-
摘要:
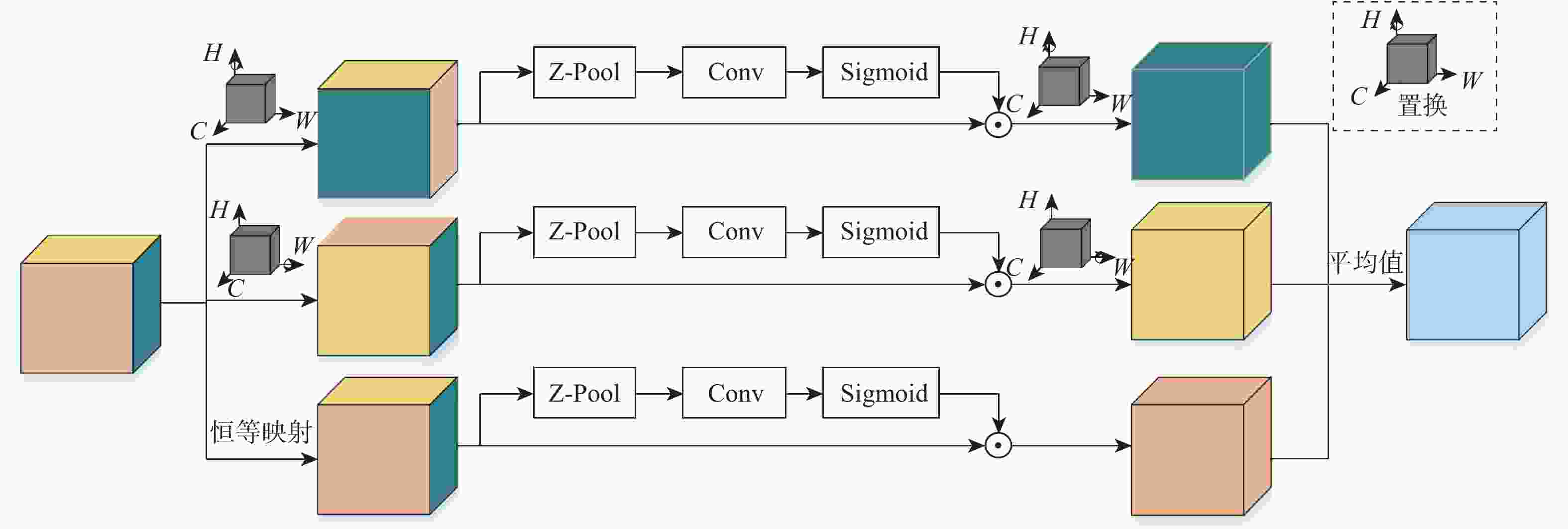
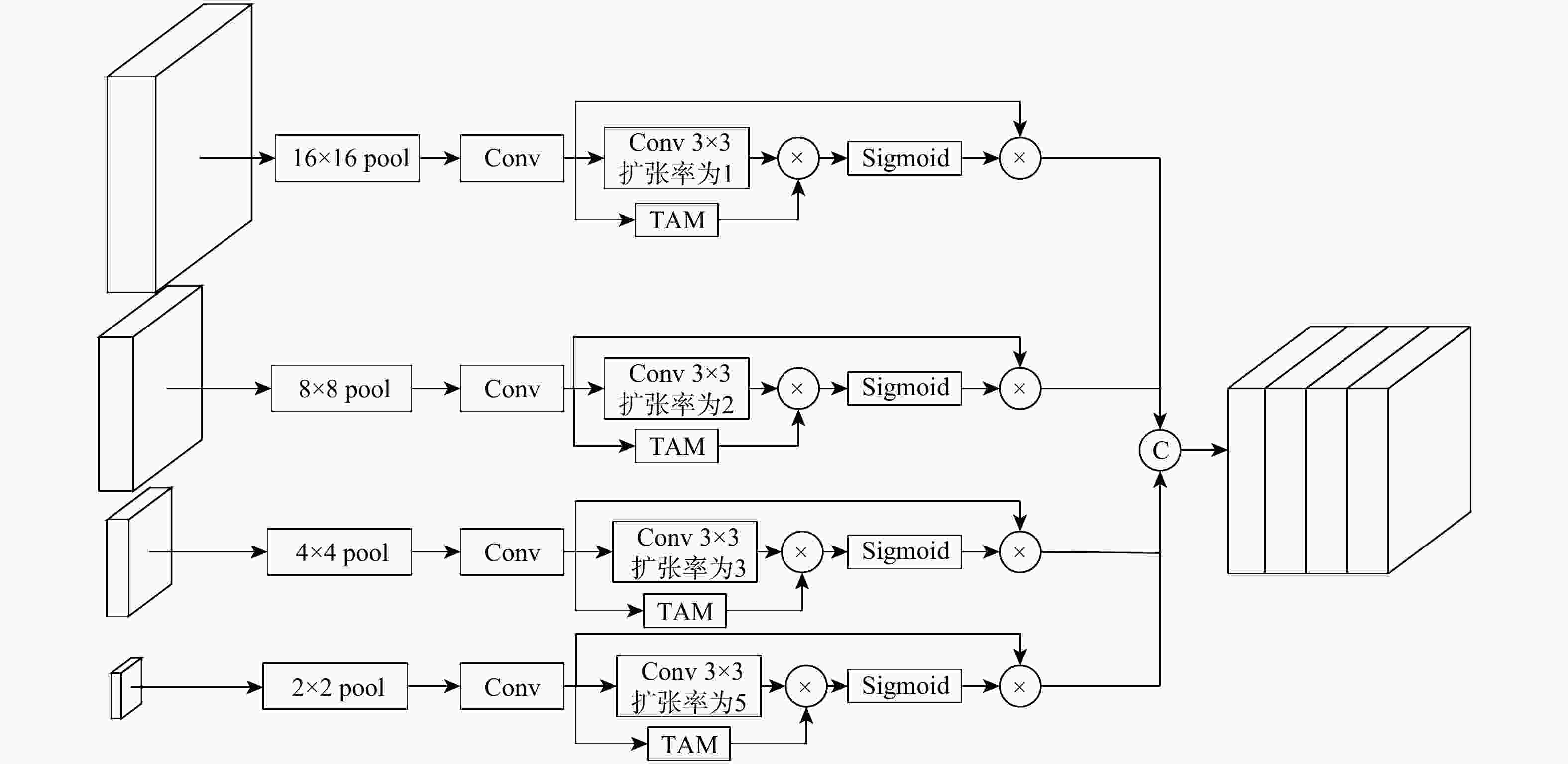
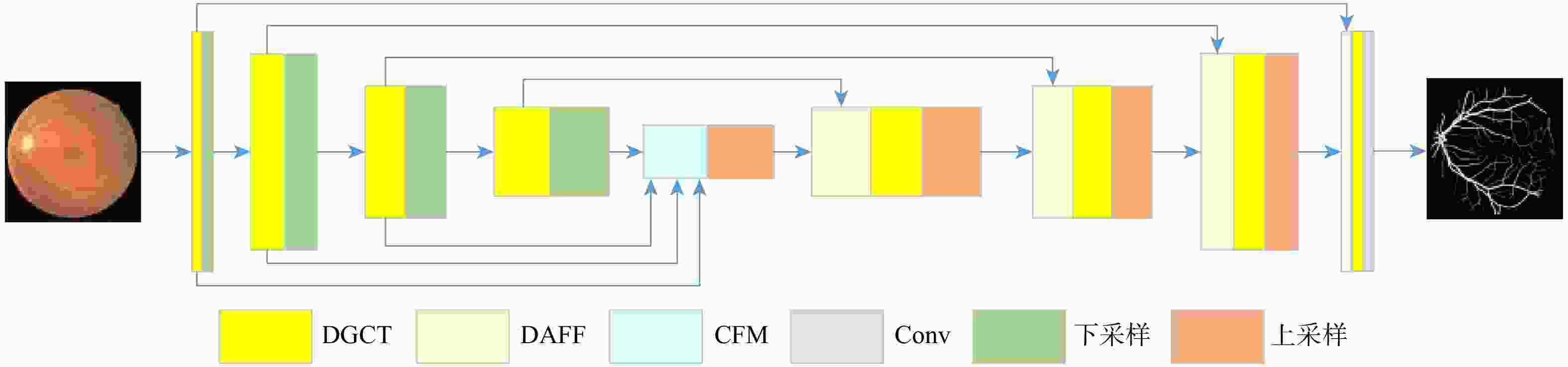
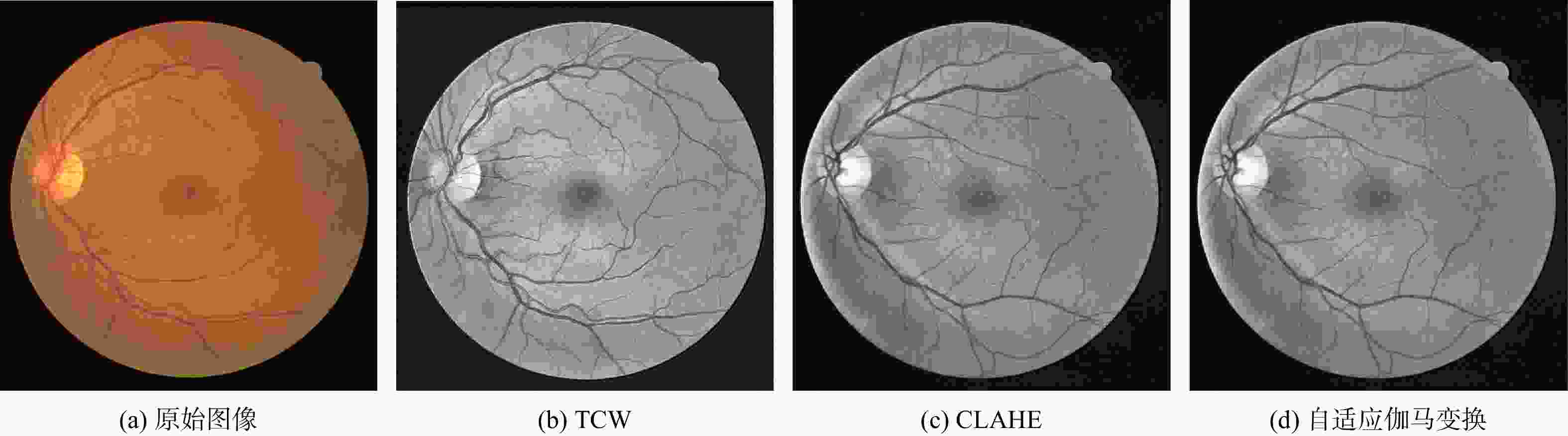
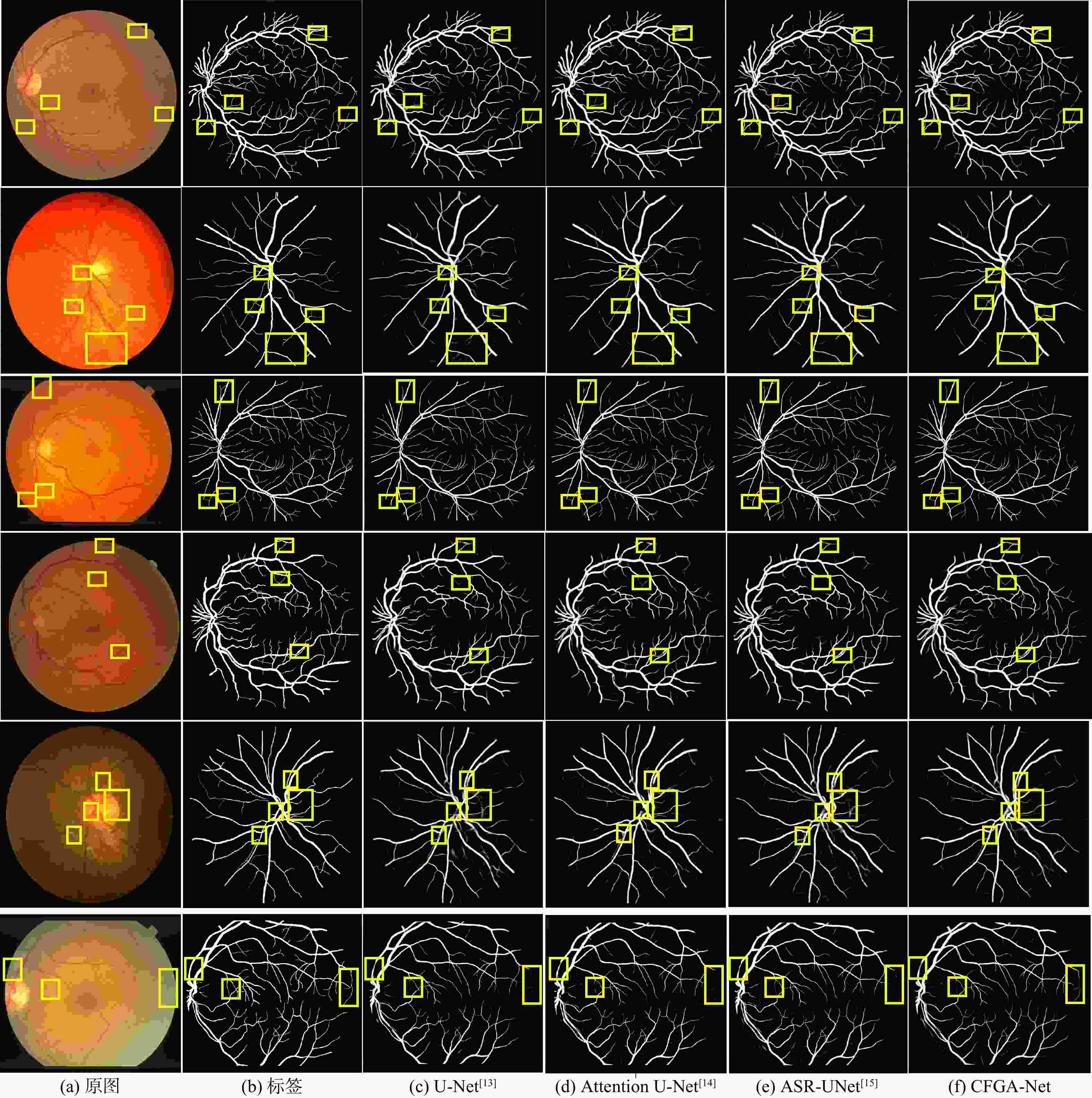
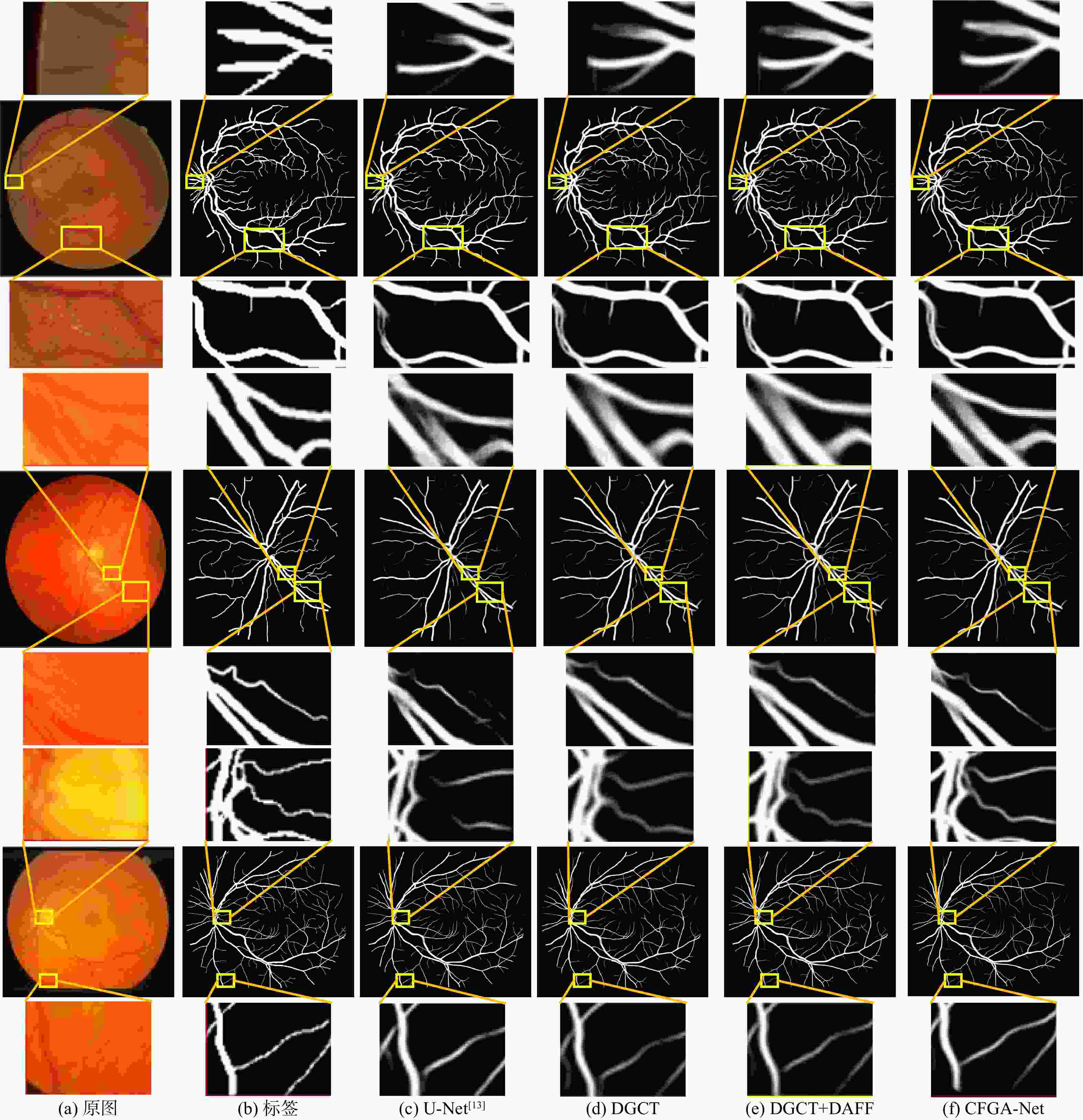
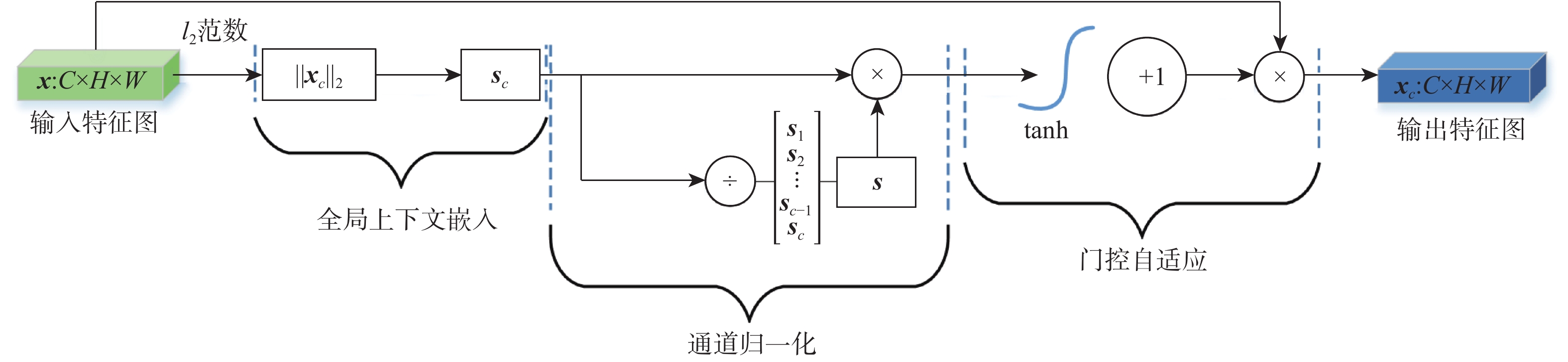
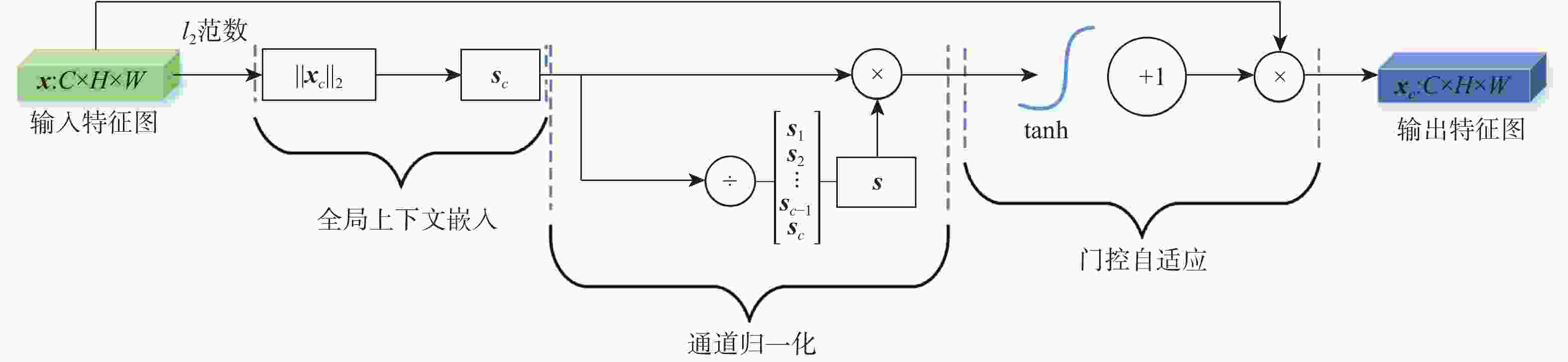
针对现有多数算法对浅层特征提取不足,导致分割结果中血管边界模糊、毛细血管欠分割且包含噪声等问题,提出一种跨级融合门控自适应网络。该网络中的密集门控通道变换模块,通过促进通道之间的竞争或协同关系充分提取浅层特征信息,避免浅层粗粒度特征信息丢失;通过跨层次融合模块捕获各层跨维度交互信息,有效聚合多尺度上下文特征;采用双自适应特征融合方法有效引导相邻层次特征融合,抑制噪声。在公共数据集DRIVE、CHASEDB1和STARE上进行验证,结果表明:所提网络准确率分别为0.9652、0.9668和0.9695,
F 1值分别为0.8544、0.8152和0.8412,在多个指标上均处于较高水平,优于现有先进算法。Abstract:To address the insufficient shallow feature extraction of most existing algorithms, which results in noise, blurred vascular boundary and capillary under segmentation, a cross-level fusion gated adaptive network is proposed. Firstly, shallow feature information is fully extracted by the dense gated channel transformation module in the network with promotion of competition or cooperation of channels to avoid the loss of shallow coarse-grained feature information. Secondly, cross-dimensional interaction information of each layer is captured by cross-level fusion module to effectively aggregate multi-scale context features. Thirdly, dual adaptive feature fusion method is used to guide the feature fusion of adjacent layers effectively and suppress noise. The validation was performed on public data sets DRIVE, CHASEDB1 and STARE, and the accuracy rates were 0.9652, 0.9668 and 0.9695 respectively; the
F 1 values were 0.8544, 0.8152 and 0.8412 respectively. The results show that the proposed network is at a high level in many indexes, and is superior to the existing advanced algorithms. -
表 1 不同注意力机制的参数复杂度和开销比较
Table 1. comparison of parameter complexity and overhead of various attentional mechanisms
注意力机制 参数量 存储开销/106 SE 2C2/r 2.514 CBAM 2C2/r+2k2 2.532 全局上下文 2C2/r+C 2.548 TAM(本文) 6k2 0.004 8 表 2 不同数据集上的平均性能指标评估结果
Table 2. Average performance index evaluation results on different datasets
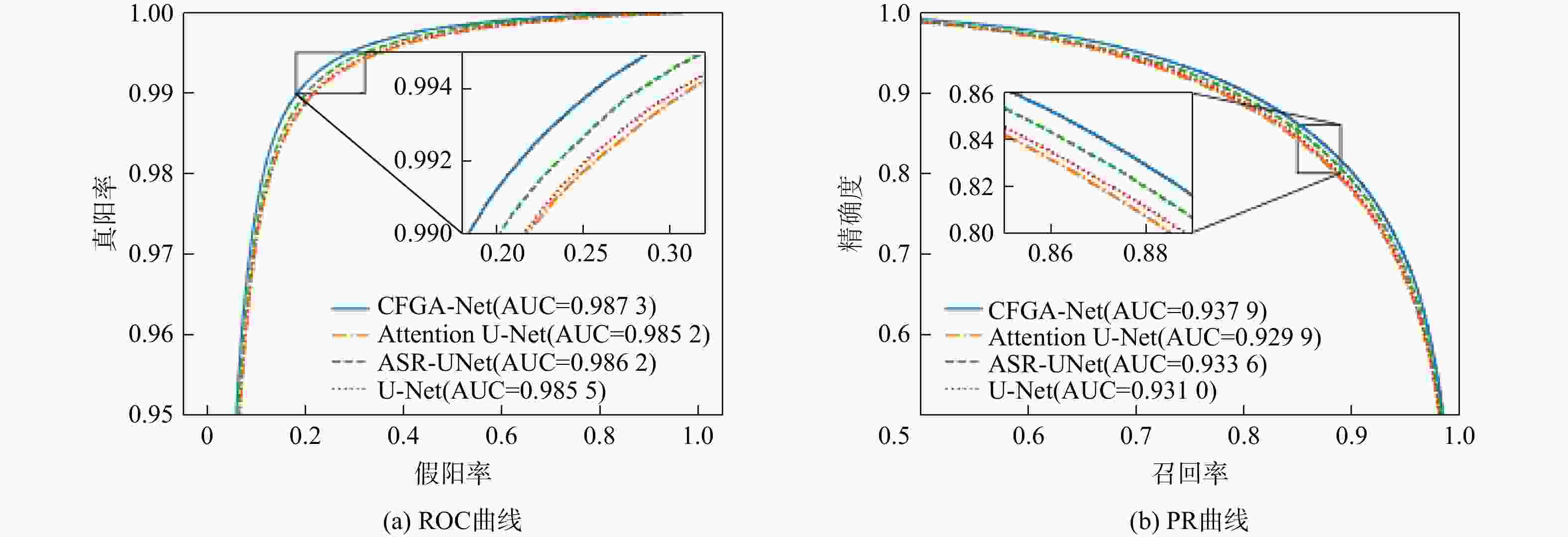
数据集 算法 F1 Acc Se Sp AUC(ROC) AUC(PR) DRIVE U-Net[13] 0.8474 0.9631 0.8302 0.9812 0.9855 0.9310 Attention U-Net[14] 0.8449 0.9627 0.8287 0.9814 0.9852 0.9299 ASR-UNet[15] 0.8507 0.9641 0.8351 0.9821 0.9862 0.9336 CFGA-Net(本文) 0.8544 0.9652 0.8326 0.9837 0.9873 0.9379 CHASEDB1 U-Net[13] 0.8002 0.9641 0.7934 0.9811 0.9834 0.8848 Attention U-Net[14] 0.8109 0.9658 0.8090 0.9813 0.9845 0.8942 ASR-UNet[15] 0.8061 0.9650 0.8047 0.9809 0.9848 0.8916 CFGA-Net(本文) 0.8152 0.9668 0.8097 0.9824 0.9866 0.9026 STARE U-Net[13] 0.8192 0.9644 0.7591 0.9888 0.9843 0.9158 Attention U-Net[14] 0.8184 0.9646 0.7522 0.9898 0.9836 0.9161 ASR-UNet[15] 0.8239 0.9653 0.7649 0.9891 0.9853 0.9201 CFGA-Net(本文) 0.8412 0.9695 0.8023 0.9886 0.9899 0.9347 表 3 不同算法在数据集DRIVE、CHASEDB1和STARE上的性能指标对比
Table 3. Comparison of performance indicators of different algorithms in DRIVE, CHASEDB1 and STARE datasets
算法 Se Sp Acc DRIVE CHASEDB1 STARE DRIVE CHASEDB1 STARE DRIVE CHASEDB1 STARE 文献[16] 0.7653 0.7633 0.7581 0.9818 0.9809 0.9846 0.9542 0.9610 0.9612 文献[17] 0.7632 0.7815 0.7423 0.9536 0.9587 0.9603 文献[18] 0.7631 0.7641 0.7735 0.9820 0.9806 0.9857 0.9538 0.9607 0.9638 文献[19] 0.7918 0.6457 0.8021 0.9708 0.9653 0.9561 0.9577 0.9340 0.9445 文献[20] 0.7941 0.8176 0.7598 0.9798 0.9704 0.9878 0.9558 0.9608 0.9640 文献[21] 0.8213 0.8035 0.9807 0.9787 0.9615 0.9639 文献[22] 0.7352 0.7279 0.7265 0.9775 0.9658 0.9759 0.9480 0.9452 0.9548 文献[23] 0.8353 0.8176 0.7946 0.9751 0.9776 0.9821 0.9579 0.9632 0.9626 文献[24] 0.8125 0.8012 0.8078 0.9763 0.9730 0.9721 0.9610 0.9578 0.9586 CFGA-Net(本文) 0.8326 0.8097 0.8023 0.9837 0.9824 0.9886 0.9652 0.9668 0.9695 表 4 算法改进前后结果对比
Table 4. Comparison of results before and after improvement
模型 F1 Acc Se Sp AUC DRIVE CHASEDB1 STARE DRIVE CHASEDB1 STARE DRIVE CHASEDB1 STARE DRIVE CHASEDB1 STARE DRIVE CHASEDB1 STARE 1 0.8474 0.8002 0.8192 0.9631 0.9641 0.9644 0.8302 0.7934 0.7591 0.9812 0.9811 0.9888 0.9855 0.9834 0.9843 2 0.8527 0.8139 0.8243 0.9648 0.9661 0.9659 0.8323 0.8193 0.7810 0.9833 0.9807 0.9873 0.9867 0.9861 0.9870 3 0.8530 0.8122 0.8241 0.9647 0.9659 0.9652 0.8296 0.8134 0.7770 0.9826 0.9811 0.9879 0.9822 0.9854 0.9860 4 0.8528 0.8136 0.8276 0.9649 0.9660 0.9665 0.8297 0.8223 0.7865 0.9839 0.9803 0.9874 0.9870 0.9860 0.9875 5 0.8530 0.8132 0.8331 0.9650 0.9661 0.9672 0.8290 0.8138 0.7839 0.9840 0.9813 0.9886 0.9855 0.9859 0.9888 6 0.8544 0.8152 0.8412 0.9652 0.9668 0.9695 0.8326 0.8097 0.8023 0.9837 0.9824 0.9886 0.9873 0.9866 0.9899 -
[1] 贾洪, 郑楚君, 李灿标, 等. 基于局部线结构约束的FCM聚类视网膜血管分割[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(9): 0910001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.0910001JIA H, ZHENG C J, LI C B, et al. Retinal blood vessel segmentation based on fuzzy C-means clustering according to the local line structural constraints[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(9): 0910001 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.0910001 [2] 周阳. 基于匹配滤波引导局部特征空间仿射传播聚类的视网膜血管分割[J]. 信息通信, 2019, 32(7): 35-39.ZHOU Y. Retinal vascular segmentation based on affine propagation clustering in local feature space guided by matched filtering[J]. Information & Communications, 2019, 32(7): 35-39(in Chinese). [3] DASH J, BHOI N. Retinal blood vessel extraction using morphological operators and Kirsch’s template[C]//Proceedings of the Soft Computing and Signal Processing. Berlin: Springer, 2019: 603-611. [4] 汪维华, 张景中, 吴文渊. 改进的形态学与Otsu相结合的视网膜血管分割[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2019, 36(7): 2228-2231.WANG W H, ZHANG J Z, WU W Y. New approach to segment retinal vessel using morphology and Otsu[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2019, 36(7): 2228-2231(in Chinese). [5] LI X, JIANG Y C, LI M L, et al. Lightweight attention convolutional neural network for retinal vessel image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(3): 1958-1967. [6] WANG C, ZHAO Z Y, REN Q Q, et al. Dense U-Net based on patch-based learning for retinal vessel segmentation[J]. Entropy, 2019, 21(2): 168. doi: 10.3390/e21020168 [7] YUE K J, ZOU B J, CHEN Z L, et al. Retinal vessel segmentation using dense U-Net with multiscale inputs[J]. Journal of Medical Imaging, 2019, 6(3): 034004. [8] 胡扬涛, 裴洋, 林川, 等. 空洞残差U型网络用于视网膜血管分割[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(7): 185-191. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2009-0215HU Y T, PEI Y, LIN C, et al. Atrous residual U-Net for retinal vessel segmentation[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2021, 57(7): 185-191(in Chinese). doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2009-0215 [9] 易三莉, 陈建亭, 贺建峰. 基于多路径输入和多尺度特征融合的视网膜血管分割[J]. 光电子·激光, 2021, 32(7): 735-741.YI S L, CHEN J T, HE J F. Retinal vascular segmentation based on multi-scale input and multi-scale feature fusion[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser, 2021, 32(7): 735-741(in Chinese). [10] HUANG G, LIU Z, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2261-2269. [11] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 3-19. [12] 姜大光, 李明鸣, 陈羽中, 等. 骨架图引导的级联视网膜血管分割网络[J]. 工程科学学报, 2021, 43(9): 1244-1252.JIANG D G, LI M M, CHEN Y Z, et al. Cascaded retinal vessel segmentation network guided by a skeleton map[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2021, 43(9): 1244-1252(in Chinese). [13] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 234-241. [14] OKTAY O, SCHLEMPER J, LE FOLGOC L, et al. Attention U-Net: Learning where to look for the pancreas[EB/OL]. (2018-05-20)[2022-05-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1804.03999. [15] 易三莉, 陈建亭, 贺建峰. ASR-UNet: 一种基于注意力机制改进的视网膜血管分割算法[J]. 山东大学学报(理学版), 2021, 56(9): 13-20.YI S L, CHEN J T, HE J F. ASR-UNet: An improved retinal vessels segmentation algorithm based on attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Natural Science), 2021, 56(9): 13-20 (in Chinese). [16] YAN Z Q, YANG X, CHENG K T. Joint segment-level and pixel-wise losses for deep learning based retinal vessel segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 65(9): 1912-1923. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2018.2828137 [17] LIN Y, ZHANG H G, HU G. Automatic retinal vessel segmentation via deeply supervised and smoothly regularized network[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 7: 57717-57724. [18] YAN Z Q, YANG X, CHENG K T. A three-stage deep learning model for accurate retinal vessel segmentation[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2019, 23(4): 1427-1436. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2018.2872813 [19] SANTOS J C M D, CARRIJO G A, CARDOSO C D F D S, et al. Fundus image quality enhancement for blood vessel detection via a neural network using CLAHE and Wiener filter[J]. Research on Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 36(2): 107-119. doi: 10.1007/s42600-020-00046-y [20] LV Y, MA H, LI J N, et al. Attention guided U-Net with atrous convolution for accurate retinal vessels segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 32826-32839. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2974027 [21] ZHANG J W, ZHANG Y C, XU X W. Pyramid U-Net for retinal vessel segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1125-1129. [22] TCHINDA B S, TCHIOTSOP D, NOUBOM M, et al. Retinal blood vessels segmentation using classical edge detection filters and the neural network[J]. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, 2021, 23: 100521. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2021.100521 [23] YANG L, WANG H X, ZENG Q S, et al. A hybrid deep segmentation network for fundus vessels via deep-learning framework[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 448: 168-178. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.03.085 [24] KHAN T M, KHAN M A U, REHMAN N U, et al. Width-wise vessel bifurcation for improved retinal vessel segmentation[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 71: 103169. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103169 -






 下载:
下载: