-
摘要:
动态避障是全向移动机器人在复杂工作环境下不可或缺的能力。针对在复杂动态环境下传统人工势场法容易陷入局部极小点、目标点不可达和振荡等问题,提出了利用水流场的思想重新定义人工势场的斥力势场函数及其方向,改进方法在不增加计算量的情况下能够使机器人平滑且安全无碰撞到达目标点,实现避障过程。为了实现三维动态仿真,提出了一种基于V-REP与MATLAB的联合仿真方法,并结合改进人工势场法实现全向移动机器人的动态避障模拟,验证了方法的平滑性和可行性。将所提方法应用于实验室内真实场景,全向移动机器人成功实现了动态规避动作,验证了方法的实用性。
Abstract:Dynamic obstacle avoidance is an indispensable ability of omnidirectional mobile robots in complex working environments. The idea of water flow field is used to redefine the repulsive potential field function of artificial potential field and its direction, which solves the problems of traditional artificial potential field method, such as easily falling into local minimum point, inaccessible target point and oscillation. The improved algorithm can make the robot reach the target point smoothly and safely without increasing the amount of calculation, and realize the obstacle avoidance process. At the same time, in order to achieve three-dimensional dynamic simulation, a joint simulation method based on V-REP and MATLAB is proposed. By constructing a three-dimensional dynamic simulation environment, the dynamic obstacle avoidance simulation of omnidirectional mobile robot was realized by the proposed method combined with the improved artificial potential field method, and the smoothness and feasibility of the algorithm are verified. Finally, the algorithm was applied to the real scene in the laboratory, and the omnidirectional mobile robot successfully realized the dynamic avoidance action, which verifies the practicability of the algorithm.
-
全向移动机器人不仅能实现圆弧运动或直线运动,而且不需要转向机构就能实现转向,并且是原地自转动作,这种灵活的运动方式、较小的工作空间要求使其可以应用到更为复杂的工作环境中,如仓储搬运、消防灭火、生产调度、实验室安防等[1]。因此,全向移动机器人除了要能够全局路径规划,还需要在自主移动过程中具备以自主避障的方式规避未知环境下的动态障碍物,保证更为安全的到达目标点完成作业。
自主避障的方法主要有A*算法[2]、人工神经网络算法[3-4]、强化学习算法[5-6]、粒子群算法[7-8]、模糊逻辑算法[9-10]及动态窗算法[11]等。Dai等[2]将A*算法与蚂蚁算法相结合,将A*算法的评价函数和弯曲抑制算子作为蚂蚁算法的启发式信息,加快了收敛速度,提高了全局路径的平滑度,该算法虽然能够规划出全局最优或较优路径,但是实时性不高。Llewyn等[4]以蝗虫的一种识别神经元为灵感,提出了一种人工神经网络模型并优化了模型参数,增强了模型的自适应性,将该模型与视觉传感器结合可以实现机器人的动态避障,该方法虽然可以应用于复杂的动态避障场景,但是由于避障过程中机器人要处理大量的视觉信息,对处理器硬件要求高。Dooraki和Lee[5]提出神经网络与强化学习算法相结合的方法,提高强化学习算法的学习效率,并且能够令机器人规避运动障碍物,但是该方法需要知道全局地图信息,应用场合有局限性。Qiang和Gao[7]提出了一种结合三次样条函数的粒子群优化算法,该算法解决了粒子群算法编码维数高、收敛过早等问题,并且求解质量高、稳定性好、速度较快,但是不能使机器人在未知环境下实现避障。Nasrinahar和Chuah[9]设计了4种基本的行为控制器,分别为目标到达行为、速度控制行为、目标搜索行为和避障行为,并利用模糊逻辑算法将其实现,能够在较为复杂的动态环境下实现自主避障,该方法具有丰富的规则库,致使计算量成指数级上升,不易保证避障的实时性。Eduardo等[11]提出了2种动态窗口的改进算法,即动态障碍物动态窗口算法(DW4DO)和动态障碍物树动态窗口算法(DW4DOT),并与基于曲率速度法的预测曲率速度法(PCVM)和动态曲率速度法(DCVM)进行了比较,表明改进后的算法可以有效规避动态障碍物,并且最后改进得到的DW4DOT算法使用建议的树构建方法减少了评估的路径数,使避障路径更为合理,但是该方法计算量增加,使得其不适用于计算能力不足的机器人之中,并且改进的方法没有在实验室内进行验证。
人工势场法(APF)由于结构简单、计算量小、反应速度快及规划结果安全可靠等优点,成为自主避障方法中高效且应用广泛的一种方法,并且优秀的实时性使其能够应用于具有动态障碍物的场景中。Guo等[12]采用分段规划的思想对人工势场法进行改进,在巡航段和末段分别应用不同的规划算法,实现了从单无人机到多无人机在三维地图下的路径规划,但未实现动态地图下的应用。Hu等[13]利用Zhukovsky变换对势场模型的结构和功能进行了优化,以满足避障的可靠性,通过仿真发现改进后的方法能够有效避开移动障碍物,防止局部极小值,但是该方法没有进行实验验证。Lazarowska[14]提出了离散人工势场算法(DAPF),该算法通过构造离散势场实现动态方法,算法规划的路径长度更为合理,并且缩短了运行时间,改进后的算法在MATLAB环境下进行了仿真,并在四轮差动驱动移动机器人上进行了实际实验,但该算法需要在全局地图已知的情况下使用,应用场景比较有限。Oscar等[15]提出了一种利用细菌进化算法(BEA)改进人工势场法的新路径规划方法,称为细菌势场(BPF),其能保证在具有静态和动态障碍物的复杂场景中规划路径的可行性、最优性和安全性,但是该方法要先获取精准的地图信息才能实现避障。Wang等[16]提出了一种改进的人工势场方法,通过引入相对距离函数,利用扇形网格生成局部虚拟目标,来解决易陷入局部最小及目标点不可达问题,仿真结果表明,改进后的方法能够找到平滑安全路径,具有较强的搜索性和适应性,但是未进行动态场景下的仿真验证。Du和Nan[17]通过加入机器人与目标之间的相对距离改进势场函数,并且改变斥力方向来避免机器人陷入局部极小值,使机器人能够顺利地到达目标点,但是该方法只是在静态环境下进行仿真,并没有在动态地图中仿真与实验。
针对全向移动机器人动态避障问题,本文以水流场为灵感提出一种改进人工势场法,创建水流场坐标系,改变传统人工势场法对斥力场的定义,解决了目标点不可达、振荡、局部极小等问题,并提出了V-REP与MATLAB联合仿真方法,在三维动态环境下对改进后方法的性能与可行性进行了验证。在实验室内搭建的动态环境中,对结合了改进人工势场法的全向移动机器人进行动态避障实验,验证了方法的可应用性。
1. 传统人工势场法及问题
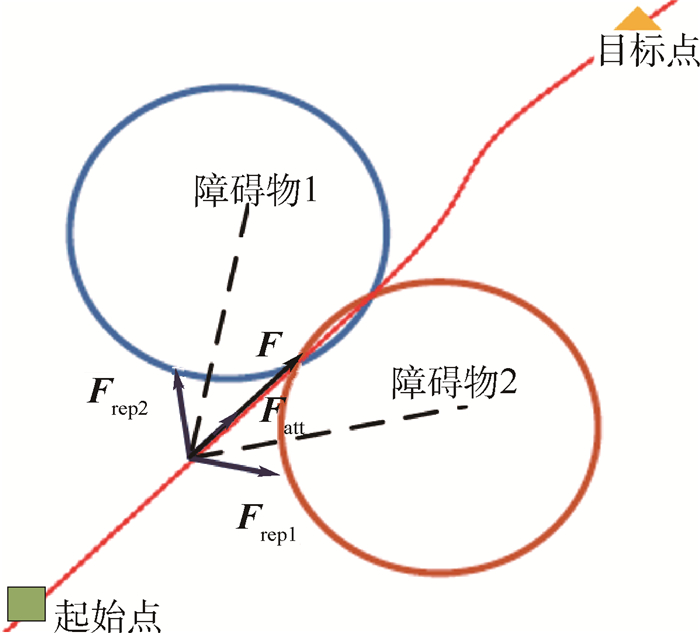
人工势场法利用势场对环境加以描述,其基本思想是:建立目标位置的引力场及障碍物产生的斥力场,两者结合形成人工势场[18]。基于人工势场法的机器人路径规划,通过判断势场的下降方向来搜寻移动机器人的无碰撞路径,移动机器人在人工势场中的受力示意图如图 1所示。
人工势场主要包括引力势场、斥力势场及全局势场。目标点产生引力势场Uatt,由此产生引力 Fatt,其方向由移动机器人指向目标点。障碍物产生斥力势场Urep,由此产生斥力 Frep,其方向由障碍物指向移动机器人。引力 Fatt和斥力 Frep组成移动机器人的合力 F 。
引力势场函数Uatt和引力 Fatt可表示为[18]

(1) 
(2) 式中:katt为引力场比例系数; x 为移动机器人当前位置; x g为移动机器人的目标位置。
斥力势场函数Urep和斥力 Frep可表示为[18]

(3) 
(4) 式中:krep为斥力场比例系数;d为移动机器人与障碍物之间的距离;d0为障碍物的作用半径。
可以得到全局势场函数U和合力 F 为

(5) 
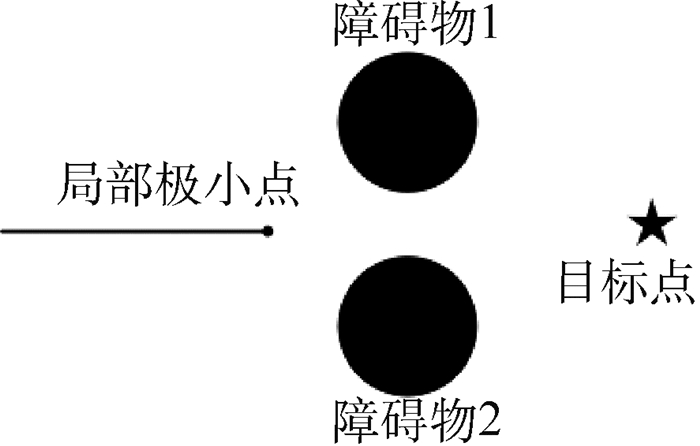
(6) 人工势场法具有很好的实时性与动态性,但仍存在一些特殊的情况。第1种情况称为陷入局部极小点问题[18],如图 2所示。此时移动机器人受到的合力为0但未达到目标点。
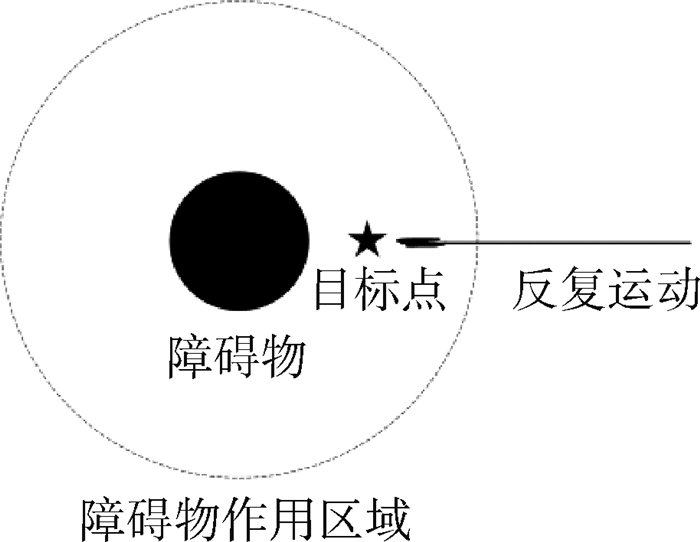
第2种情况称为目标点不可达问题[19],如图 3所示。此时目标点在障碍物作用区域范围内,越靠近目标点,引力减小,斥力反而增大,产生的合力使移动机器人无法到达目标点。
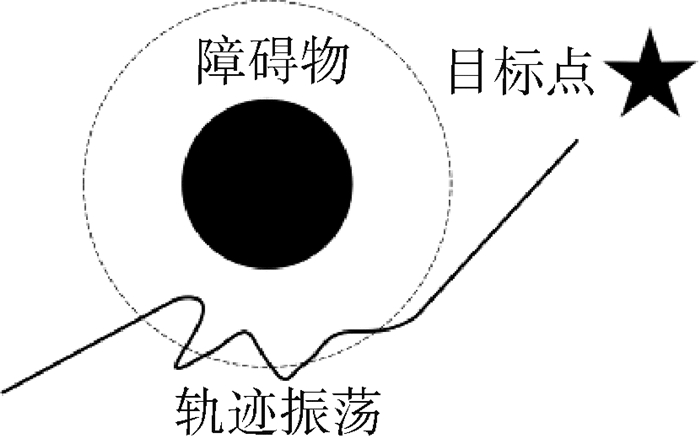
第3种情况称为轨迹振荡问题[20],如图 4所示。此时移动机器人在障碍物斥力场作用边界,产生的合力可能存在突变导致机器轨迹振荡,严重时可能会导致发生碰撞。
2. 基于水流场的人工势场法
针对传统人工势场法面临目标点不可达、振荡、局部极小等问题,提出一种基于水流场思想的改进方法。
水流场是由大自然中河流的流动而来,如图 5所示。
水流从地势高处流向地势低处,当其遇到石块或岛礁时,会平滑地绕过,并继续向地势低处流动,这是一种自然的避障现象,仔细观察水流场避开障碍物的规律可以发现,石块或岛礁对水流场的影响是使水流沿障碍物的边缘流动,从而绕开障碍物。
将水流场避障规律与传统人工势场法相结合,首先采用一种改进的人工势场法,其引力势场函数与式(1)相同,斥力势场函数如下[19]:

(7) 式中:n为待优化的参数。
改进的人工势场法将移动机器人距目标点的距离‖x - xg‖引入斥力场函数中,斥力场会随着移动机器人接近目标点而逐渐减小,能够解决目标点不可达问题。式(3)和式(7)的斥力势场产生的斥力方向从障碍物指向移动机器人,当斥力场过大,且与引力场角度为钝角时,就会造成移动机器人的后退性运动,进而引起振荡运动现象。受水流场的启发,通过改变斥力场的方向,令斥力场的方向沿障碍物边缘的切线方向,以实现移动机器人平滑避障。
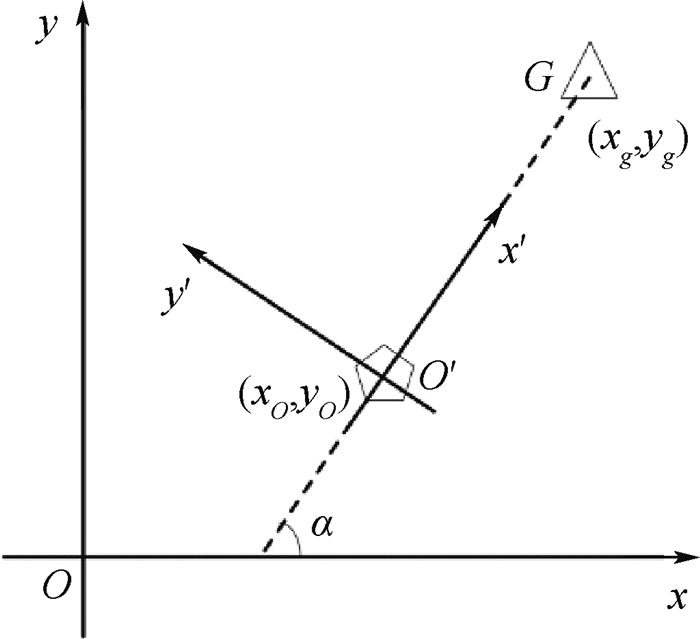
考虑实际应用场景中,移动机器人所获取的数据包括自身的位置、目标点的位置及机器人利用传感器测得的障碍物的距离和方向,为使斥力场的方向得到图 5所示水流方向的效果,将世界坐标系转换为以移动机器人为原点、x轴指向目标点的水流场坐标系,如图 6所示。图中:O'为移动机器人所在的位置,也是水流场坐标系的原点,在世界坐标系下为(xO, yO);目标点G的世界坐标系下位置为(xg, yg),坐标变换后

为了得到水流场坐标系下障碍物的坐标,先将世界坐标系做平移变换,将原点平移到O'处,如下:

(8) 式中:x1为平移后的横坐标;y1为平移后的纵坐标;xO为横坐标平移量,即移动机器人世界坐标系下横坐标;yO为纵坐标平移量,即移动机器人世界坐标系下纵坐标。
再通过坐标系旋转变换,得到最终的水流场坐标系,如下:

(9) 式中:x'为水流场坐标系下的横坐标;y'为水流场坐标系下的纵坐标;α为坐标系旋转的角度。
为了达到水流场的特征,利用障碍物在水流场坐标系下的坐标描述斥力场,并用如下的复势场表示:

(10) 式中:x'为障碍物在水流场坐标系下的横坐标;y'为障碍物在水流场坐标系下的纵坐标。
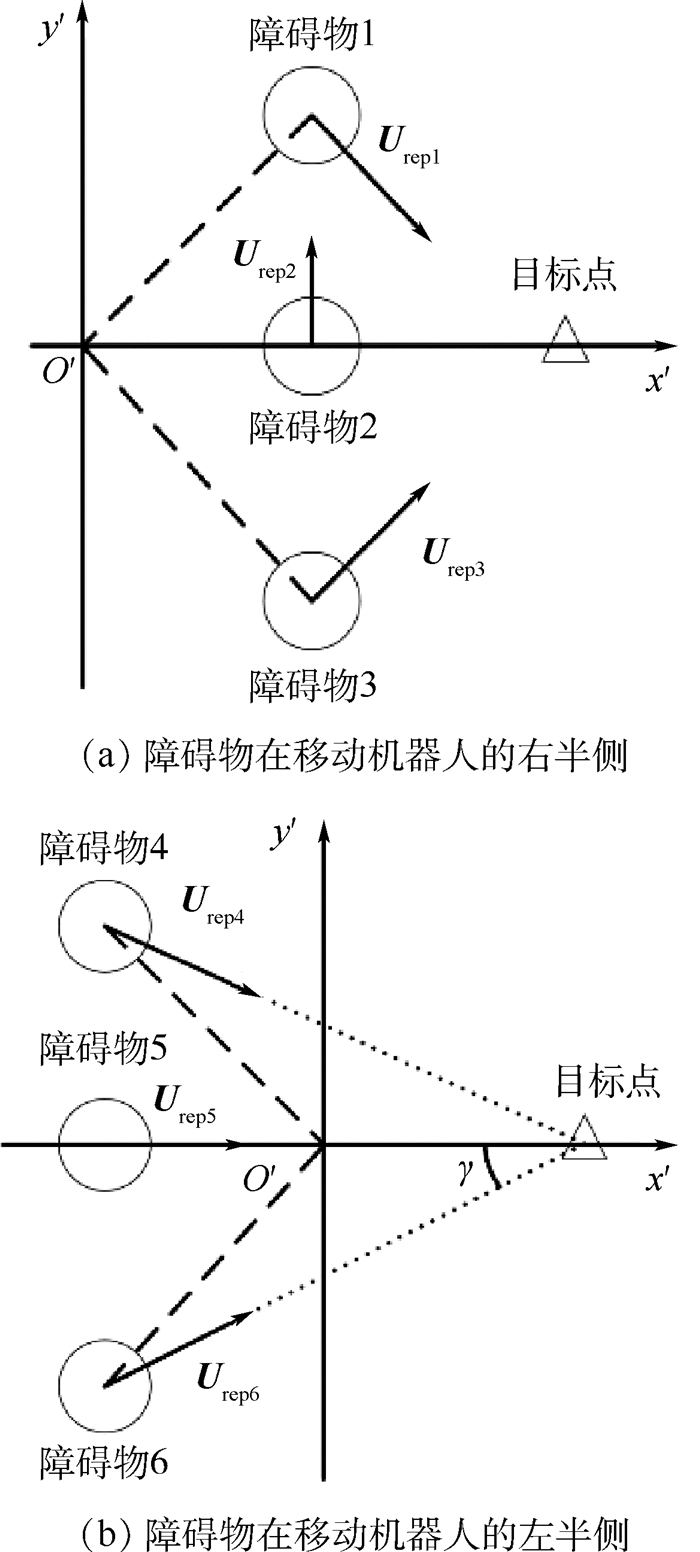
斥力场示意图如图 7所示。当障碍物在移动机器人的右半侧(x'≥0)时(见图 7(a)),若y'=0,障碍物位于移动机器人与目标点之间,可能产生局部极小值问题,此时将复势场变换为y'-x' i或y'+x' i (如 Urep2所示),可以使移动机器人离开局部极小点,随着移动机器人的运动,将会进入y'≠0状态。若y'≠0,可能会出现斥力场与引力场间的夹角为钝角从而产生轨迹振荡问题,此时在y'>0时将斥力场变换为-(-y'+x' i)(如 Urep1所示),在y' < 0时将斥力场变换为-(y'-x' i)(如 Urep3所示),从而使得斥力场与引力场间的夹角不再为钝角。当障碍物在移动机器人的左半侧(见图 7(b)),此时障碍物不对移动机器人到达目标点造成障碍,对于静态障碍物可不予处理,考虑更实际的动态障碍物对移动机器人的影响,将斥力势场变换为


通过上述变换可以得到新的斥力场函数,并通过微分得出斥力。

(11) 式中: erep为沿水流场 Urep方向的单位向量; eatt为沿引力场 Uatt方向的单位向量;Frep1为在水流场方向的斥力值大小,表示为

(12) Frep2为在引力场方向的斥力值大小,表示为

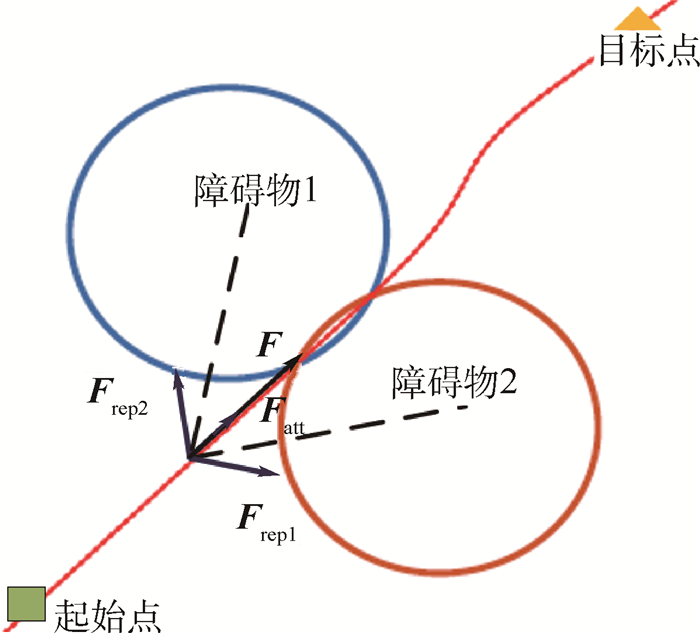
(13) 经斥力场变换,可使其特征变为水流场,解决了传统人工势场法的振荡、陷入局部极小值问题。但是由于水流场的固有特性,在障碍物重叠的情况下会出现穿越障碍物的情况,如图 8所示。
此时2个障碍物水流场方向都流向目标点,使得斥力 Frep1+ Frep2和引力 Fatt同向,在合势场的作用下会引导移动机器人在其之间穿过,将相近或重叠的障碍物实现填充合并成单个障碍物并修正斥力场的方向。
采用水流场的思想对斥力函数中 eatt方向向量进行改进,当障碍物在移动机器人与目标点之间并造成影响时, eatt为引力角α正向旋转90°;并且若障碍物间隙小于移动机器人宽度或发生重叠,则将障碍物进行填充使其成为整体,可有效解决标点不可达、振荡、局部极小问题,并避免障碍物重叠。
3. V-REP与MATLAB联合仿真验证
为了验证本文方法的有效性,对其进行仿真验证。首先在基于MATLAB的二维环境下进行避障仿真,并与传统人工势场法进行对比。然后在V-REP仿真模拟器中与MATLAB联合编程对全向移动机器人的避障方法进行仿真,为之后的实验验证奠定基础。
3.1 基于MATLAB的二维环境避障仿真
给定地图大小为450 cm×450 cm,目标点位置坐标为(410, 410)cm,全向移动机器人的初始位置为(0, 0),并按(x轴坐标,y轴坐标,半径)的数据形式设置障碍物,共设置9个障碍物分别为(40, 45, 15)cm、(150, 150, 25)cm、(240, 140, 20)cm、(300, 120, 30)cm、(230, 300, 30)cm、(380, 240, 30)cm、(390, 360, 15)cm、(360, 390, 15)cm、(250, 210, 15)cm。
为了便于比较,2种方法采用相同的参数,如表 1所示。
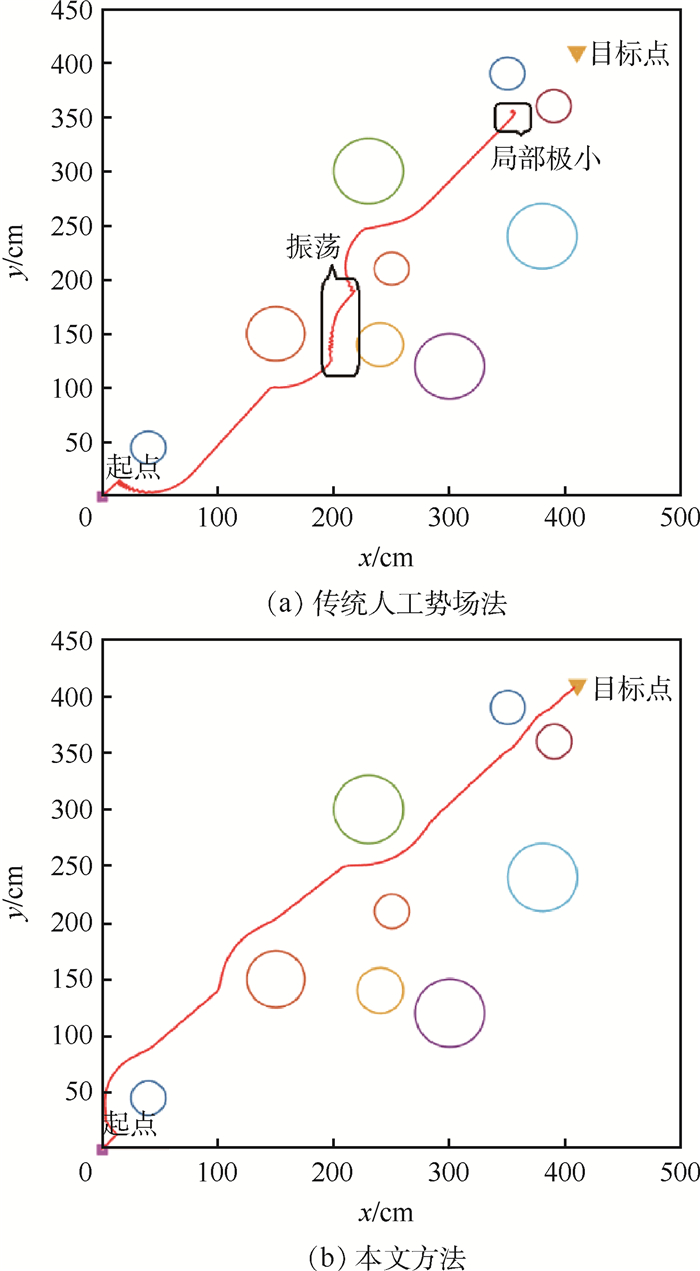
表 1 方法参数Table 1. Algorithm parameters参数 数值 引力场比例系数katt 15 斥力场比例系数krep 25 障碍物作用半径d0/cm 30 优化参数n 2 步长l 3 分别采用传统人工势场法和本文方法进行仿真,结果如图 9所示。
图 9中,红线为机器人的移动路径,9个圆圈表示障碍物,三角形为目标点,起点为坐标系原点。由图 9(a)可知,采用传统的人工势场法面临了轨迹振荡和陷入局部极小问题(见图 9(a)中矩形框),移动机器人无法到达目标点。而从图 9(b)可以看出,移动机器人能够到达目标点,且无轨迹振荡。经过仿真对比发现,本文方法在相对复杂的静态环境中,能够平滑且安全无碰撞的到达目标点,实现避障过程。
3.2 基于V-REP的三维动态避障仿真
为了进一步验证本文方法的有效性,利用一种具有物理引擎,能够三维建模,并且可以创建全向移动机器人运动学模型的仿真软件V-REP仿真模拟器与MATLAB联合对全向移动机器人的避障方法较为真实的模拟仿真。
采用V-REP建立全向移动机器人的模型(见图 10)和仿真环境(见图 11)。
全向移动机器人安全保护范围为2 m,扫描角度为270°。利用全向移动机器人逆运动学方程来计算4个输出轴的转速,进而控制移动机器人的运动。
仿真环境中添加了6个静态的障碍物及1个移动机器人和1个人形机器人NAO的动态障碍物,蓝色砖块位置为目标点。
采用本文提出的避障方法,参数如表 2所示。
表 2 V-REP仿真参数Table 2. V-REP simulation parameters参数 数值 katt 20 krep 3 d0/m 0.6 n 5 vmax/(m·s-1) 5 av 0.1 ωmax/(rad·s-1) 0.9 αω 0.4 注:vmax为移动机器人最大运动速度;av为移动机器人加速度系数;ωmax为移动机器人最大转弯角速度;αω为移动机器人角加速度系数。 根据以上参数进行动态环境下的V-REP与MATLAB的联合三维避障仿真验证,可以得到仿真结果,关键时刻的运动轨迹如图 12所示。
图 12中,红色为雷达扫描范围, 右上角为跟踪摄像头记录的视野,左下角则为雷达数据可视化界面,粉色线条为全向移动机器人的行走轨迹。在时间t=9 s时全向移动机器人检测到另一个移动机器人的威胁;在t=23 s时可以发现已经成功规避开动态的移动机器人,并检测到了静态障碍物;在t=36 s时全向移动机器人已经平滑地避开了静态障碍物,并且检测到了NAO的存在;在t=60 s时全向移动机器人已经避开移动中的NAO,并且成功无碰撞地到达了目标点,可以验证本文方法的合理性。
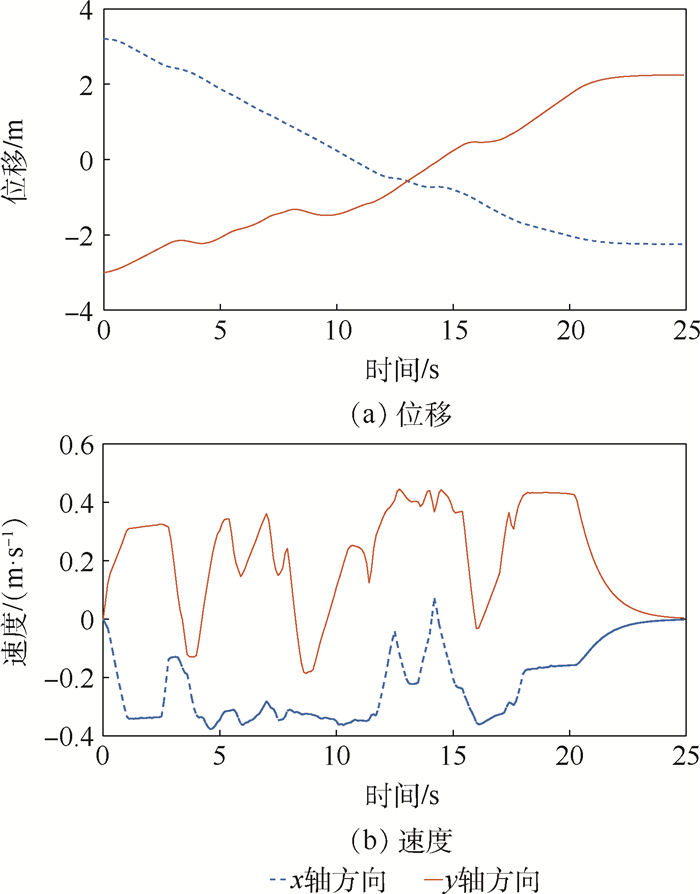
同时V-REP记录的全向移动机器人在世界坐标系下x、y轴方向的位移与速度如图 13所示。
由图 13可发现,全向移动机器人在运动过程中,移动方向基本延一个方向运动,并没有出现巨大的波峰与波谷,证明了移动路径比较平滑,没有产生振荡现象。再一次验证了本文方法的有效性。
4. 实验验证
在实验室内设计避障实验平台,包括通信系统、定位系统、动力系统、车载控制系统及控制站等5个部分,并搭建动态避障场景。
在室内设置2.6 m×2.6 m的实验地图,正方形4个顶点的世界坐标分别为(-0.5, 0.5)m、(-0.5, -2.1)m、(2.1, -2.1)m、(2.1, 0.5)m,设置目标点位置为(1.9, -1.9)m,移动机器人的起始点为(-0.25, 0.5)m。设置3个障碍物,其中障碍物2为动态障碍物,其起始位置为(2.5,-0.7)m,并以匀速向(-0.5,-0.7)m运动,速度系数为0.001,最大速度可达0.2 m/s,障碍物1和障碍物3为静态障碍物,其位置分别为(0.05,-0.05)m和(1.25,-1.4)m,避障方法的参数如表 3所示。
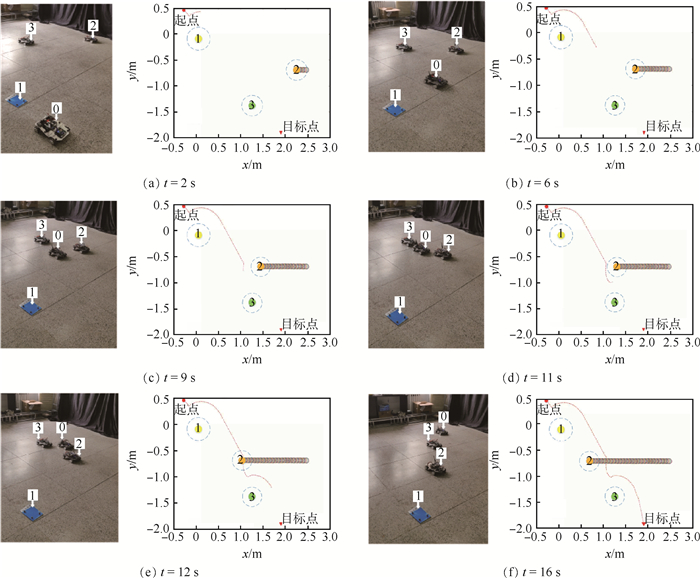
表 3 实验参数Table 3. Parameters in experiment参数 数值 katt 15 krep 5 d0/m 0.5 n 2 vmax/(m·s-1) 0.2 实验关键时刻的真实场景与同时刻的可视化地图界面显示如图 14所示。
图 14中,被控制的全向移动机器人标号为0,其轨迹可在可视化地图界面中显示,标号为1、2、3的分别为障碍物1、障碍物2和障碍物3,其中2为动态障碍物,其轨迹也可在可视化地图界面中显示,本实验将障碍物视为圆形,其半径为中心至边界的最大距离,蓝色虚线为障碍物的圆形范围,实线圆形为障碍物的中心位置。
如图 14(a)所示,在t=2 s时移动机器人进入障碍物1的影响范围并开始实施规避行为。如图 14(b)所示,在t=6 s时全向移动机器人已经顺利避开障碍物1并离开障碍物1的影响范围,可以看出其避障轨迹较为平滑。如图 14(c)所示,在t=9 s时全向移动机器人进入了动态障碍物2的影响范围内,开始其动态避障过程。如图 14(d)所示,在t=11 s时全向移动机器人进入了障碍物2与障碍物3的共同影响范围内,其开始了双障碍物避障过程。如图 14(e)所示,在t=12 s时全向移动机器人已经成功避开动态障碍物2的影响范围,但依然在障碍物3的影响范围内,并继续向目标点前进。如图 14(f)所示,在t=16 s时全向移动机器人已经成功的到达目标点。
实验可发现,本文提出的避障方法使全向移动机器人成功完成避障任务,并成功到达目标点,其路径比较平滑,未发现振荡现象,在遇到动态障碍物时也同样稳定避障,体现了本文方法较好的稳定性与适应性,证明了方法具有可实际应用的有效性与可行性。
5. 结论
1) 改进人工势场法通过创建水流场坐标系,改善了传统人工势场法易陷入局部极小值点、目标点不可达及轨迹振荡等问题。
2) 通过斥力场修正方向,解决了改进人工势场法穿透重叠障碍物的问题,保证了方法的可靠性。
3) 通过基于MATLAB的二维地图仿真、V-REP与MATLAB联合仿真,验证了方法可以平滑、稳定地规避静态和动态障碍物,并应用于多个场景,验证了动态避障方法的有效性与通用性。
4) 通过室内全向移动机器人动态避障实验,验证了改进人工势场法能够应用于真实的场景中,验证了本文动态避障方法的可实现性。
-
表 1 方法参数
Table 1. Algorithm parameters
参数 数值 引力场比例系数katt 15 斥力场比例系数krep 25 障碍物作用半径d0/cm 30 优化参数n 2 步长l 3 表 2 V-REP仿真参数
Table 2. V-REP simulation parameters
参数 数值 katt 20 krep 3 d0/m 0.6 n 5 vmax/(m·s-1) 5 av 0.1 ωmax/(rad·s-1) 0.9 αω 0.4 注:vmax为移动机器人最大运动速度;av为移动机器人加速度系数;ωmax为移动机器人最大转弯角速度;αω为移动机器人角加速度系数。 表 3 实验参数
Table 3. Parameters in experiment
参数 数值 katt 15 krep 5 d0/m 0.5 n 2 vmax/(m·s-1) 0.2 -
[1] QIAN J, ZI B, WANG D, et al. The design and development of an omnidirectional mobile robot oriented to an intelligent manufacturing system[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(9): 2073. doi: 10.3390/s17092073 [2] DAI X L, LONG S, ZHANG Z W, et al. Mobile robot path planning based on ant colony algorithm with A* heuristic method[J/OL]. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2019(2019-04-16)[2020-04-01]. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbot.2019.00015. [3] WEI W Q. Research on path planning of mobile robot based on artificial neural network[C]//20192nd International Conference on Intelligent Systems Research and Mechatronics Engineering. London: Francis Academic Press, 2019: 433-436. [4] LLEWYN S, DAVID H, GIACOMO I, et al. Parameter optimization and learning in a spiking neural network for UAV obstacle avoidance targeting neuromorphic processors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(9): 3305-3318. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2941506 [5] DOORAKI A R, LEE D J. An end-to-end deep reinforcement learning-based intelligent agent capable of autonomous exploration in unknown environments[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 2-17. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2815425 [6] MIHAI D, MOGAN G. Neural networks based reinforcement learning for mobile robots obstacle avoidance[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2016, 62: 104-115. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.06.021 [7] QIANG N, GAO J. A new method for mobile robot path planning based on particle swarm optimization algorithm[C]//20172nd International Conference on Advances in Materials Mechatronics and Civil Engineering. Amsterdam: Atlantis Press, 2017, 131: 95-98. [8] WANG B F, LI S, GUO J, et al. Car-like mobile robot path planning in rough terrain using multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 282: 42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.12.015 [9] NASRINAHAR A, CHUAH J H. Intelligent motion planning of a mobile robot with dynamic obstacle avoidance[J]. Journal on Vehicle Routing Algorithms, 2018, 1: 89-104. doi: 10.1007/s41604-018-0007-4 [10] KUNDU S, DDYAL R P. Reactive navigation of underwater mobile robot using ANFIS approach in a manifold manner[J]. International Journal of Automation and Computing, 2017, 14(3): 307-320. doi: 10.1007/s11633-016-0983-5 [11] EDUARDO J M, ÁNGEL L, MANUEL O. Dynamic window based approaches for avoiding obstacles in moving[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2019, 118: 112-130. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2019.05.003 [12] GUO Z T, HU H J, FENG F. 3D path planning for multi-UAV base on artificial potential field method[C]//International Conference on Electronic, Control, Automation and Mechanical Engineering, 2017: 86-91. [13] HU X P, LI Z Y, CAO J. A path planning method based on artificial potential field improved by potential flow theory[C]//20172nd International Conference on Computer Science and Technology, 2017: 617-625. [14] LAZAROWSKA A. Discrete artificial potential field approach to mobile robot path planning[J]. IFAC PapersOnLine, 2019, 52(8): 277-282. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2019.08.083 [15] OSCAR M, ULISES O R, ROBERTO S. Path planning for mobile robots using bacterial potential field for avoiding static and dynamic obstacles[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, 42(12): 5177-5191. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2015.02.033 [16] WANG L, LI B J, YIN Z H, et al. An improved artificial potential field for unmanned aerial vehicles path planning[C]//20172nd International Conference on Computer Science and Technology, 2017: 510-515. [17] DU Y, NAN Y Y. Research of robot path planning based on improved artificial potential field[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Informatics. Amsterdam: Atlantis Press, 2016: 1024-1029. [18] 罗强, 王海宝, 崔小劲, 等. 改进人工势场法自主移动机器人路径规划[J]. 控制工程, 2019, 26(6): 1091-1098.LUO Q, WANG H B, CUI X J, et al. Improved artificial potential field method for autonomous mobile robot path planning[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2019, 26(6): 1091-1098(in Chinese). [19] 梁献霞, 刘朝英, 宋雪玲, 等. 改进人工势场法的移动机器人路径规划研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2018, 35(4): 291-294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2018.04.063LIANG X X, LIU C Y, SONG X L, et al. Research on path planning of mobile robot based on improved artificial potential field method[J]. Computer Simulation, 2018, 35(4): 291-294(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2018.04.063 [20] 杨萌, 王玥. 基于改进人工势场法的无人机避让航迹规划[J]. 导航与控制, 2019, 18(1): 76-83.YANG M, WANG Y. UAV evasion trajectory planning based on improved artificial potential field method[J]. Navigation and Control, 2019, 18(1): 76-83(in Chinese). 期刊类型引用(12)
1. 王红勇,郭宇鹏. 终端区离场航空器自主路径规划. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2025(02): 446-456 .  本站查看
本站查看2. 李科宇,杨尚志,张刚,陈跃华,苏雪华. 基于改进人工势场法的多智能体编队避障. 控制工程. 2024(01): 168-177 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 刘钰铭,黄海松,范青松,朱云伟,陈星燃,韩正功. 基于改进A~*-DWA算法的移动机器人路径规划. 计算机集成制造系统. 2024(01): 158-171 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 安燕霞,郑晓霞. 基于分层强化学习的机器人自主避障算法仿真. 计算机仿真. 2024(04): 397-401 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 王建玲,王换换. 增强蚁群算法在移动机器人路径规划的应用研究. 机床与液压. 2024(10): 70-77 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 张延军,韩雨. 基于改进DWA的四轮差速移动底盘模型算法研究. 组合机床与自动化加工技术. 2024(09): 98-103+107 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 张茉莉. 基于深度卷积CNN的采摘机器人动态避障方法研究. 黑龙江工业学院学报(综合版). 2024(07): 122-129 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 王琳玲,庞文,朱大奇. 事件触发的多AUV编队模型预测控制算法. 兵工自动化. 2023(10): 67-77 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 张贺,缪存孝,唐友军,闫晓强,时彦洋,余远金. 移动机器人自主动态避障方法. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2022(06): 1013-1021 .  本站查看
本站查看10. 槐创锋,金志裕. 基于麦克纳姆轮的打磨机器人移动平台仿真分析. 华东交通大学学报. 2022(05): 112-118 .  百度学术
百度学术11. 刘冰雁,叶雄兵,方胜良,刘怀兴,贾珺. 基于Frenet和改进人工势场的在轨规避路径自主规划. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2021(04): 731-741 .  本站查看
本站查看12. 吴亚辉,刘春阳,谢赛宝,班宇煊,隋新,黄艳,张毅晖. 基于视觉深度学习的机器人环境感知及自主避障. 电子测量技术. 2021(20): 99-106 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(15)
-








 下载:
下载:














 下载:
下载:








 百度学术
百度学术