-
摘要:
无人机(UAV)数据链在复杂电磁和地理自然环境中可靠性受到严重威胁,针对如何通过选择信道和调整信号发送功率保证UAV通信质量的问题,提出了一种结合相关向量回归(RVR)的信道选择和功率控制方法。方法采用RVR建立干扰信息、误码率(BER)与信噪比(SNR)的映射模型,通过该模型可根据实时干扰参数,预测信道满足UAV数据链BER要求的最小化SNR,进而可计算最小化的发送功率,把最小化功率作为标准判断信道质量好坏,选择信道的同时确定发送功率,简化过程,以最小化信道发送功率达到抗干扰的目的。仿真实验证明,该方法能够有效选择可用信道并调整发送功率,抑制干扰,时间和能量开销低,具有较强实用性。
-
关键词:
- 无人机 (UAV) 数据链 /
- 信道选择 /
- 功率控制 /
- 信道质量 /
- 相关向量回归 (RVR)
Abstract:In complex electromagnetic and natural environment, the reliability of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) data link is under serious threat. To solve the problem of channel selection and power control to ensure UAV communication quality, a new channel selection and power control method in combination with relevance vector regression (RVR) is proposed. This method builds mapping model among interference information, bit error rate (BER) and signal noise ratio (SNR) based on RVR. Through the model and real-time interference information, the minimum channel SNR meeting the BER requirements of UAV data link can be predicted, and then minimum transmitted power can be calculated. Channel quality is judged based on the minimum channel transmitted power. The method selects channel while determining transmitted power, and makes the process simpler, using the minimum channel power to realize anti-jamming. Simulation experiment shows that this method can select available channel and adjust power effectively, and restrain interference. The proposed method has low time and energy cost, and is practical.
-
表 1 RVR和SVR训练结果
Table 1. Training results of RVR and SVR
训练结果 RVR SVR 高斯 5阶多项式 Laplace RBF 多项式 RVs,SVs 71 73 3 564 604 1 404 RMSE 0.023 1 0.020 3 0.062 6 0.074 0.58 RPE/% 0.198 0.180 0.325 0.887 5.17 表 2 采用PCA降维后RVR训练结果
Table 2. Training results of RVR after dimensionality reduction using PCA
训练结果 RVR (高斯核函数) 特征向量为6维 特征向量为5维 特征向量为4维 RMSE 0.301 0.302 6.479 RPE/% 4.30 4.56 24.65 表 3 不同标准下的信道质量排序
Table 3. Channel quality ranking based on different criteria
INR1/dB pmin标准 SINR标准 BER标准 -6~-2.5 1-4-3-5-2 1-4-3-5-2 1-4-3-5-2 -2.5~-1.5 1-4-3-5-2 1-4-3-2-5 1-4-3-5-2 -1.5~0 1-4-5-3-2 1-4-3-2-5 1-4-5-3-2 0~0.5 1-4-5-2-3 1-4-3-2-5 1-4-5-2-3 0.5~2 1-4-5-2-3 1-4-2-3-5 1-4-5-2-3 2~3.5 1-4-2-5-3 1-4-2-3-5 1-4-2-5-3 3.5~6 1-4-2-5-3 1-4-2-5-3 1-4-2-5-3 表 4 信道检测次数对比
Table 4. Comparison of channel detected iterations
检测方法 不考虑信道5 考虑信道5 随机检测 相关检测 随机检测 相关检测 检测次数 1.67 1.5 2 1.6 表 5 信道选择和功率控制方法仿真结果
Table 5. Simulation results of channel selection and power control method
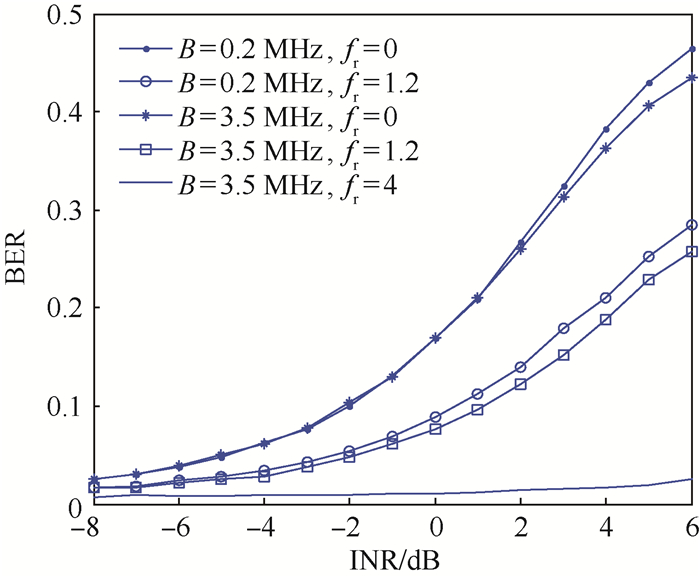
信道 位置1 位置2 位置3 位置4 位置5 位置6 pmin/dBm BER/dB pmin/dBm BER/dB pmin/dBm BER/dB pmin/dBm BER/dB pmin/dBm BER/dB pmin/dBm BER/dB 1 18.72 -1.98 15.12 -1.93 11.80 -1.97 13.55 -1.96 17.39 -1.99 20.40 -2.00 2 27.49 -1.94 25.56 -1.99 24.27 -1.98 25.69 -2.01 27.74 -2.00 29.91 -2.00 3 25.77 -2.02 22.74 -1.98 20.23 -2.01 23.09 -2.01 28.74 -2.02 34.08 -1.98 4 23.60 -1.99 20.07 -2.02 16.84 -2.01 18.69 -2.01 23.00 -2.02 26.98 -2.00 5 30.22 -1.99 26.62 -2.00 23.28 -1.99 24.94 -2.00 28.77 -1.98 31.78 -1.98 注:BER取对数,故单位为dB。 -
[1] VACHTSEVANOS G J, VALAVANIS K P.Military and civilian unmanned aircraft[M]//Handbook of unmanned aerial vehicles.Berlin:Springer Netherlands, 2015:93-103. [2] ⅡDUKA H.Fixed point optimization algorithm and its application to power control in CDMA data networks[J].Mathematical Programming, 2012, 133(1):227-242. [3] ZENGEN G, BUESCHING F, POETTNER W B, et al.Adaptive channel selection for interference reduction in wireless sensor networks[C]//Proceedings, ARCS 2015-The 28th International Conference on Architecture of Computing Systems.Nuremberg:VDE, 2015:1-7. [4] SKOKOWSKI P, MALON K, KELNER J M, et al.Adaptive channels' selection for hierarchical cluster based cognitive radio networks[C]//2014 8th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ICSPCS).Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2014:1-6. [5] PAL A, NASIPURI A.A distributed channel selection scheme for multi-channel wireless sensor networks[C]//Proceedings of the thirteenth ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing.New York:ACM, 2012:263-264. [6] XIAO L, DAI H, NING P. Jamming-resistant collaborative broadcast using uncoordinated frequency hopping[J].IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2012, 7(1):297-309. [7] MORIMOTO A, MIKI N, ISHⅡ H, et al.Investigation on transmission power control in heterogeneous network employing cell range expansion for LTE-Advanced uplink[C]//2012 18th European Wireless Conference European Wireless, EW.Nuremberg:VDE, 2012:1-6. [8] 李思佳, 毛玉泉, 郑秋容, 等.UAV数据链抗干扰的关键技术研究综述[J].计算机应用研究, 2011, 28(6):2020-2024. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSYJ201106007.htmLI S J, MAO Y Q, ZHENG Q R, et al.Overview of research on key techniques for anti-jamming of UAV data link[J].Application Research of Computers, 2011, 28(6):2020-2024(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSYJ201106007.htm [9] BACCOUR N, KOUBAA A, MOTTOLA L, et al.Radio link quality estimation in wireless sensor networks:A survey[J].ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN), 2012, 8(4):34. [10] WANG Y, MARTONOSI M, PEH L S.Predicting link quality using supervised learning in wireless sensor networks[J].ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review, 2007, 11(3):71-83. [11] 李建东, 郭梯云, 邬国扬.移动通信[M].4版.西安:西安电子科技大学出版社, 2009:94-132.LI J D, GUO T Y, WU G Y.Mobile communication[M].4th ed.Xi'an:Xidian University Press, 2009:94-132(in Chinese). [12] PHILLIPS C, SICKER D, GRUNWALD D.The stability of the Longley-Rice irregular terrain model for typical problems:CU-CS-1086-11[R].Boulder:University of Colorado at Boulder, 2011. [13] VALAVANIS K P, VACHTSEVANOS G J.Handbook of unmanned aerial vehicles[M].[S.l.]:Springer Publishing Company, Incorporated, 2014:749-844. [14] 崔蓉. 基于序贯决策的无线传感网络频谱感知策略与分配方法[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2015: 18-29.CUI R.Wireless sensor network spectrum sensing and allocation strategy based on sequential decision[D].Beijing:Beijing University of Posts and Communications, 2015:18-29(in Chinese). [15] BASAK D, PAL S, PATRANABIS D C.Support vector regression[J].Neural Information Processing-Letters and Reviews, 2007, 11(10):203-224. [16] TIPPING M E.Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine[J].The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2001, 1:211-244. [17] CAMPS-VALLS G, MARTíNEZ-RAMÓN M, ROJO-ÁLVAREZ J L, et al.Nonlinear system identification with composite relevance vector machines[J].IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2007, 14(4):279-282. [18] NICOLAOU M A, GUNMES H, PANTIC M.Output-associative RVM regression for dimensional and continuous emotion prediction[J].Image and Vision Computing, 2012, 30(3):186-196. [19] TANTUM S L, SCOTT W R, MORTON K D, et al.Target classification and identification using sparse model representations of frequency-domain electromagnetic induction sensor data[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(5):2689-2706. [20] JOLLIFFE I T.Principal component analysis[M].Berlin:Springer, 2002:41-64. -







 下载:
下载: