Sensitivity encoding reconstruction algorithm based on multi-category dictionary learning
-
摘要:
灵敏度编码(SENSE) 方法利用多个线圈的灵敏度信息来减少扫描时间,利用SENSE模型重构的图像易存在伪影,不利于医学诊断。为减少重叠伪影,提高磁共振成像质量,将分类图像块的快速正交字典引入SENSE模型中,得到一种基于多分类字典学习的灵敏度编码重建算法。该算法通过对图像块分类,在每个类中训练字典,得到不同类别的多个字典,运用交替方向乘子法进行图像重构。在人体脑部和膝盖数据上进行实验,结果表明:相比于TV-SENSE、TV-LORAKS-SENSE和LpTV-SENSE算法,所提算法的平均信噪比分别提高了1.53 dB、1.22 dB和1.05 dB,重构图像与参考图像的一致性较高,图像细节部分和边缘轮廓信息保留完整。
Abstract:The sensitivity encoding (SENSE) method explicitly utilizes sensitivity information from multiple receiving coils to reduce scan time. The images reconstructed using the SENSE model have a portion of blurring artifacts that are not conducive to medical diagnosis. We propose a sensitivity coding reconstruction approach based on multi-classification dictionary learning to minimize overlap artifacts and enhance the quality of parallel magnetic resonance imaging by integrating fast dictionary learning on classed patches into the SENSE model. In order to obtain picture reconstructions using alternating direction method of multipliers, the algorithm first classifies the image blocks and then trains multiple dictionaries of various classes in each category. The results on the human brain and knee data show that the algorithm improves the average signal-to-noise ratio by 1.53 dB, 1.22 dB and 1.05 dB over the TV-SENSE, TV-LORAKS-SENSE and LpTV-SENSE algorithms, respectively. The reconstructed image is in high agreement with the reference image, and the image detail part and edge contour information are kept intact.
-
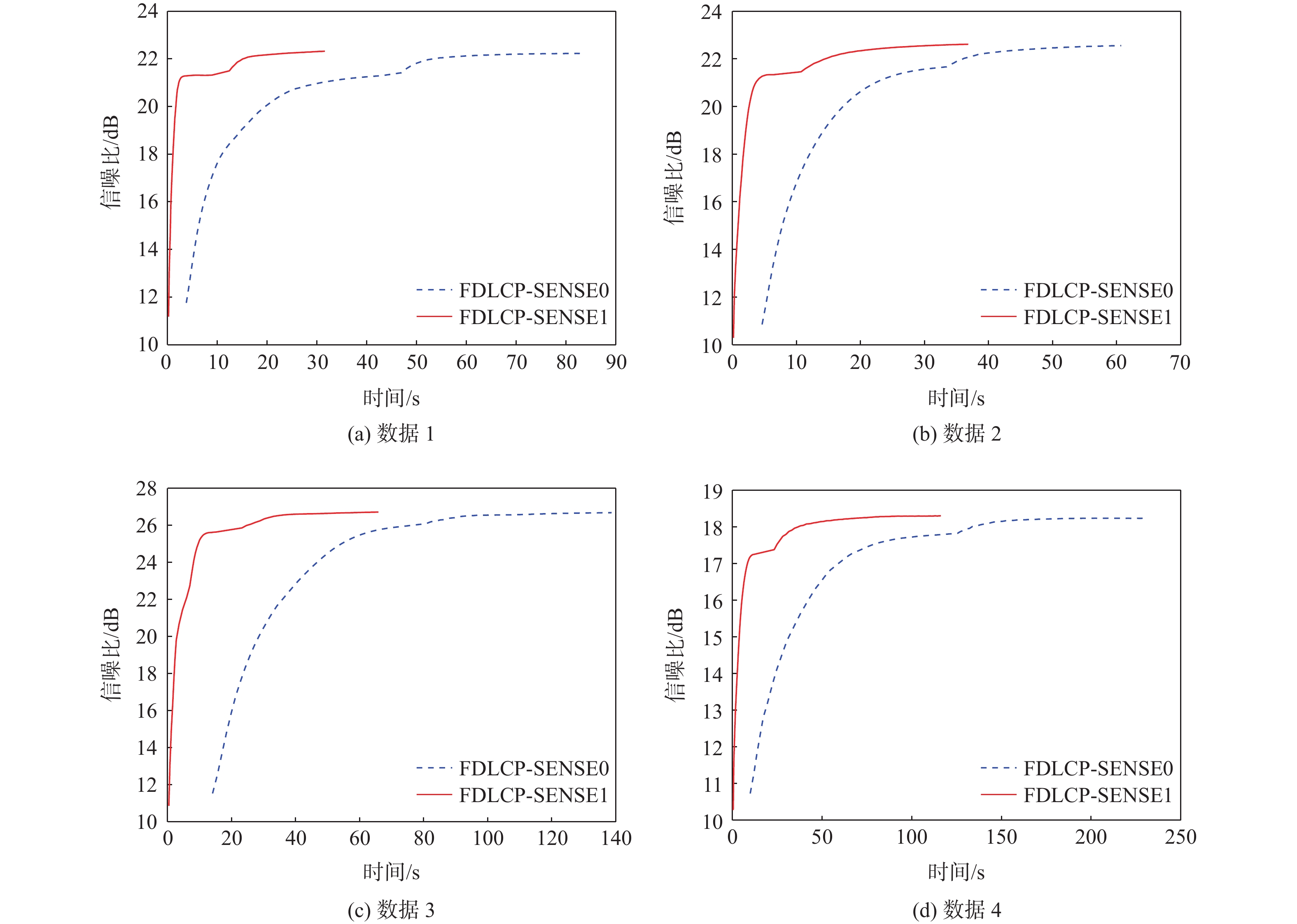
表 1 AF=3~7时数据1在泊松圆盘欠采样下各算法的重构结果
Table 1. Reconstruction results of different algorithms for data 1 under Poisson disc undersampling when acceleration factor is 3−7
算法 SNR/dB SSIM HFEN AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 TV-SENSE[15] 24.06 22.40 20.97 20.05 19.07 0.9729 0.963 5 0.952 2 0.942 6 0.931 5 0.113 9 0.147 8 0.184 8 0.211 6 0.245 9 TV-LORAKS-SENSE[16] 23.80 22.32 21.10 20.24 19.28 0.970 0 0.960 8 0.951 0 0.942 6 0.932 2 0.108 6 0.139 4 0.171 6 0.196 3 0.230 0 LpTV-SENSE[17] 24.19 22.61 21.32 20.43 19.45 0.973 7 0.964 6 0.954 3 0.944 5 0.933 0 0.111 2 0.140 5 0.173 1 0.199 0 0.231 8 FDLCP-SENSE1 24.84 23.40 22.35 21.59 20.52 0.977 1 0.969 8 0.962 1 0.955 7 0.944 9 0.100 3 0.125 2 0.150 3 0.169 1 0.203 9 表 2 AF=3~7时数据2在泊松圆盘欠采样下各算法的重构结果
Table 2. Reconstruction results of different algorithms for data 2 under Poisson disc undersampling when acceleration factor is 3−7
算法 SNR/dB SSIM HFEN AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 TV-SENSE[15] 23.77 22.24 20.87 19.79 19.04 0.966 2 0.955 4 0.943 7 0.931 6 0.922 4 0.105 5 0.134 2 0.167 5 0.198 7 0.220 5 TV-LORAKS-SENSE[16] 23.97 22.57 21.40 20.31 19.62 0.967 1 0.957 1 0.947 7 0.937 1 0.928 8 0.092 9 0.115 7 0.142 5 0.170 9 0.190 8 LpTV-SENSE[17] 24.13 22.57 21.28 20.12 19.29 0.969 4 0.958 7 0.947 9 0.933 7 0.922 9 0.098 0 0.125 3 0.154 6 0.188 2 0.210 6 FDLCP-SENSE1 25.09 23.80 22.61 21.44 20.71 0.975 2 0.968 2 0.959 8 0.948 6 0.941 1 0.085 4 0.105 3 0.130 3 0.159 5 0.177 9 表 3 AF=3~7时数据3在泊松圆盘欠采样下各算法的重构结果
Table 3. Reconstruction results of different algorithms for data 3 under Poisson disc undersampling when acceleration factor is 3−7
算法 SNR/dB SSIM HFEN AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 TV-SENSE[15] 27.78 26.32 25.41 24.58 23.77 0.981 4 0.976 2 0.972 5 0.969 1 0.965 0 0.075 5 0.091 8 0.105 6 0.118 4 0.133 2 TV-LORAKS-SENSE[16] 27.76 26.44 25.64 24.89 24.18 0.980 5 0.975 3 0.971 8 0.968 7 0.965 2 0.070 9 0.085 2 0.097 5 0.109 8 0.122 9 LpTV-SENSE[17] 27.85 26.48 25.64 24.98 24.25 0.980 9 0.975 6 0.971 8 0.968 8 0.965 1 0.074 5 0.088 8 0.101 2 0.110 4 0.123 8 FDLCP-SENSE1 28.63 27.47 26.72 26.15 25.51 0.984 1 0.979 9 0.976 9 0.974 3 0.971 5 0.065 9 0.077 2 0.087 4 0.095 8 0.105 3 表 4 AF=3~7时数据4在泊松圆盘欠采样下各算法的重构结果
Table 4. Reconstruction results of different algorithms for data 4 under Poisson disc undersampling when acceleration factor is 3−7
算法 SNR/dB SSIM HFEN AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 TV-SENSE[15] 19.03 17.73 16.95 16.20 15.69 0.923 5 0.902 4 0.888 9 0.877 3 0.866 6 0.227 5 0.278 2 0.309 1 0.345 5 0.376 6 TV-LORAKS-SENSE[16] 19.15 17.95 17.25 16.59 16.08 0.924 2 0.903 6 0.891 1 0.880 8 0.870 9 0.201 9 0.250 2 0.276 9 0.309 5 0.341 1 LpTV-SENSE[17] 19.01 17.82 17.19 16.59 16.11 0.921 6 0.899 7 0.887 1 0.876 5 0.865 2 0.216 0 0.267 6 0.289 5 0.317 9 0.343 8 FDLCP-SENSE1 20.01 18.93 18.30 17.75 17.34 0.936 2 0.919 1 0.908 0 0.897 5 0.889 9 0.182 0 0.216 2 0.236 3 0.254 5 0.274 1 表 5 AF=3~7时22个数据在泊松圆盘欠采样下平均SNR、平均SSIM、平均HFEN差值
Table 5. Difference of mean SNR, mean SSIM, and mean HFEN for 22 sets of data at Poisson disc undersampling when acceleration factor is 3−7
算法 平均SNR/dB 平均SSIM 平均HFEN AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 AF=3 AF=4 AF=5 AF=6 AF=7 FDLCP-SENSE1 &
TV-SENSE1.23 1.44 1.61 1.68 1.71 0.055 6 0.072 1 0.082 3 0.090 6 0.097 2 −0.032 8 −0.045 4 −0.055 8 −0.063 9 −0.069 5 FDLCP-SENSE1 &
TV-LORAKS-SENSE0.85 1.06 1.26 1.43 1.51 0.007 1 0.009 8 0.012 3 0.014 0 0.015 3 −0.014 2 −0.026 5 −0.037 5 −0.049 4 −0.058 2 FDLCP-SENSE1 &
LpTV-SENSE0.86 1.01 1.10 1.13 1.14 0.029 6 0.038 2 0.043 2 0.047 5 0.050 6 −0.023 8 −0.031 4 −0.036 8 −0.041 5 −0.043 9 表 6 AF=4时不同算法在欠采样的4个数据上的重构时间
Table 6. Reconstruction time of different algorithms on four data at undersampling when acceleration factor is 4
s 数据 TV-SENSE TV-LORAKS-
SENSELpTV-SENSE FDLCP-SENSE1 数据1 38 153 15 27 数据2 53 281 23 31 数据3 213 866 41 63 数据4 196 319 40 105 -
[1] LUSTIG M, DONOHO D, PAULY J M. Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2007, 58(6): 1182-1195. doi: 10.1002/mrm.21391 [2] SONG L X, ZHANG J G, WANG Q. MRI reconstruction based on three regularizations: Total variation and two wavelets[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2016, 30: 64-69. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2016.06.003 [3] WANG S S, XIA Y, LIU Q G, et al. Fenchel duality based dictionary learning for restoration of noisy images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(12): 5214-5225. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2282900 [4] ELAD M, AHARON M. Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(12): 3736-3745. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.881969 [5] RAVISHANKAR S, BRESLER Y. MR image reconstruction from highly undersampled k-space data by dictionary learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2011, 30(5): 1028-1041. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2010.2090538 [6] QU X B, GUO D, NING B D, et al. Undersampled MRI reconstruction with patch-based directional wavelets[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2012, 30(7): 964-977. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2012.02.019 [7] ZHAN Z F, CAI J F, GUO D, et al. Fast multiclass dictionaries learning with geometrical directions in MRI reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Bio-Medical Engineering, 2016, 63(9): 1850-1861. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2015.2503756 [8] FRANCAVILLA M A, LEFKIMMIATIS S, VILLENA J F, et al. Maxwell parallel imaging[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2021, 86(3): 1573-1585. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28718 [9] 蒋明峰, 朱礼涛, 汪亚明, 等. 结合非线性GRAPPA与SENSE的并行磁共振成像[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2014, 48(10): 1865-1870.JIANG M F, ZHU L T, WANG Y M, et al. Parallel MRI based on combination of nonlinear GRAPPA and SENSE[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2014, 48(10): 1865-1870 (in Chinese). [10] PRUESSMANN K P, WEIGER M, SCHEIDEGGER M B, et al. SENSE: Sensitivity encoding for fast MRI[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 1999, 42(5): 952-962. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1522-2594(199911)42:5<952::AID-MRM16>3.0.CO;2-S [11] GRISWOLD M A, JAKOB P M, HEIDEMANN R M, et al. Generalized auto-calibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA)[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2002, 47(6): 1202-1210. doi: 10.1002/mrm.10171 [12] LUSTIG M, PAULY J M. SPIRiT: Iterative self-consistent parallel imaging reconstruction from arbitrary k-space[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2010, 64(2): 457-471. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22428 [13] 吴春俐, 朱学欢, 翟江南, 等. 基于快速分裂Bregman迭代的全变差正则化SENSE磁共振图像重建[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 35(1): 24-28.WU C L, ZHU X H, ZHAI J N, et al. Total variation regularized SENSE MRI reconstruction based on fast split Bregman iteration[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2014, 35(1): 24-28(in Chinese). [14] 李建武, 康杨, 周金鹏. PF-FICOTA-SENSE: 一种 MRI 快速重构方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(5): 897-908.LI J W, KANG Y, ZHOU J P. PF-FICOTA-SENSE: An MRI fast reconstruction method[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(5): 897-908(in Chinese). [15] RAMANI S, FESSLER J A. Parallel MR image reconstruction using augmented Lagrangian methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2011, 30(3): 694-706. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2010.2093536 [16] KIM T H, SETSOMPOP K, HALDAR J P. LORAKS makes better SENSE: Phase-constrained partial Fourier SENSE reconstruction without phase calibration[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2017, 77(3): 1021-1035. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26182 [17] 鲍中文. 磁共振成像的稀疏重构算法研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2020: 1-70.BAO Z W. Research on sparse reconstruction algorithm of magnetic resonance imaging[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2020: 1-70(in Chinese) . [18] YANG J F, ZHANG Y, YIN W T. A fast alternating direction method for TVL1-L2 signal reconstruction from partial Fourier data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(2): 288-297. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2010.2042333 [19] AFONSO M V, BIOUCAS-DIAS J M, FIGUEIREDO M A T. Fast image recovery using variable splitting and constrained optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(9): 2345-2356. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2047910 [20] SOUZA R, BENTO M, NOGOVITSYN N, et al. Dual-domain cascade of U-nets for multi-channel magnetic resonance image reconstruction[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2020, 71: 140-153. [21] KNOLL F, ZBONTAR J, SRIRAM A, et al. FastMRI: A publicly available raw k-space and DICOM dataset of knee images for accelerated MR image reconstruction using machine learning[J]. Radiology Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 2(1): e190007. [22] SAWYER A M, LUSTIG M, ALLEY M, et al. Creation of fully sampled MR data repository for compressed sensing of the knee[C]//Proceedings of the SMRT Conference. Salt Lake City: SMRT, 2013. [23] HUANG J Z, ZHANG S T, METAXAS D. Efficient MR image reconstruction for compressed MR imaging[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2011, 15(5): 670-679. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2011.06.001 [24] CORRIVEAU P, WEBSTER A. VQEG evaluation of objective methods of video quality assessment[J]. SMPTE Journal, 1999, 108(9): 645-648. doi: 10.5594/J17594 [25] WANG Z, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600-612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 -







 下载:
下载: