-
摘要:
在精密测量和航空航天领域,原子陀螺仪、原子磁强计等对线圈产生磁场的均匀度有很高的要求,而传统的亥姆霍兹线圈磁场均匀度较差,难以满足应用需求。为了设计产生高均匀度磁场的线圈组,基于线圈轴向磁场的泰勒展开式,提出了任意线圈数的圆柱形线圈组参数的计算方法,并给出了9线圈以内的线圈参数,分析了磁场均匀度、线圈尺寸、线圈最大安匝比随线圈个数的变化趋势。结果表明随着线圈个数的增加,均匀区面积几乎线性增大,9线圈组磁场均匀度优于0.01%的区域面积约为亥姆霍兹线圈的30倍。在要求各个线圈由整数匝线圈组成且各匝线圈电流相同的情况下,提出了一种线圈安匝比取整的方法,并给出2~9线圈组的安匝比取整结果,计算结果表明相同线圈个数下设计的线圈组产生磁场的均匀度优于已有文献。以5线圈组为例,对实际线圈组制作工艺产生的误差进行了仿真分析,仿真结果表明,考虑误差的情况下,设计的尺寸和磁场也满足原子陀螺仪、原子磁强计等的实际要求。
Abstract:In the field of precision measurement and aerospace, atomic gyroscope and atomic magnetometer have high requirements on the uniformity of magnetic field, while the uniformity of magnetic field generated by the traditional Helmholtz coil is not good enough for these applications. To obtain better field uniformity, a method to calculate the parameters of cylindrical coil systems is proposed based on the Taylor expansion of the axial magnetic field. The parameters of two-coil to nine-coil systems are computed, and the variation trends of magnetic field uniformity, coils' size, and coils' maximum ampere-turn ratio with coil number are analyzed. Numerical results demonstrate that the uniform region area of magnetic field increases almost linearly with the increasing of coil number, and the region area where the field uniformity is better than 0.01% in nine-coil system is about 30 times as large as that in Helmholtz coil. A method of rounding coil ampere-turn ratio is presented when integer coil turns and the same current in each coil turn are required, and the integer ampere-turn ratios of two-coil to nine-coil systems are given. Numerical results show that the uniformity of our coil systems is better than those in other papers. Finally, simulation analysis for the error caused by fabrication technique in practical five-coil system is conducted. Simulation results demonstrate that both the designed size and magnetic field of the coil meet the practical demand of atomic gyroscope and atomic magnetometer when error is taken into consideration.
-
表 1 圆柱形线圈组的理论参数
Table 1. Theoretical parameters of cylindrical coil systems
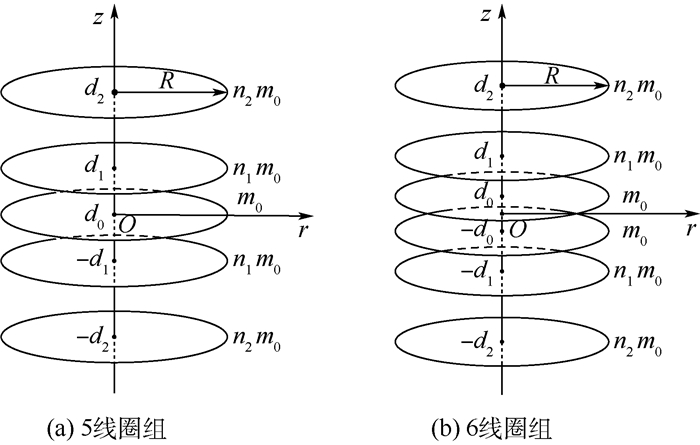
线圈个数N 各线圈到中心的距离(坐标)di 各线圈与中心线圈的安匝比ni 2 ±0.5R 1 3 0,±0.760 1R 1/1.881 6 4 ±0.243 2R,±0.940 8R 1/2.260 4 5 0,±0.409 2R,±1.080 1R 1/1.223 2/3.000 7 6 ±0.162 6R,±0.537 0R,±1.193 9R 1/1.347 7/3.455 2 7 0,±0.286 2R,±0.641 6R,±1.290 2R 1/1.105 8/1.575 0/4.146 8 8 ±0.122 4R,±0.386 7R,±0.730 3R,±1.373 6R 1/1.173 3/1.730 5/4.636 0 9 0,±0.221 1R,±0.471 8R,±0.807 7R,±1.447 3R 1/1.062 3/1.2952/1.955 8/5.3028 表 2 各线圈组ε≤0.01%和ε≤0.1%区域比较
Table 2. Comparison of each coil system between regions of ε≤0.01% and ε≤0.1%
线圈个数N ε≤0.01%区域 ε≤0.1%区域 |z|/R最大值 r/R最大值 面积/R2 |z|/R最大值 r/R最大值 面积/R2 2 0.097 0.123 0.065 0.173 0.217 0.206 3 0.226 0.267 0.271 0.336 0.384 0.584 4 0.350 0.387 0.561 0.478 0.504 1.001 5 0.458 0.479 0.873 0.597 0.588 1.396 6 0.563 0.544 1.179 0.701 0.648 1.754 7 0.649 0.608 1.467 0.791 0.696 2.074 8 0.717 0.645 1.733 0.868 0.731 2.354 9 0.789 0.679 1.979 0.940 0. 759 2.595 表 3 各线圈组在η分别达到85%、95%和99%时的最小整数安匝比及实际面积
Table 3. Minimum integer ampere-turn ratio and actual area for each coil system when η is greater than or equal to 85%, 95% and 99%
线圈个数N η ≥85% η ≥95% η ≥99% 最小整数安匝比 实际面积/R2 最小整数安匝比 实际面积/R2 最小整数安匝比 实际面积/R2 2 1/1 0.065 1/1 0.065 1/1 0.065 3 15/8/15 0.262 15/8/15 0.262 32/17/32 0.271 4 34/15/15/34 0.501 43/19/19/43 0.534 52/23/23/52 0.561 5 27/11/9/11/27 0.873 27/11/9/11/27 0.873 27/11/9/11/27 0.873 6 38/15/11/11/15/38 1.007 121/47/35/35/47/121 1.147 159/62/46/46/62/159 1.171 7 124/47/33/30/33/47/124 1.363 187/71/50/45/50/71/187 1.403 195/74/52/47/52/74/195 1.467 8 186/69/47/40/40/47/69/186 1.487 190/71/48/41/41/48/71/190 1.648 241/90/61/52/52/61/90/241 1.727 9 164/61/40/33/31/33/40/61/164 1.912 164/61/40/33/31/33/40/61/164 1.912 389/143/95/78/73/78/95/143/389 1.960 -
[1] MEYER D, LARSEN M.Nuclear magnetic resonance gyro for inertial navigation[J]. Gyroscopy and Navigation, 2014, 5(2):75-82. doi: 10.1134/S2075108714020060 [2] FANG J C, WAN S A.Atomic spin gyroscope based on 129Xe-Cs comagnetometer[J]. Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(13):1512-1515. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5759-5 [3] DANG H B, MALOOF A C, ROMALIS M V.Ultrahigh sensitivity magnetic field and magnetization measurements with an atomic magnetometer[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 97(15):151110. doi: 10.1063/1.3491215 [4] HILSCHENZ I, ITO Y, NATSUKAWA H, et al.Remote detected low-field MRI using an optically pumped atomic magnetometer combined with a liquid cooled pre-polarization coil[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2017, 274:89-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2016.11.006 [5] GUSAROV A, LEVRON D, PAPERNO E, et al.Three-dimensional magnetic field measurements in a single SERF atomic-magnetometer cell[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2009, 45(10):4478-4481. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2009.2021404 [6] EKLUND E J. Microgyroscope based on spin-polarized nuclei[D]. Irvine: University of California, 2008: 87-88. [7] HANSON R J, PIPKIN F M.Magnetically shielded solenoid with field of high homogeneity[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1965, 36(2):179-188. doi: 10.1063/1.1719514 [8] SCHILL R A, HOFF K.Characterizing and calibrating a large Helmholtz coil at low ac magnetic field levels with peak magnitudes below the earth's magnetic field[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2001, 72(6):2769-2776. doi: 10.1063/1.1368853 [9] WANG L, LI G X, XU C L, et al.Effect of characteristic parameters on the magnetic properties of solenoid valve for high-pressure common rail diesel engine[J]. Energy Conversion & Management, 2016, 127:656-666. [10] SONG X C.Comparison of magnetic field distribution and homogeneity between Helmholtz coil and Maxwell coil[J]. Journal of Magnetic Materials & Devices, 2016, 47(5):16-19. [11] GARRETT M W.Axially symmetric systems for generating and measuring magnetic fields.Part Ⅰ[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1951, 22(9):1091-1107. doi: 10.1063/1.1700115 [12] EVERETT J E, OSEMEIKHIAN J E.Spherical coils for uniform magnetic fields[J]. Journal of Scientific Instruments, 1966, 43(43):470-474. [13] GOTTARDI G, MESIRCA P, AGOSTINI C, et al.A four coil exposure system (tetracoil) producing a highly uniform magnetic field[J]. Bioelectromagnetics, 2003, 24(2):125-133. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-186X [14] WANG J, SHE S, ZHANG S.An improved Helmholtz coil and analysis of its magnetic field homogeneity[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2002, 73(5):2175-2179. doi: 10.1063/1.1471352 [15] KIRSCHVINK J L.Uniform magnetic fields and double-wrapped coil systems:Improved techniques for the design of bioelectro-magnetic experiments[J]. Bioelectromagnetics, 1991, 13(5):401-411. [16] BARANOVA V E, BARANOV P F, MURAVYOV S V, et al.The production of a uniform magnetic field using a system of axial coils for calibrating magnetometers[J]. Measurement Techniques, 2015, 58(5):550-555. doi: 10.1007/s11018-015-0752-9 -







 下载:
下载: