-
摘要:
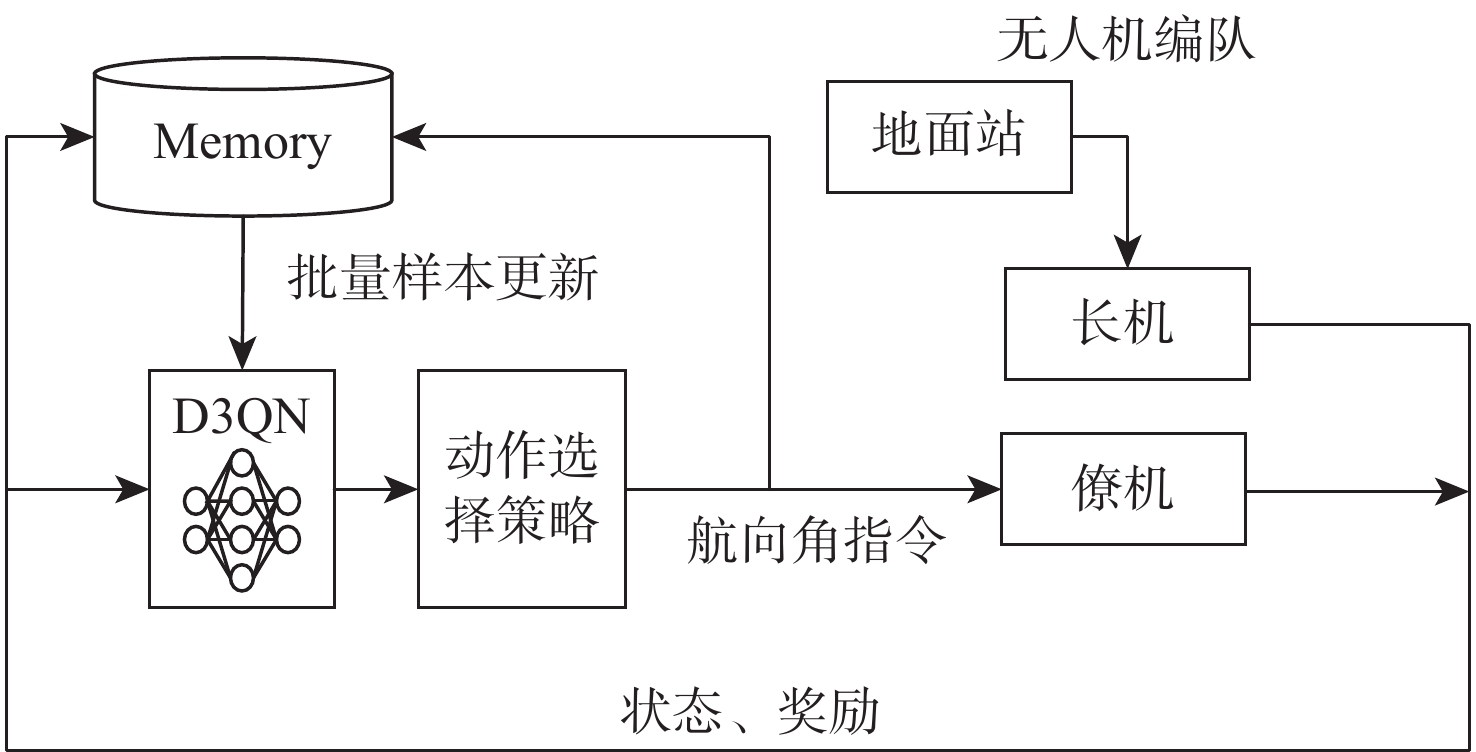
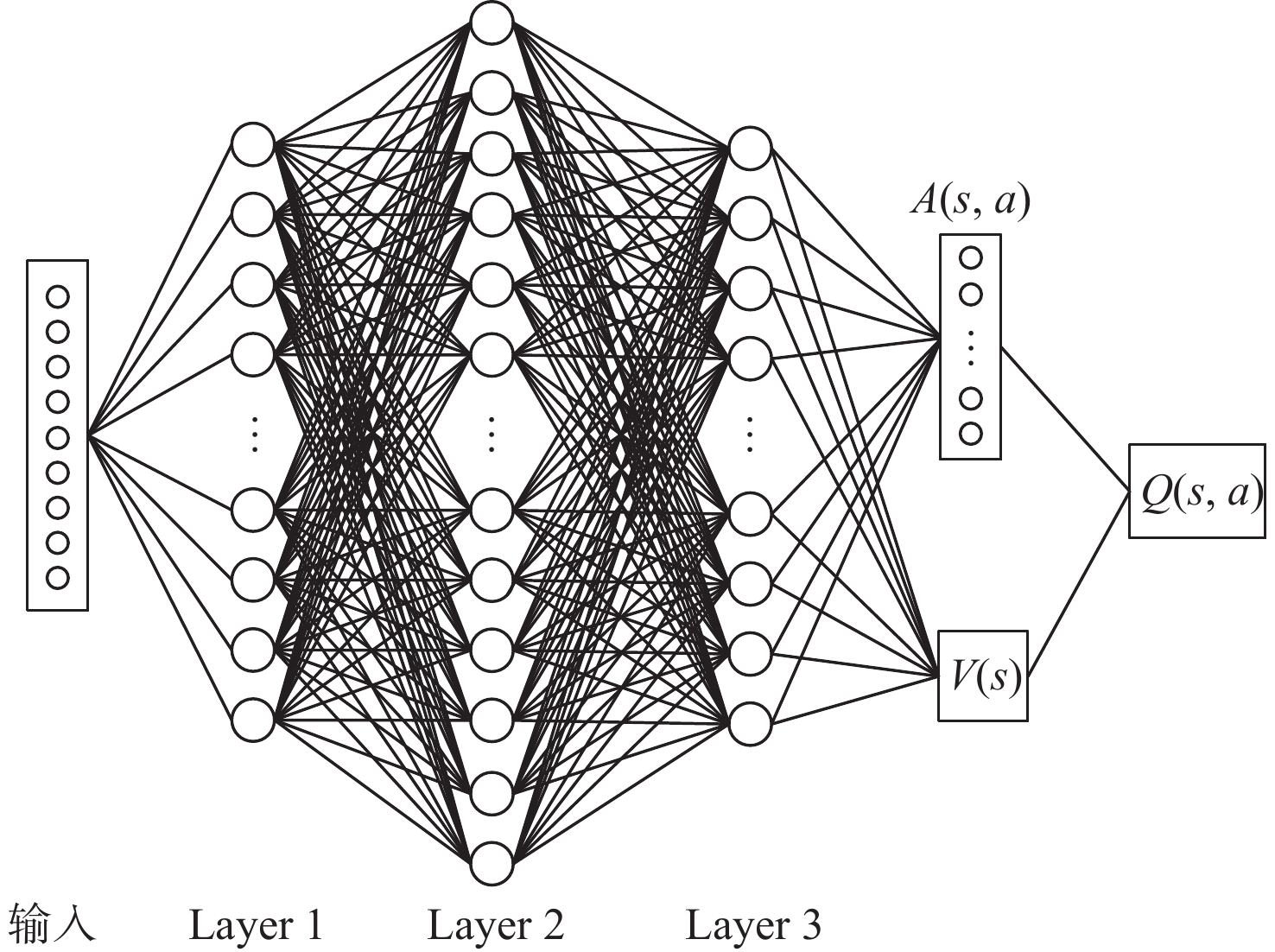
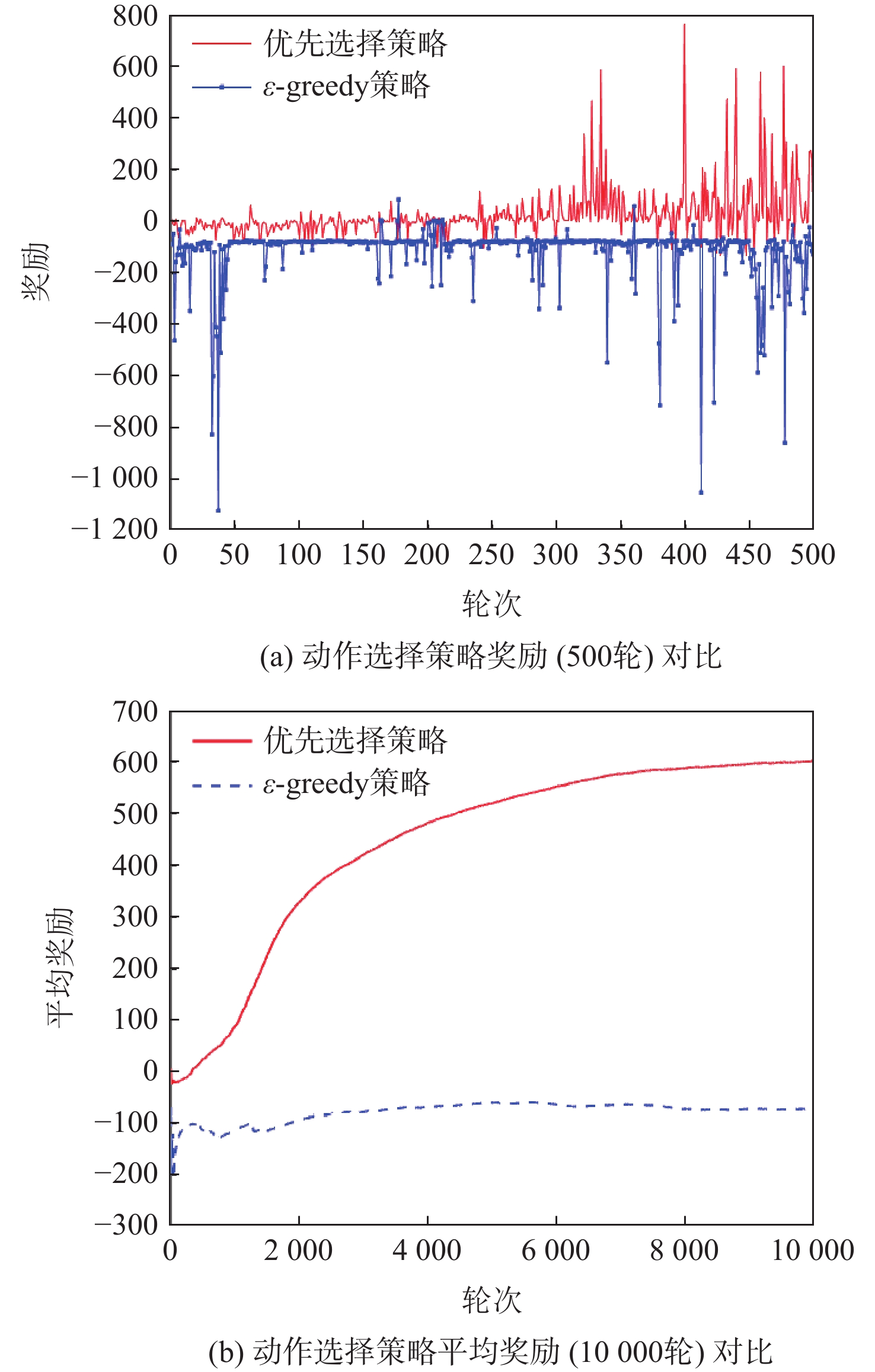
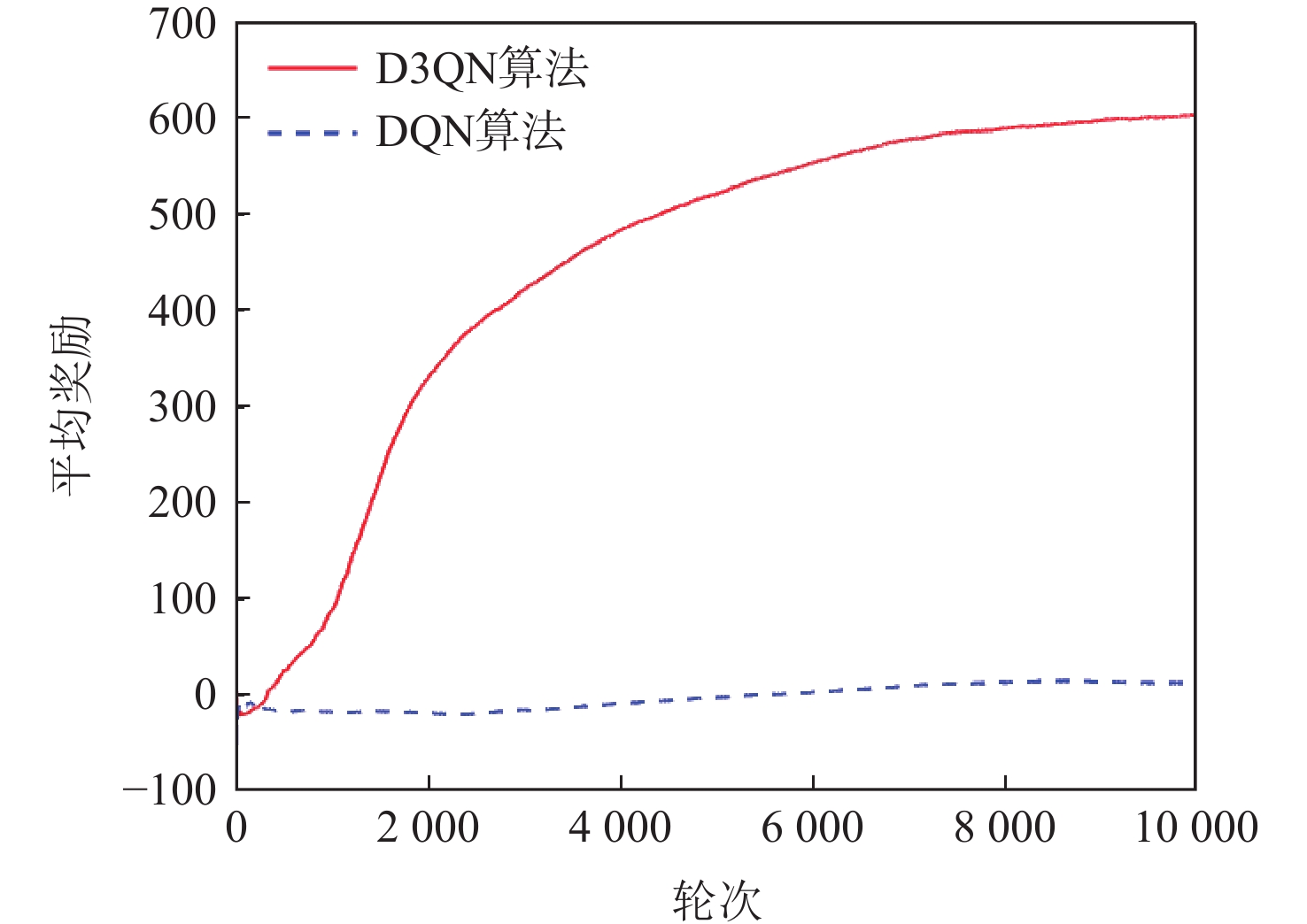
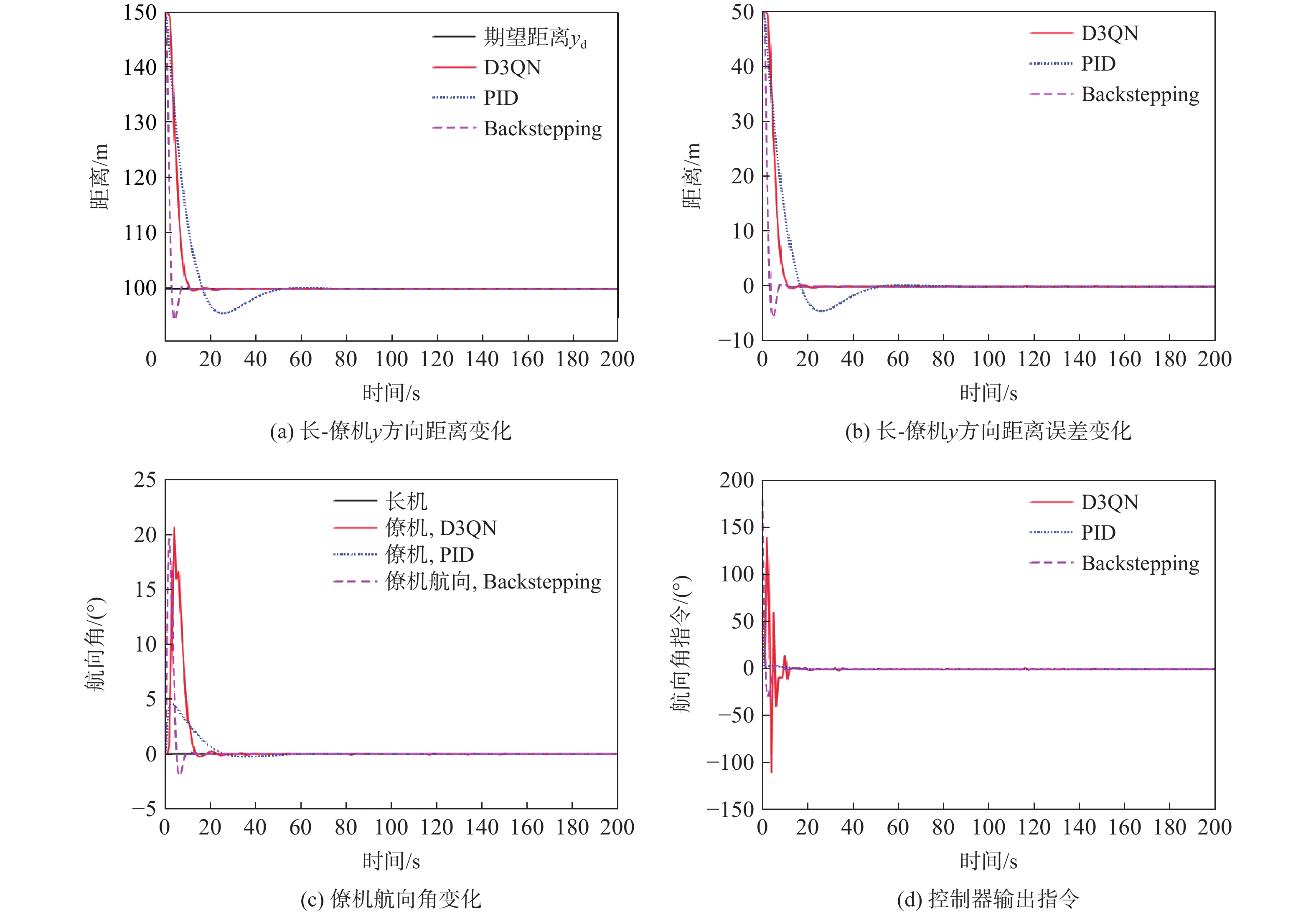
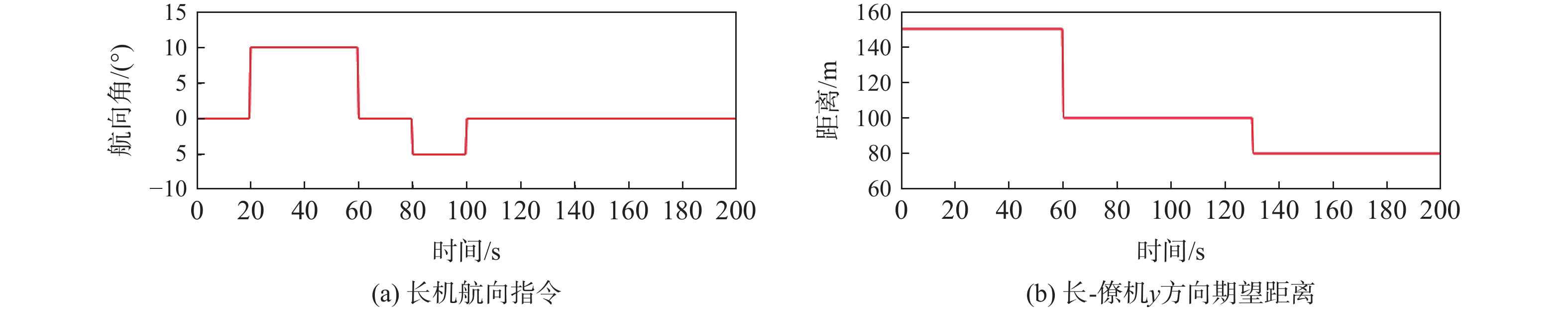
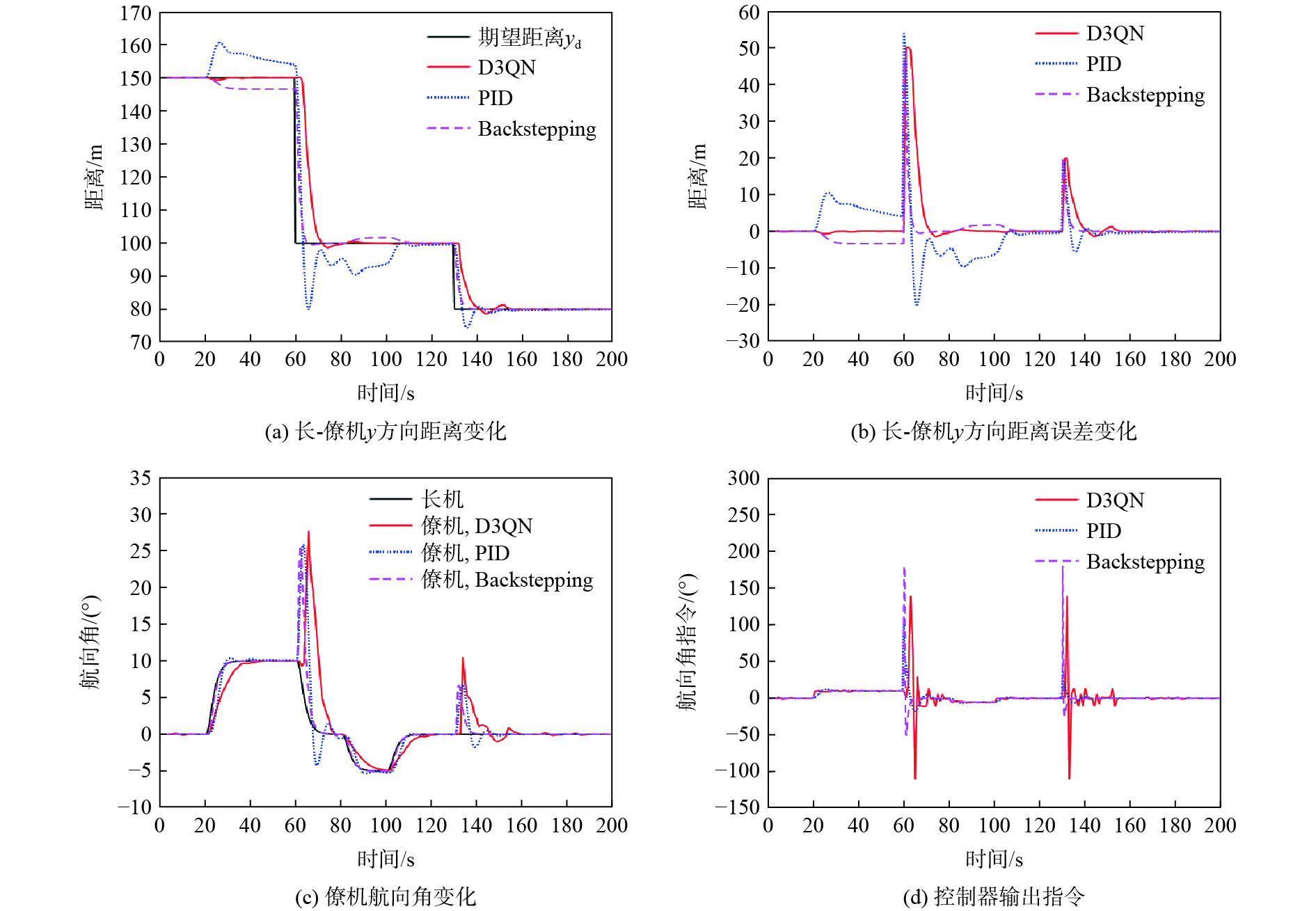
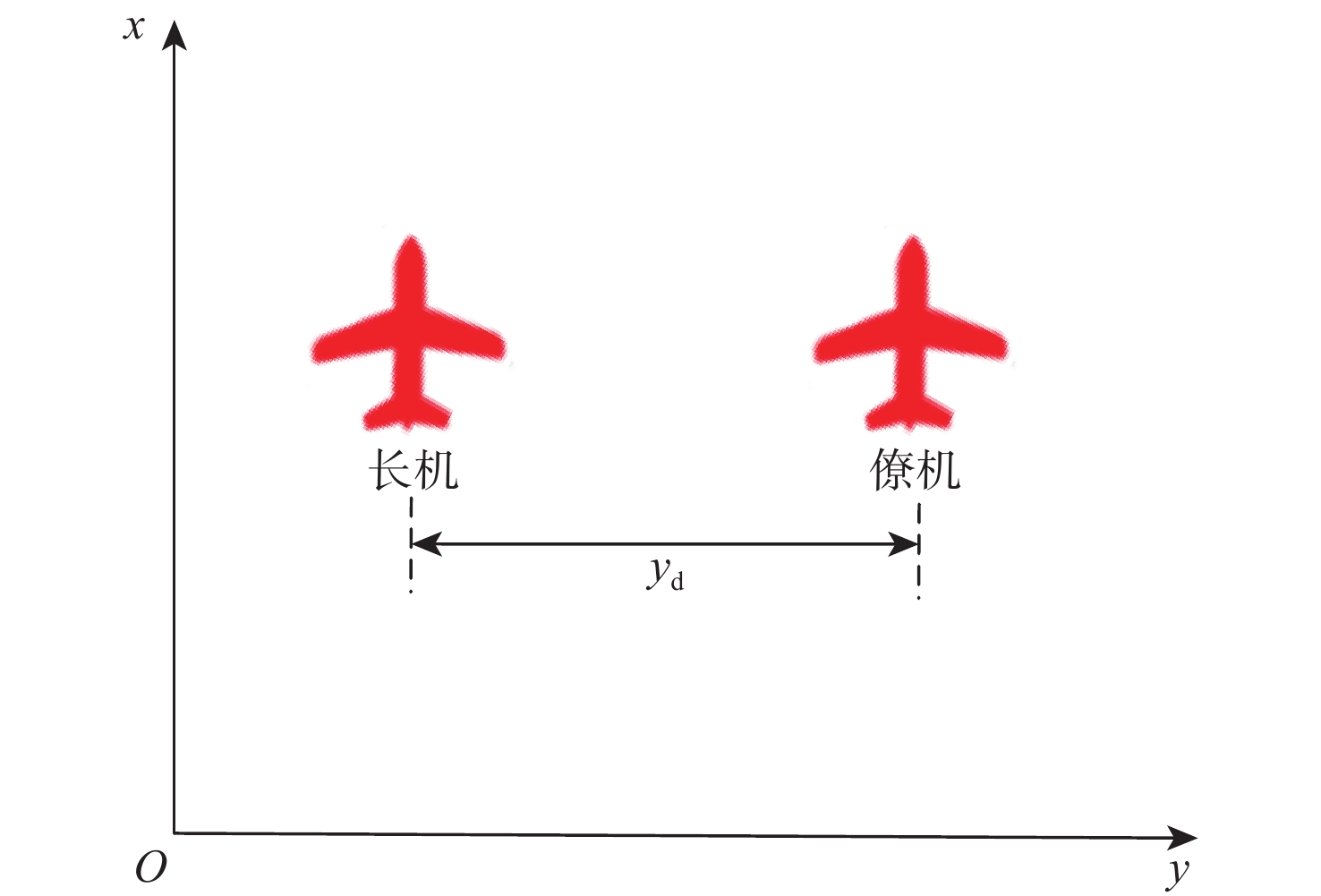
针对无人机编队中控制器设计需要基于模型信息,以及无人机智能化程度低等问题,采用深度强化学习解决编队控制问题。针对编队控制问题设计对应强化学习要素,并设计基于深度强化学习对偶双重深度Q网络(D3QN)算法的编队控制器,同时提出一种优先选择策略与多层动作库结合的方法,加快算法收敛速度并使僚机最终能够保持到期望距离。通过仿真将设计的控制器与PID控制器、Backstepping控制器对比,验证D3QN控制器的有效性。仿真结果表明:该控制器可应用于无人机编队,提高僚机智能化程度,自主学习保持到期望距离,且控制器设计无需模型精确信息,为无人机编队智能化控制提供了依据与参考。
Abstract:To address issues such as the need for controller design based on model information in UAV formation and the low level of UVA intelligence, deep reinforcement learning is used to solve formation control problems. In this paper, the corresponding reinforcement learning elements are designed for the formation control problem, then a formation controller based on dueling double deep Q-network (D3QN) is designed. Moreover, to speed up the convergence of the algorithm and make the follower accurately keep the desired distance, a priority strategy is proposed and combined with a multi-layer action library. Finally, through simulation, the proposed controller is compared with the PID controller and the Backstepping controller to verify its effectiveness. The results show that the controller based on D3QN can be applied to formation flight of UAV, improve the intelligence degree of the follower, and keep the desired distance without the need for precise model information, which provides a basis and reference for UAV intelligent control.
-
表 1 参数设置
Table 1. Parameter setting
参数 数值 epimax 10000 Maxstep 200 ψmax 180 batchsize 128 ε 1→0.1 α 0.0001 n 1 μ1,μ2 50 τψa 0.919 Ts 0.5 Td 200 M 1×106 γ 0.95 m 8 τ 0.9 σ1,σ2,σ3 1 μ3 20 τψb 0.919 -
[1] 宗群, 王丹丹, 邵士凯, 等. 多无人机协同编队飞行控制研究现状及发展[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2017, 49(3): 1-14. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.2017.03.001ZONG Q, WANG D D, SHAO S K, et al. Research status and development of multi UAV coordinated formation flight control[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017, 49(3): 1-14(in Chinese). doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.2017.03.001 [2] DESAI J P, OSTROWSKI J, KUMAR V. Controlling formations of multiple mobile robots[C]//1998 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2002: 2864-2869. [3] LEWIS M A, TAN K H. High precision formation control of mobile robots using virtual structures[J]. Autonomous Robots, 1997, 4(4): 387-403. doi: 10.1023/A:1008814708459 [4] QIU H, DUAN H, FAN Y. Multiple unmanned aerial vehicle autonomous formation based on the behavior mechanism in pigeon flocks[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2015, 32(10): 1298-1304. [5] LAMAN G. On graphs and rigidity of plane skeletal structures[J]. Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 1970, 4(4): 331-340. doi: 10.1007/BF01534980 [6] OLFATI-SABER R, MURRAY R M. Consensus problems in networks of agents with switching topology and time-delays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2004, 49(9): 1520-1533. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2004.834113 [7] 邓婉, 王新民, 王晓燕, 等. 无人机编队队形保持变换控制器设计[J]. 计算机仿真, 2011, 28(10): 73-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2011.10.018DENG W, WANG X M, WANG X Y, et al. Controller design of UAVs formation keep and change[J]. Computer Simulation, 2011, 28(10): 73-77(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2011.10.018 [8] 于美妍, 杨洪勇, 孙玉娇. 基于Backstepping的三轮机器人编队控制[J]. 复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2021, 18(3): 28-34. doi: 10.13306/j.1672-3813.2021.03.005YU M Y, YANG H Y, SUN Y J. Formation control of three wheeled robots based on Backstepping[J]. Complex Systems and Complexity Science, 2021, 18(3): 28-34(in Chinese). doi: 10.13306/j.1672-3813.2021.03.005 [9] 周彬, 郭艳, 李宁, 等. 基于导向强化Q学习的无人机路径规划[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(9): 325109. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2021.25109ZHOU B, GUO Y, LI N, et al. Path planning of UAV using guided enhancement Q-learning algorithm[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(9): 325109(in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2021.25109 [10] 李波, 越凯强, 甘志刚, 等. 基于MADDPG的多无人机协同任务决策[J]. 宇航学报, 2021, 42(6): 757-765. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.06.009LI B, YUE K Q, GAN Z G, et al. Multi-UAV cooperative autonomous navigation based on multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2021, 42(6): 757-765(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.06.009 [11] HUANG X, LUO W Y, LIU J R. Attitude control of fixed-wing UAV based on DDQN[C]//2019 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 4722-4726. [12] HUNG S M, GIVIGI S N, NOURELDIN A. A Dyna-Q(Lambda) approach to flocking with fixed-wing UAVs in a stochastic environment[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1918-1923. [13] WANG C, WANG J, SHEN Y, et al. Autonomous navigation of UAVs in large-scale complex environments: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(3): 2124-2136. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2890773 [14] WANG C, YAN C, XIANG X, et al. A continuous actor-critic reinforcement learning approach to flocking with fixed-wing UAVs[C]//The Eleventh Asian Conference on Machine Learning. New York: PMLR, 2019, 101: 1-16. [15] HUNG S M, GIVIGI S N. A Q-learning approach to flocking with UAVs in a stochastic environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 47(1): 186-197. [16] IIMA H, KUROE Y. Swarm reinforcement learning methods improving certainty of learning for a multi-robot-formation problem[C]//2015 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 3026-3033. [17] 相晓嘉, 闫超, 王菖, 等. 基于深度强化学习的固定翼无人机编队协调控制方法[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(4): 524009.XIANG X J, YAN C, WANG C, et al. Coordination control method for fixed-wing UAV formation through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(4): 524009(in Chinese). [18] PACHTER M, AZZO J J D, DARGAN J L. Automatic formation flight control[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 1994, 17(6): 1380-1383. [19] 王晓燕, 王新民, 肖亚辉, 等. 无人机三维编队飞行的鲁棒H∞控制器设计[J]. 控制与决策, 2012, 27(12): 1907-1911.WANG X Y, WANG X M, XIAO Y H, et al. Design of robust H∞ controller for UAVs three-dimensional formation flight[J]. Control and Decision, 2012, 27(12): 1907-1911(in Chinese). [20] MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature (London), 2015, 518(7540): 529-533. doi: 10.1038/nature14236 [21] VAN HASSELT H. Double Q-learning[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2010: 2613-2621. [22] VAN HASSELT H, GUEZ A, SILVER D. Deep reinforcement learning with double Q-learning[C]//AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI, 2016: 2094-2100. [23] WANG Z Y, SCHAUL T, HESSEL M, et al. Dueling network architectures for deep reinforcement learning[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2016: 1995-2003. [24] HU H A, WANG Q L. Proximal policy optimization with an integral compensator for quadrotor control[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2020, 21(5): 777-795. 期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(2)
-







 下载:
下载: