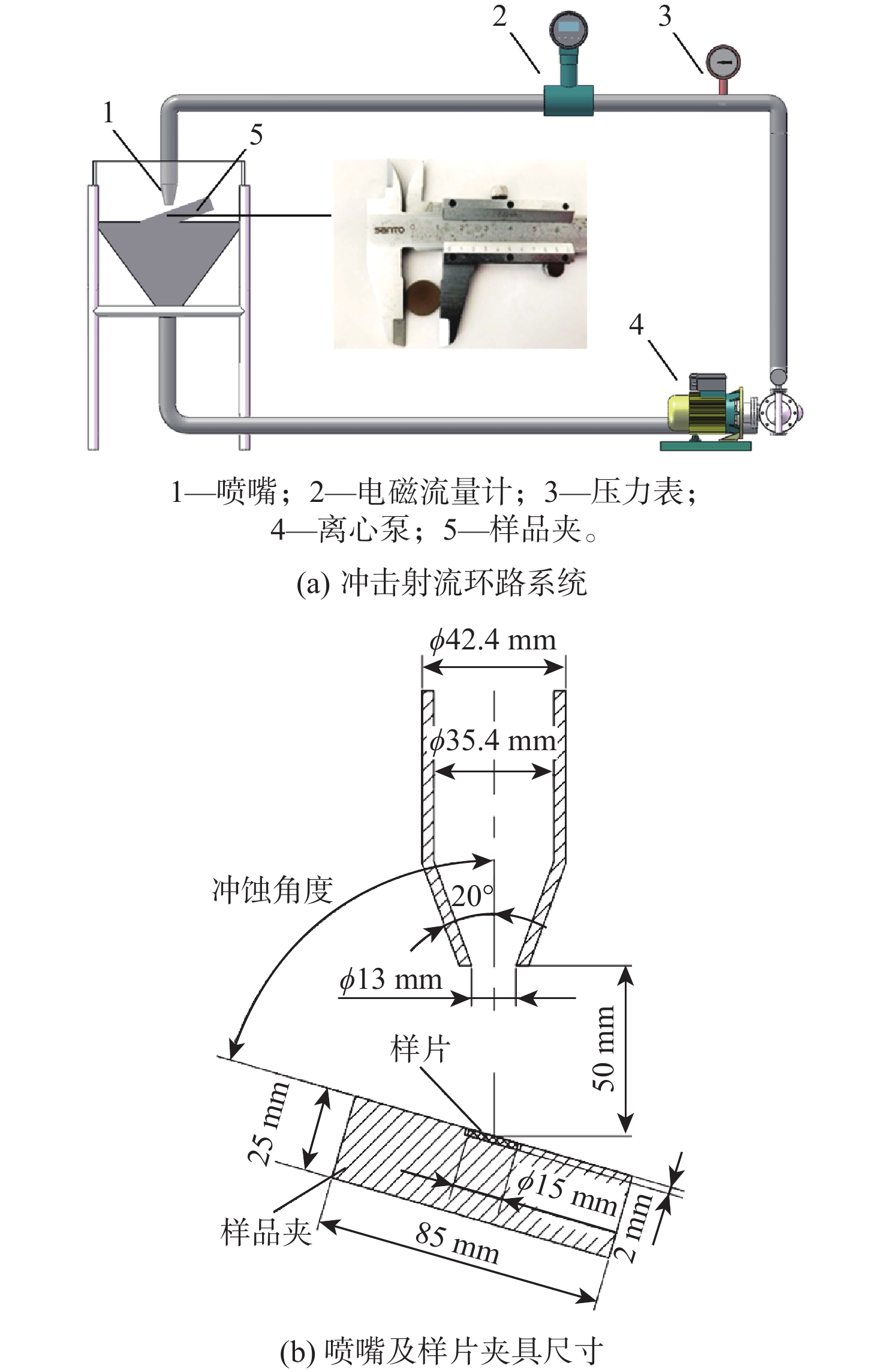
-
摘要:
冲蚀磨损广泛存在于民用、工业、军工等领域中,常导致设备受颗粒撞击形成不同程度的损伤。选用Q345钢开展液固两相流冲蚀实验,基于失重法和表面分析技术研究颗粒粒径、颗粒质量分数、冲蚀角度(15°~90°)、冲蚀时间等因素对冲蚀磨损的影响,并对冲蚀后的样品表面形貌特征进行分区。实验结果表明:随颗粒质量分数增大,冲蚀失重量上升的速率逐渐趋于平缓;3D形貌观测发现,颗粒质量分数高于0.1%后,材料表面全部受到了侵蚀,最大冲蚀深度降低;30°冲蚀角度附近Q345钢的质量损失最大,这与其较强的韧塑性有关。基于金相显微拍照分析,90° 射流冲击后样品表面分成3个区域,靠近喷嘴外边缘的2区内坑洞和犁沟数量最多,损伤最为严重,这与射流流场特性和颗粒分布有关。
Abstract:Erosion is a common occurrence in the civic, industrial, military, and other sectors, and it frequently results in equipment being struck by particles and suffering varied degrees of damage. This paper selects Q345 steel to carry out the erosion experiment under the liquid-solid two-phase flow condition. Based on the weight loss method and surface analysis technology, the effect of particle size, particle concentration, erosion angle (15°-90°), erosion time and other factors on erosion were studied. And the morphological characteristics of the surface of the sample after the erosion were partitioned. The experimental results show that as the particle mass concentration increases, the rate of erosion weight loss gradually tends to be flat. 3D morphological observation found that after the concentration was higher than 0.01%, all of the material surface was eroded, and the maximum erosion depth was reduced. Q345 steel has the largest mass loss near the 30° attack angle, which is related to its strong toughness and plasticity. Based on the analysis of metallographic microscopy, the sample surface is divided into three zones after the 90° jet impact. The 2 zones near the outer edge of the nozzle have the largest number of pits and furrows and the most serious damage, which is related to the characteristics of the jet flow field and particle distribution.
-
Key words:
- Q345 steel /
- two-phase flow /
- erosion /
- weightlessness method /
- surface analysis technique
-
表 1 样品力学性能
Table 1. Sample mechanical properties of samples
参数 材料 屈服强度/MPa 布氏硬度/HB 抗拉强度/MPa 延伸率/% 数值 Q345 345 180 490-630 21 表 2 样品化学成分
Table 2. Sample chemical composition
元素 C Si Cr Ni P S Mo Fe 含量/% 0.2 0.5 0.3 0.5 0.03 0.03 0.1 96.1 表 3 实验条件参数
Table 3. Experimental condition parameters
参数 数值 颗粒材料 SiO2 颗粒质量分数/% 0.01、0.05、0.1、0.3、0.5 颗粒粒径/目 20~40、40~60、60~80 冲蚀角度/(°) 15、30、45、60、75、90 冲蚀温度/℃ 40~50 喷嘴高度/mm 50 冲蚀时间/h 0~24 冲击速度/(m·s−1) 10 表 4 表面形貌特征参数
Table 4. Surface topography characteristic parameters
冲蚀角度/(°) 分区 平均长径比 数量 坑洞比例/% 犁沟比例/% 30 1区 1.29 54 63.5 36.5 2区 1.69 12 25.7 74.3 90 1区 1.11 51 90. 9.8 2区 1.14 69 87.3 12.7 3区 1.19 30 72.1 27.9 -
[1] 赵彦琳, 杨少帅, 姚军. 304不锈钢两相流冲蚀腐蚀的实验研究[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(8): 1504-1511.ZHAO Y L, YANG S S, YAO J. Experimental study on erosion-corrosion of 304 stainless steel under two-phase flow condition[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(8): 1504-1511(in Chinese). [2] 马志宏, 李运泽, 张华, 等. 砂尘环境试验设备中颗粒浓度场的实验研究[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2005, 31(8): 884-887. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2005.08.012MA Z H, LI Y Z, ZHANG H, et al. Experimental study on particle concentration in sand and dust equipment[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2005, 31(8): 884-887(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2005.08.012 [3] 张超, 方鑫, 刘建春. 复合材料层板冰雹高速冲击损伤预测及失效分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(4): 698-707.ZHANG C, FANG X, LIU J C. Damage prediction and failure mechanism of composite laminates under high-velocity hailstone impact[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(4): 698-707(in Chinese). [4] 何光宇, 李应红, 柴艳, 等. 航空发动机压气机叶片砂尘冲蚀防护涂层关键问题综述[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(6): 1733-1743.HE G Y, LI Y H, CHAI Y, et al. Review of key issues on coating against sand erosion of aero-engine compressor blade[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(6): 1733-1743(in Chinese). [5] PEPI M, SQUILLACIOTI R, PFLEDDERER L, et al. Solid particle erosion testing of helicopter rotor blade materials[J]. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2012, 12(1): 96-108. doi: 10.1007/s11668-011-9531-3 [6] 姚军, 曹培根, 周芳, 等. 两相流冲蚀不锈钢材料的实验研究[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 54(5): 746-750.YAO J, CAO P G, ZHOU F, et al. Experimental investigation of the erosion-corrosion of stainless steel by two-phase flow jets[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2015, 54(5): 746-750(in Chinese). [7] ZHAO Y L, TANG C Y, YAO J, et al. Investigation of erosion behavior of 304 stainless steel under solid-liquid jet flow impinging at 30°[J]. Petroleum Science, 2020, 17(4): 1135-1150. doi: 10.1007/s12182-020-00473-7 [8] LIU Y F, ZHAO Y L, YAO J. Synergistic erosion-corrosion behavior of X80 pipeline steel at various impingement angles in two-phase flow impingement[J]. Wear, 2021, 466-467: 203572. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2020.203572 [9] MOLINA N, WALCZAK M, MICHALCZEWSKI R. Erosion under turbulent slurry flow: An experimental determination of particle impact angle, impact direction, and distribution thereof by image processing[J]. Wear, 2020, 454-455: 203302. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2020.203302 [10] MOLINA N, WALCZAK M, KALBARCZYK M, et al. Erosion under turbulent slurry flow: Effect of particle size in determining impact velocity and wear correlation by inverse analysis[J]. Wear, 2021, 474-475: 203651. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2021.203651 [11] YAO J, ZHOU F, ZHAO Y L, et al. Investigation of erosion of stainless steel by two-phase jet impingement[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2015, 88: 353-362. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.08.056 [12] ELEMUREN R, TAMSAKI A, EVITTS R, et al. Erosion-corrosion of 90° AISI 1018 steel elbows in potash slurry: Effect of particle concentration on surface roughness[J]. Wear, 2019, 430-431: 37-49. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2019.04.014 [13] ZHAO Y L, ZHOU F, YAO J, et al. Erosion-corrosion behavior and corrosion resistance of AISI 316 stainless steel in flow jet impingement[J]. Wear, 2015, 328-329: 464-474. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2015.03.017 [14] TANG E L, WANG J R, HAN Y F, et al. Microscopic damage modes and physical mechanisms of CFRP laminates impacted by ice projectile at high velocity[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2019, 8(6): 5671-5686. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.09.035 [15] 刘建华, 李松梅, 杨应广, 等. A3钢在厌氧环境中的新型缓蚀剂性能研究[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2000, 26(6): 624-627. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2000.06.002LIU J H, LI S M, YANG Y G, et al. Novel inhibitors of microbiologically inducing corrosion of A3 steel in anaerobic environment[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2000, 26(6): 624-627(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2000.06.002 [16] 杜娟, 李松梅, 刘建华, 等. 氧化硫硫杆菌和芽孢杆菌协作下Q235钢腐蚀行为[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2014, 40(1): 31-38.DU J, LI S M, LIU J H, et al. Corrosion behavior of steel Q235 co-influenced by Thiobacillus thiooxidans and Bacillus[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014, 40(1): 31-38(in Chinese). [17] 赵彦琳, 柳灏, 姬忠礼, 等. 316不锈钢在含沙两相射流中长时间冲蚀的实验研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2018, 39(2): 361-365.ZHAO Y L, LIU H, JI Z L, et al. Experimental investigation of long time erosion behavior of 316 stainless steel by sand-water flow jet impingement[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2018, 39(2): 361-365(in Chinese). [18] American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard guide for examination and evaluation of pitting corrosion: ASTM G46-94[S]. West Conshohocken: American Society for Testing and Materials, 2003. [19] CLARK H M. The influence of the flow field in slurry erosion[J]. Wear, 1992, 152(2): 223-240. [20] 曾子华, 姚军, 周芳, 等. 液固两相射流中304不锈钢冲蚀行为研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2019, 40(12): 2853-2858.ZENG Z H, YAO J, ZHOU F, et al. Investigation of particle impact on 304SS under the liquid-solid two phase flow[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2019, 40(12): 2853-2858(in Chinese). [21] 姚军, 曾子华, 周芳, 等. 颗粒射流冲击材料行为研究[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(11): 2266-2272.YAO J, ZENG Z H, ZHOU F, et al. Investigation of behaviour of particle impact on material by impinging jet[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(11): 2266-2272(in Chinese). [22] 张伟浩. 两相射流及冲蚀的大涡模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2021: 36-39.ZHANG W H. Large-eddy simulation of two-phase impinging jet and erosion[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum(Beijing), 2021: 36-39(in Chinese). [23] NGUYEN V B, NGUYEN Q B, LIU Z G, et al. A combined numerical-experimental study on the effect of surface evolution on the water-sand multiphase flow characteristics and the material erosion behavior[J]. Wear, 2014, 319(1-2): 96-109. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2014.07.017 [24] LI D B, FAN J R, LUO K, et al. Direct numerical simulation of a particle-laden low Reynolds number turbulent round jet[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2011, 37(6): 539-554. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2011.03.013 -







 下载:
下载: