-
摘要:
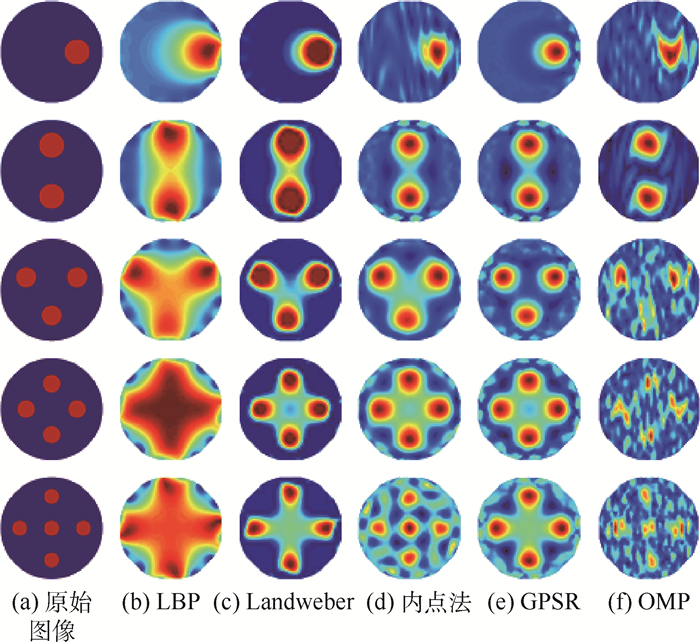
压缩感知(CS)理论是在充分利用信号稀疏性或可压缩性的情况下,对信号进行少量采样即可实现信号的精确重建。本文尝试将CS理论应用于电容层析成像(ECT)图像重建中,首先,使用快速傅里叶变换(FFT)基将原始图像灰度信号进行稀疏化处理;其次,将ECT灵敏度矩阵的各行按随机顺序进行排列,得到ECT系统随机观测矩阵;最后,选取当前普遍使用的基于内点法、梯度投影(GPSR)算法以及贪婪算法的CS图像重建算法进行ECT图像重建,并与线性反投影及Landweber迭代算法进行了对比。仿真实验结果表明:基于CS图像理论的ECT图像重建算法,其重建精度有所提高。本文同时分析了3种CS图像重建算法的优缺点及适用范围。
Abstract:Based on the sparsity or compressibility of the signal, compressed sensing (CS) theory can achieve high-accuracy reconstruction of the signal by sampling a small amount of data. In this paper, CS theory was used for the image reconstruction of electrical capacitance tomography (ECT). First, using the fast Fourier transformation (FFT) basis, the gray signals of original images can be transformed into the sparse signals. Then, the random observation matrix of ECT system was designed by rearranging the rows of the sensitivity matrix of ECT in a random order. Finally, interior point method, gradient projection for sparse reconstruction (GPSR) algorithm and greedy algorithm which are the three commonly used reconstruction algorithms of CS were used for ECT image reconstruction and the comparison was made with linear back projection algorithm and Landweber iterative algorithm. Simulation results indicate that reconstructed images with higher accuracy can be obtained using the ECT image reconstruction algorithm based on CS theory. Meanwhile, the advantages and disadvantages of the three CS image reconstruction algorithms were analyzed. The advice of selecting which type of image reconstruction algorithm was given.
-
表 1 初始重建图像相对误差
Table 1. Relative error of initial reconstructed image
流型 Er LBP Landweber 内点法 GPSR OMP 流型1 1.405 3 0.793 3 0.807 8 0.590 7 0.798 8 流型2 1.238 3 0.807 0 0.689 1 0.675 2 0.689 3 流型3 1.570 9 0.882 6 0.718 9 0.774 0 0.863 9 流型4 2.002 7 1.020 4 0.892 5 0.883 7 0.938 1 流型5 2.052 8 1.114 7 0.904 1 1.091 0 0.971 5 表 2 初始重建图像相关系数
Table 2. Correlation coefficient of initial reconstructed image
流型 Cc LBP Landweber 内点法 GPSR OMP 流型1 0.616 9 0.769 6 0.813 8 0.874 2 0.737 5 流型2 0.569 3 0.742 3 0.843 1 0.839 0 0.855 8 流型3 0.445 8 0.685 0 0.730 3 0.812 9 0.575 2 流型4 0.357 8 0.603 0 0.662 7 0.728 8 0.551 6 流型5 0.322 8 0.536 6 0.675 2 0.632 2 0.525 6 表 3 后处理重建图像相对误差
Table 3. Relative error of reconstructed image after processing
流型 Er 后处理
LBP后处理
Landweber后处理内点法 后处理
GPSR后处理
OMP流型1 0.854 9 0.339 7 0.392 2 0.277 4 0.425 1 流型2 0.784 5 0.392 2 0.240 2 0.219 3 0.325 2 流型3 0.872 0 0.692 2 0.489 5 0.102 1 0.747 8 流型4 1.258 3 0.640 3 0.517 4 0.408 2 0.822 9 流型5 1.030 8 0.698 2 0.497 6 0.559 0 0.702 0 表 4 后处理重建图像相关系数
Table 4. Correlation coefficient of reconstructed image after processing
流型 Cc 后处理
LBP后处理
Landweber后处理内点法 后处理
GPSR后处理
OMP流型1 0.630 6 0.943 1 0.813 8 0.958 4 0.738 8 流型2 0.696 6 0.920 4 0.966 6 0.972 2 0.938 3 流型3 0.681 9 0.700 6 0.870 6 0.994 1 0.507 8 流型4 0.552 2 0.846 1 0.797 4 0.915 4 0.542 7 流型5 0.500 2 0.716 9 0.819 3 0.799 4 0.663 0 表 5 重建图像所用时间
Table 5. Consumed time of image reconstruction
流型 重建图像所用时间/s LBP Landweber 内点法 GPSR OMP 流型1 0.013 43 4.799 04 8.609 49 2.779 11 0.060 46 流型2 0.014 73 4.585 68 8.791 92 2.623 62 0.043 96 流型3 0.011 82 5.560 35 9.095 21 3.539 22 0.054 18 流型4 0.013 81 5.262 73 9.862 51 4.610 25 0.087 01 流型5 0.015 43 5.040 01 9.932 23 4.735 56 0.119 94 -
[1] 王化祥.电学层析成像[M].北京:科学出版社, 2013:4-20.WANG H X.Electrical tomography[M].Beijing:Science Press, 2013:4-20(in Chinese). [2] 赵玉磊, 郭宝龙, 闫允一.电容层析成像技术的研究进展与分析[J].仪器仪表学报, 2012, 33(8):1909-1920.ZHAO Y L, GUO B L, YAN Y Y.Latest development and analysis of electrical capacitance tomography technology[J].Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2012, 33(8):1909-1920(in Chinese). [3] 郝魁红, 范文茹, 马敏, 等.平面式电容传感器阵列测量复合材料技术研究[J].传感器与微系统, 2014, 33(2):35-38.HAO K H, FAN W R, MA M, et al.Research on technology of composite materials measurement by planar capacitance sensor array[J].Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2014, 33(2):35-38(in Chinese). [4] 马敏, 周苗苗, 李新建, 等.基于ECT技术的航空发动机尾气监测系统设计[J].传感器与微系统, 2015, 34(5):88-91.MA M, ZHOU M M, LI X J, et al.Design of aero-engine off gas monitoring system based on ECT technology[J].Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2015, 34(5):88-91(in Chinese). [5] 吴新杰, 黄国兴, 王静文.粒子滤波算法在ECT图像重建中的应用[J].光学精密工程, 2012, 20(8):1826-1830.WU X J, HUANG G X, WANG J W.Application of particle filtering algorithm to image reconstruction of ECT[J].Optics and Precision Engineering, 2012, 20(8):1826-1830(in Chinese). [6] DONOHO D L.Compressed sensing[J].IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4):1289-1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [7] YU Y, HONG M, LIU F, et al.Compressed sensing MRI using singular value decomposition based sparsity basis[C]//Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2011:5734-5737. [8] 吴新杰, 黄国兴, 王静文.压缩感知在电容层析成像流型辨识中的应用[J].光学精密工程, 2013, 21(4):1062-1068.WU X J, HUANG G X, WANG J W.Application of compressed sensing to flow pattern identification of ECT[J].Optics and Precision Engineering, 2013, 21(4):1062-1068(in Chinese). [9] 张玲玲, 王化祥, 范文茹, 等.基于1范数的电阻层析成像图像重建算法[J].天津大学学报, 2011, 44(9):786-790.ZHANG L L, WANG H X, FAN W R, et al.Image reconstruction algorithm based on 1-norm for electrical resistance tomography[J].Journal of Tianjin University, 2011, 44(9):786-790(in Chinese). [10] 常甜甜, 魏雯婷, 丛伟杰.电阻抗成像的稀疏重建算法[J].西安邮电学院学报, 2013, 18(2):92-96.CHANG T T, WEI W T, CONG W J.Electrical impedance tomography based on sparse reconstruction[J].Journal of Xi'an University of Post and Telecom, 2013, 18(2):92-96(in Chinese). [11] 王丕涛, 王化祥, 孙犇渊.基于l1范数的电容层析成像图像重建算法[J].中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35(18):4709-4714.WANG P T, WANG H X, SUN B Y.l1-norm-based image reconstruction algorithm for electrical capacitance tomography[J].Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35(18):4709-4714(in Chinese). [12] YE J M, WANG H G, YANG W Q.Image reconstruction for electrical capacitance tomography based on sparse representation[J].IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2015, 64(1):89-102. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2014.2329738 [13] 马坚伟, 徐杰, 鲍跃全, 等.压缩感知及其应用:从稀疏约束到低秩约束优化[J].信号处理, 2012, 28(5):609-623.MA J W, XU J, BAO Y Q, et al.Compressive sensing and its application:From sparse to low-rank regularized optimization[J].Signal Processing, 2012, 28(5):609-623(in Chinese). [14] CANDES E J, ROMBERG J, TAO T.Robust uncertainty principles:Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information[J].IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(2):489-509. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.862083 [15] BARANIUK R G.Compressive sensing[lecture notes] [J].IEEE Trans on Signal Processing Magazine, 2007, 24(4):118-121. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.4286571 [16] 陈宇, 高宝庆, 张立新, 等.基于加权奇异值分解截断共轭梯度的电容层析图像重建[J].光学精密工程, 2010, 18(3):701-707.CHEN Y, GAO B Q, ZHANG L X, et al.Image reconstruction based on weighted SVD truncation conjugate gradient algorithm for electrical capacitance tomography[J].Optics and Precision Engineering, 2010, 18(3):701-707(in Chinese). [17] NATARAJAN B K.Sparse approximate solutions to linear systems[J].SIAM Journal on Computing, 1995, 24(2):227-234. doi: 10.1137/S0097539792240406 [18] CHEN S S, DONOHO D L, SAUNDERS M A.Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit[J].SIAM Review, 2001, 43(1):129-159. doi: 10.1137/S003614450037906X [19] SEUNG J K, KOH K, LUSTIG M, et al.An interior-point method for large-scale l1-regularized least squares[J].IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2007, 1(4):606-617. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2007.910971 [20] FIGUEIREDO M A T, NOWAK R D, WRIGHT S J.Gradient projection for sparse reconstruction:Application to compressed sensing and other inverse problem[J].IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2007, 1(4):586-597. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2007.910281 [21] TROPP J A, GILBERT A C.Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit[J].IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(12):4655-4666. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2007.909108 [22] BLUMENSATH T, DAVIES E.Iterative hard thresholding for compressed sensing[J].Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2009, 27(3):265-274. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2009.04.002 [23] GILBERT A C, INDYK P, IWEN M, et al.Recent developments in the sparse fourier transform:A compressed Fourier transform for big data[J].IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(5):91-100. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2329131 -







 下载:
下载: