-
摘要:
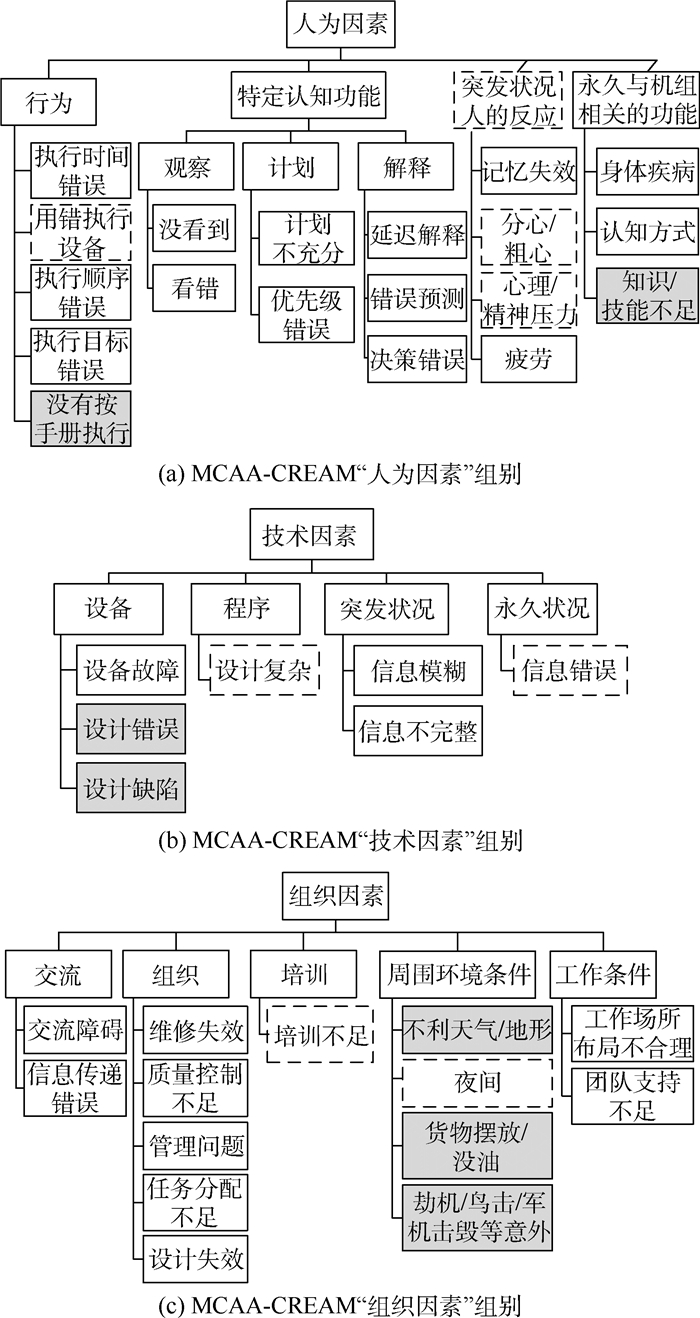
为充分认知民机风险, 实现从事故中学习, 以重大民机事故(MCAA)为研究对象挖掘出事故深层次的致因特征。针对MCAA信息具有可读性差, 系统行为具有非线性导致的无法直接获取运行风险信息, 难以直接建立事故致因的关联与映射关系, 提出一种从MCAA中学习民机运行风险特征的方法。针对民机运行特点, 结合事故信息及认知可靠性和失误分析方法(CREAM), 设计出MCAA-CREAM模型, 并构建民机多属性技术重大事故数据集。采用自组织映射(SOM)模型, 完成对事故的聚类分析和抽象特征映射, 以2D地图形式增强风险因素可读性, 利用关联规则有效挖掘风险因素间的强关联关系。
Abstract:To fully understand the risks of civil aircraft and learning from accidents, the major civil aircraft accidents (MCAA) are used as the research object to dig out its deep-level causal characteristics. Due to the poor readability information and nonlinear system behavior of MCAA, it is difficult to directly obtain the operational risk information or establish association with mapping relationship of accident factors, a method of learning the operational risk characteristics of civil aircraft from major accidents is proposed. According to the operation characteristics of civil aircraft, and drawing on MCAA information and cognitive reliability, and error analysis method (CREAM), the MCAA-CREAM model is designed. Furthermore, the civil aircraft multi-attribute technology major accident dataset was constructed. To complete the cluster analysis and abstract feature mapping, we take the dataset as a sample, input it into the self-organizing maps (SOM) model, and enhance the readability of risk factors in the form of a 2D map. The strong association between risk factors can be mined by association rules.
-
表 1 聚类特征
Table 1. Clusters features
聚类族编号 包含案例数/个 频率/% 风险因素 最小值/个 最大值/个 平均值/个 中位数 众数 C1 111 46.06 1 12 5.16 5 4 C2 93 38.59 1 12 3.67 3 2 C3 37 15.35 3 15 8.5 8 7, 8 表 2 风险特征聚类统计结果
Table 2. Characteristic clustering statistical results of each risk factor
风险类别 风险子类别 C1
频率/%C2
频率/%C3
频率/%设备 设备故障 18.90 40.09 27.00 设计错误 0 12.90 0 设计缺陷 15.30 39.80 21.60 程序 设计复杂 0.90 12.90 2.70 突发状况 信息模糊 14.40 6.50 8.10 信息不完整 5.40 4.30 0 永久状况 信息错误 8.10 5.40 0 行为 执行时间错误 25.20 3.20 16.20 用错执行设备 19.80 3.20 24.30 执行顺序错误 17.10 2.20 10.80 执行目标错误 9.90 0 8.10 没有按手册执行 27.00 4.30 48.60 观察 没看到 11.70 2.20 16.20 看错 4.50 1.10 5.40 计划 计划不充分 10.80 1.10 21.60 优先级错误 10.80 1.10 21.60 解释 延迟措施 15.30 2.20 18.90 错误预测 17.10 2.20 13.50 决策错误 29.70 11.80 35.10 突发状况人的反应 记忆失效 5.40 0 10.80 分心/粗心 28.80 1.10 40.50 心理/精神压力 10.80 0 43.20 疲劳 11.70 3.20 27.00 永久与机组相关的功能 身体疾病 0 0 16.20 认知方式 11.70 8.60 56.80 技能/知识不足 32.40 9.70 40.50 交流 交流障碍 5.40 1.10 18.90 信息传递错误 24.30 5.40 2.80 组织 维修失效 1.80 19.40 8.10 质量控制不足 9.90 35.50 10.80 管理问题 35.10 38.70 73.00 任务分配不足 0.90 0 62.20 设计失效 2.70 21.50 13.50 培训 培训不足 3.60 5.40 18.90 周围环境条件 不利天气/地形 60.40 7.50 37.80 夜间 6.30 6.50 10.80 货物摆放/没油 0.90 9.70 0 劫机/鸟击/军机击毁等意外 0 31.20 0 工作条件 工作场所布局不合理 0.90 4.30 2.70 团队支持不足 7.20 2.20 67.60 -
[1] 张凡, 魏法杰, 李权葆. 复杂装备研制项目的风险源识别[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(5): 975-980. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0368ZHANG F, WEI F J, LI Q B. Risk source identification of complex equipment development project[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(5): 975-980(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0368 [2] IMAI S, BLASCH E, GALLI A, et al. Airplane flight safety using error-tolerant data stream processing[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2017, 32(4): 4-17. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2017.150242 [3] KELLY D, EFTHYMIOU M. An analysis of human factors in fifty controlled flight into terrain aviation accidents from 2007 to 2017[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2019, 69: 155-165. doi: 10.1016/j.jsr.2019.03.009 [4] PAN Y, ZHANG L M, WU X G, et al. Multi-classifier information fusion in risk analysis[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 60: 121-136. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2020.02.003 [5] CHEN Z Y, HUANG X P, YU S, et al. Risk analysis for clustered check dams due to heavy rainfall[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research, 2021, 36(2): 291-305. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsrc.2020.06.001 [6] 董雷霆, 周轩, 赵福斌, 等. 飞机结构数字孪生关键建模仿真技术[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(3): 113-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB202103012.htmDONG L T, ZHOU X, ZHAO F B, et al. Key technologies for modeling and simulation of airframe digital twin[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(3): 113-141(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB202103012.htm [7] GOERLANDT F, GOITEAB H, VALDEZ B O, et al. An analysis of wintertime navigational accidents in the Northern Baltic Sea[J]. Safety Science, 2017, 92: 66-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2016.09.011 [8] MOURA R, BEER M, PATELLI E, et al. Learning from major accidents: Graphical representation and analysis of multi-attribute events to enhance risk communication[J]. Safety Science, 2017, 99: 58-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2017.03.005 [9] 余冠华. 基于多属性铁路事故数据集的聚类和关联规则分析方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2019: 15-19.YU G H. Research on clustering and association rule analysis method based on multi-attribute railway accident dataset[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019: 15-19(in Chinese). [10] ZARANEZHAD A, MAHABADI H A, DEHGHANI R M. Development of prediction models for repair and maintenance-related accidents at oil refineries using artificial neural network, fuzzy system, genetic algorithm, and ant colony optimization algorithm[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019, 131: 331-348. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2019.08.031 [11] ASGARY A, ANSARI S, DUNCAN R, et al. Mapping potential airplane hazards and risks using airline traffic data[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2015, 13: 276-280. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2015.07.002 [12] 李哲, 徐浩军, 薛源, 等. 基于风险预测的飞行安全操纵空间构建方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(9): 1839-1849. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0686#viewType=AbstractLI Z, XU H J, XUE Y, et al. Construction method of flight safety manipulation space based on risk prediction[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(9): 1839-1849(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0686#viewType=Abstract [13] ZHANG Z H, HE Q, GAO J, et al. A deep learning approach for detecting traffic accidents from social media data[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 2018, 86: 580-596. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2017.11.027 [14] HOLLNAGEL E. Cognitive reliability and error analysis method (CREAM)[M]. Oxford: Elsevier Science Ltd., 1998: 151-190. [15] HU R J, RATNER K, RATNER E, et al. ELM-SOM+: A continuous mapping for visualization[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 365: 147-156. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.06.093 [16] AVSAR B, ALIABADI D E. Parallelized neural network system for solving euclidean traveling salesman problem[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 34: 862-873. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.06.011 [17] MERLIN P, SORJAMAA A, MAILLET B, et al. X-SOM and L-SOM: A double classification approach for missing value imputation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2009, 73(7): 1103-1108. [18] COMBERTⅡ L, DEMICHELA M, BALDISSONE G. A combined approach for the analysis of large occupational accident databases to support accident-prevention decision making[J]. Safety Science, 2018, 106: 191-202. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2018.03.014 [19] 安璐. 基于自组织映射的期刊主题研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2009: 26-29.AN L. Studying journal subjects with self-organizing map[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2009: 26-29(in Chinese). [20] ZHOU Y, LI C S, DING L Y, et al. Combining association rules mining with complex networks to monitor coupled risks[J]. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2019, 186: 194-208. doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2019.02.013 [21] TEW C, GIRAUD C C, TANNER K, et al. Behavior-based clustering and analysis of interestingness measures for association rule mining[J]. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2014, 28(4): 1004-1045. -







 下载:
下载: