-
摘要:
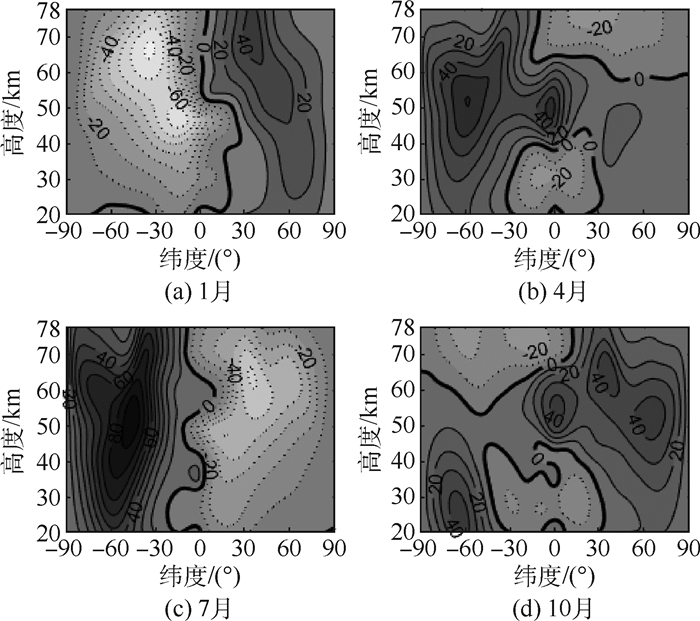
基于MERRA再分析资料的风场数据,根据数理统计理论,对酒泉(39.1°N,98.5°E)上空临近空间的20~78 km的大气风场进行了风切变特征分析,并分析了临近空间风切变对飞行器的影响。研究表明,临近空间最多风向在1月和10月为西风,7月为东风,4月在50 km以下为西风,以上为东风;99%概率最大风速在1月最大;最大风引起的风切变存在一定的高度范围。根据最大风和最小风给出了综合矢量风。此外发现临近空间风切变对飞行器产生的风攻角显著,对马赫数为3、5和8的飞行器产生风攻角在69 km最大,分别为8.5°、5.1°和3.2°。
Abstract:Based on the near-space wind field data from MERRA reanalysis data, the seasonal variation of atmospheric wind field at 20-78 km is investigated. The characteristics of wind shear over Jiuquan (39.1°N, 98.5°E) are analyzed by the method of mathematical statistics. Moreover, the effect of wind shear on the near-space aircraft is studied. The results show that the wind in near space is eastward in January and October, westward in July, and eastward (westward) below (above) 50 km in April. The maximum wind speed occurs in January with 99% probability and the shear induced by the maximum wind has a certain height range. The synthetical wind vector is also given by the maximum wind and minimum wind. In addition, the wind attack angle of the near-space aircraft caused by the wind shear is significant. The wind attack angles for air vehicle with Mach numbers 3, 5 and 8 are biggest at 69 km, which are 8.5°, 5.1° and 3.2° respectively.
-
Key words:
- near space /
- wind shear /
- synthetical wind vector /
- air vehicle /
- wind attack angle
-
-
[1] 肖存英, 胡雄, 杨钧烽, 等.临近空间38°N大气密度特性及建模技术[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(9):1757-1765.XIAO C Y, HU X, YANG J F, et al.Characteristics of atmospheric density at 38°N in near space and its modeling technique[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(9):1757-1765(in Chinese). [2] 刘强, 武哲, 祝明, 等.平流层气球热动力学仿真[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2013, 39(12):1578-1583.LIU Q, WU Z, ZHU M, et al.Thermal-dynamic simulation of stratospheric balloon[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013, 39(12):1578-1583(in Chinese). [3] 阎啸, 唐博, 张天虹, 等.临近空间飞行器信息系统一体化载荷平台[J].航空学报, 2016, 37(S1):127-132.YAN X, TANG B, ZHANG T H, et al.Payload platform of near space vehicle information system[J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2016, 37(S1):127-132(in Chinese). [4] 陈闽慷, 杜涛, 胡雄, 等.北半球高空大气参数波动对临近空间飞行热环境的影响[J].科学通报, 2017, 62(13):1402-1409.CHEN M K, DU T, HU X, et al.Effect of atmosphere parameter oscillation at high altitude in the northern hemisphere for near space hypersonic flight aerothermodynamic prediction[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2017, 62(13):1402-1409(in Chinese). [5] 孙磊, 廉璞, 常晓飞, 等.临近空间大气环境建模及其对飞行器影响[J].指挥控制与仿真, 2016, 38(5):107-111.SUN L, LIAN P, CHANG X F, et al.Near space atmosphere modeling and its effect on the aircraft command control & simulation[J].Command Control & Simulation, 2016, 38(5):107-111(in Chinese). [6] MARTYUSHEY S G, SHEREMET M A.Conjugate natural convection combined with surface thermal radiation in an air filled cavity with internal heat source[J].International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2014, 76(2):51-67. [7] 童靖宇, 向树红.临近空间环境及环境试验[J].装备环境工程, 2012, 9(3):1-4.TONG J Y, XIANG S H.Near space environment and environment tests[J].Equipment Environmental Engineering, 2012, 9(3):1-4(in Chinese). [8] 陈凤贵, 陈光明, 刘克华.临近空间环境及其影响分析[J].装备环境工程, 2013, 10(4):71-75.CHEN F G, CHEN G M, LIU K H.Analysis of near space environment and its effect[J].Equipment Environmental Engineering, 2013, 10(4):71-75(in Chinese). [9] 蔡明辉, 张振龙, 封国强, 等.临近空间中子环境及其对电子设备的影响研究[J].装备环境工程, 2007, 4(5):23-29.CAI M H, ZHANG Z L, FENG G Q, et al.Study of near space neutron environment and its effects to electronic device[J].Equipment Environmental Engineering, 2007, 4(5):23-29(in Chinese). [10] SMITH A K.Global dynamics of the MLT[J].Surveys in Geophysics, 2012, 33(6):1177-1230. [11] 杨钧烽, 肖存英, 胡雄, 等.中国廊坊(39.4°N, 116.7°E)中间层和低热层潮汐的季节变化[J].地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(4):1501-1509.YANG J F, XIAO C Y, HU X, et al.Seasonal variations of wind tides in mesosphere and lower thermosphere over Langfang, China (39.4°N, 116.7°E)[J].Progress in Geophysics, 2017, 32(4):1501-1509(in Chinese). [12] 郭文杰, 胡雄, 闫召爱, 等.利用瑞利激光雷达观测北京地区上平流层地形重力波活动[J].地球物理学报, 2015, 58(10):3481-3486.GUO W J, HU X, YAN Z A, et al.Terrain-generated gravity waves in the upper stratosphere detected by Rayleigh lidar[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(10):3481-3486(in Chinese). [13] HALE N, LAMOTTE N, GARNER T.Operational experience with hypersonic flight of the space shuttle[C]//AIAA/AAAF 11th International Space Planes and Hypersonic Systems and Technologies Conference.Reston: AIAA, 2002: 17_5259. [14] 郭建国, 周军.临近空间低动态飞行器控制研究综述[J].航空学报, 2014, 35(2):320-331.GUO J G, ZHOU J.Review of the control of low dynamic vehicles in near space[J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(2):320-331(in Chinese). [15] RIENECKER M M, SUAREZ M J, GELARO R, et al.MERRA:NASA's modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications[J].Journal of Climate, 2011, 24(14):3624-3648. [16] 赵人濂, 陈振官, 付维贤.风切变与运载火箭设计[J].宇航学报, 1998, 19(2):105-108.ZHAO R L, CHEN Z G, FU W X.Wind shear and rocket design[J].Journal of Astronautics, 1998, 19(2):105-108(in Chinese). [17] 李锋, 叶川, 李广佳, 等.临近空间太阳能飞行器横航向稳定性[J].航空学报, 2016, 37(4):1148-1158.LI F, YE C, LI G J, et al.Lateral-directional stability of near-space solar-powered aircraft[J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2016, 37(4):1148-1158(in Chinese). [18] 刘海东, 包为民, 李惠峰, 等.高超声速飞行器全局有限时间姿态控制方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(9):1864-1873.LIU H D, BAO W M, LI H F, et al.Attitude control method within finite time globally for hypersonic vehicles[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(9):1864-1873(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: