Strong tracking CKF adaptive interactive multiple model tracking algorithm based on hypersonic target
-
摘要:
高超目标运动状态复杂且具有高机动性,传统的交互多模型(IMM)跟踪精度低、收敛速度慢,基于此,提出了一种基于多重渐消因子的强跟踪容积卡尔曼滤波(CKF)自适应交互多模型(AIMM)跟踪算法。以IMM-CKF算法为基础,通过对CKF算法的结构进行分析,在时间更新和量测更新的协方差矩阵中引入强跟踪算法的渐消因子,在线实时调整滤波增益,减小模型不匹配导致的滤波精度下降;在IMM的模型集中选择Singer模型、“当前”统计模型和Jerk模型,并针对模型扩维导致CKF算法中无法 Cholesky分解的问题引入奇异值分解(SVD)算法;对IMM算法中马尔可夫矩阵提出自适应算法,通过模型似然函数值对转移概率进行自适应修正,增强匹配模型所占比例。仿真结果表明:所提算法跟踪收敛速度提高了约37.5%,跟踪精度提高了16.51%。
Abstract:Hypersonic targets have complex motion states and high maneuverability. The conventional interactive multiple model (IMM) technique converges slowly and tracks poorly. Based on numerous fading variables, an adaptive interactive multiple model (AIMM) algorithm with strong tracking for cubature Kalman filter (CKF) is proposed. The structure of CKF is examined based on IMM-CKF, and the fading factor of the strong tracking algorithm is added to the covariance matrix of time updating and measurement updating. This allows for the online and real-time adjustment of the filter gain, which can lessen the decrease in filter accuracy brought on by model mismatch. Choose the Singer, ‘current’ and Jerk models from the IMM model collection. These models introduce singular value decomposition (SVD) decomposition as a solution to the issue that the model dimension expansion prevents Cholesky decomposition in CKF. An adaptive algorithm for Markov matrix in IMM algorithm is proposed. The transition probability is adaptively modified by the value of the model likelihood function to enhance the proportion of the matching model. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm improves tracking convergence speed by 37.5% and tracking accuracy by 16.51%.
-
表 1 仿真初始参数设置
Table 1. Simulation initial parameter settings
参数 数值 仿真步长/s 1 弱化因子 1 遗忘因子 0.95 采样时长/s 350 初始模型概率 ${\boldsymbol{u}} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {1/3}&{1/3}&{1/3} \end{array}} \right]$ 马尔可夫转移矩阵 $ {{\boldsymbol{P}}_{\text{m}}} = \left[{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0.9&0.05&0.05 \\ 0.05&0.9&0.05 \\ 0.05&0.05&0.9 \\ \end{array}}\right] $ 状态误差协方差矩阵 $ {\boldsymbol{Q}} = {\text{diag}}\left( {{{100}^2}}, {{{100}^2}}, {{{100}^2}} \right) $ 观测噪声协方差矩阵 $ {\boldsymbol{R}} = {\text{diag}}\left( {{{0.5}^2}}, {{{0.5}^2}}, {{{500}^2}} \right) $ 初始误差协方差矩阵 $\begin{gathered} {\boldsymbol{P}} = {\text{diag}}\left({5\;000^2},{ {3\;00}}{{ {0}}^2}{ {,10}}{{ {0}}^2}{ {,}}{5\;000^2},\right. \\ \qquad \left. { {3\;00}}{{ {0}}^2}{ {, }} { {10}}{{ {0}}^2}{ {,}}{5\;000^2}{ {, 3\;00}}{{ {0}}^2}{ {,10}}{{ {0}}^2}\right) \\ \end{gathered} $ 表 2 3种算法均方根误差均值对比
Table 2. Comparison of mean values of root mean square error of three algorithms
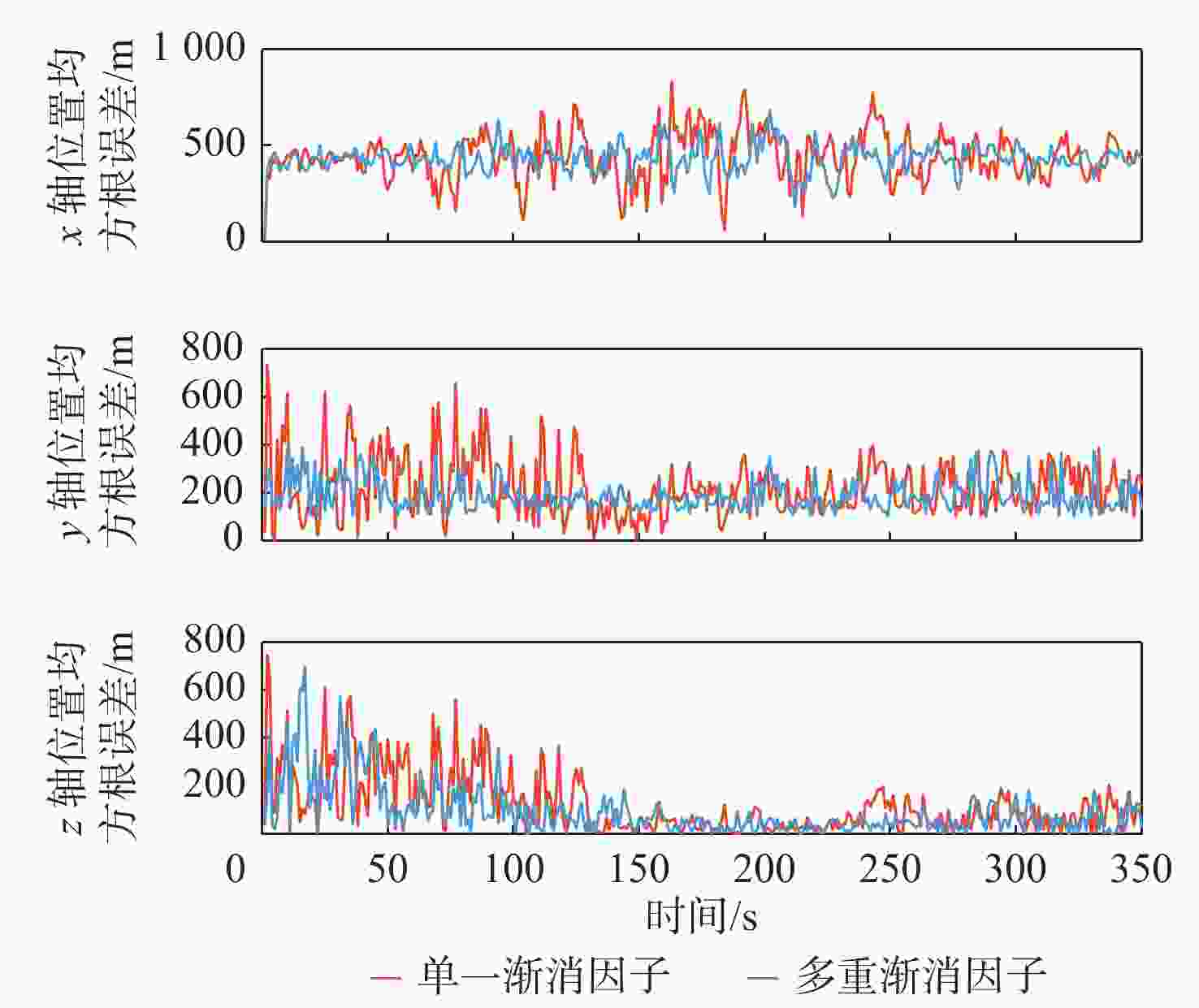
算法 位置均方根误差均值/m 速度均方根误差均值/(m·s−1) x轴 y轴 z轴 整体 x轴 y轴 z轴 整体 IMM-CKF 449.2 213.7 164 537.3 52.7 56.2 51.9 104.1 IMM-STCKF 447.9 207 158.2 530.2 37.9 56.3 49.5 92.7 AIMM-STCKF 381.9 171.3 97.1 448.6 19.4 27.7 41.4 66.9 -
[1] 周宏仁, 敬忠良, 王培德, 等. 机动目标跟踪[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1991: 1-35.ZHOU H R, JING Z L, WANG P D, et al. Maneuvering target tracking[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1991: 1-35(in Chinese). [2] SINGER R A. Estimating optimal tracking filter performance for manned maneuvering targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1970, AES-6(4): 473-483. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1970.310128 [3] 周宏仁. 机动目标“当前” 统计模型与自适应跟踪算法[J]. 航空学报, 1983, 4(1): 73-86. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.1983.01.013ZHOU H R. A “current” statistical model and adaptive tracking algorithm for maneuvering targets[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 1983, 4(1): 73-86(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.1983.01.013 [4] MEHROTRA K, MAHAPATRA P R. A Jerk model for tracking highly maneuvering targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1997, 33(4): 1094-1105. doi: 10.1109/7.624345 [5] 王磊, 程向红, 李双喜, 等. 自适应交互式多模型AUV组合导航算法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2016, 24(4): 511-516.WANG L, CHENG X H, LI S X, et al. Adaptive interacting multiple model filter for AUV integrated navigation[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2016, 24(4): 511-516(in Chinese). [6] MAGILL D. Optimal adaptive estimation of sampled stochastic processes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1965, 10(4): 434-439. doi: 10.1109/TAC.1965.1098191 [7] BLOM H A P. An efficient filter for abruptly changing systems[C]// Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1984: 656-658. [8] LI X R, BAR-SHALOM Y. Design of an interacting multiple model algorithm for air traffic control tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 1993, 1(3): 186-194. doi: 10.1109/87.251886 [9] 黄景帅, 李永远, 汤国建, 等. 高超声速滑翔目标自适应跟踪方法[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(9): 323786. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.23786HUANG J S, LI Y Y, TANG G J, et al. Adaptive tracking method for hypersonic glide target[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(9): 323786(in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.23786 [10] 戴洪德, 方君, 唐亮, 等. 高超声速机动目标的强跟踪UKF自适应交互多模型算法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2018, 26(3): 338-345.DAI H D, FANG J, TANG L, et al. Strong tracking UKF adaptive interacting multiple-model algorithm based on maneuvering hypersonic-target tracking[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2018, 26(3): 338-345(in Chinese). [11] 戴定成, 姚敏立, 蔡宗平, 等. 改进的马尔可夫参数自适应IMM算法[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(5): 1198-1205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.05.024DAI D C, YAO M L, CAI Z P, et al. Improved adaptive Markov IMM algorithm[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(5): 1198-1205(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.05.024 [12] 肖楚晗, 李炯, 雷虎民, 等. 基于AVSIMM算法的高超声速再入滑翔目标跟踪[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(2): 413-421.XIAO C H, LI J, LEI H M, et al. Hypersonic reentry gliding target tracking based on AVSIMM algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(2): 413-421(in Chinese). [13] 王姚宇, 陈仁文, 张祥. 改进的基于奇异值分解的抗差容积卡尔曼滤波算法在全球定位导航中的应用[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(6): 2356-2362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.06.032WANG Y Y, CHEN R W, ZHANG X. Application of improved robust singular value decomposition-cubature Kalman filter algorithm in global positioning system navigation[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(6): 2356-2362(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.06.032 [14] 贾晓娟. 高超声速飞行器再入轨迹估计与跟踪[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2015: 18-22.JIA X J. Reentry trajectory estimating and tracking for hypersonic vehicle[D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2015: 18-22(in Chinese) . [15] 缪天宇. 助推滑翔式高超声速飞行器雷达探测与跟踪预报算法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017: 11-13.MIAO T Y. Research on radar detection, tracking and prediction algorithm for the boost-glide hypersonic vehicle[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017: 11-13(in Chinese) . [16] ARASARATNAM I, HAYKIN S. Cubature Kalman filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2009, 54(6): 1254-1269. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2009.2019800 [17] 秦雷, 李君龙, 周荻. 临近空间非弹道式目标HTV-2跟踪滤波与预报问题[J]. 航天控制, 2015, 33(2): 56-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2015.02.010QIN L, LI J L, ZHOU D. The problems of tracking filter and prediction for non-ballistic target HTV-2 in the near space[J]. Aerospace Control, 2015, 33(2): 56-61(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2015.02.010 [18] MENG Q H, HOU B W, LI D, et al. Performance analysis and comparison for high maneuver target track based on different Jerk models[J]. Journal of Control Science and Engineering, 2018, 2018: 6432485. [19] 李广华. 高超声速滑翔飞行器运动特性分析及弹道跟踪预报方法研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2016: 19-20.LI G H. Motion characteristics analysis and trajectory prediction for hypersonic glide vehicles[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2016: 19-20(in Chinese) . -







 下载:
下载: