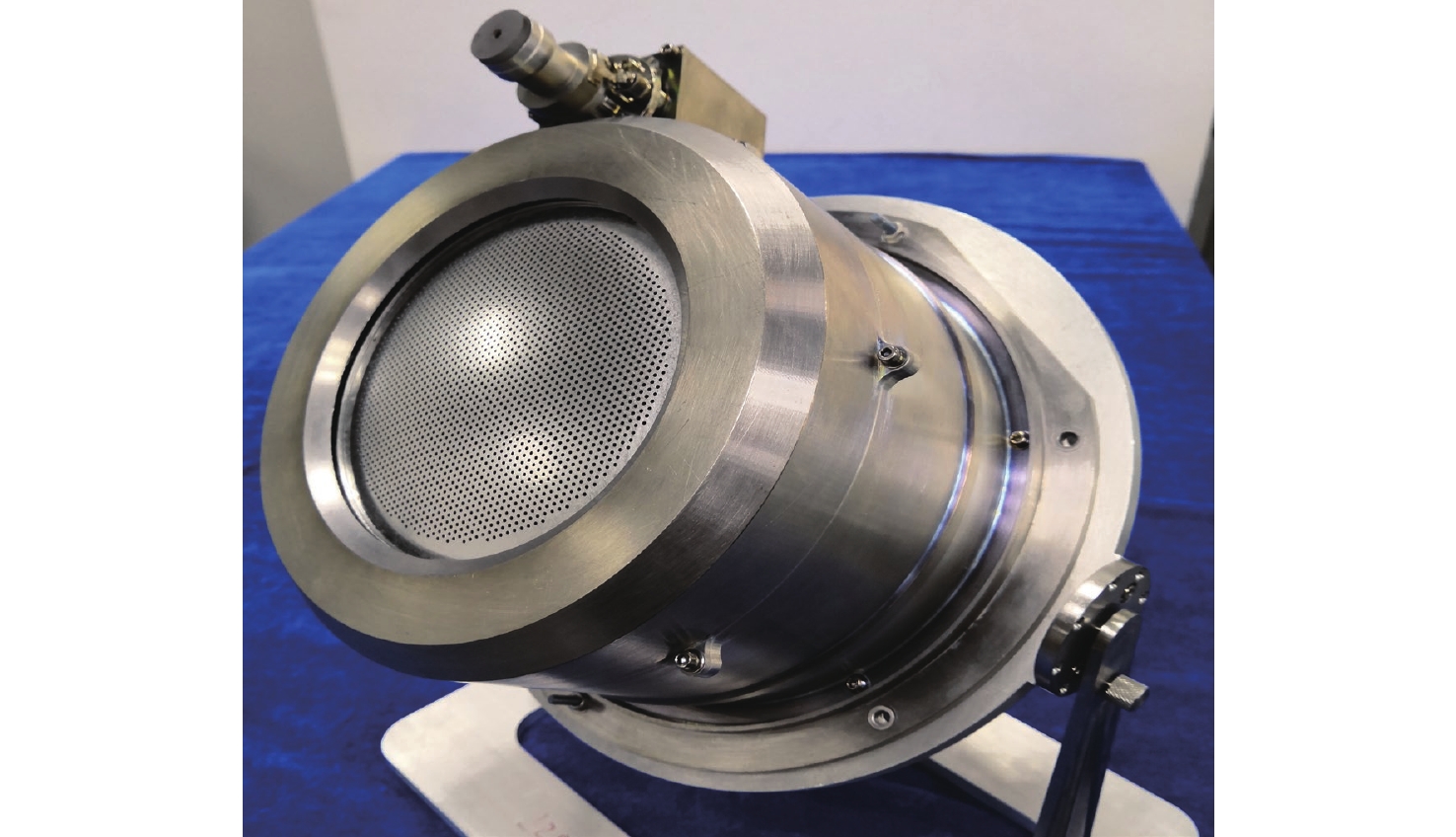
Optimization of discharge chamber key parameters for 10 cm Kaufman xenon ion thruster
-
摘要:
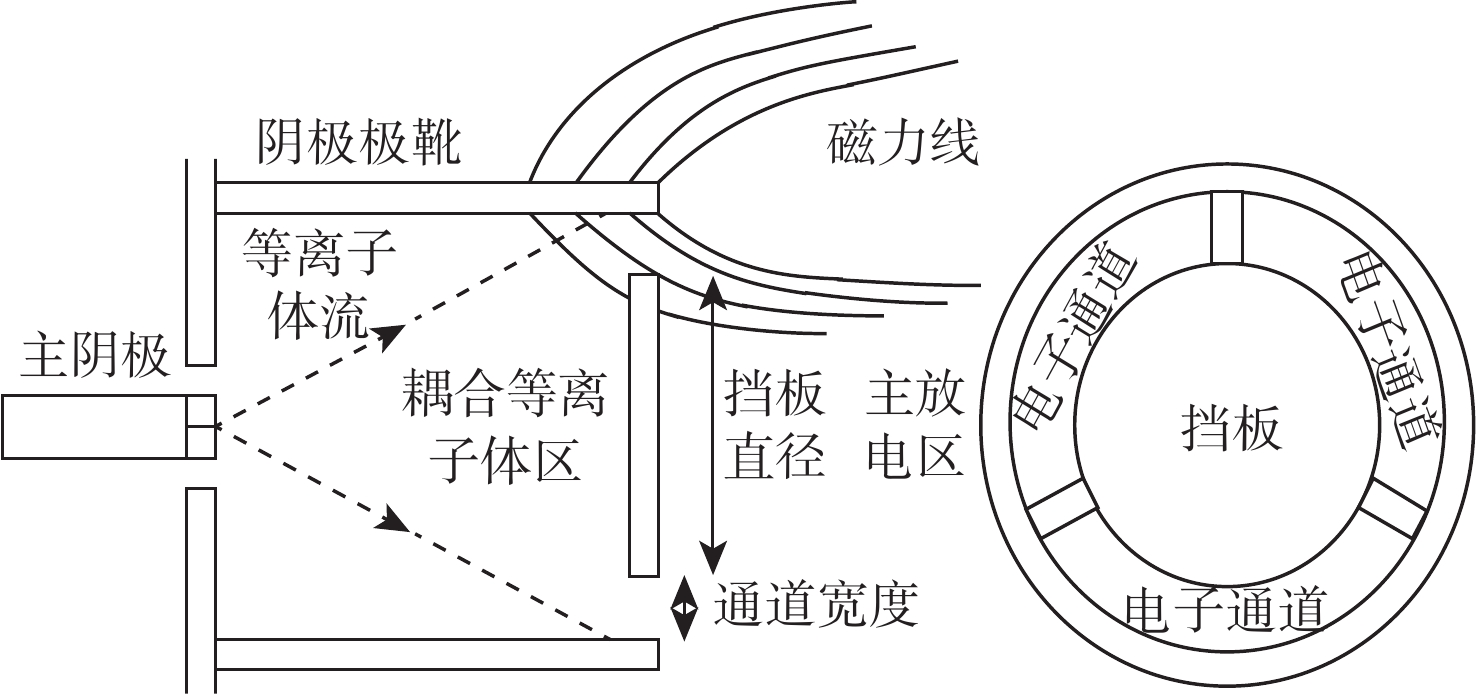
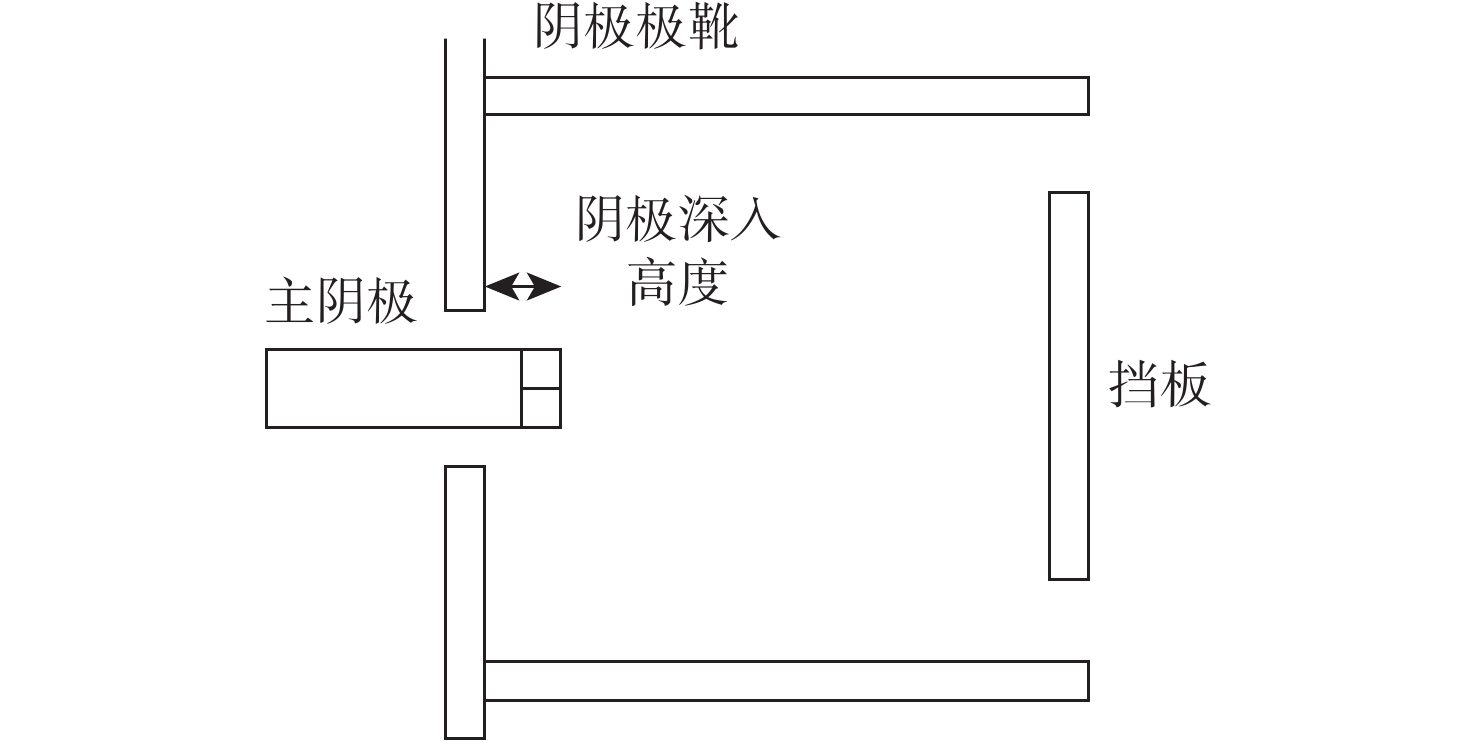
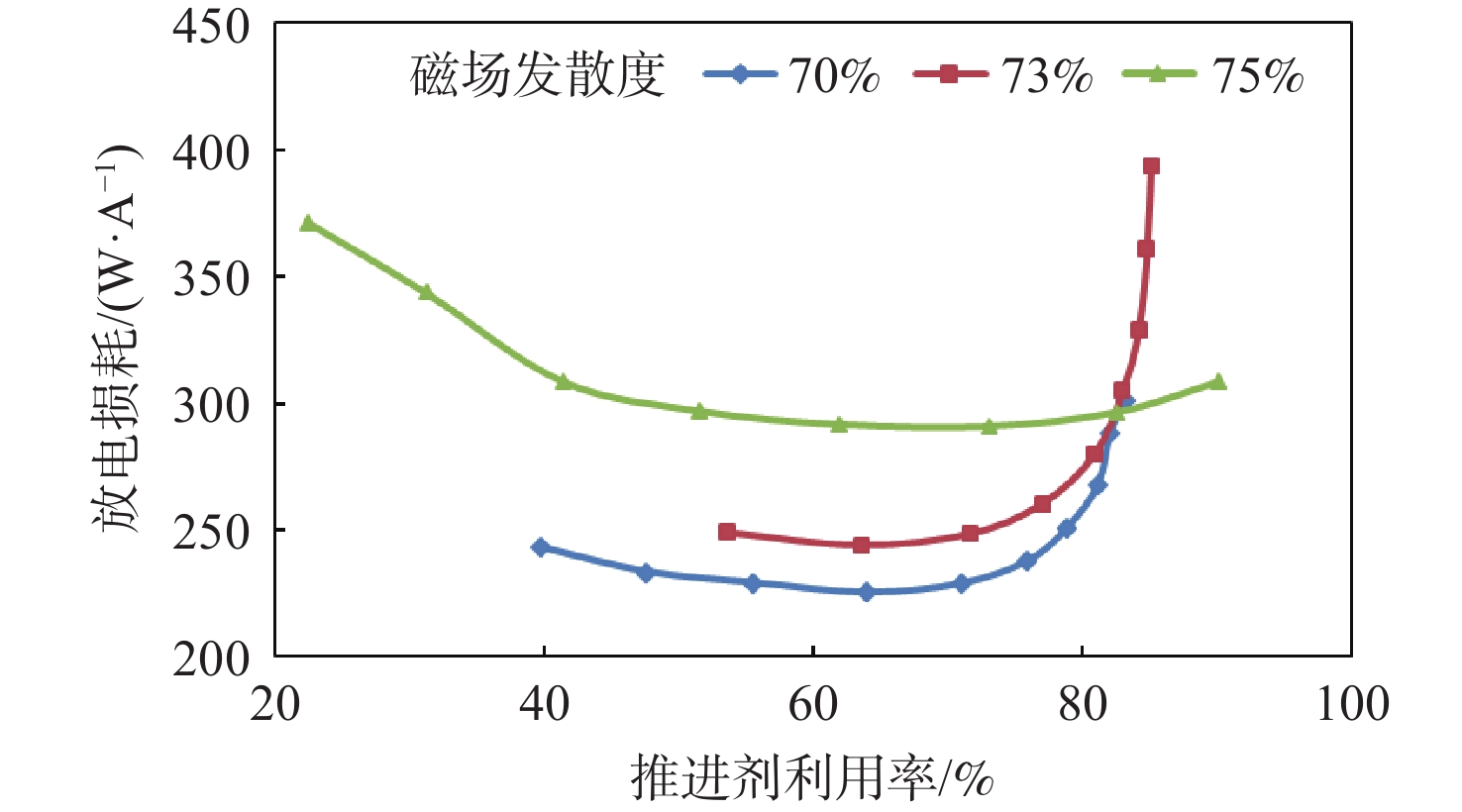
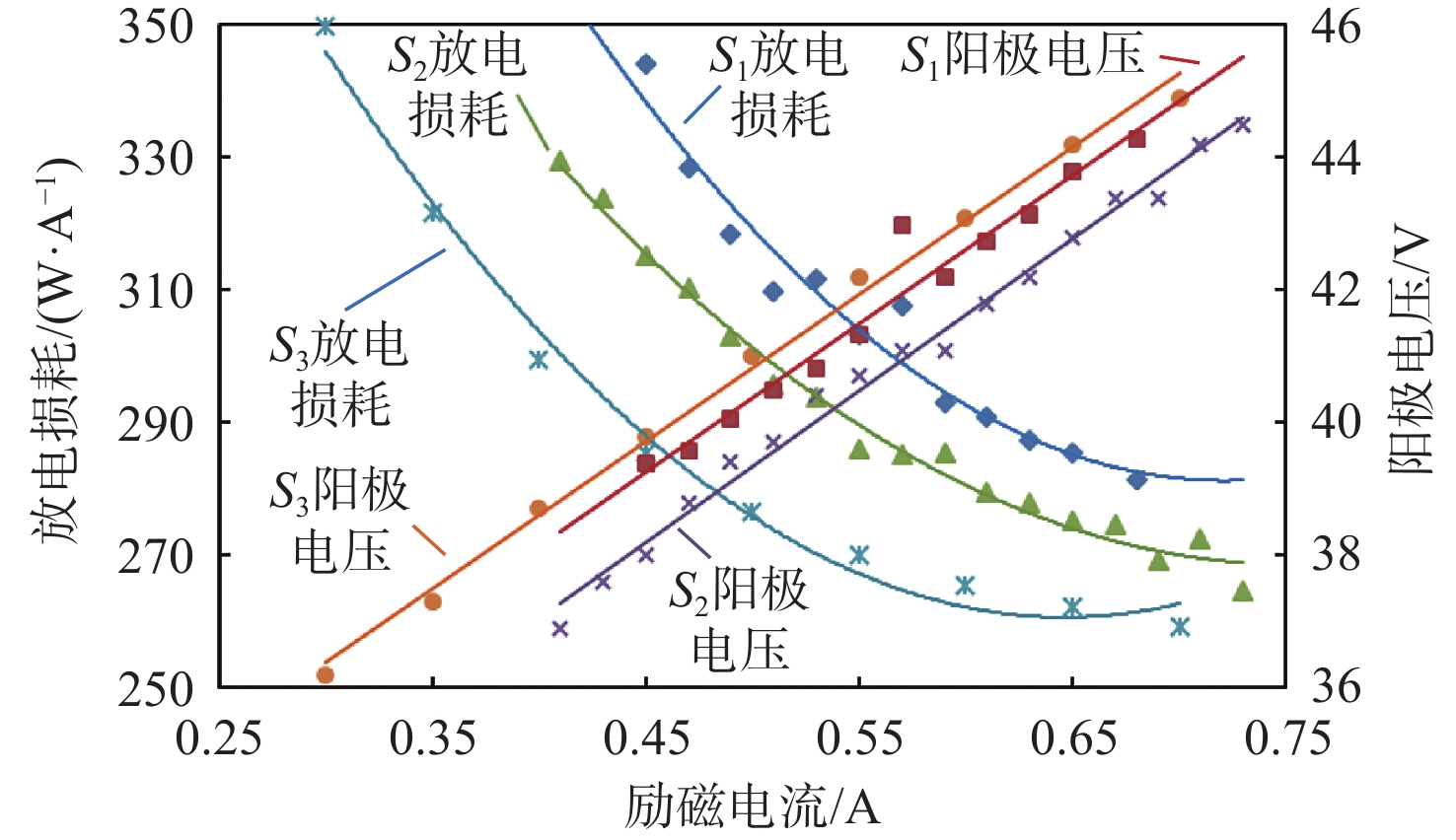
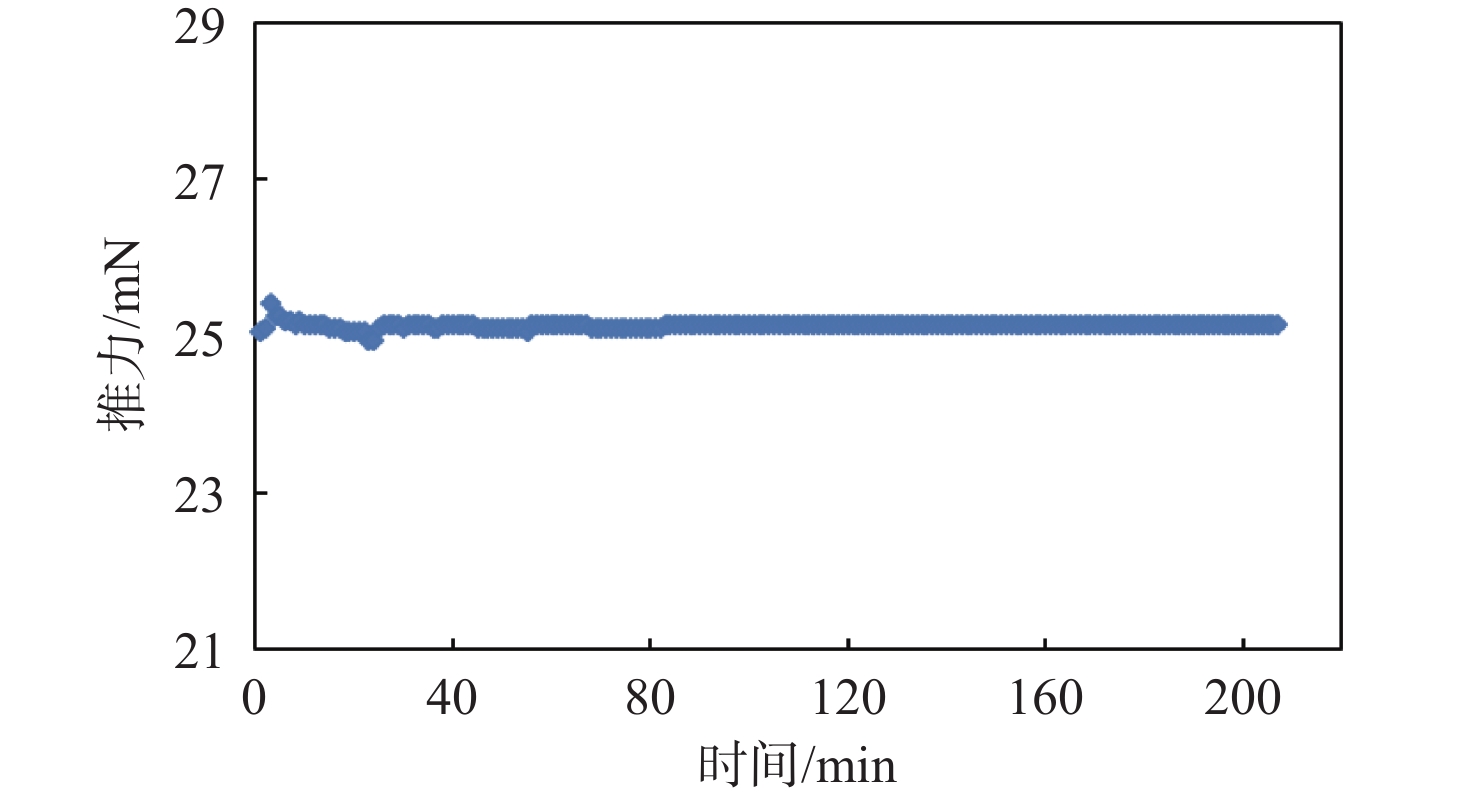
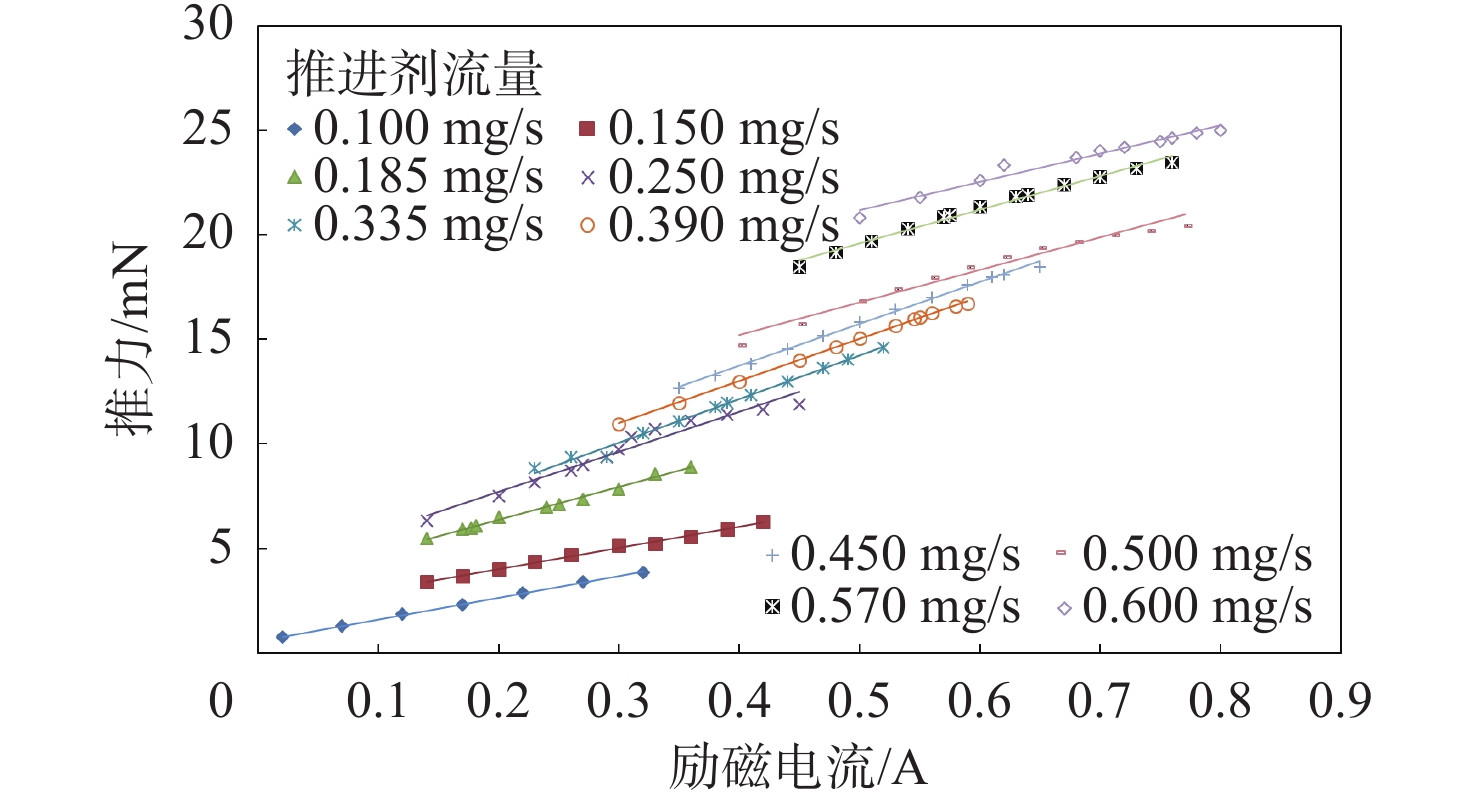
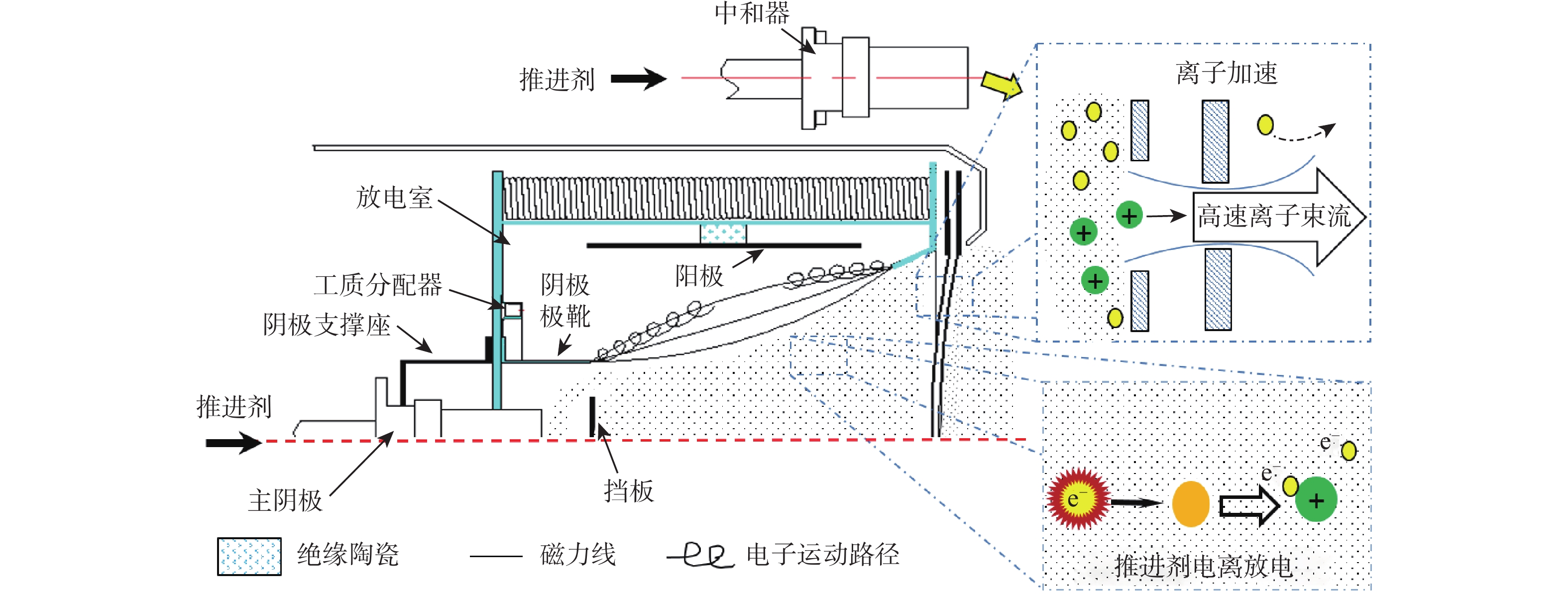
放电室构型设计是离子推力器结构设计的基础与核心,直接影响到放电室工作能效及整机工作寿命。针对新型航天器在轨飞行任务对大推力、长寿命连续变推力离子推力器的应用需求,探究了影响10 cm离子推力器整机效能的放电室关键参数因子,揭示了发散场放电室的磁场发散度、电子通道面积及阴极位置等敏感参数对放电室性能的影响作用关系。开展了10 cm离子推力器放电室参数构型的优化与验证。结果表明:在不改变整机结构的情况下,通过优化放电室关键参数,10 cm离子推力器最大输出推力由20 mN提升至25 mN,提升近25%,推力调节范围由1~20 mN扩展至1~25 mN,全范围内推力分辨率均优于50 μN,且推力器在20 mN最佳工作点的阳极电压由43.5 V降至38.4 V,放电损耗由345 W/A降至308 W/A,预估整机寿命将由15 000 h提升至17 500 h。研究为推动10 cm离子推力器的在轨扩展应用提供了一定的技术支撑。
Abstract:Discharge chamber configuration is the foundation and core of ion thruster structure design, which directly influences the working efficiency of the discharge chamber and in-orbit lifetime of the thruster. Aiming at the application requirement of new complex aerospace equipment for ion thruster with long-life, high thrust wide-range and continuous variable-thrust, this research explored the key factors of discharge chamber configuration parameters influencing the efficacy of 10 cm ion thruster, as well as the influence of magnetic field divergence, electron channel area and hollow cathode position and other sensitive parameters on discharge chamber performances. Then optimization of parameter configuration and verification of discharge chamber of 10 cm ion thruster were conducted. The results showed that by optimizing discharge chamber key parameters, the maximum thrust of 10 cm ion thruster increased from 20 mN to 25 mN, 25% higher without changing the mechanical structure of the thruster, which extended the thrust adjustment range from 1−20 mN to 1−25 mN, and enhanced the thrust resolution in the whole range to more than 50 μN. Moreover, the anode potential dropped to 38.4 V from 43.5 V, the discharge loss dropped to 308 W/A from 345 W/A, and the estimated lifetime of thruster will be increased from 15000 h to 17500 h. The above research will certainly provide technical support for the extended in-orbit application of 10 cm ion thruster.
-
Key words:
- drag-free flight /
- continuous variable-thrust /
- ion thruster /
- wide-range /
- discharge chamber
-
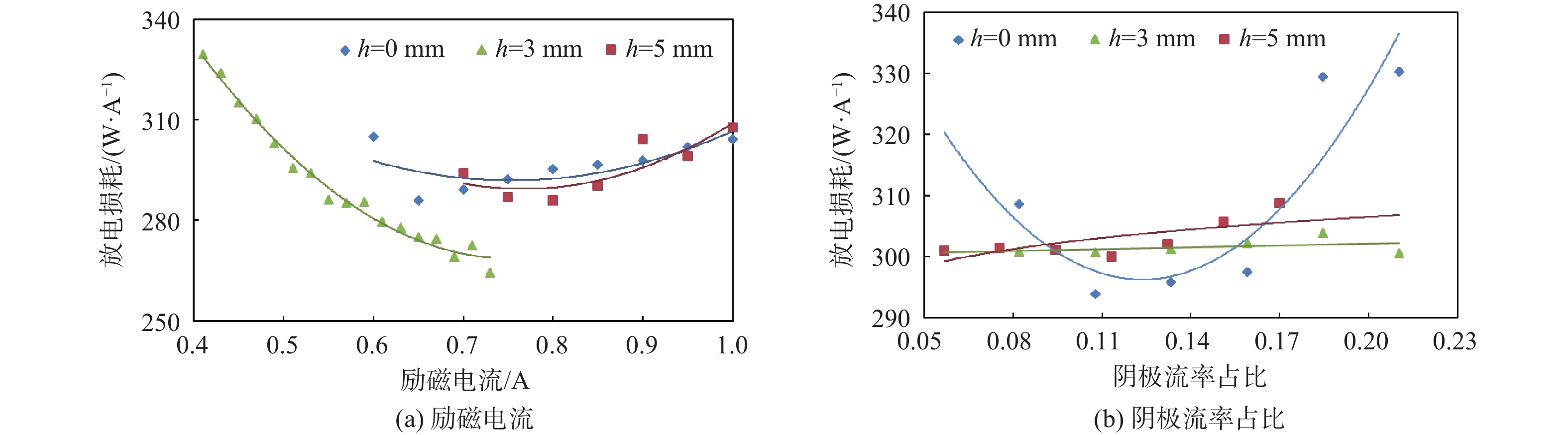
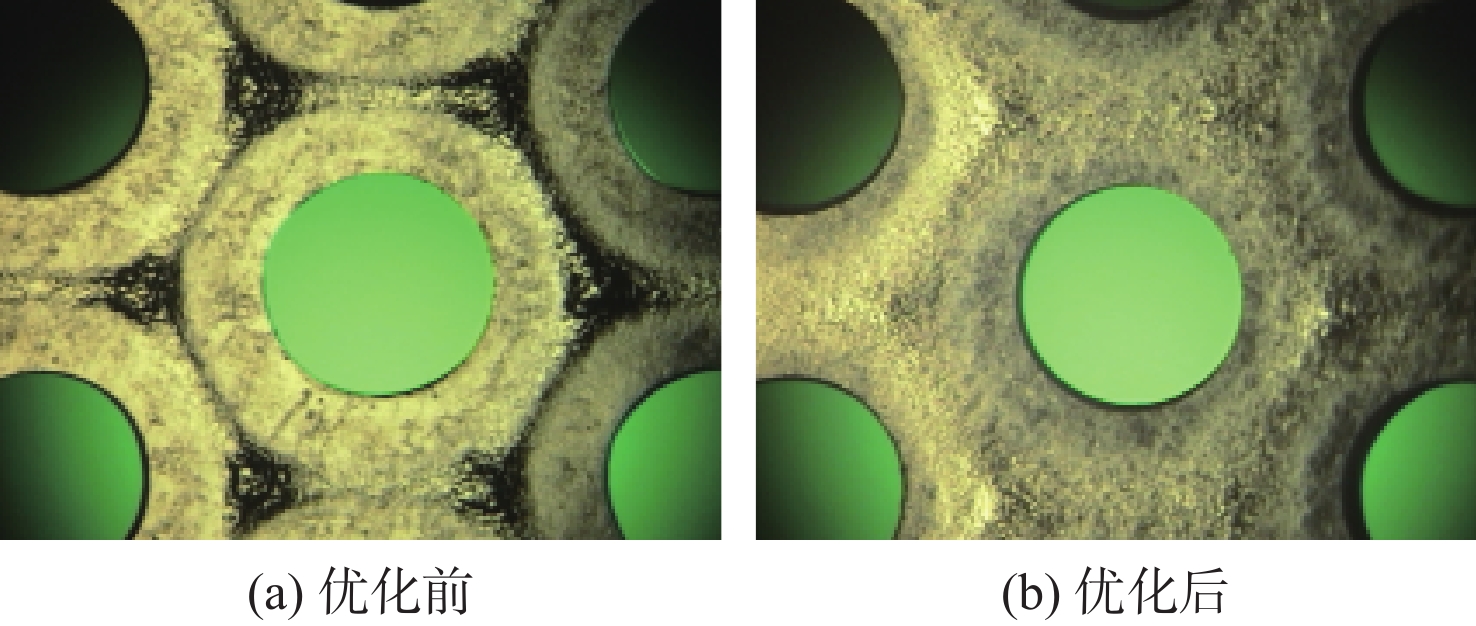
表 1 放电室关键参数优化前后状态对比
Table 1. Comparison of key parameters of discharge chamber before and after optimization
测试结果 Kd/(°) S/mm2 h/mm 优化前 65 1435 0 优化后 70 1089 3 表 2 推力器性能测试对比
Table 2. Comparison of thrust test results
优化改进 阳极电压
/V阳极电压振荡
/V阴极电压
/V阴极电压振荡
/V推力
/mN放电损耗
/ (W·A−1)推进剂利用率
/%功率
/W优化前 43.5 28 13.2 6 20.10 345 55.7 604 优化后 38.4 10 9.8 5 20.11 308 59.6 584 -
[1] 郑茂繁, 张天平, 孟伟, 等. 20 cm氙离子推力器性能扩展研究[J]. 推进技术, 2015, 36(7): 1116-1120. doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.2015.07.021ZHENG M F, ZHANG T P, MENG W, et al. Research of improvement performance for 20 cm xenon ion thruster[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2015, 36(7): 1116-1120(in Chinese). doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.2015.07.021 [2] 杨福全, 万耿民, 唐福俊, 等. 电推力器气路高电压绝缘技术研究[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2014, 34(12): 1290-1293. doi: 10.13922/j.cnki.cjovst.2014.12.03YANG F Q, WAN G M, TANG F J, et al. Novel type of high voltage xenon propellant insulator for electric thruster[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2014, 34(12): 1290-1293(in Chinese). doi: 10.13922/j.cnki.cjovst.2014.12.03 [3] 张天平, 田华兵, 孙运奎. 离子推进系统用于GEO卫星南北位保使命的能力与效益[J]. 真空与低温, 2010, 16(2): 72-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2010.02.002ZHANG T P, TIAN H B, SUN Y K. Capability and benefit of the lips-200 system for nssk mission of geo satellites[J]. Vacuum and Cryogenics, 2010, 16(2): 72-77(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2010.02.002 [4] 胡竟, 江豪成, 王亮, 等. 阴极挡板对30 cm氙离子推力器性能影响的研究[J]. 真空与低温, 2015, 21(2): 103-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2015.02.010HU J, JIANG H C, WANG L, et al. Study on performances of 30 cm xenon ion thruster subjected to cathode baffle[J]. Vacuum and Cryogenics, 2015, 21(2): 103-106(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2015.02.010 [5] 胡竟, 王亮, 张天平, 等. LIPS-300离子推力器环形会切磁场等效磁路分析研究[J]. 推进技术, 2018, 39(3): 715-720. doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.2018.03.028HU J, WANG L, ZHANG T P, et al. Research on equivalent magnetic circuit of ring-cusp magnet field for LIPS-300 ion thruster[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2018, 39(3): 715-720(in Chinese). doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.2018.03.028 [6] 杨福全, 王蒙, 郑茂繁, 等. 10 cm离子推力器放电室性能优化研究[J]. 推进技术, 2017, 38(1): 235-240. doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.2017.01.031YANG F Q, WANG M, ZHENG M F, et al. Optimization of performance of discharge chamber of a 10 cm diameter ion thruster[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2017, 38(1): 235-240(in Chinese). doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.2017.01.031 [7] 席竹君, 杨福全, 高俊, 等. 励磁电流对离子推力器推力变化影响研究[J]. 真空与低温, 2017, 23(2): 98-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2017.02.007XI Z J, YANG F Q, GAO J, et al. The research on the influence of magnet current towards the ion thruster thrust[J]. Vacuum and Cryogenics, 2017, 23(2): 98-101(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2017.02.007 [8] 胡竟, 杨福全, 郭德洲, 等. 基于CFD的10 cm氙离子推力器阳极推进剂供给方式优化[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(8): 1476-1484.HU J, YANG F Q, GUO D Z, et al. Optimization of anode propellant allocation manner of 10 cm xenon ion thruster based on CFD[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(8): 1476-1484(in Chinese). [9] 胡竟, 杨福全, 郭德洲, 等. 10 cm氙离子推力器变推力特性研究[J]. 推进技术, 2020, 41(10): 2382-2389. doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.190562HU J, YANG F Q, GUO D Z, et al. Analysis on variable-thrust characteristic of 10 cm xenon ion thruster[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2020, 41(10): 2382-2389(in Chinese). doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.190562 [10] BROPHY J R. Ion thruster performance model: NASA CR-174810 [R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 1984. [11] WILBUR P J, BROPHY J R. The effect of discharge chamber wall temperature on ion thruster performance[J]. AIAA Journal, 1986, 24(2): 278-283. doi: 10.2514/3.9257 [12] KERSLAKE W R, GOLDMAN R G, NIEBERDING W C. SERT II - Mission, thruster performance, and in-flight thrust measurements[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 1971, 8(3): 213-224. doi: 10.2514/3.30250 [13] BECHTEL R. The 30 cm J series mercury bombardment thruster: AIAA1981-714[R]. Reston: AIAA, 1981. [14] HIATT J, WILBUR P. Ring cusp discharge chamber performance optimization: AIAA1985-2007[R]. Reston: AIAA, 1985. [15] OGUNJOBI T A, MENART J A. Computational study of ring-cusp magnet configurations that provide maximum electron confinement: AIAA-2006-4489[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2006. [16] BENNETT W, OGUNJOBI T A, MENART J A. Computational study of the effects of cathode placement, electron energy, and magnetic field strength on the confinement of electrons: AIAA-2007-5248 [R]. Reston: AIAA, 2007. [17] MENART J A, PATIERSON M J. Magnetic circuit for enhanced discharge chamber performance of a small ion thruster: AIAA-1998-3343 [R]. Reston: AIAA, 1998. [18] 陈娟娟, 张天平, 贾艳辉, 等. 不同磁感强度下LIPS-200离子推力器放电室性能的研究[J]. 真空与低温, 2013, 19(3): 163-167. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2013.03.009CHEN J J, ZHANG T P, JIA Y H, et al. The study of the effect of magnetic field strength on the performance of the LIPS-200 ion thruster[J]. Vacuum and Cryogenics, 2013, 19(3): 163-167(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2013.03.009 [19] 陈娟娟, 张天平, 贾艳辉, 等. 20 cm氙离子推力器放电室性能优化[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2012, 24(10): 2469-2473. doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122410.2469CHEN J J, ZHANG T P, JIA Y H, et al. Performance optimization of 20 cm xenon ion thruster discharge chamber[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 24(10): 2469-2473(in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122410.2469 [20] 孙明明, 张天平, 吴先明. 20 cm离子推力器放电室流场计算模拟[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27(5): 206-212.SUN M M, ZHANG T P, WU X M. Flow field simulation of 20 cm diameter ion thruster discharge chamber[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27(5): 206-212(in Chinese). [21] 吴先明, 张天平, 陈娟娟, 等. 磁路对30 cm离子推力器性能影响研究[J]. 推进技术, 2016, 37(1): 193-200. doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.2016.01.025WU X M, ZHANG T P, CHEN J J, et al. Study on effects of magnetic circuit on performance of 30 cm diameter ion thruster[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2016, 37(1): 193-200(in Chinese). doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.2016.01.025 [22] 鹿畅, 夏广庆, 孙斌. 环型离子推力器放电室参数对推力器性能的影响[J]. 真空与低温, 2022, 28(1): 39-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2022.01.005LU C, XIA G Q, SUN B. Effect of discharge chamber parameters of annular ion thruster on the performance[J]. Vacuum and Cryogenics, 2022, 28(1): 39-47(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2022.01.005 [23] 鹿畅, 梁学明, 夏广庆, 等. 环型离子推力器放电机理研究进展[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2021, 44(2): 215-222.LU C, LIANG X M, XIA G Q, et al. Research progress on discharge mechanism of annular ion thruster[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2021, 44(2): 215-222(in Chinese). [24] DAVID H M. Factors affecting the beam divergence of a T5 ion engine: IEPC-1997-095 [R]. Washington, D. C. : IEPC, 1997: 1-8. [25] BROPHY J R, WILBUR P J. Baffle aperture design model for electron bombardment thrusters[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 1982, 19(6): 586-591. doi: 10.2514/3.62305 [26] MILLIGAN D J, GABRIEL S B. Investigation of the baffle annulus region of the UK25 ion thruster: AIAA-1999-2440 [R]. Reston: AIAA, 1999. [27] RAWLIN V, WILLIAMS G, PIÑERO L. Status of ion engine development for high power, high specific impulse missions: IEPC-2001-096 [R]. Washington, D. C.: IEPC, 2001: 1-17. [28] BROPHY J R. Ion engine service life validation by analysis and testing: AIAA-1996-2715[R]. Reston: AIAA, 1996. -







 下载:
下载: