Analysis on feasibility of detecting water blooms in Taihu Lake with spaceborne GNSS-R
-
摘要:
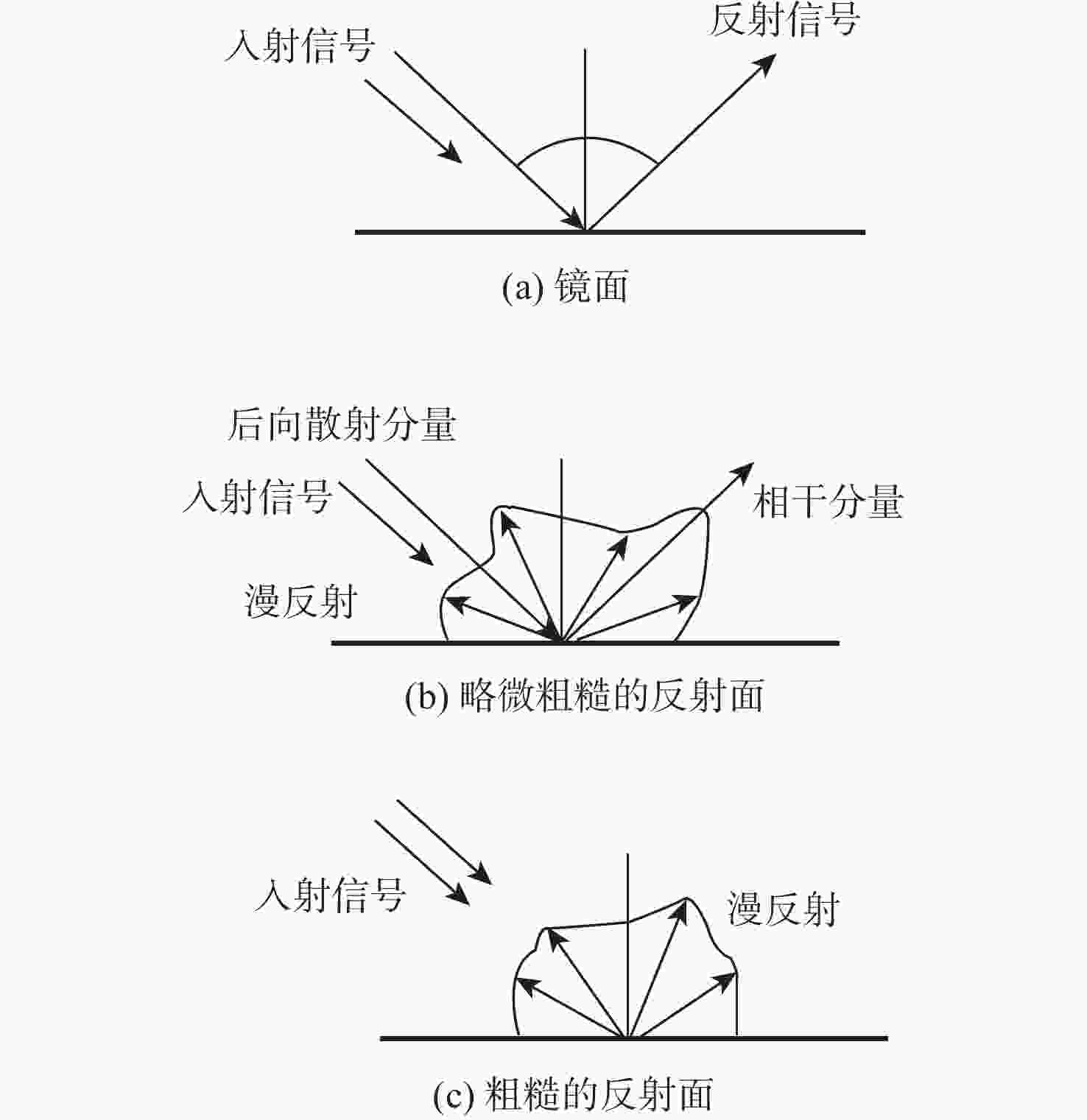
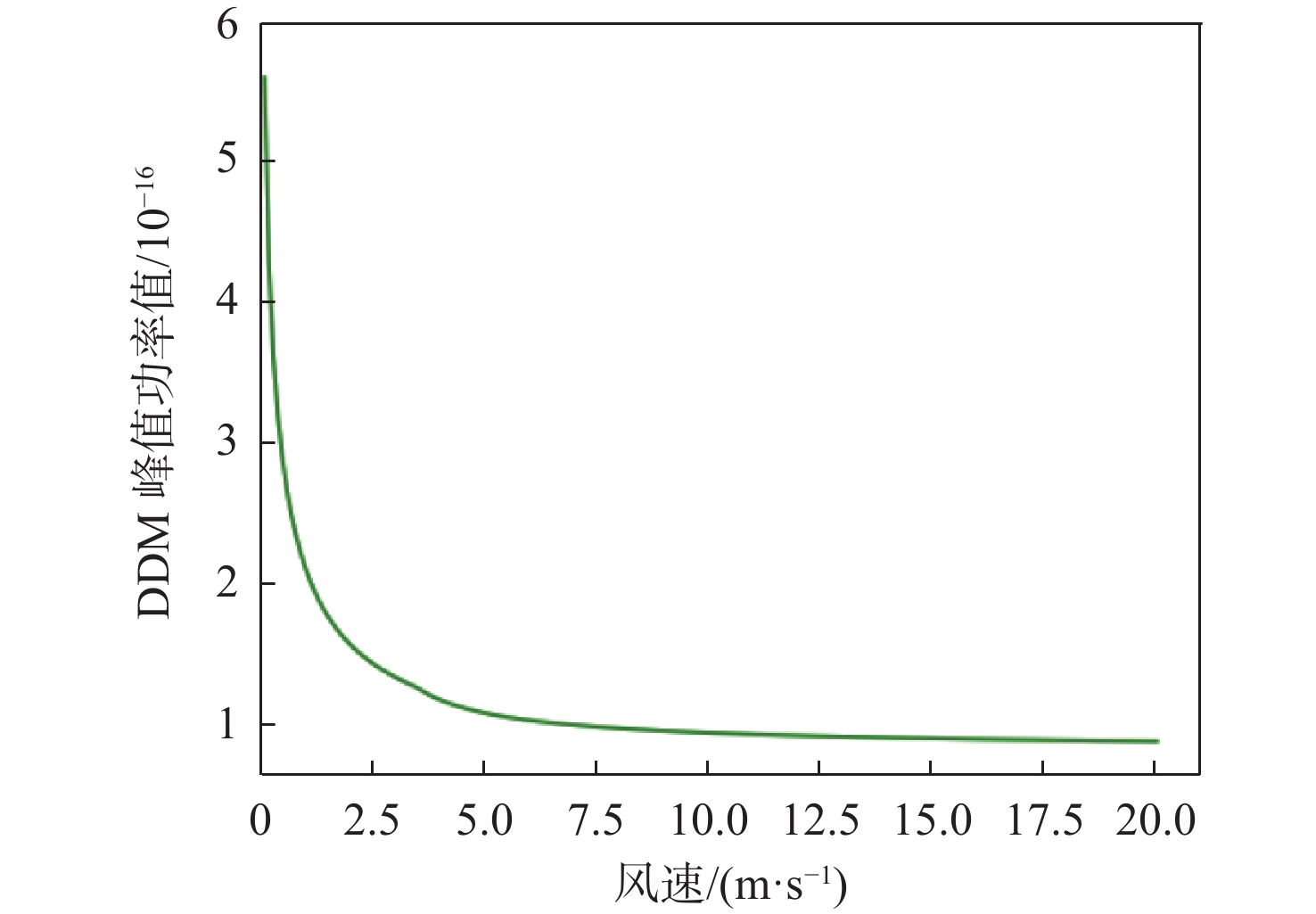
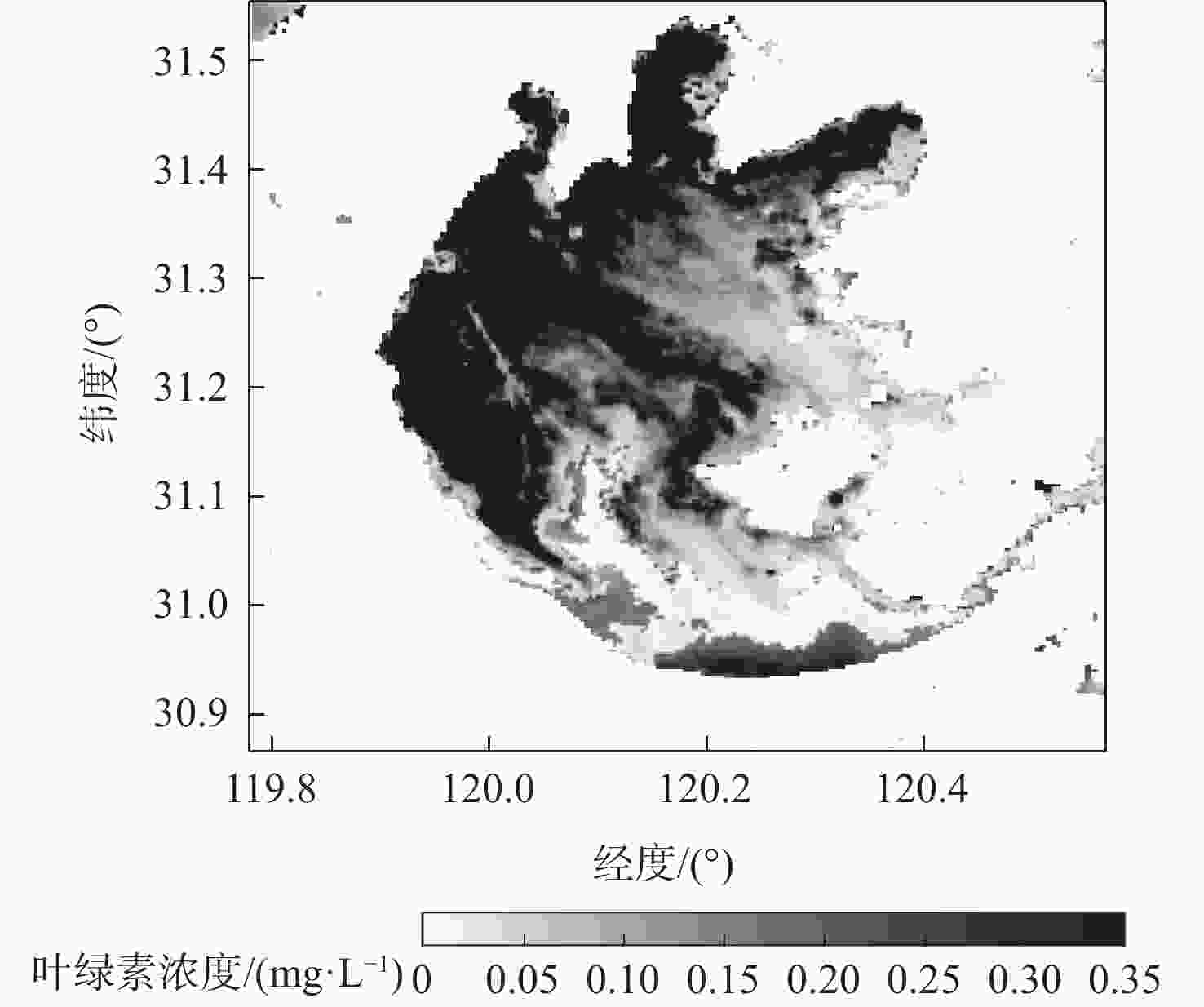
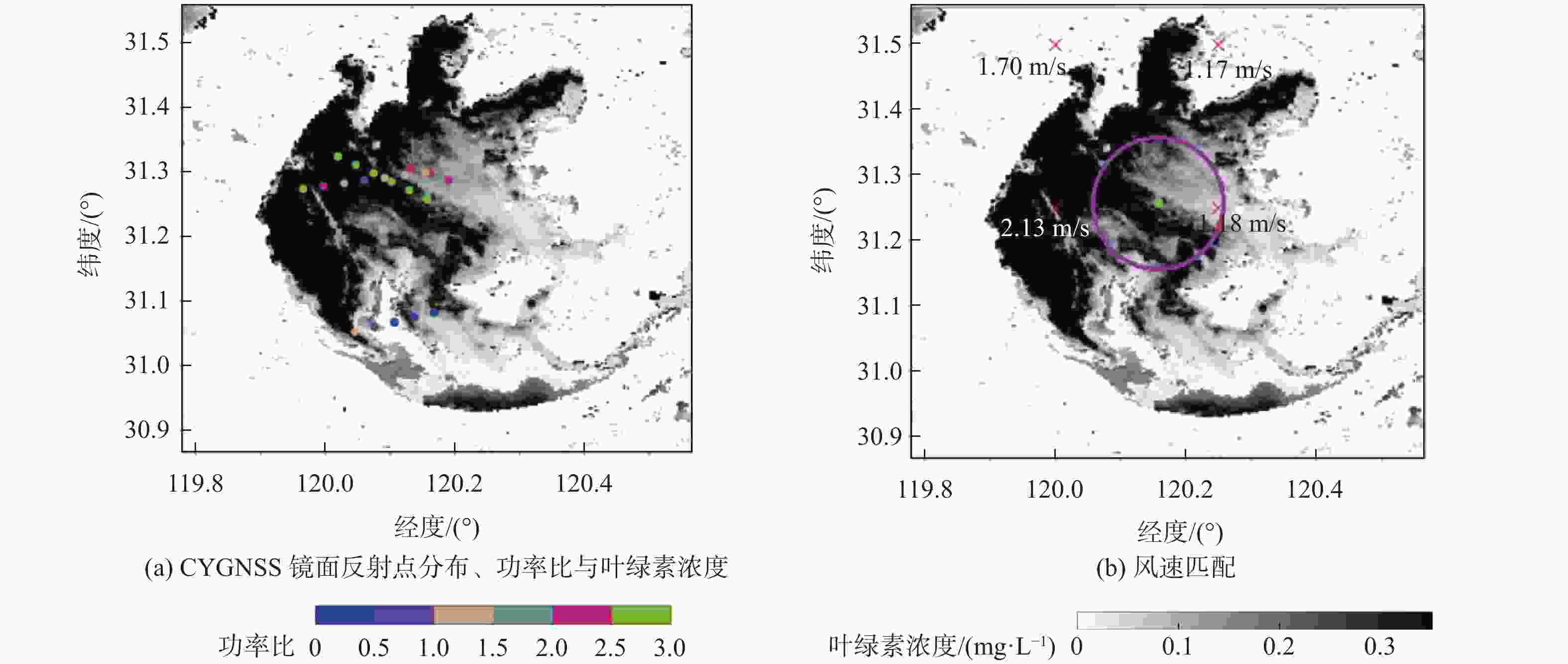
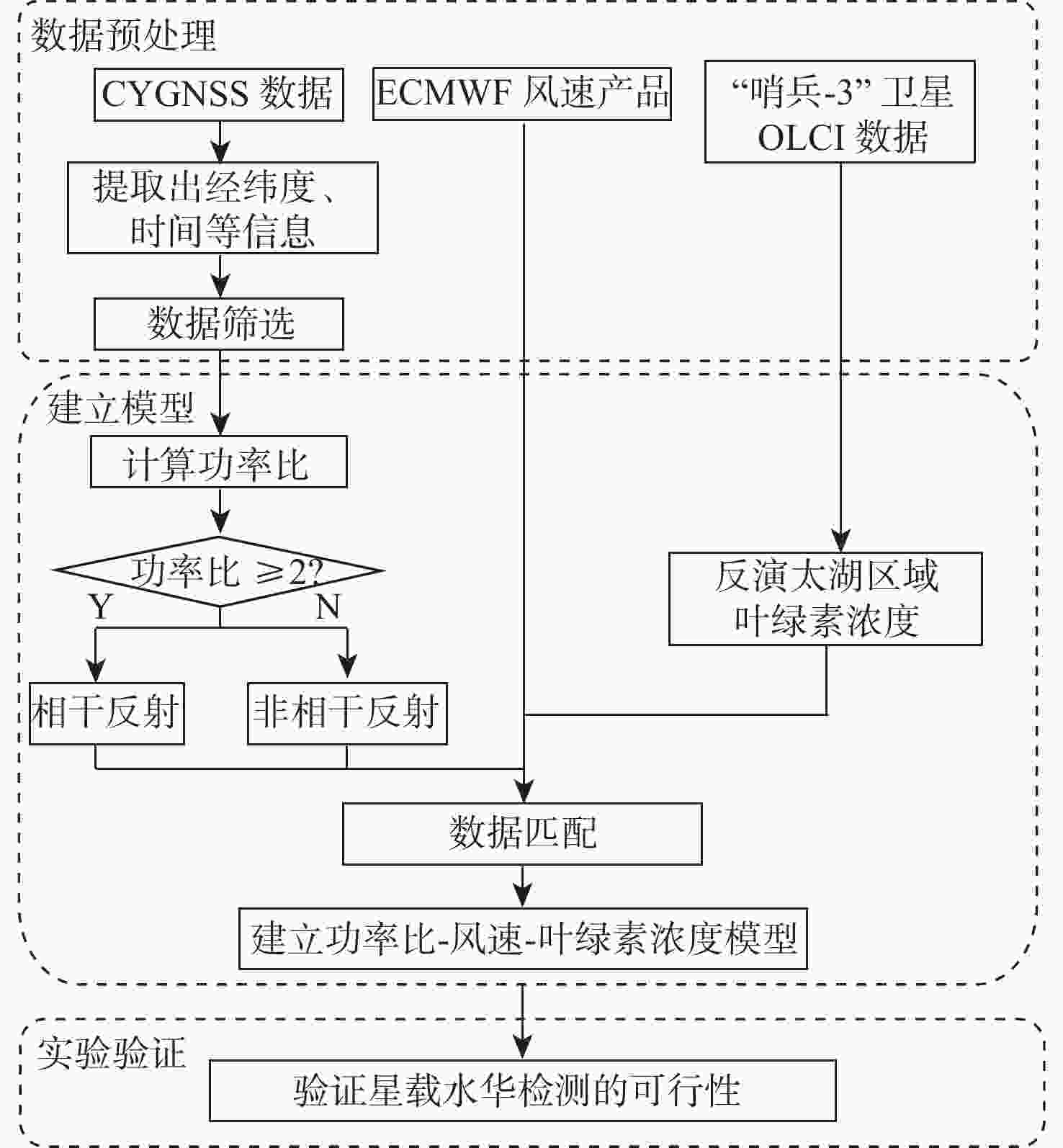
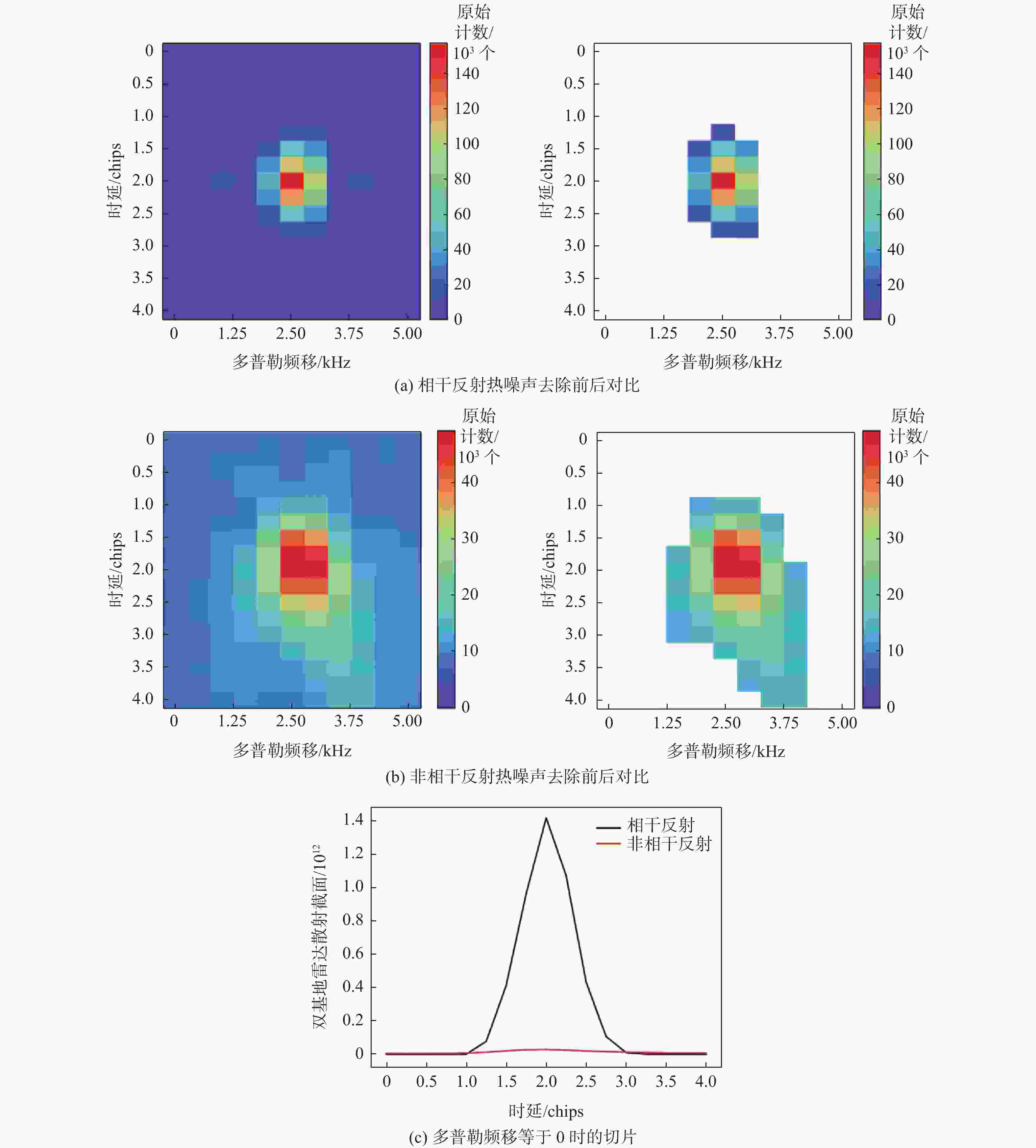
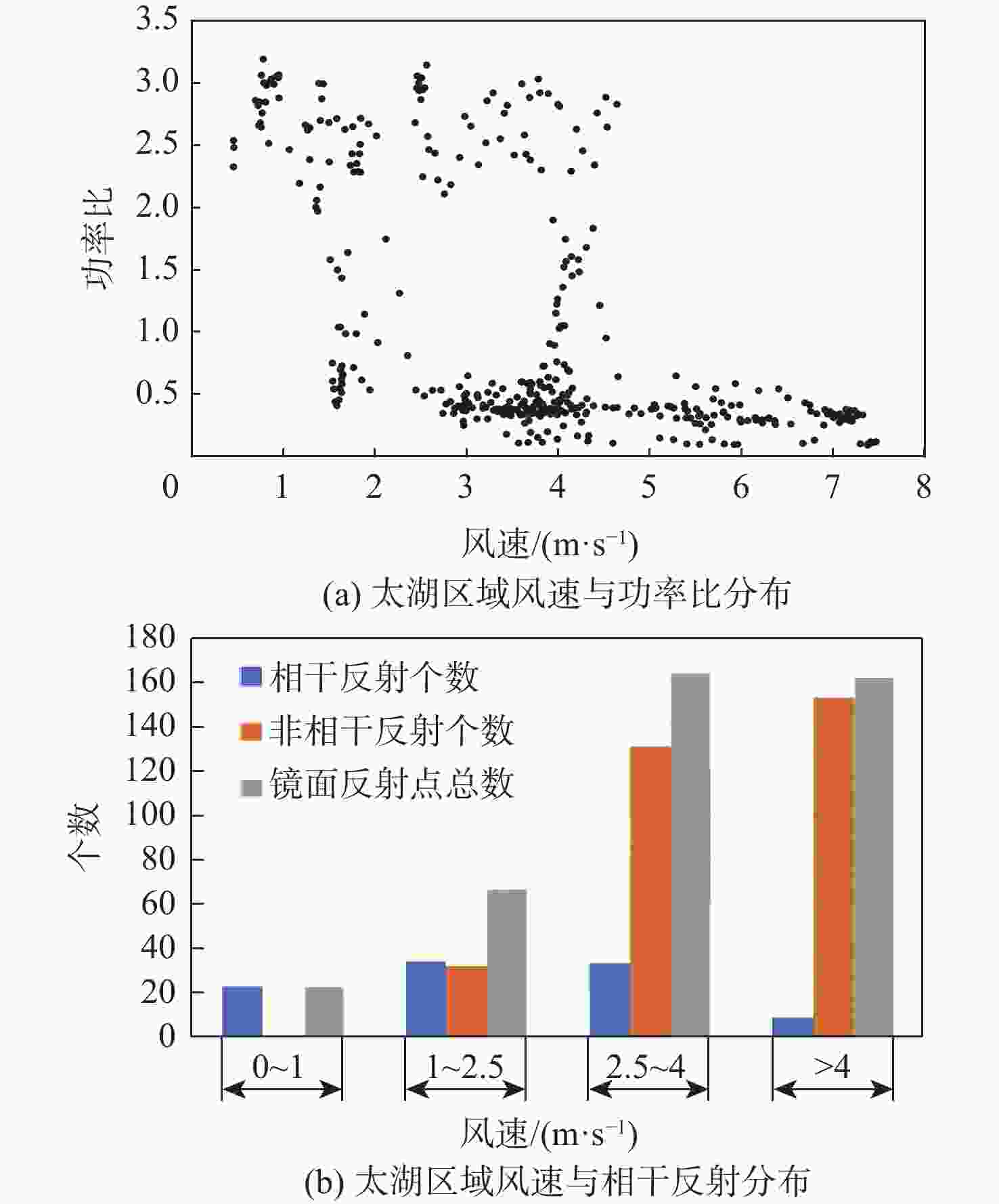
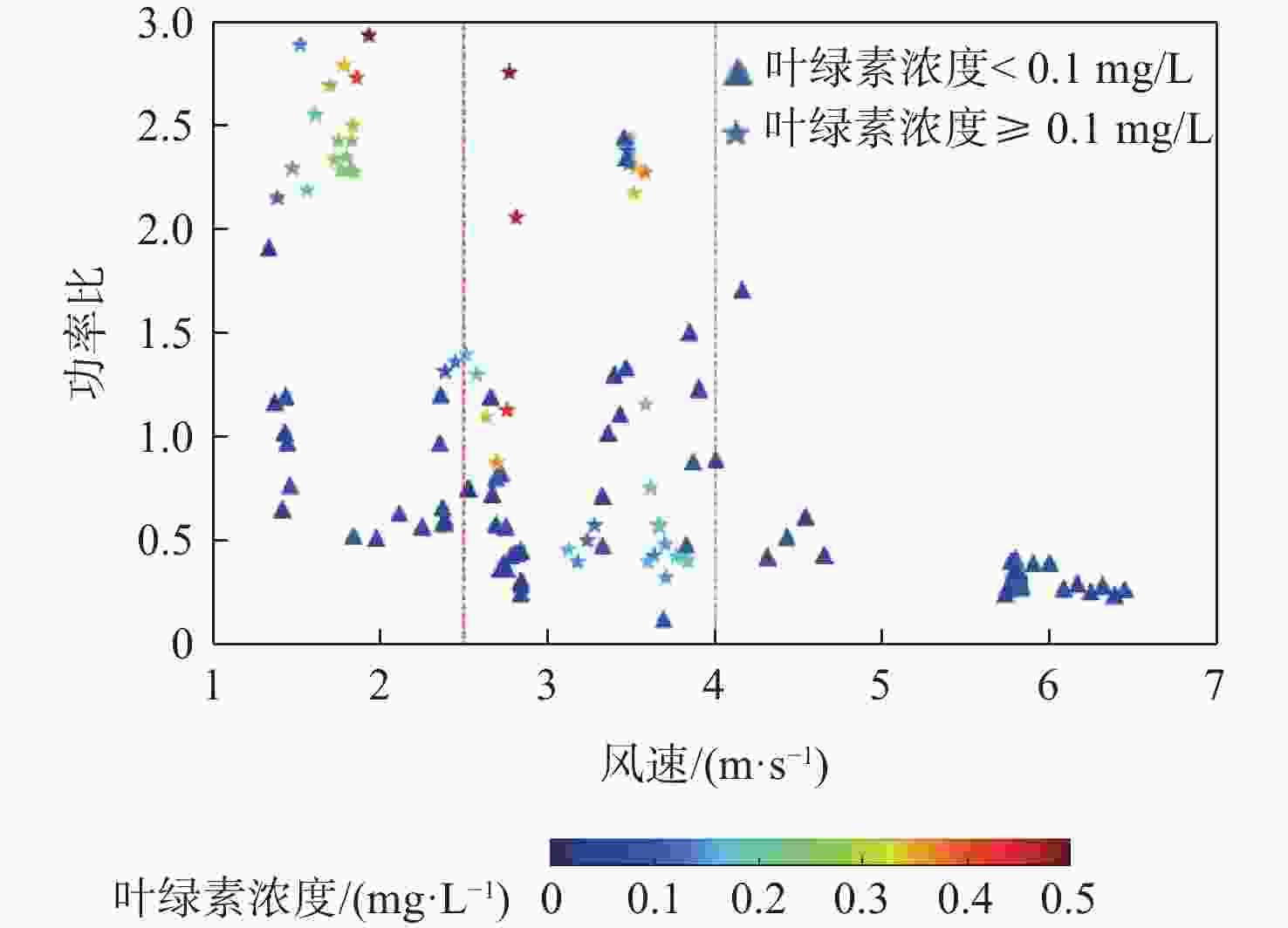
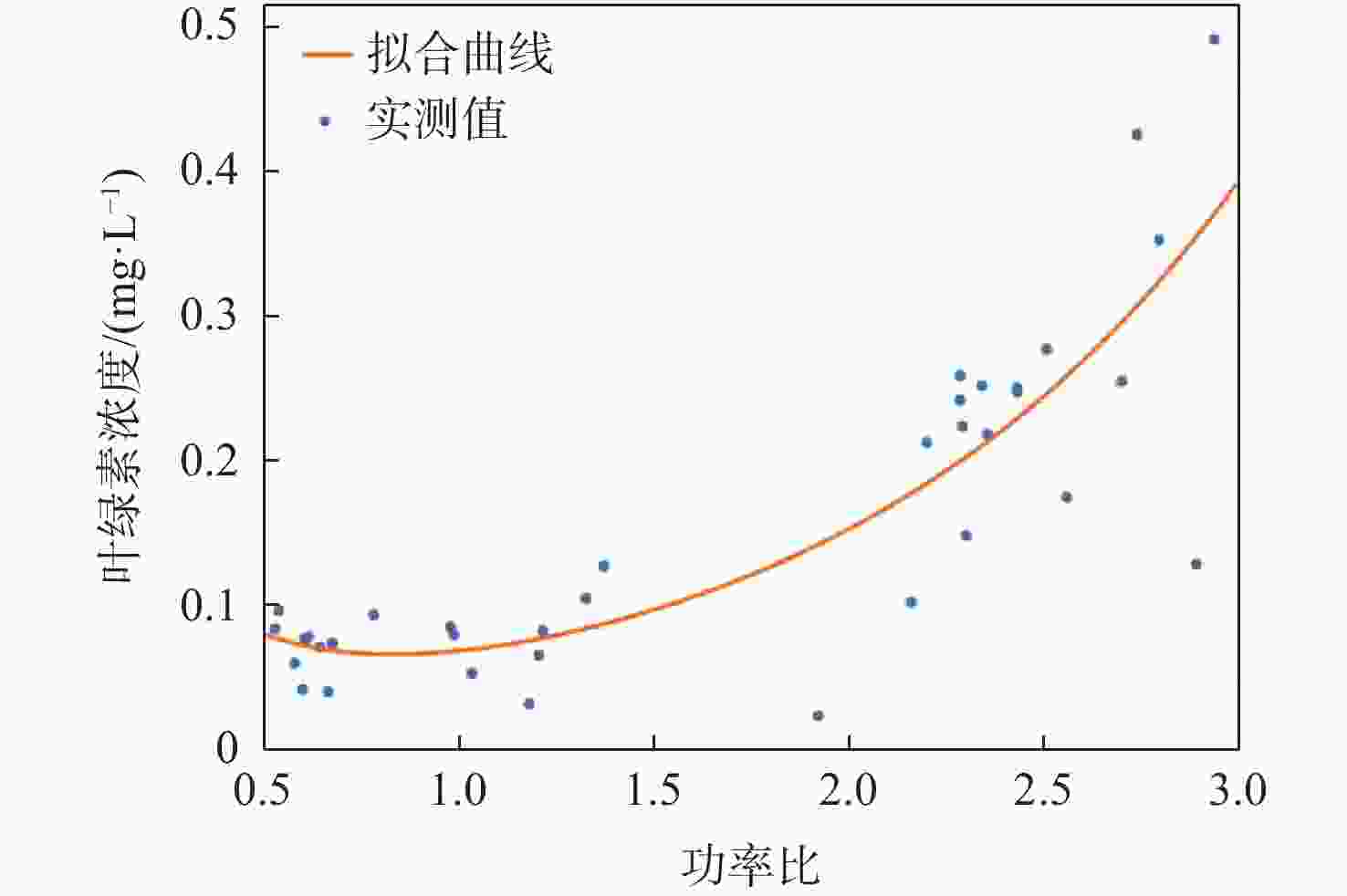
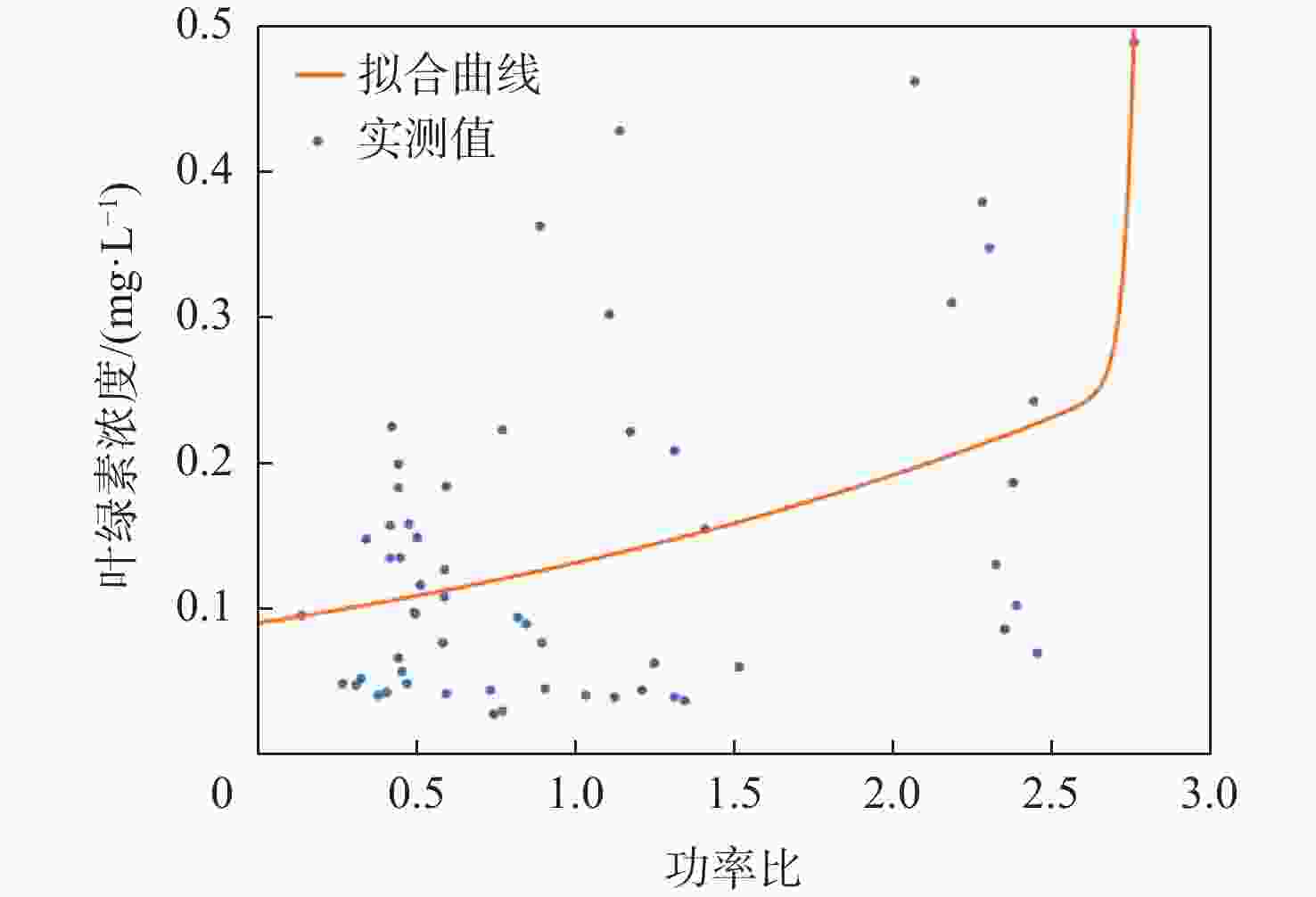
星载全球导航卫星系统反射信号(GNSS-R)属于被动遥感技术,具有数据重访周期高、全天时、全天候、信号源丰富等优势。基于此,研究星载GNSS-R检测太湖水华的可行性。星载GNSS-R可以有效检测反射面的粗糙程度,通过使用相干反射表征反射面的粗糙度,研究不同风速区间内相干反射与蓝藻水华的关系。利用2020年4—8月美国气旋全球导航卫星系统(CYGNSS)数据,计算CYGNSS镜面反射点的时延多普勒图(DDM)功率比。以“哨兵-3”卫星水色遥感仪器(OLCI) 影像最大特征峰高度(MPH)算法反演出的太湖叶绿素浓度作为参照,与欧洲中期天气预报中心(ECMWF)的风速产品进行时空间线性匹配,分析发现,在1~2.5 m/s风速区间内,叶绿素浓度达到0.1 mg/L以上时,极易引起镜面反射点发生相干反射,且功率比与叶绿素浓度的相关系数为0.84,具有良好的相关性。实验结果证明了利用星载GNSS-R的功率比及相关特性实现太湖水华检测的可行性。
-
关键词:
- 气旋全球导航卫星系统 /
- 全球导航卫星系统反射信号 /
- 功率比 /
- 水色遥感仪器 /
- 最大特征峰高度算法
Abstract:Spaceborne global navigation satellite system-reflectometry (GNSS-R) is a passive remote sensing technology with the advantages of high data revisit cycle, all-day coverage, all-weather services, and abundant signal sources. Based on this, the feasibility of detecting water blooms in the Taihu Lake by on-board GNSS-R is studied. Spaceborne GNSS-R can effectively detect the roughness of the reflective surface. By using coherent reflection to characterize the roughness of the reflective surface, the relationship between coherent reflection and cyanobacterial blooms in different wind speed ranges is studied. The US cyclone global navigation satellite system (CYGNSS) is used to track the reflected signals of the global positioning system and calculate the power ratio of the delay Doppler map (DDM) of the CYGNSS mirror reflection point using CYGNSS data from April to August 2020. The chlorophyll concentration in Taihu Lake is used as a reference, retrieved from the maximum characteristic peak height (MPH) algorithm of the imagery from the ocean and land colour instrument (OLCI) aboard on “Sentinel-3” satellite. The time-space linear matching is also conducted with wind speed products of the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF). Data analysis shows that in the range of wind speed 1−2.5 m/s and with the chlorophyll concentration reaching more than 0.1 mg/L, coherent reflection tends to occur at the specular reflection point, and the correlation coefficient between the power ratio and the chlorophyll concentration is 0.84, which has a good correlation. Experimental results verify the feasibility of detecting the Taihu Lake water bloom using the power ratio and related features.
-
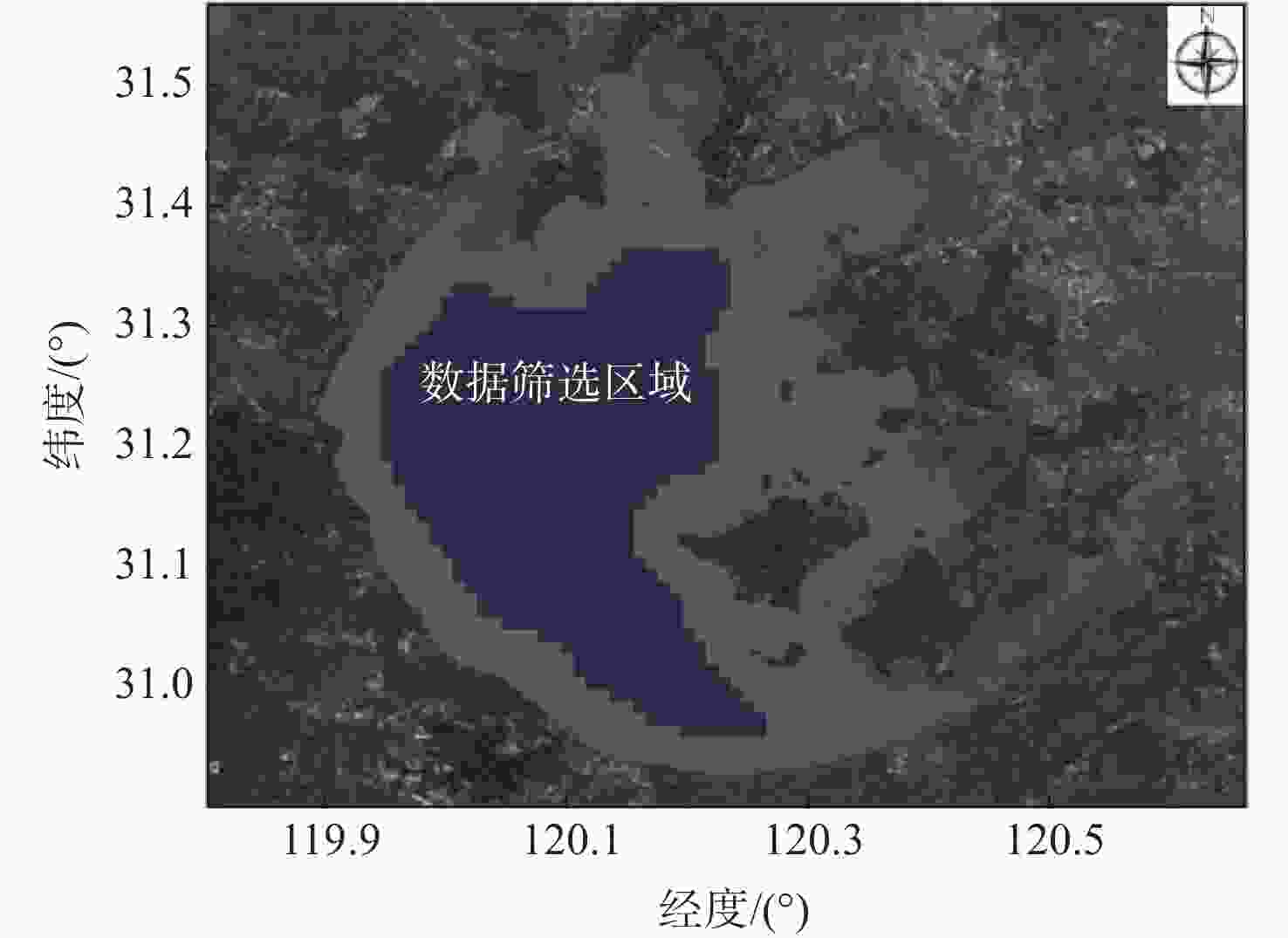
表 1 “哨兵-3”卫星光学影像与CYGNSS匹配后的数据量(风速≥1 m/s)
Table 1. Data volume of “Sentinel-3” satellite optical image after matching CYGNSS (wind speed ≥ 1 m/s)
日期 匹配前数据量 匹配后数据量 2020年4月20日 8 8 2020年4月28日 9 9 2020年4月29日 18 12 2020年5月3日 23 21 2020年5月13日 15 15 2020年5月19日 21 14 2020年6月30日 31 23 2020年8月2日 11 11 2020年8月25日 7 7 表 2 不同风速区间的异常数据统计
Table 2. Statistical of abnormal data in different wind speed intervals
风速区间/(m·s−1) 镜面反射点总数 异常数据数量 1~2.5 36 2 2.5~4 59 22 >4 25 0 -
[1] QIN B Q, ZHU G W, GAO G, et al. A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to climatic variability and lake management[J]. Environmental Management, 2010, 45(1): 105-112. doi: 10.1007/s00267-009-9393-6 [2] 张虎军, 宋挺, 朱冰川, 等. 太湖蓝藻水华暴发程度年度预测[J]. 中国环境监测, 2022, 38(1): 157-164. doi: 10.19316/j.issn.1002-6002.2022.01.15ZHANG H J, SONG T, ZHU B C, et al. Annual forecast of the extent of cyanobacteria bloom in Taihu Lake[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2022, 38(1): 157-164(in Chinese). doi: 10.19316/j.issn.1002-6002.2022.01.15 [3] 周立国, 冯学智, 王春红, 等. 太湖蓝藻水华的MODIS卫星监测[J]. 湖泊科学, 2008, 20(2): 203-207. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2008.02.011ZHOU L G, FENG X Z, WANG C H, et al. Monitoring cyanobacteria bloom based on MODIS data in Lake Taihu[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2008, 20(2): 203-207(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2008.02.011 [4] 李亚春, 孙佳丽, 谢志清, 等. 基于MODIS植被指数的太湖蓝藻信息提取方法研究[J]. 气象科学, 2011, 31(6): 737-741.LI Y C, SUN J L, XIE Z Q, et al. Extraction methods of cyanobacteria bloom in Lake Tai based on MODIS vegetation index[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences, 2011, 31(6): 737-741(in Chinese). [5] 马荣华, 孔繁翔, 段洪涛, 等. 基于卫星遥感的太湖蓝藻水华时空分布规律认识[J]. 湖泊科学, 2008, 20(6): 687-694. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2008.06.001MA R H, KONG F X, DUAN H T, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution of cyanobacteria blooms based on satellite imageries in Lake Taihu, China[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2008, 20(6): 687-694(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2008.06.001 [6] 李旭文, 张悦, 侍昊, 等. 基于哨兵-3A卫星OLCI数据的最大叶绿素指数在太湖蓝藻水华监测中的应用[J]. 中国环境监测, 2019, 35(3): 146-155. doi: 10.19316/j.issn.1002-6002.2019.03.19LI X W, ZHANG Y, SHI H, et al. Application of maximum chlorophyll index derived from Sentinel-3A satellite OLCI data for monitoring cyanobacteria blooms in Lake Taihu[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2019, 35(3): 146-155(in Chinese). doi: 10.19316/j.issn.1002-6002.2019.03.19 [7] 朱冰川, 尤凯, 石浚哲, 等. 基于GOCI数据的太湖叶绿素a浓度反演和蓝藻水华遥感监测[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(8): 1021-1025. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.08.017ZHU B C, YOU K, SHI J Z, et al. Retrieval of chlorophyll-a and remote sensing monitoring of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu Lake based on GOCI data[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2020, 42(8): 1021-1025(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.08.017 [8] WANG G L, LI J S, ZHANG B, et al. Monitoring cyanobacteria-dominant algal blooms in eutrophicated Taihu Lake in China with synthetic aperture radar images[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2015, 33(1): 139-148. doi: 10.1007/s00343-015-4019-8 [9] 陈立福, 刘燕芝, 张鹏, 等. 基于Multi-Path RefineNet的多特征高分辨率SAR图像道路提取算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2020, 47(3): 156-161. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.190100124CHEN L F, LIU Y Z, ZHANG P, et al. Road extraction algorithm of multi-feature high-resolution SAR image based on Multi-Path RefineNet[J]. Computer Science, 2020, 47(3): 156-161(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.190100124 [10] 汪航, 陈晓, 田晟兆, 等. 基于小样本学习的SAR图像识别[J]. 计算机科学, 2020, 47(5): 124-128. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.190400136WANG H, CHEN X, TIAN S Z, et al. SAR image recognition based on few-shot learning[J]. Computer Science, 2020, 47(5): 124-128(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.190400136 [11] 李凉海, 刘善伟, 周鹏, 等. SAR卫星组网观测技术与海洋应用研究进展[J]. 海洋科学, 2021, 45(5): 145-156.LI L H, LIU S W, ZHOU P, et al. Research progress of SAR satellite network observation technology and ocean application[J]. Marine Sciences, 2021, 45(5): 145-156(in Chinese). [12] RODRIGUEZ-ALVAREZ N, OUDRHIRI K. The bistatic radar as an effective tool for detecting and monitoring the presence of phytoplankton on the ocean surface[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(12): 2248. doi: 10.3390/rs13122248 [13] BAN W, ZHANG K F, YU K G, et al. Detection of red tide over sea surface using GNSS-R spaceborne observations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1-11. [14] 白晓华, 胡维平, 胡志新, 等. 2004年夏季太湖梅梁湾席状漂浮水华风力漂移入湾量计算[J]. 环境科学, 2005, 26(6): 57-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2005.06.011BAI X H, HU W P, HU Z X, et al. Importation of wind-driven drift of mat-like algae bloom into Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake in 2004 summer[J]. Environmental Science, 2005, 26(6): 57-60(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2005.06.011 [15] CAO H S, KONG F X, LUO L C, et al. Effects of wind and wind-induced waves on vertical phytoplankton distribution and surface blooms of microcystis aeruginosa in Lake Taihu[J]. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 2006, 21(2): 231-238. doi: 10.1080/02705060.2006.9664991 [16] 杨东凯, 张其善. GNSS反射信号处理基础与实践[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2012.YANG D K, ZHANG Q S. GNSS reflected signal processing: Fundamentals and applications[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2012(in Chinese). [17] ZAVOROTNY V U, VORONOVICH A G. Scattering of GPS signals from the ocean with wind remote sensing application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(2): 951-964. doi: 10.1109/36.841977 [18] GLEASON S, RUF C S, CLARIZIA M P, et al. Calibration and unwrapping of the normalized scattering cross section for the cyclone global navigation satellite system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(5): 2495-2509. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2502245 [19] BOWEN C C, JENSEN T E. Blue-green algae: Fine structure of the gas vacuoles[J]. Science, 1965, 147(3664): 1460-1462. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3664.1460 [20] CAMPS A. Spatial resolution in GNSS-R under coherent scattering[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(1): 32-36. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2916164 [21] AL-KHALDI M M, JOHNSON J T, GLEASON S, et al. An algorithm for detecting coherence in cyclone global navigation satellite system mission level-1 delay-Doppler maps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(5): 4454-4463. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3009784 [22] 刘奇, 张双成, 南阳, 等. 利用星载GNSS-R相干信号探测南亚洪水[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2021, 46(11): 1641-1648.LIU Q, ZHANG S C, NAN Y, et al. Flood detection of south Asia using spaceborne GNSS-R coherent signals[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(11): 1641-1648(in Chinese). [23] KATZBERG S J, TORRES O, GANOE G. Calibration of reflected GPS for tropical storm wind speed retrievals[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(18): 122-140. [24] ZHANG Y, YIN J W, YANG S H, et al. High wind speed inversion model of CYGNSS sea surface data based on machine learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(16): 3324. doi: 10.3390/rs13163324 [25] 杨柳燕, 杨欣妍, 任丽曼, 等. 太湖蓝藻水华暴发机制与控制对策[J]. 湖泊科学, 2019, 31(1): 18-27. doi: 10.18307/2019.0102YANG L Y, YANG X Y, REN L M, et al. Mechanism and control strategy of cyanobacterial bloom in Lake Taihu[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2019, 31(1): 18-27(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2019.0102 [26] GEREMIA-NIEVINSKI F, SILVA M F E, BONIFACE K, et al. GPS diffractive reflectometry: Footprint of a coherent radio reflection inferred from the sensitivity kernel of multipath SNR[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(10): 4884-4891. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2579599 [27] 李云梅, 黄家柱, 韦玉春, 等. 湖泊富营养化状态的地面高光谱遥感评价[J]. 环境科学, 2006, 27(9): 1770-1775. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2006.09.013LI Y M, HUANG J Z, WEI Y C, et al. Evaluating eutrophic state of Taihu Lake by in situ hyperspectra[J]. Environmental Science, 2006, 27(9): 1770-1775(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2006.09.013 [28] 李旭文, 姜晟, 张悦, 等. “哨兵-3”卫星OLCI影像MPH算法反演太湖叶绿素a及藻草区分的研究[J]. 环境监控与预警, 2019, 11(5): 59-65.LI X W, JIANG S, ZHANG Y, et al. Maximum peak height (MPH) algorithm applied to Sentinel-3 OLCI data for retrieving chlorophyll-a and distinguishing cyanobacteria and floating vegetation areas in Lake Taihu[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning, 2019, 11(5): 59-65(in Chinese). [29] MATTHEWS M W, ODERMATT D. Improved algorithm for routine monitoring of cyanobacteria and eutrophication in inland and near-coastal waters[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2015, 156: 374-382. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2014.10.010 [30] RUF C, GLEASON S, JELENAK Z, et al. The NASA EV-2 cyclone global navigation satellite system (CYGNSS) mission[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 1-7. -






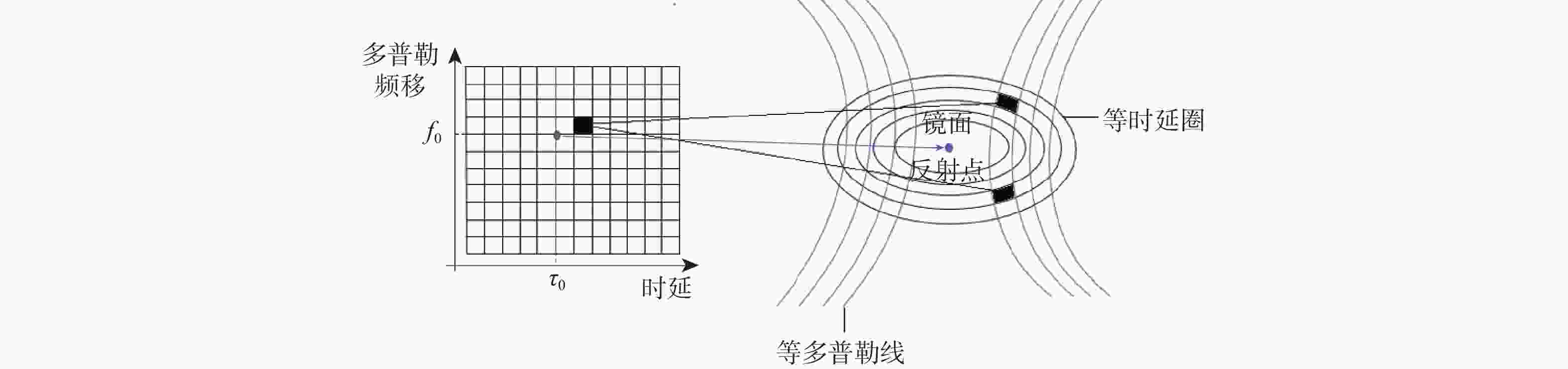
 下载:
下载: