An algorithm for generating geometric models of microscopic specimens of PVC foam based on μCT images
-
摘要:
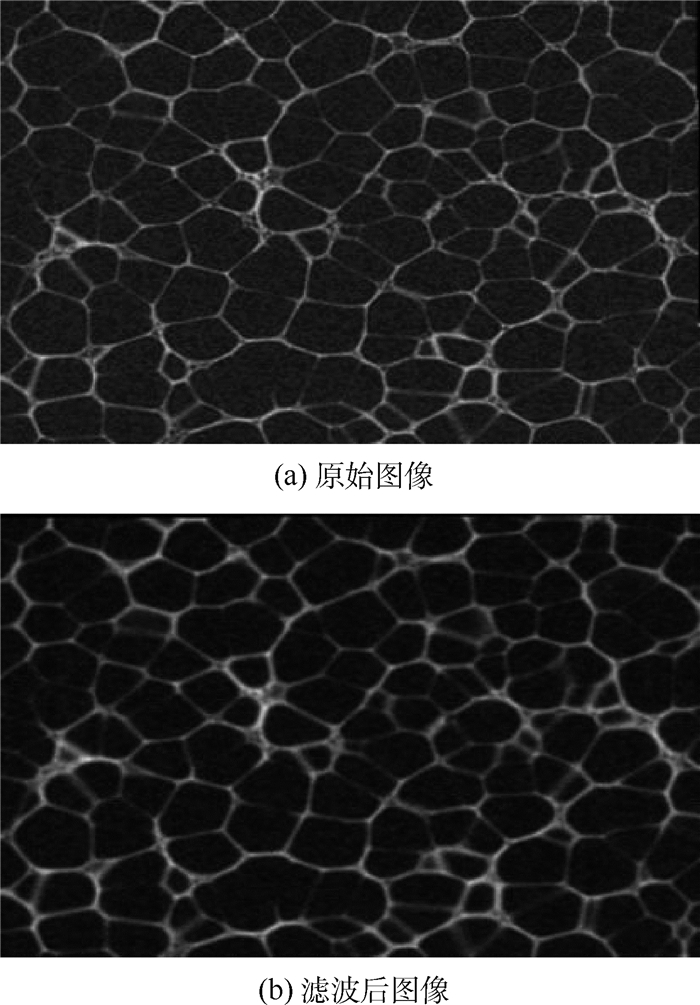
在泡沫微观结构的数值模拟中,泡沫空腔的几何特征和排列状态对计算效率及计算结果有着重要的影响,基于前进面搜索几何构造算法和Laguerre划分算法,提出了一种新的PVC泡沫微观试样几何模型生成算法。从μCT扫描图像重构泡沫的真实几何模型,测量泡沫空腔的几何特征及体积分布规律,将测量得到的泡沫空腔体积转化为球体,并通过前进面搜索几何构造算法投入空间,通过Laguerre划分算法将空间球体进行区域划分,赋予壁厚参数,构建出闭孔PVC泡沫的微观几何模型。所建立的模型在微观几何特征上与实际材料符合较好。
-
关键词:
- CT扫描 /
- 前进面法 /
- Laguerre划分 /
- 闭孔泡沫 /
- 微观模型
Abstract:In numerical simulation of foam microstructure, the geometric characteristics and arrangement of foam cavities have an important influence on calculation efficiency and calculation results. We propose a new algorithm, based on the advancing surface search geometric construction algorithm and the Laguerre partition algorithm, to generate the geometric model of the PVC foam microscopic specimen. First, reconstruct the authentic geometric model of the foam from μCT scan image, and measure the geometric characteristics of the foam cavity and the volume distribution pattern. Then, convert the measured foam cavity volume into a sphere, and put it into the space through the advancing surface search geometric construction algorithm. Finally, divide the space sphere into regions by means of Laguerre division, and assign wall thickness parameters to form a geometric model of the microstructure. The established model is in good agreement with the actual material in terms of micro-geometric characteristics.
-
Key words:
- CT scan /
- advancing surface method /
- Laguerre division /
- closed cell foam /
- microstructural model
-
表 1 不同密度泡沫空腔率的数值模型与实验对比
Table 1. Numerical model and experimental comparison of foam cavity ratio of different densities
泡沫类型 空腔壁厚/μm 真实空腔率/% 数值模型平均空腔率/% 误差/% H45 7.44 96.79 94.77 2.09 H80 8.84 94.29 93.79 0.53 H100 11.9 92.86 91.57 1.39 H130 13.86 90.71 90.26 0.50 H200 20.41 85.71 85.67 0.05 -
[1] CHEN Y M, DAS R, BATTLEY M. Effects of cell size and cell wall thickness variations on the stiffness of closed-cell foams[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2015, 52: 150-164. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2014.09.022 [2] GIBSON L J, ASHBY M F. Cellular solids[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1997. [3] MILLS N J, ZHU H X. The high strain compression of closed-cell polymer foams[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1999, 47(3): 669-695. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5096(98)00007-6 [4] WEAIRE D, PHELAN R. A counter-example to Kelvin's conjecture on minimal surfaces[J]. Philosophical Magazine Letters, 1994, 69(2): 107-110. doi: 10.1080/09500839408241577 [5] WISMANS J G F, GOVAERT L E, VAN DOMMELEN J A W. X-ray computed tomography-based modeling of polymeric foams: The effect of finite element model size on the large strain response[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics, 2010, 48(13): 1526-1534. doi: 10.1002/polb.22055 [6] VESENJAK M, VEYHL C, FIEDLER T. Analysis of anisotropy and strain rate sensitivity of open-cell metal foam[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2012, 541: 105-109. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.02.010 [7] SUN Y L, LOWE T, MCDONALD S A, et al. In situ investigation and image-based modelling of aluminium foam compression using micro X-ray computed tomography[M]//LETA F R. Visual computing. Belin: Springer, 2014: 189-197. [8] SUN Y L, LI Q M, LOWE T, et al. Investigation of strain-rate effect on the compressive behaviour of closed-cell aluminium foam by 3D image-based modelling[J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 89: 215-224. [9] KIM S H, CHUNG H J, RHEE K Y. Numerical analysis on the compressive behaviors of aluminum foam material using computed tomography imaging[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2010, 123-125: 567-570. [10] JEON I, ASAHINA T, KANG K J, et al. Finite element simulation of the plastic collapse of closed-cell aluminum foams with X-ray computed tomography[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2010, 42(3): 227-236. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2010.01.003 [11] HUANG R X, LI P F, LIU T. X-ray microtomography and finite element modelling of compressive failure mechanism in cenosphere epoxy syntactic foams[J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 140: 157-165. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.12.040 [12] DAPHALAPURKAR N P, HANAN J C, PHELPS N B, et al. Tomography and simulation of microstructure evolution of a closed-cell polymer foam in compression[J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2008, 15(8): 594-611. doi: 10.1080/15376490802470523 [13] CATY O, MAIRE E, YOUSSEF S, et al. Modeling the properties of closed-cell cellular materials from tomography images using finite shell elements[J]. Acta Materialia, 2008, 56(19): 5524-5534. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2008.07.023 [14] 李侯贞强, 张亚栋, 张锦华, 等. 基于CT的泡沫铝三维细观模型重建及应用[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(1): 160-168. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0959LI H Z Q, ZHANG Y D, ZHANG J H, et al. Reconstruction and application of three-dimensional mesoscopic model of aluminum foam based on CT[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(1): 160-168(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0959 [15] LI K, GAO X L, SUBHASH G. Effects of cell shape and strut cross-sectional area variations on the elastic properties of three-dimensional open-cell foams[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2006, 54(4): 783-806. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2005.10.007 [16] SONG Y Z, WANG Z H, ZHAO L M, et al. Dynamic crushing behavior of 3D closed-cell foams based on Voronoi random model[J]. Materials & Design, 2010, 31(9): 4281-4289. [17] ZHU H X, HOBDELL J R, WINDLE A H. Effects of cell irregularity on the elastic properties of open-cell foams[J]. Acta Materialia, 2000, 48(20): 4893-4900. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(00)00282-2 [18] ZHU H X, WINDLE A H. Effects of cell irregularity on the high strain compression of open-cell foams[J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50(5): 1041-1052. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(01)00402-5 [19] ZHU W Q, BLAL N, CUNSOLO S, et al. Effective elastic behavior of irregular closed-cell foams[J]. Materials, 2018, 11(11): 2100. doi: 10.3390/ma11112100 [20] RIBEIRO-AYEH S. Finite element modelling of the mechanics of solid foam materials[D]. Karlstad: Karlstad University, 2005. [21] REDENBACH C, SHKLYAR I, ANDRÄ H. Laguerre tessellations for elastic stiffness simulations of closed foams with strongly varying cell sizes[J]. International Journal of Engineering Science, 2012, 50(1): 70-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ijengsci.2011.09.002 [22] GHAZI A, BERKE P, KAMEL K E M, et al. Multiscale computational modelling of closed cell metallic foams with detailed microstructural morphological control[J]. International Journal of Engineering Science, 2019, 143: 92-114. doi: 10.1016/j.ijengsci.2019.06.012 [23] MATZKE E B. The three-dimensional shape of bubbles in foam—An analysis of the rôle of surface forces in three-dimensional cell shape determination[J]. American Journal of Botany, 1946, 33(1): 58-80. doi: 10.1002/j.1537-2197.1946.tb10347.x [24] 李勇俊, 季顺迎. 基于球形颗粒几何排列的离散元试样高效生成方法[J]. 应用力学学报, 2020, 37(2): 469-476. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYLX202002001.htmLI Y J, JI S Y. Construction approach of DEM samples with high efficiency based on geometrical packing of spherical particles[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2020, 37(2): 469-476(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYLX202002001.htm [25] VALERA R R, MORALES I P, VANMAERCKE S, et al. Modified algorithm for generating high volume fraction sphere packings[J]. Computational Particle Mechanics, 2015, 2(2): 161-172. doi: 10.1007/s40571-015-0045-8 [26] RYCROFT C H. Voro+ +: A three-dimensional voronoi cell library in C+ +[J]. Chaos, 2009, 19(4): 041111. doi: 10.1063/1.3215722 [27] LIU Y, RAHIMIDEHGOLAN F, ALTENHOF W. Anisotropic compressive behavior of rigid PVC foam at strain rates up to 200 s-1[J]. Polymer Testing, 2020, 91: 106836. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2020.106836 -







 下载:
下载: