Fine-grained image classification method with noisy labels based on retrieval augmentation
-
摘要:
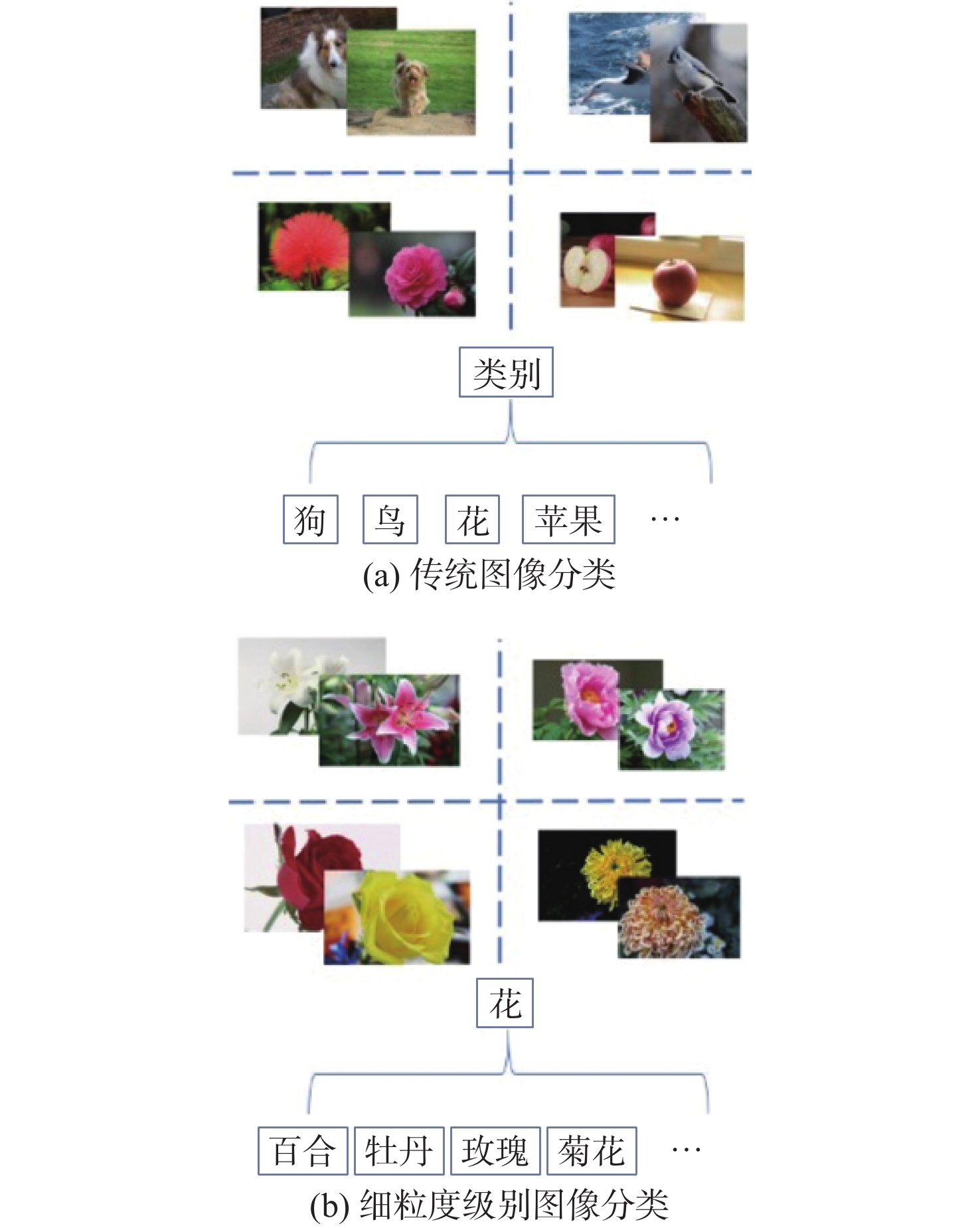
在互联网音视频内容分析的应用中,快速建立低标注代价的图像细粒度分类方法具有重要意义。由于类别间具有相似的外观特征,并且存在光照、视角、背景遮挡等干扰因素,细粒度图像分类面临类别数量多、类间差异性小,以及标注代价高、标签信噪比低等挑战。为改善在带有噪声标签的数据环境下海量图像细粒度分类的效果,提出一种基于检索增强的图像细粒度分类方法,在迭代清洗噪声标签的基础上,利用检索范式通过简单类别标注获取更具表达性的特征,提升分类器的识别能力,并在包含1500个细粒度的食物类别和超过50万张图像的数据集上取得良好的效果。
Abstract:In the application of Internet audio and video content analysis, it is of great significance to establish a fast fine-grained image classification method with lowlabeling costs. Due to the more similar appearance features between categories and the existence of interference factors such as illumination, viewing angle, and background occlusion, fine-grained image classification faces challenges such as large number of categories, small differences between categories, high labeling cost, and low label signal-to-noise ratio. In order to improve the effect of fine-grained classification of massive images in a data environment with noisy labels, a fine-grained image classification method based on retrieval augmentation was proposed. Based on iterative cleaning of noisylabels, the retrieval paradigm was used to obtain more expressive features through simple category labeling, so as to improve the recognition ability of the classifier. In addition, favorableresults wereachieved on the dataset containing 1500 fine-grained food categories and more than 500000 images.
-
Key words:
- fine-grained image classification /
- network security /
- image retrieval /
- data cleaning /
- noisy labels
-
表 1 图像分类方法结果
Table 1. Results of image classification methods
主干网络 ttop-1/% ResNet 38.57 EfficientNet-b1 42.30 EfficientNet-b5 47.52 Swin Transformer 52.41 ConvNeXt 54.88 表 2 本文方法实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results of proposedmethod
主干网络 方法 ttop-1/% ttop-5/% 平均精度/% BaseLine 56.73 88.30 53.89 ResNet 重排序 79.92 94.80 66.05 本文方法 86.58 94.77 71.64 BaseLine 60.61 91.30 61.77 EfficientNet-b1 重排序 90.3 94.80 69.69 本文方法 94.20 97.40 77.75 BaseLine 66.50 93.27 66.90 EfficientNet-b5 重排序 94.42 97.30 74.73 本文方法 95.49 98.00 75.80 BaseLine 87.76 95.91 80.33 Swin Transformer 重排序 95.13 98.48 84.75 本文方法 97.05 99.13 88.06 BaseLine 94.60 99.50 81.62 ConvNeXt 重排序 97.85 99.61 88.66 本文方法 98.02 99.70 90.56 -
[1] 李赫. 人工智能中的图像识别技术分析[J]. 无线互联科技, 2021, 18(17): 93-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6944.2021.17.046LI H. Analysis of image recognition technology in artificial intelligence[J]. Wireless Internet Technology, 2021, 18(17): 93-94(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6944.2021.17.046 [2] 任继明, 呼晓璐. 图像识别技术在公共安全领域的运用[J]. 计算机产品与流通, 2019(5): 108.REN J M, HU X L. Application of image recognition technology in the field of public safety[J]. Computer Products and Distribution, 2019(5): 108(in Chinese). [3] WEI X S, LUO J H, WU J X, et al. Selective convolutional descriptor aggregation for fine-grained image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing:A Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2017, 26(6): 2868-2881. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2688133 [4] JI X, VEDALDI A, HENRIQUES J. Invariant information clustering for unsupervised image classification and segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 9864-9873. [5] LIN T Y, ROYCHOWDHURY A, MAJI S. Bilinear CNN models for fine-grained visual recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1449-1457. [6] 罗建豪, 吴建鑫. 基于深度卷积特征的细粒度图像分类研究综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(8): 1306-1318.LUO J H, WU J X. A survey on fine-grained image categorization using deep convolutional features[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8): 1306-1318(in Chinese). [7] MAJI S, RAHTU E, KANNALA J, et al. Fine-grained visual classification of aircraft[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 1-6. [8] HAN B, YAO Q, YU X, et al. Co-teaching: Robust training of deep neural networks with extremely noisy labels[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2018, 3: 8527-8537. [9] ZHANG Y, WEI X S, WU J X, et al. Weakly supervised fine-grained categorization with part-based image representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing:A Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2016, 25(4): 1713-1725. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2531289 [10] SIMON M, RODNER E. Neural activation constellations: Unsupervised part model discovery with convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1143-1151. [11] MATSUDA Y, HOASHI H, YANAI K. Recognition of multiple-food images by detecting candidate regions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 25-30. [12] BOSSARD L, GUILLAUMIN M, VAN GOOL L. Food-101–mining discriminative components with random forests[C]//Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 446-461. [13] BOLANOS M, RADEVA P. Simultaneous food localization and recognition[C]//Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 3140-3145. [14] GORDO A, ALMAZÁN J, REVAUD J, et al. End-to-end learning of deep visual representations for image retrieval[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2017, 124(2): 237-254. doi: 10.1007/s11263-017-1016-8 [15] LI W, DUAN L, XU D. Text-based image retrieval using progressive multi-instance learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011:2049-2055. [16] HIRATA K, KATO T. Query by visual example - content based image retrieval[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Extending Database Technology: Advances in Database Technology. Berlin: Springer, 1992: 56-71. [17] LEE S H, CHOI J Y, RO Y M, et al. Local color vector binary patterns from multichannel face images for face recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing:A Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2012, 21(4): 2347-2353. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2181526 [18] BABENKO A, SLESAREV A, CHIGORIN A, et al. Neural codes for image retrieval[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 584-599. [19] HUANG H K, CHIU C F, KUO C H, et al. Mixture of deep CNN-based ensemble model for image retrieval[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 5th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1-2. [20] 魏秀参. 深度学习下细粒度级别图像的视觉分析研究[M]. 南京: 南京大学, 2018: 18-24.WEI X S. Visual analysis of fine-grained images under deep learning [M]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2018: 18-24(in Chinese). [21] BRANSON S, VAN HORN G, BELONGIE S, et al. Bird species categorization using pose normalized deep convolutional nets[EB/OL]. (2014-06-11)[2022-04-05]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1406.2952. [22] ZHUANG P Q, WANG Y L, QIAO Y. Learning attentive pairwise interaction for fine-grained classification[J]. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(7): 13130-13137. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i07.7016 [23] 白瑜颖, 刘宁钟, 姜晓通. 结合注意力混合裁剪的细粒度分类网络[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2021, 31(10): 38-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2021.10.007BAI Y Y, LIU N Z, JIANG X T. Fine grained image classification network combined with attention CutMix[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2021, 31(10): 38-42(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2021.10.007 [24] ZHU H W, KE W J, LI D, et al. Dual cross-attention learning for fine-grained visual categorization and object re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 4682-4692. [25] DING Y, ZHOU Y Z, ZHU Y, et al. Selective sparse sampling for fine-grained image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 6598-6607. [26] CHANG D L, DING Y F, XIE J Y, et al. The devil is in the channels: Mutual-channel loss for fine-grained image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing: A Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2020: 4683-4695. [27] 李海飞. 图像检索中的重排序算法研究[M]. 郑州: 河南大学, 2015: 7-17.LI H F. Research on reordering algorithms in image retrieval[M]. Zhengzhou: Henan University, 2015: 7-17(in Chinese). [28] JING Y S, BALUJA S. VisualRank: Applying PageRank to large-scale image search[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2008, 30(11): 1877-1890. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2008.121 [29] AMBAI M, YOSHIDA Y. Multiclass VisualRank: Image ranking method in clustered subsets based on visual features[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. New York: ACM, 2009: 732-733. [30] CHUM O, PHILBIN J, SIVIC J, et al. Total recall: Automatic query expansion with a generative feature model for object retrieval[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2007: 1-8. [31] SHEN X H, LIN Z, BRANDT J, et al. Object retrieval and localization with spatially-constrained similarity measure and k-NN re-ranking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 3013-3020. [32] QIN D F, GAMMETER S, BOSSARD L, et al. Hello neighbor: Accurate object retrieval with k-reciprocal nearest neighbors[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 777-784. [33] ZHONG Z, ZHENG L, CAO D L, et al. Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 3652-3661. [34] TAN M X, LE Q V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[EB/OL]. (2020-09-11)[2022-04-05]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946. [35] LIU Z, LIN Y T, CAO Y, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 9992-10002. [36] LIU Z, MAO H Z, WU C Y, et al. A ConvNet for the 2020s[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 11966-11976. [37] WANG H, WANG Y T, ZHOU Z, et al. CosFace: Large margin cosine loss for deep face recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 5265-5274. [38] MIN W Q, WANG Z L, LIU Y X, et al. Large scale visual food recognition [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 9932-9949. -







 下载:
下载: