-
摘要:
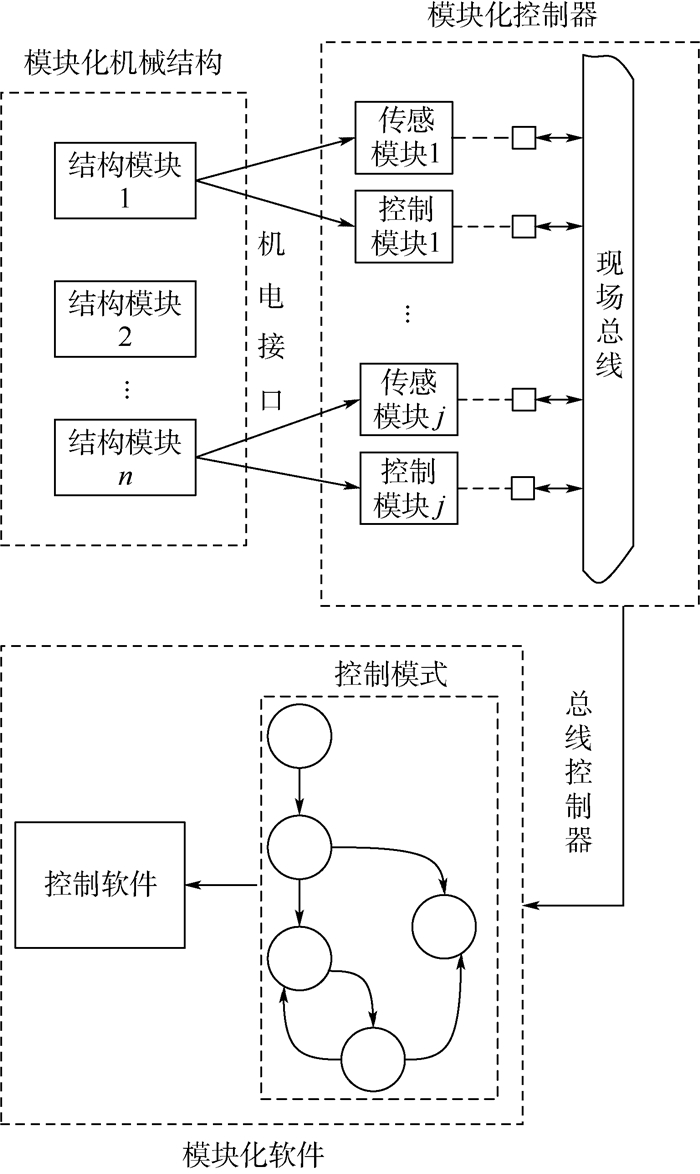
缠绕机具有生产效率高、产品质量稳定等特点,是碳纤维复合材料成型的关键工艺装备。针对产品小批量、定制化的生产需求,提出了针对缠绕机结构和控制系统的模块化设计方法(MDM),拓展缠绕机的功能多样性。将缠绕机的结构部件进行功能分解和关联强度分析,采用组遗传算法(GGA)将部件聚类为标准化的模块,根据产品需求,以产品性能最好和成本最低为目标建立模块配置模型,基于快速分类的非支配遗传算法(NSGA-Ⅱ)求解多目标优化模型完成机械结构模块化配置。提出基于现场总线的分布式网络控制器结构,将控制器的接口标准化和网络化,根据机械结构的模块化配置实现控制器的快速重构。基于模型组件对象(COM)技术将软件模块设计为COM组件,采用k近邻(kNN)方法进行控制模式分类,并进行COM组件的重构,控制软件动态解析控制模式并管理COM组件的状态转移关系,从而实现软件的快速重构。对结构、控制器和软件模块化方法的研究能够实现缠绕机的快速重构,拓展缠绕机的功能。
-
关键词:
- 缠绕机 /
- 模块化方法 /
- 多目标优化 /
- 分布式控制 /
- 模型组件对象(COM)技术
Abstract:Winding machine is the core equipment for filament winding with the features of high production efficiency and stable product quality. To meet the requirements of customized and small batch production, the modular design method (MDM) is proposed to expand the function of winding machine. The system structure is analyzed, relation matrices between components are established, and the grouping genetic algorithm (GGA) is then employed to conduct modular optimization to cluster components into standard modules. Multi-objective optimization method based on non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm Ⅱ (NSGA-Ⅱ) is proposed to create a complete system by combining instances with consideration of performance and cost simultaneously. The modular design method for the control system is presented based on distributed network controller for a bus system, and the network interface of the controller is standardized as independent function module, and then the rapid configuration of the controller is achieved according to the modular configuration of the mechanical structure. The k-nearest neighbor (kNN) method is used to classify the control mode by detecting the connection state of the module and the dynamic reconfiguration method based on component object model (COM) component to realize the state transition sequence and data exchange of the modules. The research on the modularization of mechanical structure, controller and software can realize the rapid reconfiguration of the winding machine, and expand the function of the winding machine.
-
表 1 不同测试样本数量和k值的加权kNN方法准确率
Table 1. Woighted kNN method accuracy for different test sample sizes and values of k
样本数量 加权kNN方法准确率/% k=5 k=7 k=9 100 94 91.3 93.3 200 92.7 92.3 91.5 -
[1] 顾轶卓, 李敏, 李艳霞, 等.飞行器结构用复合材料制造技术与工艺理论进展[J].航空学报, 2015, 36(8):2773-2797.GU Y Z, LI M, LI Y X, et al.Progress on manufacturing technology and process theory of aircraft composite structure[J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(8):2773-2797(in Chinese). [2] SOUTIS C.Carbon fiber reinforced plastics in aircraft construction[J].Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2005, 412(1-2):171-176. [3] PIRAN F A S, LACERDA D P, ANTUNES J A V, et al.Modularization strategy:Analysis of published articles on production and operations management(1999 to 2013)[J].The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 86(1-4):507-519. [4] HUANG C C.Overview of modular product development[J].Proceedings of the National Science Council, 2000, 24(3):149-165. [5] LAU A K W, YAM R C M, TANG E.The impacts of product modularity on competitive capabilities and performance:An empirical study[J].International Journal of Production Economics, 2007, 105(1):1-20. [6] STONE R B, WOOD K L, CRAWFORD R H.A heuristic method for identifying modules for product architectures[J].Design Studies, 2000, 21(1):5-31. [7] KRENG V B, LEE T.Modular product design with grouping genetic algorithm-A case study[J].Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2004, 46(3):443-460. [8] WEI W, LIU A, LU S C Y, et al.A multi-principle module identification method for product platform design[J].Journal of Zhejiang University-Science A(Applied Physics & Engineering), 2015, 16(1):1-10. [9] JOSE A, TOLLENAERE M.Modular and platform methods for product family design:Literature analysis[J].Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2005, 16(3):371-390. [10] KIMURA F, KATO S, HATA T, et al.Product modularization for parts reuse in inverse manufacturing[J].CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 2001, 50(1):89-92. [11] HUANG C C, KUSIAK A.Modularity in design of products and systems[J].IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part A:Systems and Humans, 1998, 28(1):66-77. [12] 高飞, 肖刚, 潘双夏, 等.产品功能模块划分方法[J].机械工程学报, 2007, 43(5):29-35.GAO F, XIAO G, PAN S X, et al.Method of product function module partition[J].Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2007, 43(5):29-35(in Chinese). [13] FAN B, QI G, HU X, et al.A network methodology for structure-oriented modular product platform planning[J].Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2015, 26(3):553-570. [14] PANDREMENOS J, CHRYSSOLOURIS G.A neural network approach for the development of modular product architectures[J].International Journal of Computer Integrated, 2011, 24(10):879-887. [15] KRENG V B, LEE T P.MPD with grouping genetic algorithm:A case study[J].Computers and Industrial Engineering, 2004, 46(3):443-460. [16] 陆良, 杨殿阁, 顾铮珉, 等.采用模块化思想的汽车电器智能化设计方法[J].西安交通大学学报, 2010, 44(5):111-115.LU L, YANG D G, GU Z M, et al.Designing strategy for smart vehicle electrical/electronic devices based on modularization[J].Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2010, 44(5):111-115(in Chinese). [17] PRITSCHOW G, KIRCHER C, KREMER M, et al.Control systems for RMS and methods of their reconfiguration[M].Berlin:Springer, 2006:195-211. [18] 何岭松, 张登攀, 赖红.可重构虚拟仪器系统[J].机械工程学报, 2005, 41(9):78-81.HE L S, ZHANG D P, LAI H.Reconfigurable virtual instrument system[J].Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2005, 41(9):78-81(in Chinese). [19] DEB K, PRATAP A, AGARWAL S, et al.A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm:NSGA-Ⅱ[J].IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2):182-197. -







 下载:
下载: