A GNSS/IMU/vision multi-source fusion localization method based on refined pre-integration
-
摘要:
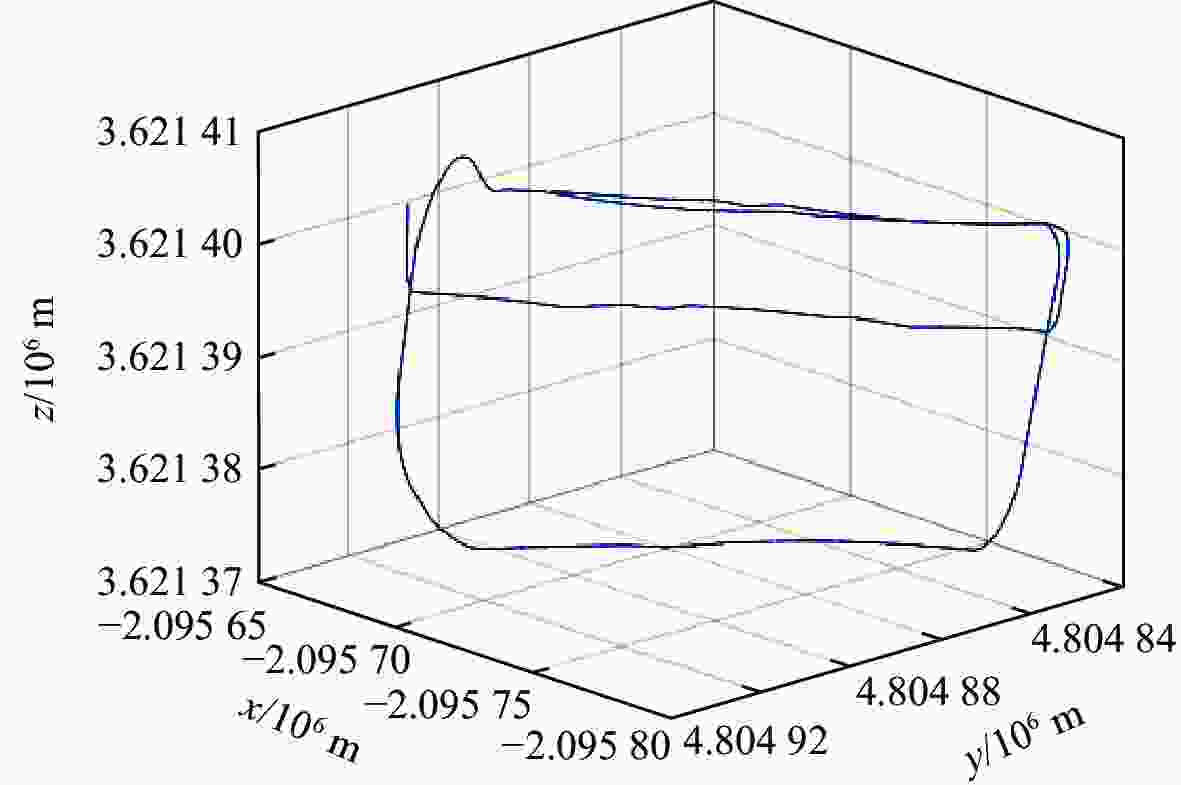
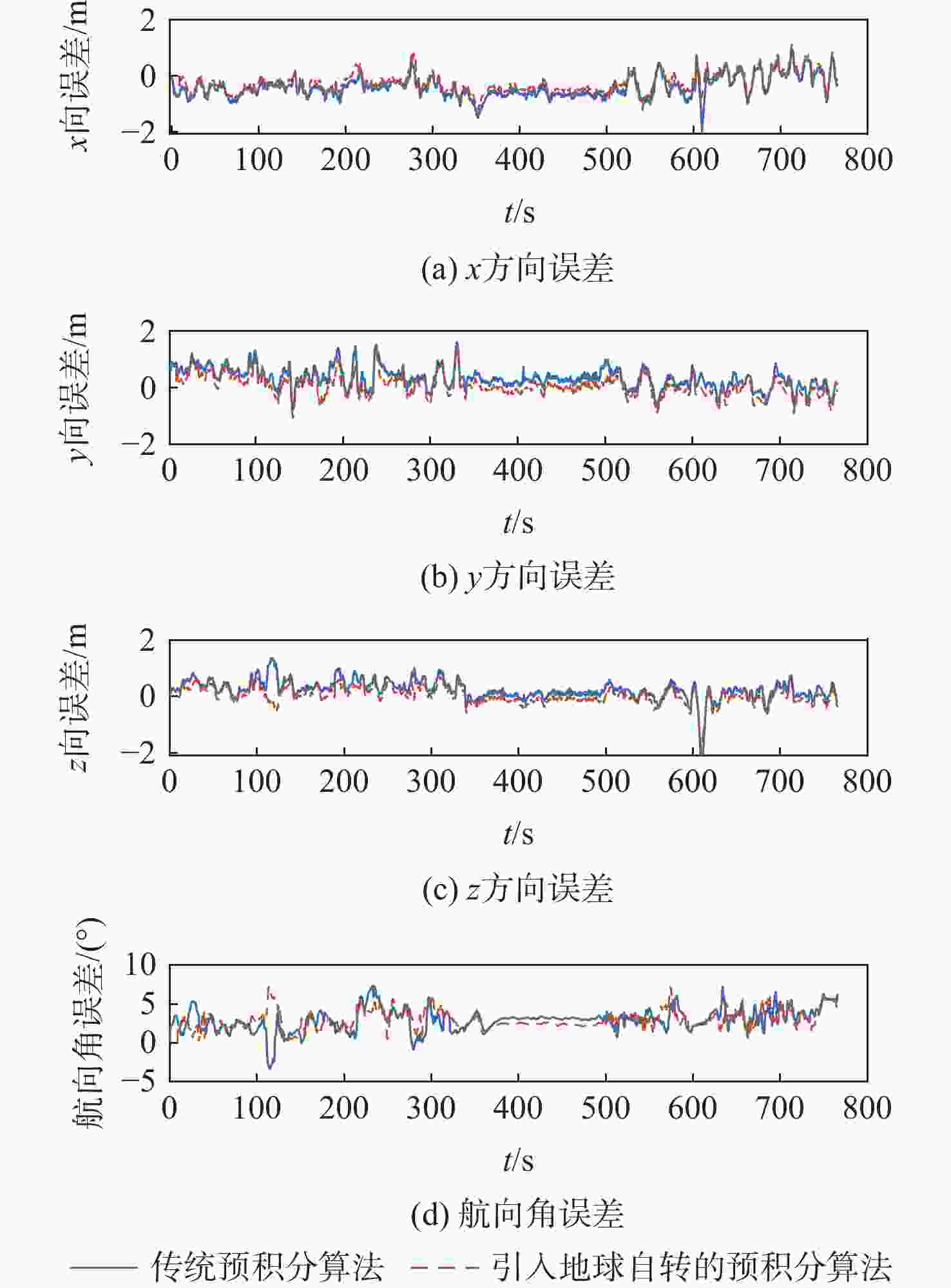
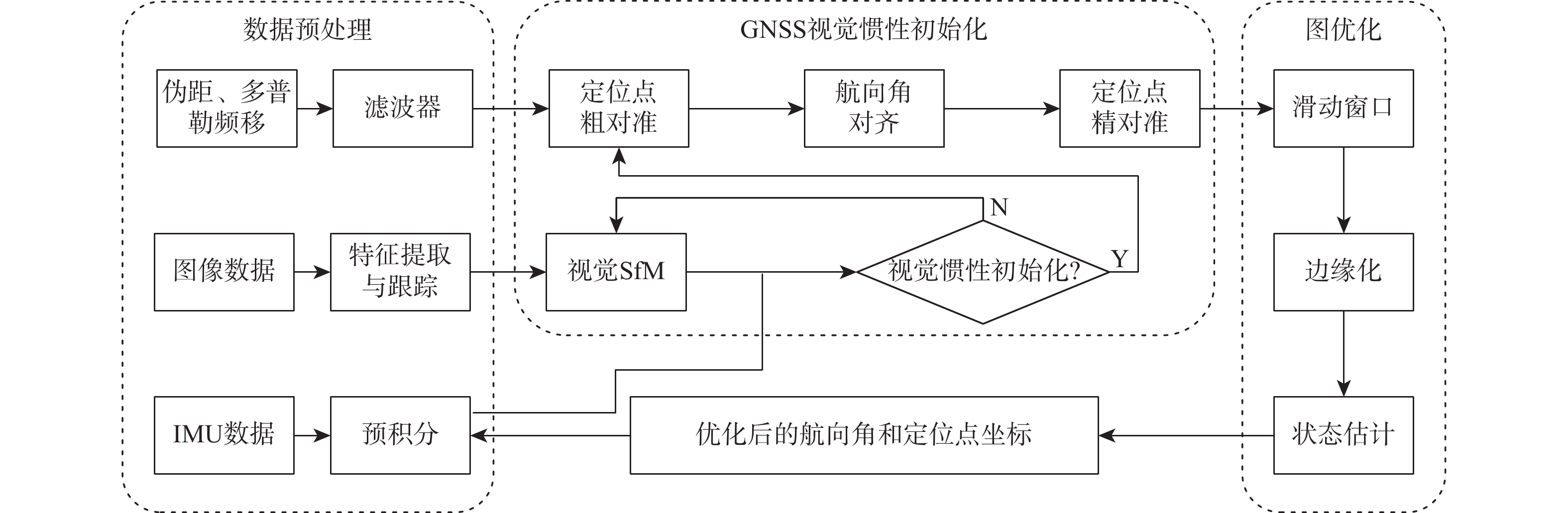
针对传统预积分算法固定地球重力值和忽略地球自转的问题,提出一种考虑地球自转和重力变化的惯性测量单元(inertial measurement unit, IMU)预积分算法。参照高精度捷联惯性导航解算的动力学模型,在IMU预积分动力学模型的姿态更新中引入地球自转角速率,速度和位置更新中引入由地球自转引起的科里奥利加速度,同时将由载体位置引起的地球重力变化及时反馈至预积分算法中,详细推导了引入地球自转和重力变化后预积分算法的具体过程,实现对传统预积分模型的精化。并将精化的预积分算法应用于基于紧耦合全球导航卫星系统(global navigation satellite system, GNSS)/IMU/视觉多源融合系统中,实测实验结果表明:利用精化的预积分模型可使系统预积分的模型误差有效减小,显著提升多源融合系统整体的定位定姿精度,其中系统定位精度提升32.41%,航向角精度提升4.23%。
Abstract:A pre-integration algorithm taking into account the earth's rotation and gravity change is developed in order to address the issue that the conventional pre-integration algorithm fixes the value of the earth's gravity and ignores the Earth's rotation. Referring to the dynamic model of high-precision strapdown inertial navigation, the earth rotation angle rate is introduced in the attitude update of the pre-integral dynamic model, and the Coriolis acceleration caused by the earth rotation is introduced in the velocity and position update. Simultaneously, the traditional pre-integral model is improved, taking into account that the carrier's position can feed back the gravity change to the pre-integral algorithm in time. All the process of the pre-integral algorithm are derived in detail after the Earth's rotation and the gravity change are introduced. The refined pre-integration algorithm is applied to a multi-source fusion system based on tightly coupled GNSS/INS/vision. The experimental results show that the model error of the system pre-integration can be effectively reduced by using the refined pre-integration model, and the positioning and attitude accuracy of the multi-source fusion system is improved by 32.41% and 4.23%, respectively.
-
表 1 IMU误差设置
Table 1. IMU error setting
陀螺仪
零偏误差/
((°)·hr−1)加速度计
零偏误差/
$({\mathrm{m}}\cdot({\mathrm{s}}\cdot{\mathrm{ hr}}^{\tfrac{1}{2}})^{-1}) $陀螺仪
随机噪声/
((°)·hr−1)加速度计
随机噪声/
$({\mathrm{m}}\cdot({\mathrm{s}}\cdot{\mathrm{ hr}}^{\tfrac{1}{2}})^{-1}) $3 0.02 0.15 0.02 表 2 预积分残差的均方根
Table 2. The root-mean-square of pre-integration residual
不同情况 位置RMSE/m 姿态RMSE/(°) x y z x y z 传统预积分 0.011 5 0.006 8 0.012 0 0.048 5 0.001 8 0.023 7 引入重力变化 0.005 9 0.006 2 0.009 4 0.028 1 0.015 2 0.021 8 引入地球自转 0.006 6 0.007 7 0.009 8 0.028 3 0.016 4 0.022 2 引入地球自转和
重力变化0.004 8 0.004 0 0.007 5 0.025 6 0.015 0 0.020 6 表 3 系统定位误差和航向角误差的均方根
Table 3. The root-mean-square of positioning and heading angle error
不同情况 位置
RMSE/m位置RMSE
精度提升/%航向角
RMSE/(°)航向角RMSE
精度提升/%传统预积分 0.404 3 3.357 9 引入重力变化 0.299 1 26.00 3.308 0 1.48 引入地球自转 0.322 8 20.15 3.245 9 3.34 引入地球自转和
重力变化0.273 2 32.42 3.216 0 4.23 -
[1] 李团. 单频多模GNSS/INS/视觉紧组合高精度位姿估计方法研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2019: 1-5.LI T. Research on the tightly coupled single-frequency multi-GNSS/INS/vision integration for precise position and orientation estimation[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2019: 1-5 (in Chinese). [2] GAO Z Z, GE M R, SHEN W B, et al. Evaluation on the impact of IMU grades on BDS + GPS PPP/INS tightly coupled integration[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2017, 60(6): 1283-1299. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2017.06.022 [3] 朱锋. GNSS/SINS/视觉多传感器融合的精密定位定姿方法与关键技术[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2020: 3-5.ZHU F. GNSS/SINS/Vision multi-sensors integration for precise positioning and orientation determination[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2020: 3-5 (in Chinese). [4] HUANG G Q. Visual-inertial navigation: a concise review[C]// 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). New York: ACM, 2019: 9572-9582. [5] MASCARO R, TEIXEIRA L, HINZMANN T, et al. GOMSF: graph-optimization based multi-sensor fusion for robust UAV pose estimation[C]// 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1421-1428. [6] QIN T, CAO S Z, PAN J, et al. A general optimization-based framework for global pose estimation with multiple sensors[EB/OL]. (2019-01-11) [2022-09-30]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1901.03642. [7] CIOFFI G, SCARAMUZZA D. Tightly-coupled fusion of global positional measurements in optimization-based visual-inertial odometry[C]// 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 5089-5095. [8] GONG Z, LIU P L, WEN F, et al. Graph-based adaptive fusion of GNSS and VIO under intermittent GNSS-degraded environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 70: 8501116. [9] LIU J X, GAO W, HU Z Y. Optimization-based visual-inertial SLAM tightly coupled with raw GNSS measurements[C]// 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). New York: ACM, 2021: 11612–11618. [10] CAO S Z, LU X Y, SHEN S J. GVINS: tightly coupled GNSS-visual-inertial fusion for smooth and consistent state estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2022, 38(4): 2004-2021. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2021.3133730 [11] QIN T, LI P L, SHEN S J. VINS-mono: a robust and versatile monocular visual-inertial state estimator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2018, 34(4): 1004-1020. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2018.2853729 [12] 白师宇, 赖际舟, 吕品, 等. 基于IMU/ODO预积分的多传感器即插即用因子图融合方法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2020, 28(5): 624-628.BAI S Y, LAI J Z, LV P, et al. Multisensory plug-and-play factor graph fusion method based on IMU/odometer preintegration[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2020, 28(5): 624-628 (in Chinese). [13] 徐晓苏, 吴贤. 基于IMU预积分封闭解的单目视觉惯性里程计算法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2020, 28(4): 440-447.XU X S, WU X. Monocular visual-inertial odometry method based on IMU pre-integrated closed solution[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2020, 28(4): 440-447 (in Chinese). [14] LUPTON T, SUKKARIEH S. Visual-inertial-aided navigation for high-dynamic motion in built environments without initial conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2012, 28(1): 61-76. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2011.2170332 [15] FORSTER C, CARLONE L, DELLAERT F, et al. On-manifold preintegration for real-time visual: inertial odometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2017, 33(1): 1-21. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2016.2597321 [16] BARRAU A, BONNABEL S. A mathematical framework for IMU error propagation with applications to preintegration[C]// 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 5732-5738. [17] TANG H L, NIU X J, ZHANG T S, et al. Exploring the accuracy potential of IMU preintegration in factor graph optimization[EB/OL]. (2021-09-07)[2022-09-30]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2109.03010. [18] JIANG J X, NIU X J, LIU J N. Improved IMU preintegration with gravity change and earth rotation for optimization-based GNSS/VINS[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(18): 3048. doi: 10.3390/rs12183048 [19] BUDIYONO A. Principles of GNSS, inertial, and multi-sensor integrated navigation systems[J]. Industrial Robot, 2013, 67(3):191-192. -






 下载:
下载: