-
摘要:
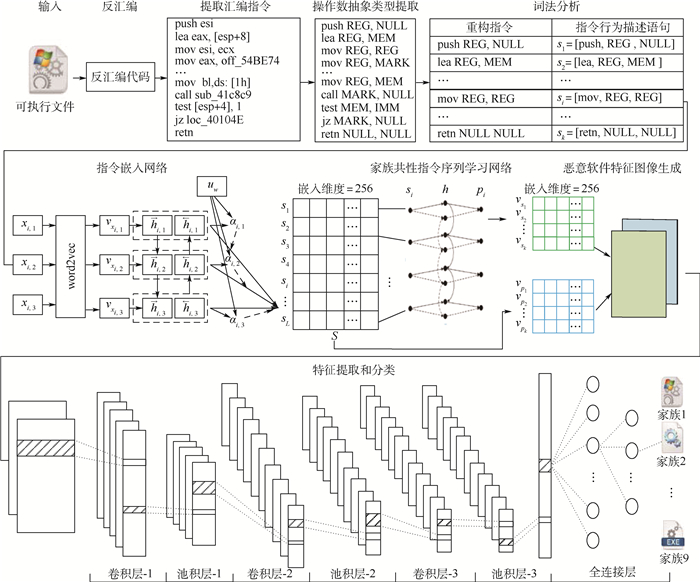
恶意软件变体的大量出现对网络安全造成巨大威胁。针对基于汇编指令的恶意软件家族分类方法中,操作数语义与运行环境密切相关而难以提取,导致指令语义缺失,难以正确分类恶意软件变体的问题。提出了一种基于抽象汇编指令的恶意软件家族分类方法。通过抽象出操作数类型重构指令,使操作数语义脱离运行环境的约束;利用词注意力机制与双向门循环单元(Bi-GRU)构建指令嵌入网络以捕获指令行为语义,并结合双向循环神经网络(Bi-RNN)学习恶意软件家族共性指令序列,以减小变体技术对指令序列的干扰;融合原始指令和家族共性指令序列构建特征图像,并通过卷积神经网络实现恶意软件家族分类。公开数据集上的实验结果表明:所提方法能够有效提取操作数信息,抵抗恶意软件变体中无关指令的干扰,实现恶意软件变体的家族分类。
Abstract:The emergence of malware variants poses a great threat to network security. In malware family classification methods based on assembly instructions, the semantics of operands are closely related to the operating environment and difficult to extract, which leads to the lack of instruction semantics and the difficulty in correctly classifying malware variants. A malware family classification method based on abstract assembly instructions is proposed. The instruction is reconstructed by abstracting the operand type, so that the semantics of the operands can be separated from the constraints of the operating environment. The word attention mechanism and bidirectional gate recurrent unit (Bi-GRU) are used to construct an instruction embedding network and to capture the instruction behavior semantics. Combined with bidirectional recursive neural networks (Bi-RNN), the common instruction sequence of malware family is learned to reduce the interference of variation technology on the instruction sequence. The original instruction and family common instruction sequence are integrated to construct feature images, and the malware family classification is realized through convolutional neural network. The experimental results on the public dataset show that the proposed method can effectively extract operand information, resist the interference of irrelevant instructions in malware variants, and realize the family classification of malware variants.
-
表 1 数据集家族标签及样本数量
Table 1. Family label and number of the sample in the dataset
序号 家族名称 样本数量 1 Ramnit 1 541 2 Lollipop 2 478 3 Kelihos_ver3 2 942 4 Vundo 475 5 Simda 42 6 Tracur 751 7 Kelihos_ver1 398 8 Obfuscator.ACY 1 228 9 Gatak 1 013 表 2 消融实验结果
Table 2. Results of ablation experiments
% 方法 准确率 召回率 精确率 F1 1 91.49 88.87 87.81 88.32 2 80.99 71.53 69.53 70.28 3 92.49 88.04 87.27 87.57 4 96.04 91.13 96.28 93.01 5 98.51 98.36 97.07 97.66 表 3 对比实验结果
Table 3. Comparative experimental results
% 方法 准确率 召回率 精确率 F1 MCSC 91.4 88.87 87.81 88.32 RMVC 94.20 95.92 89.07 91.00 MCAI 98.51 98.36 97.07 97.66 -
[1] YE Y F, LI T, ADJEROH D, et al. A survey on malware detection using data mining techniques[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2017, 50(3): 1-40. [2] YE Y F, LI T, ZHU S H, et al. Combining file content and file relations for cloud based malware detection[C]//Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM Press, 2011: 222-230. [3] TAMERSOY A, ROUNDY K, CHAU D H. Guilt by association: Large scale malware detection by mining file-relation graphs[C]//Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2014: 1524-1533. [4] DING Y X, XIA X L, CHEN S, et al. A malware detection method based on family behavior graph[J]. Computers & Security, 2018, 73: 73-86. [5] HARDY W, CHEN L, HOU S, et al. D14md: A deep learning framework for intelligent malware detection[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Mining(DMIN). New York: CSREA, 2016: 61. [6] NATARAJ L, KARTHIKEYAN S, JACOB G, et al. Malware images: Visualization and automatic classification[C]//Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Visualization for Cyber Security. New York: ACM, 2011: 1-7. [7] CUI Z H, XUE F, CAI X J, et al. Detection of malicious code variants based on deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(7): 3187-3196. doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2822680 [8] TRINIUS P, HOLZ T, GÖBEL J, et al. Visual analysis of malware behavior using treemaps and thread graphs[C]//20096th International Workshop on Visualization for Cyber Security. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 33-38. [9] ZHANG J X, QIN Z, YIN H, et al. IRMD: Malware variant detection using opcode image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1175-1180. [10] NI S, QIAN Q, ZHANG R. Malware identification using visualization images and deep learning[J]. Computers & Security, 2018, 77: 871-885. [11] SUN G S, QIAN Q. Deep learning and visualization for identifying malware families[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2021, 18(1): 283-295. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2018.2884928 [12] MIKOLOV T, CHEN K, CORRADO G, et al. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space[C]//Proceedings of ICLR Workshops Track. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2013: 21-29. [13] CHO K, VAN MERRIENBOER B, BAHDANAU D, et al. On the properties of neural machine translation: Encoder-decoder approaches[C]//Proceedings of SSST-8, Eighth Workshop on Syntax, Semantics and Structure in Statistical Translation, 2014: 103-111. [14] YANG Z C, YANG D Y, DYER C, et al. Hierarchical attention networks for document classification[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, 2016: 33-38. [15] SCHUSTER M, PALIWAL K K. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1997, 45(11): 2673-2681. doi: 10.1109/78.650093 [16] Microsoft. Microsoft malware classification challenge (Big 2015)[EB/OL]. (2019-06-11)[2020-09-01]. https://www.kaggle.com/c/malware-classification. -







 下载:
下载: