 1 空战参数
Table 1. Parameters of air combat
参数 值域 目标方位角λ/rad [0, π] 目标进入角ψ/rad [0, π] 速度矢量夹角η/rad [0, π] 两机距离r/km [0, 10] 两机速度平方差Δv2 我机速度vR 两机高度差Δh/m [0, 18 000] 我机高度h/m [0, 18 000] 表 2 不同深度训练结果
Table 2. Training result of different depth
网络深度 测试错误率/% 训练时间/s 1 10.12 266.758 7 2 9.46 431.971 7 3 8.72 578.341 0 4 8.40 933.181 1 5 9.88 1 269.745 0 表 3 3种算法效果对比
Table 3. Effect comparison of three algorithms
算法 训练集正确率/%(正确样本/训练样本) 测试集正确率/%(正确样本/测试样本) 运行总时间/s 单组数据运行时间/s 内存占用率峰值/% BP神经网络 87.88 86.5 21.553 7 0.010 4 1.62 支持向量机 89.50 89.1 15.482 9 0.004 1 0.82 DBN 93.01 92.7 23.105 9 0.011 5 1.99 -
[1] 孙永芹, 世文荣, 彭海军, 等.基于改进非参量法的现代空战威胁评估研究[J].火控雷达技术, 2013, 42(3):28-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKLD201303007.htmSUN Y Q, SHI W R, PENG H J, et al.Study on improved non-parameter model based threat assessment in modern air combat [J].Fire Control Radar Technology, 2013, 42(3):28-33(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKLD201303007.htm [2] 李望西, 黄长强, 王勇, 等.三维空间空战态势评估角度优势建模与仿真[J].电光与控制, 2012, 19(2):21-25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGKQ201202008.htmLI W X, HUANG C Q, WANG Y, et al.Modeling and simulation of air combat situation assessment's angle superiority in three dimensional space[J].Electronics Optics and Control, 2012, 19(2):21-25(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGKQ201202008.htm [3] 吴文海, 周思羽, 高丽, 等.基于导弹攻击区的超视距空战态势评估改进[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2011, 33(12):2679-2685. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2011.12.20WU W H, ZHOU S Y, GAO L, et al.Improvements of situation assessment for beyond-visual-range air combat based on missile launching envelope analysis[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2011, 33(12):2679-2685(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2011.12.20 [4] 顾佼佼, 刘卫华, 姜文志.基于攻击区和杀伤概率的视距内空战态势评估[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2015, 37(6):1306-1312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.06.13GU J J, LIU W H, JIANG W Z.WVR air combat situation assessment model based on weapon engagement zone and kill probability[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(6):1306-1312(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.06.13 [5] 胡云安, 刘振, 史建国.态势评估的变结构区间概率动态贝叶斯网络方法[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2013, 35(9):1891-1897. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD201309016.htmHU Y A, LIU Z, SHI J G.Situation assessment using variable structure interval probability dynamic Bayesian network[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(9):1891-1897(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD201309016.htm [6] 史建国, 高晓光, 李相民.基于离散模糊动态贝叶斯网络的空战态势评估及仿真[J].系统仿真学报, 2006, 18(5):1093-1097. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ200605002.htmSHI J G, GAO X G, LI X M.Modeling air combat situation assessment by using fuzzy dynamic Bayesian network [J].Journal of System Simulation, 2006, 18(5):1093-1097(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ200605002.htm [7] 王向华, 覃征, 刘宇, 等.径向基神经网络解决威胁排序问题[J].系统仿真学报, 2004, 16(7):1576-1579. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ200407056.htmWANG X H, QIN Z, LIU Y, et al.RBF neural network for threat sequencing[J].Journal of System Simulation, 2004, 16(7):1576-1579(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ200407056.htm [8] 郭辉, 徐浩军, 刘凌.基于回归型支持向量机的空战目标威胁评估[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2010, 36(1):123-126.GUO H, XU H J, LIU L.Target threat assessment of air combat based on support vector machines for regression [J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010, 36(1):123-126(in Chinese). [9] 张文忠, 孙永芹, 杨洪立, 等.基于Rough集和回归型SVM的超视距空战威胁评估[J].四川兵工学报, 2013, 34(7):14-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CUXI201307005.htmZHANG W Z, SUN Y Q, YANG H L, et al.Threat assessment based on rough set and support vector machines for regression in beyond-visual-range air combat [J].Journal of Sichuan Ordnance, 2013, 34(7):14-18(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CUXI201307005.htm [10] 尹宝才, 王文通, 王立春.深度学习研究综述[J].北京工业大学学报, 2015, 41(1):48-59.YIN B C, WANG W T, WANG L C.Review of deep learning[J].Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2015, 41(1):48-59(in Chinese). [11] 左家亮, 杨任农, 张滢, 等.基于模糊聚类的近距空战决策过程重构与评估[J].航空学报, 2015, 36(5):1650-1660. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB201505028.htmZUO J L, YANG R N, ZHANG Y, et al.Reconstruction and evaluation of close air combat decision making process based on fuzzy clustering [J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(5):1650-1660(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB201505028.htm [12] 马耀飞, 龚光红, 彭晓媛.基于强化学习的航空兵认知行为模型[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2010, 36(4):379-383.MA Y F, GONG G H, PENG X Y.Cognition behavior model for air combat based on reinforcement learning[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010, 36(4):379-383(in Chinese). [13] 朱建益. 空战中的威胁评估与态势评估研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2013: 1-22.ZHU J Y.A study of threat and situation assessment in air combat[D].Xi'an:Xidian University, 2013:1-22(in Chinese). [14] ALEX R, ALESSANDRO L.Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks[J].Science, 2014, 344(6191):1492-1496. doi: 10.1126/science.1242072 [15] HINTON G E, SALAKHUDINOV R R.Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural network[J].Science, 2006, 313(5786):504-507. doi: 10.1126/science.1127647 [16] 张春霞, 姬楠楠, 王冠伟.受限波尔兹曼机[J].工程数学学报, 2015, 32(2):159-173. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCSX201502001.htmZHANG C X, JI N N, WANG G W.Restricted Boltzmann machines [J].Chinese Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 2015, 32(2):159-173(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCSX201502001.htm [17] 黄海波, 李人宪, 杨琪, 等.基于DBN的车辆悬架减振器异响鉴别方法[J].西南交通大学学报, 2015, 50(5):776-782. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT201505002.htmHUANG H B, LI R X, YANG Q, et al.Identifying abnormal noise of vehicle suspension shock absorber based on deep belief networks[J].Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(5):776-782(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT201505002.htm [18] 潘广源, 柴伟, 乔俊飞.DBN网络的深度确定方法[J].控制与决策, 2015, 30(2):256-260. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201502010.htmPAN G Y, CHAI W, QIAO J F.Calculation for depth of deep belief network[J].Control and Decision, 2015, 30(2):256-260(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201502010.htm [19] BENGIO Y. Learning deep architectures for AI [J].Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 2009, 2(1):1-127. doi: 10.1561/2200000006 [20] 周树森. 基于深度置信网络的分类方法[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2012: 5-25.ZHOU S S.Deep belief networks based classification methods[D].Harbin:Harbin Institute of Technology, 2012:5-25(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: