-
摘要:
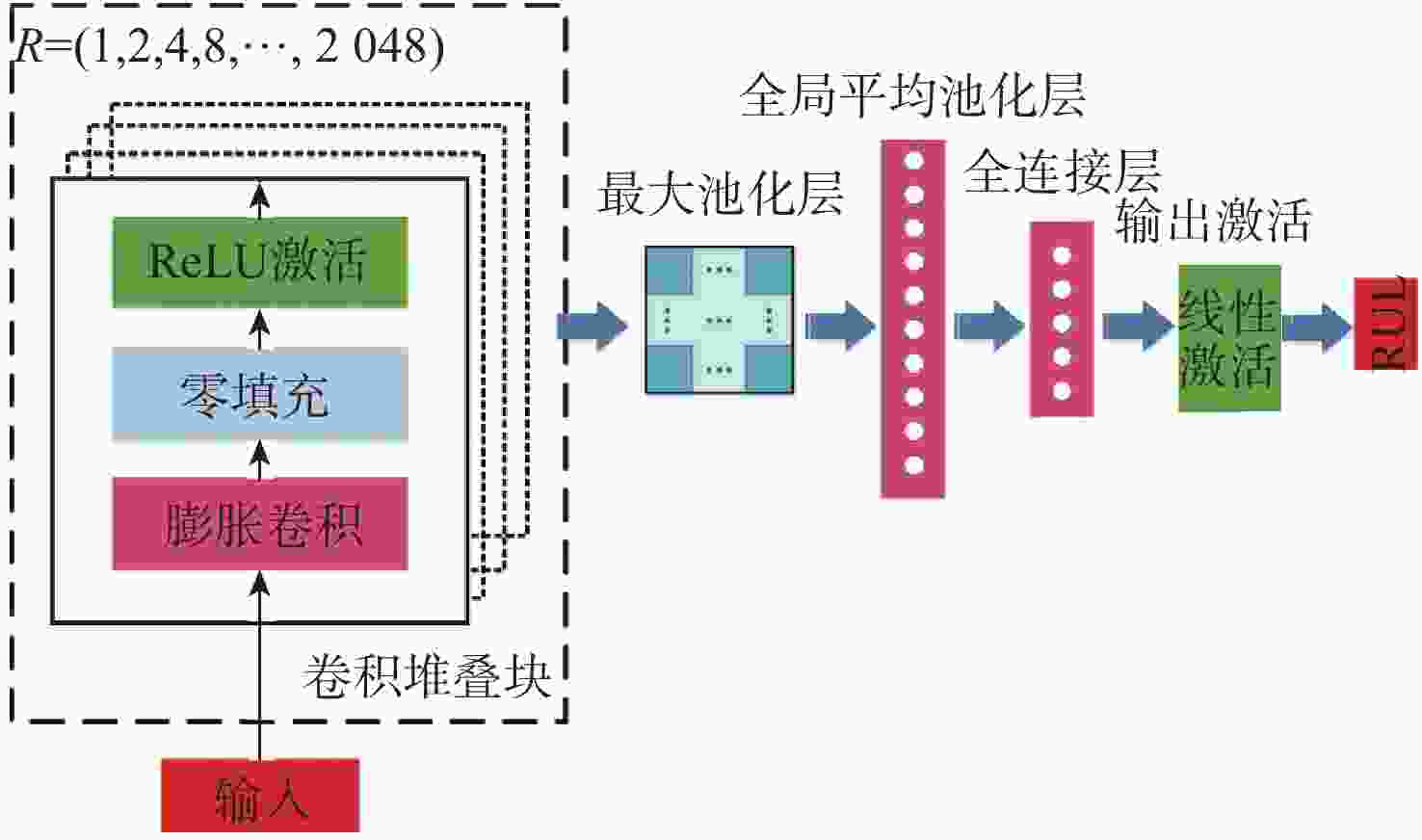
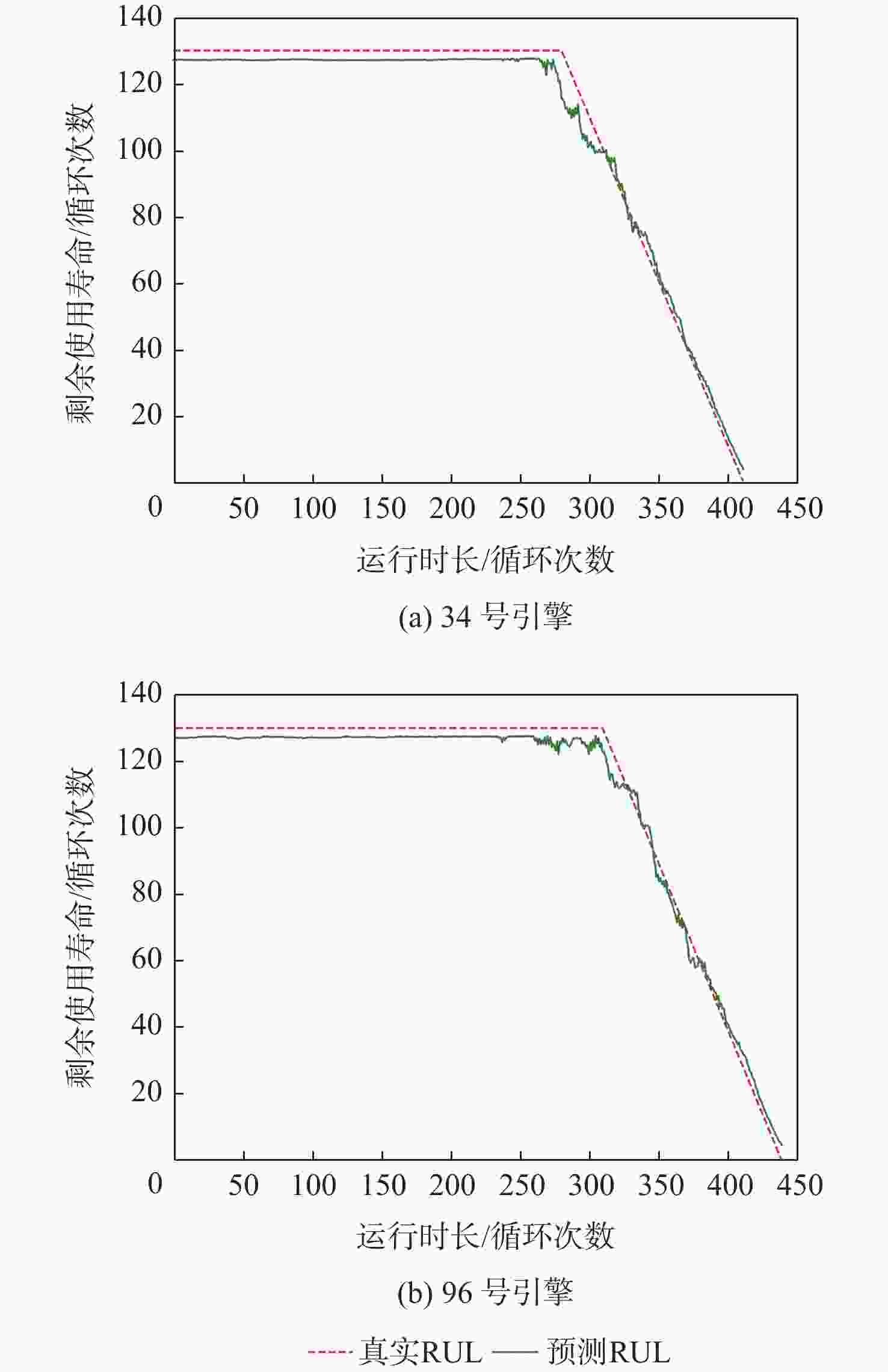
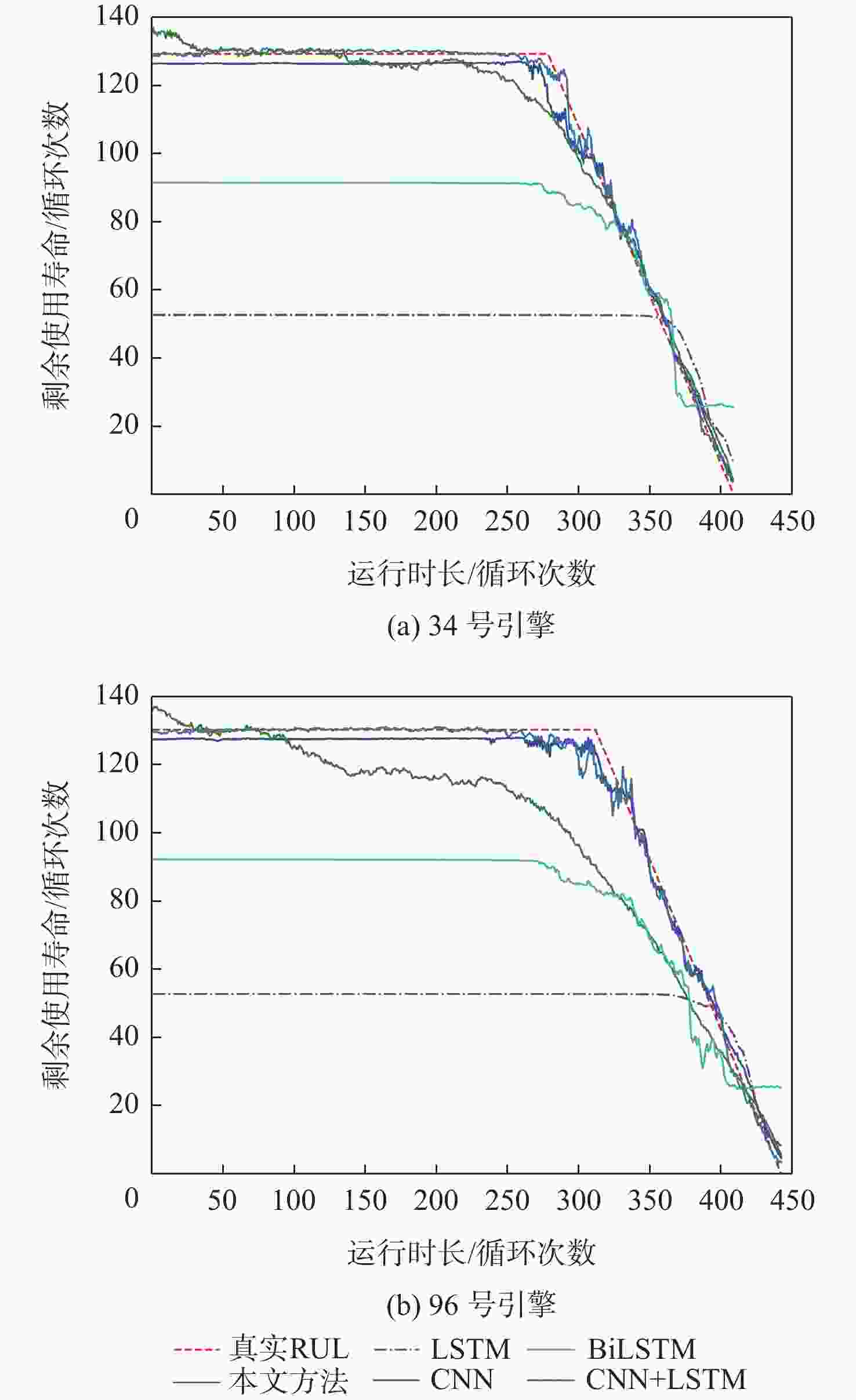
针对多传感器长序列数据下航空发动机剩余使用寿命预测方法存在预测准确度不足的问题,提出一种基于堆叠膨胀卷积神经网络(SDCNN)的航空发动机剩余使用寿命预测方法。将多传感器长序列数据归一化处理,降低因量纲和取值范围不同引起的误差;构建预测目标函数表征航空发动机的真实退化情况;搭建基于SDCNN的预测模型,扩大模型感受野,提取数据中的长期、深层和全局时序特征用于回归分析,得到航空发动机的剩余使用寿命预测结果;采用Hyperband优化算法和StratifiedKFold交叉验证方法优化模型,提升模型预测准确度和不同条件下的适应性,并采用商用模块化航空推进系统仿真(C-MAPSS)数据集验证所提方法的有效性。在C-MAPSS中FD003数据集上的实验结果表明:所提方法可有效提高基于长序列的航空发动机剩余使用寿命预测准确度,模型预测准确度得分指标明显降低32.62%。
-
关键词:
- 堆叠膨胀卷积 /
- 剩余使用寿命预测 /
- Hyperband超参数优化算法 /
- 航空发动机 /
- 长序列信号
Abstract:A method for forecasting the remaining useful life of an aero-engine based on a stack-dilated convolution neural network (SDCNN) was presented in order to address the inadequate prediction accuracy of the engine’s useful life with long-sequence data from many sensors.The multi-sensor long sequence data was normalized to eliminate errors caused by different dimensions and value ranges. A prediction objective function was constructed to represent the real degradation of the aero-engine. A degradation prediction model was built, based on SDCNN, and long-term, deep, and global time series features were extracted by expanding the receptive field of the model for regression analysis, and then the remaining useful life prediction result of aero-engine was obtained.The model’s hyperparameters were optimized using the Hyperband optimization algorithm and the StratifiedKFold cross-validation method to increase prediction accuracy and adaptability under various conditions. The commercial modular aero-propulsion system simulation (C-MAPSS) dataset was used to confirm the efficacy of the suggested method. The experimental results based on the FD003 dataset in C-MAPSS show that the proposed method can effectively improve the prediction accuracy of aero-engine remaining life based on long-sequence signals, and the score index to evaluate the prediction accuracy of the model is significantly reduced by 32.62%.
-
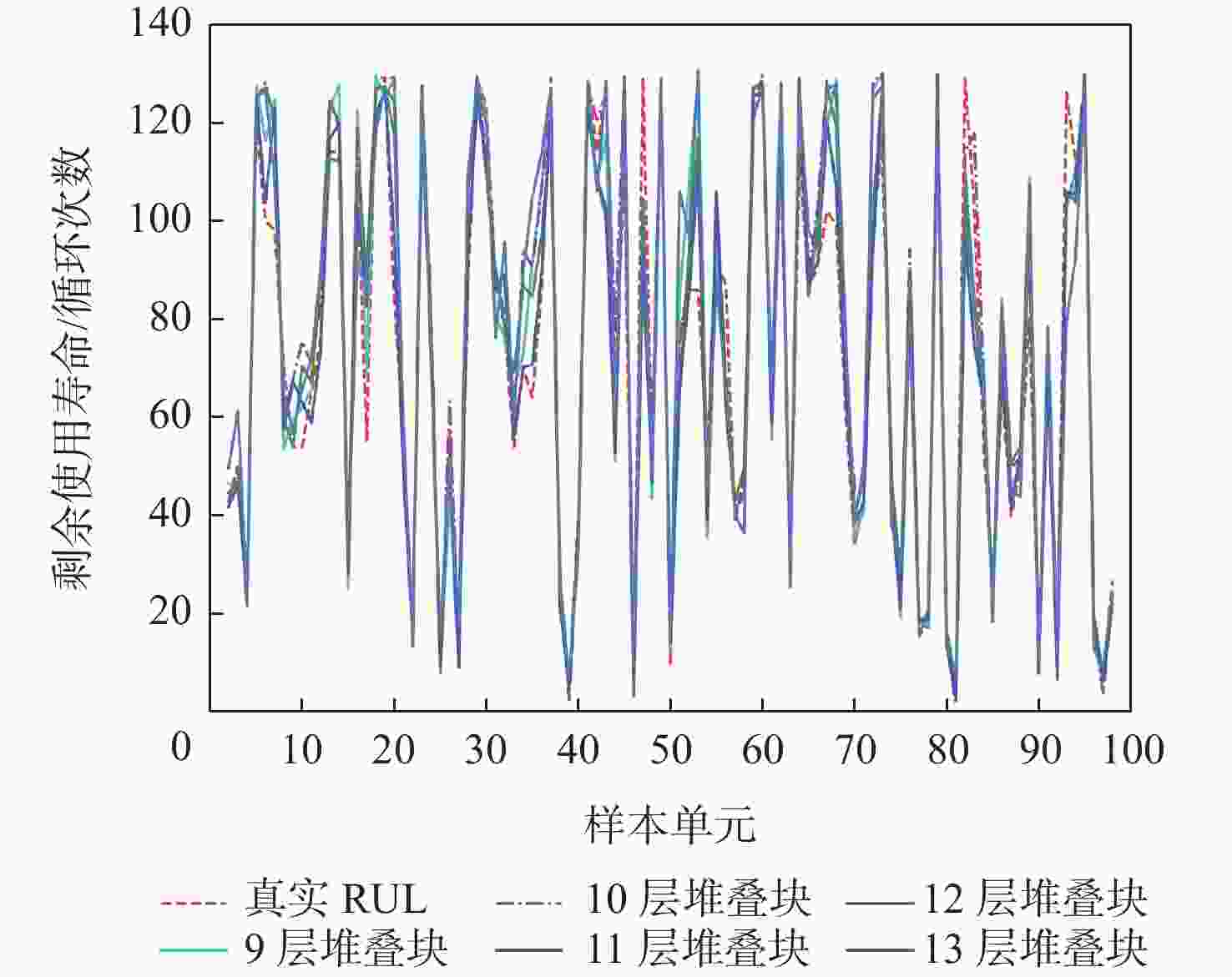
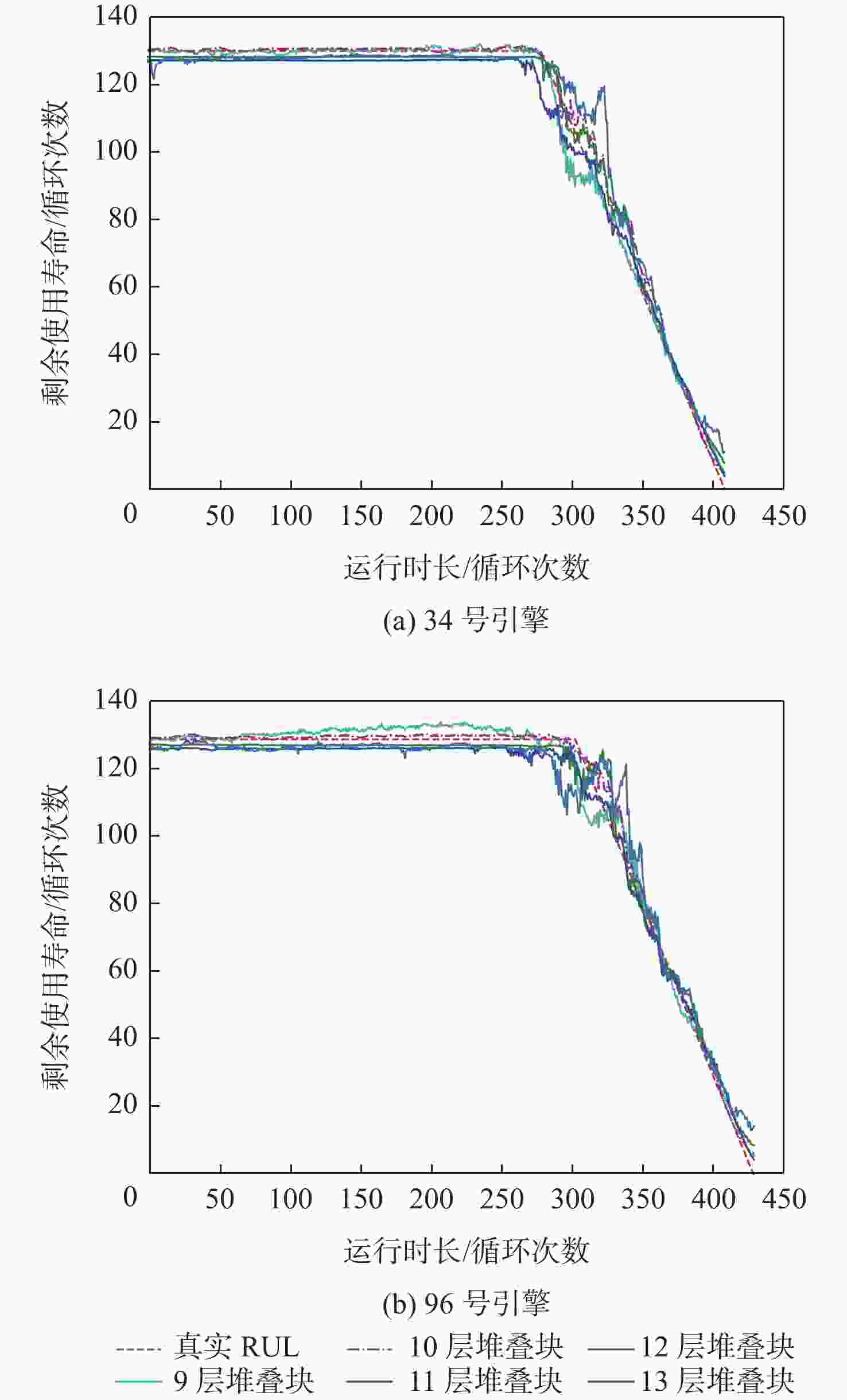
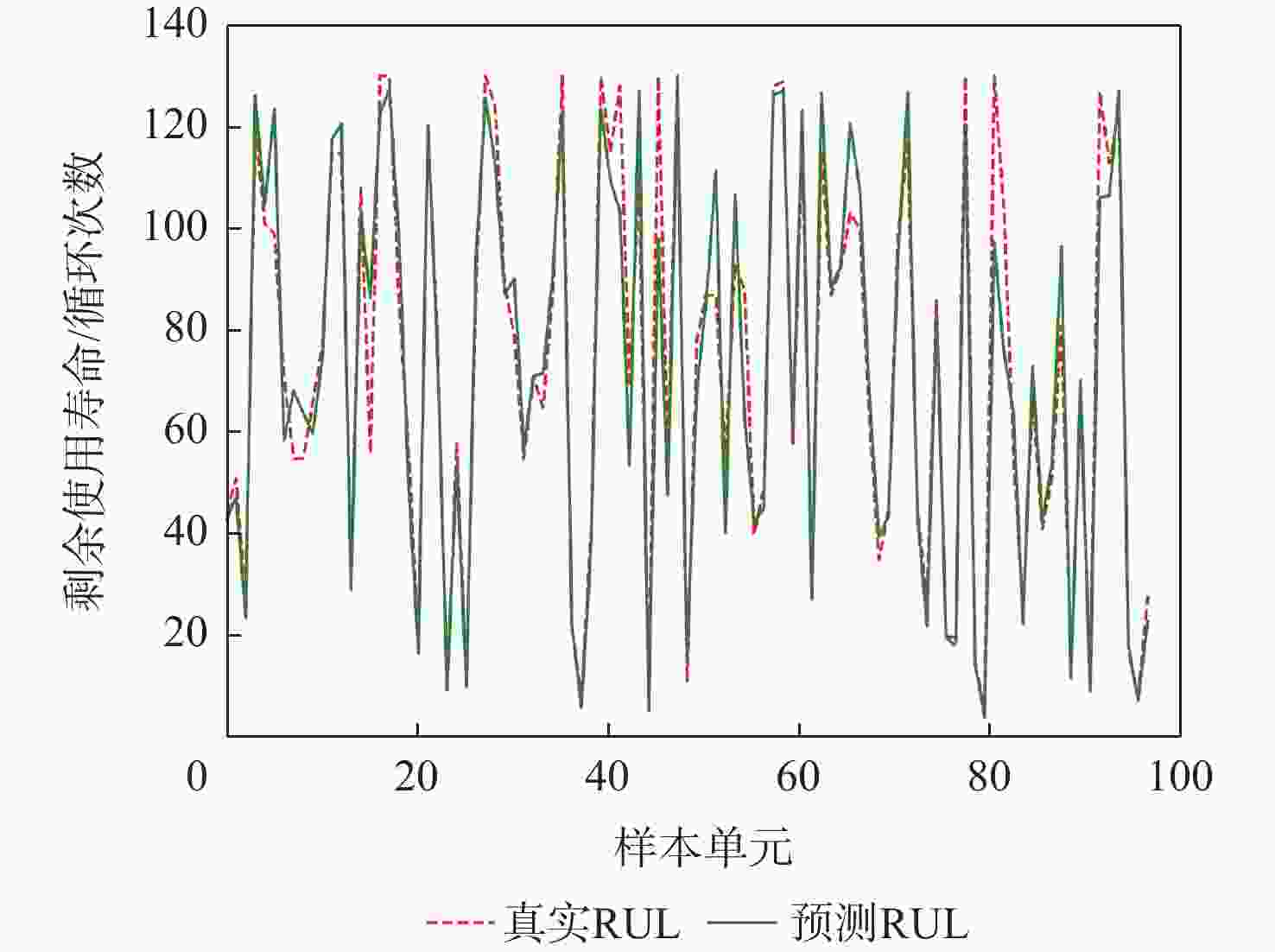
表 1 本文方法不同堆叠块的预测结果
Table 1. Prediction results for different stacked blocks in the proposed method
堆叠块层数 得分 均方根误差 9 91.10 10.55 10 80.05 10.20 11 73.41 10.42 12 37.41 9.01 13 107.81 11.75 表 2 本文方法与常用预测方法的实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results of the proposed method and commonly used prediction methods
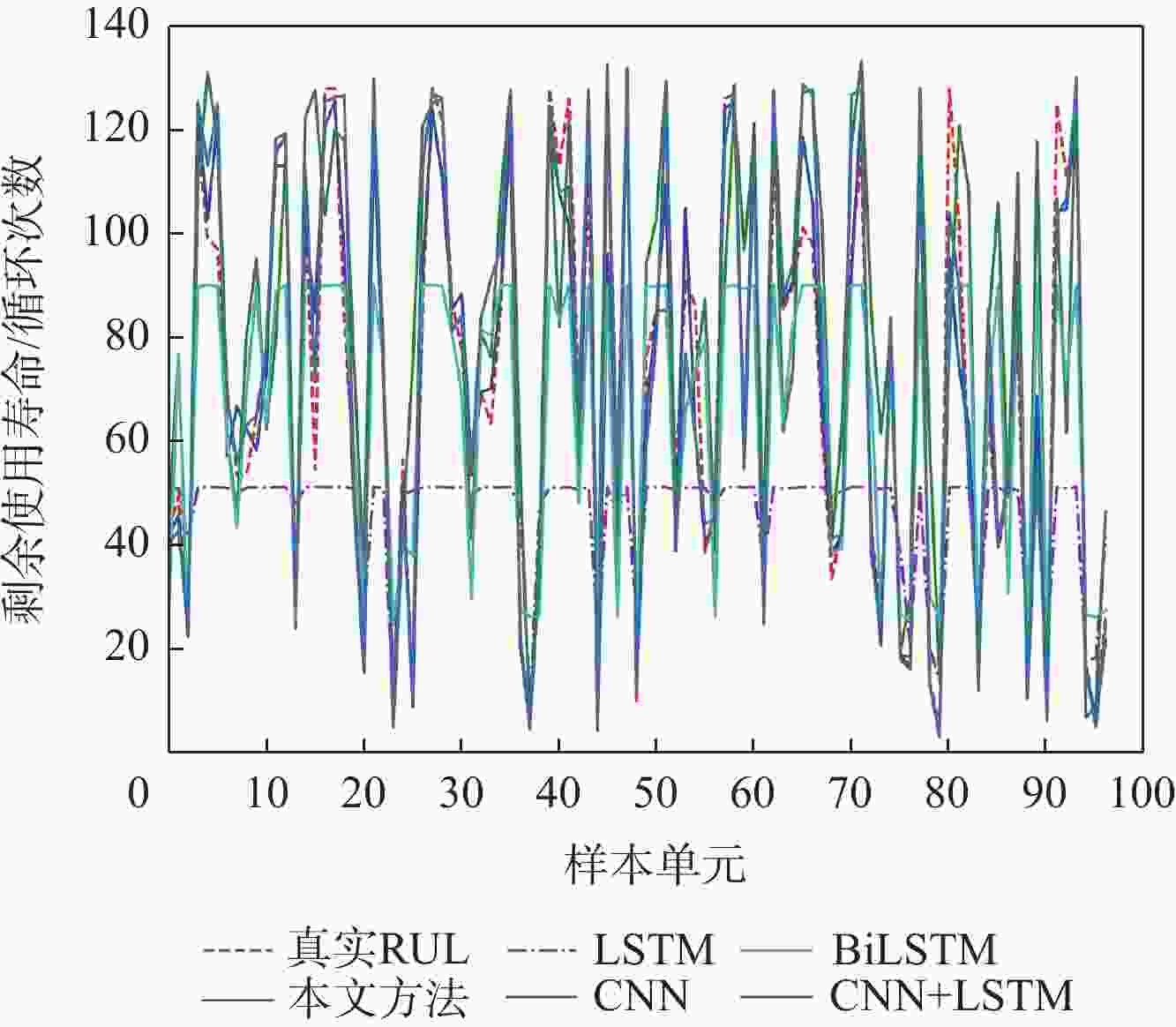
预测方法 得分 均方根误差 LSTM 1796.28 35.12 CNN 1126.72 23.80 BiLSTM 214.07 17.38 CNN+LSTM 80.14 9.75 本文方法 37.41 9.01 -
[1] 林京, 张博瑶, 张大义, 等. 航空燃气涡轮发动机故障诊断研究现状与展望[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(8): 626565.LIN J, ZHANG B Y, ZHANG D Y, et al. Research status and prospect of fault diagnosis for gas turbine engine[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(8): 626565(in Chinese). [2] JOZEFOWICZ R, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I. An empirical exploration of recurrent network architectures[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machin Learning. New York: PMLR, 2015, 37: 2342-2350. [3] WANG Y D, ZHAO Y F, ADDEPALLI S. Remaining useful life prediction using deep learning approaches: A review[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2020, 49: 81-88. doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.06.015 [4] 袁利, 王淑一. 航天器控制系统智能健康管理技术发展综述[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(4): 525044.YUAN L, WANG S Y. A review on development of intelligent health management technology for spacecraft control systems[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(4): 525044(in Chinese). [5] 曹明, 黄金泉, 周健, 等. 民用航空发动机故障诊断与健康管理现状、挑战与机遇Ⅰ:气路、机械和FADEC系统故障诊断与预测[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(9): 625573.CAO M, HUANG J Q, ZHOU J, et al. Current status, challenges and opportunities of civil aero-engine diagnostics & health management Ⅰ: Diagnosis and prognosis of engine gas path, mechanical & FADEC[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(9): 625573(in Chinese). [6] LEI Y G, LI N P, GUO L, et al. Machinery health prognostics: A systematic review from data acquisition to RUL prediction[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 104: 799-834. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.11.016 [7] GHORBANI S, SALAHSHOOR K. Estimating remaining useful life of turbofan engine using data-level fusion and feature-level fusion[J]. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2020, 20(1): 323-332. doi: 10.1007/s11668-020-00832-x [8] HU Y, BARALDI P, MAIO F D, et al. Online performance assessment method for a model-based prognostic approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2016, 65(2): 718-735. doi: 10.1109/TR.2015.2500681 [9] 王玺, 胡昌华, 任子强, 等. 基于非线性Wiener过程的航空发动机性能衰减建模与剩余寿命预测[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(2): 223291.WANG X, HU C H, REN Z Q, et al. Performance degradation modeling and remaining useful life prediction for aero-engine based on nonlinear Wiener process[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(2): 223291(in Chinese). [10] 黄亮, 刘君强, 贡英杰. 基于Wiener过程的发动机多阶段剩余寿命预测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(5): 1081-1087.HUANG L, LIU J Q, GONG Y J. Multi-phase residual life prediction of engines based on Wiener process[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(5): 1081-1087(in Chinese). [11] 刘君强, 胡东斌, 潘春露, 等. 基于超统计的多阶段航空发动机剩余寿命预测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(1): 56-64.LIU J Q, HU D B, PAN C L, et al. Remaining useful life prediction of multi-stage aero-engine based on super statistics[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(1): 56-64(in Chinese). [12] ORDÓÑEZ C, LASHERAS F S, ROCA-PARDIÑAS J, et al. A hybrid ARIMA-SVM model for the study of the remaining useful life of aircraft engines[J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2019, 346: 184-191. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2018.07.008 [13] WANG B, LEI Y G, LI N P, et al. A hybrid prognostics approach for estimating remaining useful life of rolling element bearings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2020, 69(1): 401-412. doi: 10.1109/TR.2018.2882682 [14] CHEN J L, JING H J, CHANG Y H, et al. Gated recurrent unit based recurrent neural network for remaining useful life prediction of nonlinear deterioration process[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2019, 185: 372-382. [15] XIANG S, QIN Y, LUO J, et al. Multicellular LSTM-based deep learning model for aero-engine remaining useful life prediction[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2021, 216: 107927. [16] 全航, 张强, 邵思羽, 等. 基于CNN-WaveNet的滚动轴承剩余寿命预测[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2021, 38(10): 3098-3103.QUAN H, ZHANG Q, SHAO S Y, et al. Remaining life prediction of rolling bearing based on CNN-WaveNet[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2021, 38(10): 3098-3103(in Chinese). [17] LI X, DING Q, SUN J Q. Remaining useful life estimation in prognostics using deep convolution neural networks[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2018, 172: 1-11. [18] CHADHA G S, PANARA U, SCHWUNG A, et al. Generalized dilation convolutional neural networks for remaining useful lifetime estimation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 452: 182-199. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.04.109 [19] BAKHTEEV O Y, STRIJOV V V. Comprehensive analysis of gradient-based hyperparameter optimization algorithms[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2020, 289(1): 51-65. doi: 10.1007/s10479-019-03286-z [20] LI L, JAMIESON K G, DESALVO G, et al. Hyperband: A novel bandit-based approach to hyperparameter optimization[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2017, 18(185): 1-52. [21] 车畅畅, 王华伟, 倪晓梅, 等. 基于1D-CNN和Bi-LSTM的航空发动机剩余寿命预测[J]. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(14): 304-312.CHE C C, WANG H W, NI X M, et al. Residual life prediction of aeroengine based on 1D-CNN and Bi-LSTM[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(14): 304-312(in Chinese). [22] AYODEJI A, WANG Z Y, WANG W H, et al. Causal augmented ConvNet: A temporal memory dilated convolution model for long-sequence time series prediction[J]. ISA Transactions, 2022, 123: 200-217. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2021.05.026 [23] VAN DEN OORD A, DIELEMAN S, ZEN H G, et al. WaveNet: A generative model for raw audio[EB/OL]. (2016-09-19)[2022-03-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.03499.pdf. [24] 胡启国, 白熊, 杜春超. 基于KPCA-BLSTM的航空发动机多信息融合剩余寿命预测[J]. 航空工程进展, 2022, 13(3): 157-170.HU Q G, BAI X, DU C C. Remaining useful life prediction of aero-engine multi-information fusion based on KPCA-BLSTM[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering, 2022, 13(3): 157-170(in Chinese). [25] ANDONIE R. Hyperparameter optimization in learning systems[J]. Journal of Membrane Computing, 2019, 1(4): 279-291. doi: 10.1007/s41965-019-00023-0 [26] AZIZ M, JAMIESON K, ASLAM J. Pure-exploration for infinite-armed bandits with general arm reservoirs[EB/OL]. (2019-01-13)[2022-03-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.06149.pdf. [27] XIA Y F, LIU C Z, LI Y Y, et al. A boosted decision tree approach using Bayesian hyper-parameter optimization for credit scoring[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2017, 78: 225-241. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2017.02.017 [28] FREDERICK D, DECASTRO J A, LITT J. User’s guide for the commercial modular aero-propulsion system simulation (C-MAPSS) TM-2007-215026[R]. Washington, D.C.: SA, 2007. [29] SAXENA A, GOEBEL K, SIMON D, et al. Damage propagation modeling for aircraft engine run-to-failure simulation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2008: 1-9. [30] HONG C W, LEE K, KO M S, et al. Multivariate time series forecasting for remaining useful life of turbofan engine using deep-stacked neural network and correlation analysis[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing . Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 63-70. [31] 柳长源, 何先平, 于会越. 基于数据驱动的涡轮发动机剩余寿命预测[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2021, 25(7): 68-74.LIU C Y, HE X P, YU H Y. Prediction of remaining life of turbine engine based on data drive[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2021, 25(7): 68-74(in Chinese). [32] WANG Q Y, ZHENG S, FARAHAT A, et al. Remaining useful life estimation using functional data analysis[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management . Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-8. [33] YU W N, KIM I Y, MECHEFSKE C. Remaining useful life estimation using a bidirectional recurrent neural network based autoencoder scheme[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 129: 764-780. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.05.005 [34] CAI H S, FENG J S, LI W Z, et al. Similarity-based particle filter for remaining useful life prediction with enhanced performance[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 94: 106474. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106474 [35] HOU G S, XU S, ZHOU N, et al. Remaining useful life estimation using deep convolutional generative adversarial networks based on an autoencoder scheme[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2020, 2020: 1-14. -






 下载:
下载: