Active disturbance rejection based formation tracking and collision avoidance control for second-order multi-agent system
-
摘要:
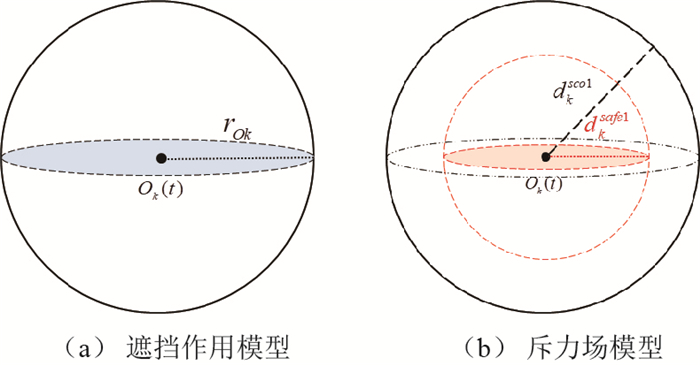
在多智能体编队的目标跟踪任务中,智能体受环境中的障碍物的遮挡作用会丢失目标,而外部扰动会影响系统的时变编队跟踪的控制效果。为此,研究了这两种因素同时存在情况下的二阶多智能体系统时变编队跟踪和避撞控制。采用基于目标跟踪优先级的切换拓扑控制策略以实现在障碍物遮挡环境中对目标的持续跟踪,根据自抗扰理论设计包含扰动补偿项的编队跟踪控制器。首先,基于一致性方法提出切换拓扑下自抗扰时变编队跟踪控制协议,并给出一种基于跟踪微分器的编队指令生成方法;其次,设计了求解控制参数的算法并给出协议作用下系统的稳定性分析和证明;然后,基于人工势场法设计避撞控制协议;最后,提出障碍物遮挡环境下自抗扰时变编队跟踪控制协议。仿真实验结果表明:所设计的控制协议在上述两种因素存在时仍具有良好的控制效果。
Abstract:In target tracking task for multi-agent formation, the agent will lose the target when it is blocked by obstacles in the environment and external disturbances can affect the time-varying formation tracking control for multi-agent systems. This paper studies the time-varying formation tracking and collision avoidance control for second-order multi-agent systems under the simultaneous existence of these two factors. A switching topology control strategy based on target tracking priority is adopted to achieve continuous tracking of the target in the obstacle occlusion environment. A formation tracking controller including the disturbance compensation term is designed based on active disturbance rejection theory. First, an active disturbance rejection time-varying formation target tracking control protocol is proposed for multi-agent systems with switching topologies based on consensus methods, and a formation command generation method based on tracking differentiator is presented. Then, an algorithm is designed to determine the control coefficient matrix, and the stability of the system under the protocol is analyzed and proved. Moreover, a collision avoidance control protocol is designed based on artificial potential field method. Finally, the active disturbance rejection time-varying formation target tracking and collision avoidance control protocol is proposed considering the occlusion of target tracking by obstacles in the environment. The simulation results show that the control protocol designed in this paper still has good control effect when the above two factors exist.
-
表 1 目标和无人机的初始状态向量
Table 1. Initial state vectors of target and UAVs
智能体 位置向量/m 速度向量/(m·s-1) 目标 (0, 0, 0) (0, 0, 0.1) 2号无人机 (0, 6, 0) (0, 0, 0) 3号无人机 
(0, 0, 0) 4号无人机 
(0, 0, 0) 表 2 障碍物位置向量
Table 2. Position vectors of obstacles
实体类障碍物 位置向量/m 1号障碍物 (0, -6, 1) 2号障碍物 
3号障碍物 
4号障碍物 (0, -6, 11) 5号障碍物 
6号障碍物 
表 3 作用拓扑的切换规则
Table 3. Switching rule of interaction topologies
障碍物对无人机的遮挡情况 通信拓扑 2号无人机未被遮挡,其他无人机被遮挡或未被遮挡 A 2号无人机被遮挡,3号无人机未被遮挡,4号无人机被遮挡或未被遮挡 B 2号和3号无人机均被遮挡,4号无人机未被遮挡 C -
[1] ZHANG X Y, DUAN H B.An improved constrained differential evolution algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicle global route planning[J].Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 26:270-284. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2014.09.046 [2] 罗京, 刘成林, 刘飞.多移动机器人的领航-跟随编队避障控制[J].智能系统学报, 2017, 12(2):202-212. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xdkjyc201702012LUO J, LIU C L, LIU F.Piloting-following formation and obstacle avoidance control of multiple mobile robots[J].CAAI Tran-sactions on Intelligent Systems, 2017, 12(2):202-212(in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xdkjyc201702012 [3] 刘洋, 章卫国, 李广文, 等.动态环境中的无人机路径规划方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2014, 40(2):252-256. https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract12857.shtmlLIU Y, ZHANG W G, LI G W, et al.Path planning of UAV in dynamic environment[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014, 40(2):252-256(in Chinese). https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract12857.shtml [4] GAZI V, FIDAN B.Adaptive formation control and target tracking in a class of multi-agent systems: Formation maneuvers[C]//2013 13th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 78-85. [5] LEE Y H, KIM S G, KUC T Y, et al.Virtual target tracking of mobile robot and its application to formation control[J].Inter-national Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2014, 12(2):390-398. doi: 10.1007/s12555-012-0461-y [6] DONG X W, XIANG J, HAN L, et al.Distributed time-varying formation tracking analysis and design for second-order multi-agent systems[J].Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2017, 86(2):277-289. [7] 连克非, 董云峰.电磁航天器编队位置跟踪自适应协同控制[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(10):2154-2162. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0809LIAN K F, DONG Y F.Adaptive cooperative control for electro-magnetic spacecraft formation flight position tracking[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(10):2154-2162(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0809 [8] TAN Z Y, CAI N, ZHOU J, et al.On performance of peer review for academic journals:Analysis based on distributed parallel system[J].IEEE Access, 2019, 7:19024-19032. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2896978 [9] CAI N, DENG C L, WU Q X.On non-consensus motions of dynamical linear multiagent systems[J].Pramana, 2017, 91(2):16. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d9787ebe758803a491eeb9bc5b036cde [10] XI J, YANG J, LIU H, et al.Adaptive guaranteed-performance consensus design for high-order multiagent systems[J].Infor-mation Sciences, 2018, 467:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.07.069 [11] JI Z J, YU H S.A new perspective to graphical characterization of multi-agent controllability[J].IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(6):1471-1483. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2549034 [12] DONG X W, HAN L, LI Q D, et al.Time-varying formation tracking for second-order multi-agent systems with one leader[C]//2015 Chinese Automation Congress.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1046-1051. [13] HAN L, DONG X W, LI Q D, et al.Formation tracking control for second-order multi-agent systems with time-varying delays[C]//2016 35th Chinese Control Conference.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 7902-7907. [14] XIONG T, PU Z, YI J, et al.Time-varying formation finite-time tracking control for multi-UAV systems under jointly connected topologies[J].International Journal of Intelligent Computing and Cybernetics, 2017, 10(4):478-490. doi: 10.1108/IJICC-02-2017-0015 [15] LAI J G, CHEN S H, LU X Q, et al.Formation tracking for non-linear multi-agent systems with delays and noise disturbance[J].Asian Journal of Control, 2015, 17(3):879-891. doi: 10.1002/asjc.937 [16] NIU H, GENG Z Y.Almost-global formation tracking control for multiple vehicles with disturbance rejecttion[J].IEEE Access, 2018, 6:25632-25645. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2820718 [17] 邵壮, 祝小平, 周洲, 等.三维动态环境下多无人机编队分布式保持控制[J].控制与决策, 2016, 31(6):1065-1072. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzyjc201606017SHAO Z, ZHU X P, ZHOU Z, et al.Distributed formation keeping control of UAVs in 3-D dynamic environment[J].Control and Decision, 2016, 31(6):1065-1072(in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzyjc201606017 [18] 胡春鹤, 王健豪.多运动体分布式最优编队构型形成算法[J].控制与决策, 2018, 33(11):87-91. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzyjc201811011HU C H, WANG J H.Distributed optimal formation shaping algorithm for multi-agent[J].Control and Decision, 2018, 33(11):87-91(in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzyjc201811011 [19] CHEN M, SHI P, LIM C.Robust constrained control for MIMO nonlinear systems based on disturbance observer[J].IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(12):3281-3286. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2450891 [20] XIONG Y, SAIF M.Sliding mode observer for nonlinear system:Theory and application[J].Nonlinear Dynamics, 2001, 46(12):2012-2017. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_arXiv.org_1303.5387 [21] 韩京清.自抗扰控制技术——估计补偿不确定因素的控制技术[M].北京:国防工业出版社, 2008:56-75.HAN J Q.Active disturbance rejection control technique-the Technique for estimating and compensating the uncertainties[M].Beijing:National Defense Industry Press, 2008:56-75(in Chinese). [22] REN W, BEARD R W.Consensus seeking in multiagent systems under dynamically changing interaction topologies[J].IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2005, 50(5):665-671. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddf4e82552bbff09bd5ba88bf55c7922 [23] 黄琳.系统与控制理论中的线性代数[M].北京:科学出版社, 1984:92-101.HUANG L.Linear algebra in system and control theory[M].Beijing:Science Press, 1984:92-101(in Chinese). [24] SABOORI I, KHORASANI K.H∞ consensus achievement of multi-agent systems with directed and switching topology net-works[J].IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2014, 59(11):3104-3109. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2014.2358071 [25] 朱大奇, 颜明重.移动机器人路径规划技术综述[J].控制与决策, 2010, 25(7):961-967. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzyjc201007001ZHU D Q, YAN M Z.Survey on technology of mobile robot path planning[J].Control and Decision, 2010, 25(7):961-967(in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzyjc201007001 -







 下载:
下载: