Lane line detection incorporating CBAM mechanism and deformable convolutional network
-
摘要:
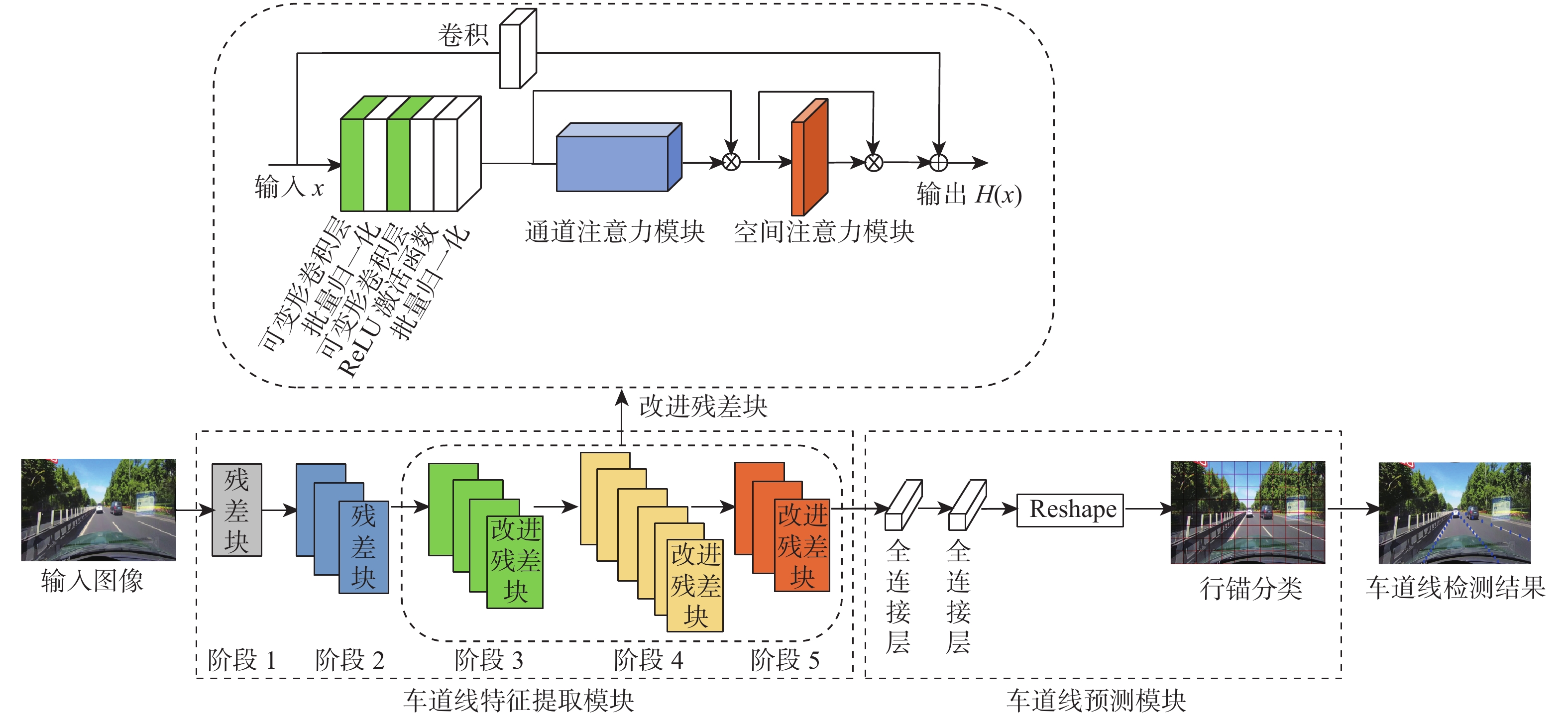
为满足自动驾驶及汽车高级驾驶辅助系统(ADAS)对车道线检测准确性和实时性的要求,提出一种融合卷积块注意力机制(CBAM)与可变形卷积网络(DCN)的车道线检测方法CADCN。在特征提取模块中嵌入CBAM注意力机制,增强有用特征并抑制无用特征响应;引入可变形卷积替换常规卷积,用带偏移的采样学习车道线的几何形变,提高卷积核的建模能力;基于行锚分类思想,对行方向上的位置进行选择和分类分析,预测车道线的位置信息,提高车道线检测模型的实时性。在车道线公开数据集上对所提CADCN方法进行训练及验证,在满足实时性的情况下,CADCN方法在TuSimple数据集上准确率达到96.63%,在CULane数据集上综合评估指标
F 1平均值达到74.4%,验证了所提方法的有效性。Abstract:In order to meet the accuracy and real-time requirements of autonomous driving and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) for lane line detection, a CADCN lane line detection method incorporating convolutional block attention module (CBAM) mechanism and deformable convolutional network (DCN) was proposed. Firstly, the CBAM mechanism was embedded in the feature extraction module to enhance the useful features and suppress the useless feature responses. Secondly, DCN was used to replace the conventional convolutional network, and the geometric deformation of lane lines was learned by sampling with offset to improve the modeling capability of the convolution kernel. Finally, based on the idea of row anchor classification, the location point along the row was selected and classified, so as to predict the lane line location information and thus improve the real-time performance of the lane line detection model. The CADCN model was trained and validated on the public lane line dataset. While ensuring real-time performance, the accuracy rate of the model on the TuSimple dataset reaches 96.63%, and the comprehensive evaluation index
F 1 on the CULane dataset reaches 74.4%, which verifies the effectiveness of the algorithm. -
表 1 车道线数据集的详细信息
Table 1. Details of lane line dataset
数据集 总帧数 训练集 验证集 测试集 分辨率/(像素×像素) 标注方式 多天气 多时段 多线型 道路类型 车道数 场景种类 TuSimple 6408 3268 358 2782 1280×720 点坐标 是 是 否 公路 ≤5 1 CULane 133235 88880 9675 34680 1640×590 点坐标 是 是 否 公路、城市、农村 ≤4 9 表 2 CULane数据集场景分类及占比
Table 2. CULane dataset scene classification and proportion
场景 场景描述 占比/% 正常 驾驶员视野良好,车道线标记清晰可见 27.74 拥挤 道路上大量车辆缓行,车道线被车辆遮挡 23.39 夜间 晚上能见度低,车道线模糊,各类灯光干扰 20.27 无车道线 无车道线标记,通常道路狭窄且路边停车较多 11.73 阴影 天桥或高架桥下光线较暗,树荫或建筑阴影 2.68 箭头 车道线之间的直行、转弯、调头等标记 2.57 亮光 各类强光造成路边反光,道路上车道线不清晰 1.40 弯道 前方车道线弯曲 1.22 十字路口 十字路口中斑马线标记干扰,路口中间无车道线 9.00 表 3 TuSimple数据集上不同模型检测结果比较
Table 3. Comparison of detection results of different models on TuSimple dataset
表 4 CULane数据集上不同模型检测结果比较
Table 4. Comparison of detection results of different models on CULane dataset
方法 F1/% FP (十字路口) 平均值/% 帧率/(帧·s−1) 正常 拥挤 夜间 无车道线 阴影 箭头 亮光 弯道 LaneNet[10] 82.9 61.1 53.4 37.7 56.2 72.2 54.5 59.3 5928 61.8 44 DeepLabV2 87.4 64.1 60.6 38.1 60.7 79 54.1 59.8 2505 66.7 77.31 FastDraw[18] 85.9 63.6 57.8 40.6 59.9 79.4 57.0 65.2 7013 69.7 90.3 SAD[9] 89.8 68.1 64.2 42.5 67.5 83.9 59.8 65.5 1995 70.5 39.53 SCNN[8] 90.6 69.7 66.1 43.4 66.9 84.1 58.5 64.4 1990 71.6 7.5 PINet[19] 89.6 71.9 67.0 49.3 67.0 84.2 65.2 66.2 1505 73.8 35 CADCN 90.9 72.4 67.7 46.1 69.3 85.9 62.3 69.5 2016 74.4 92.4 注:加粗字体为每行最优结果。 表 5 消融实验结果对比
Table 5. Comparison of ablation test results
组别 可变形
卷积通道注意
力机制空间注意
力机制CBAM注
意力机制准确率/% 1 95.87 2 √ 96.07 3 √ √ 96.23 4 √ √ 96.30 5 √ √ 96.63 -
[1] WAYKOLE S, SHIWAKOTI N, STASINOPOULOS P. Review on lane detection and tracking algorithms of advanced driver assistance system[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(20): 11417. doi: 10.3390/su132011417 [2] 杜恩宇, 张宁, 李艳荻. 基于Gabor滤波器的车道线快速检测方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2018, 47(8): 314-321.DU E Y, ZHANG N, LI Y D. Lane line quick detection method based on Gabor filter[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(8): 314-321(in Chinese). [3] ANDRADE D C, BUENO F, FRANCO F R, et al. A novel strategy for road lane detection and tracking based on a vehicle’s forward monocular camera[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(4): 1497-1507. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2018.2856361 [4] LUO S, ZHANG X Q, HU J, et al. Multiple lane detection via combining complementary structural constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(12): 7597-7606. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.3005396 [5] 蔡英凤, 张田田, 王海, 等. 基于实例分割和自适应透视变换算法的多车道线检测[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 50(4): 775-781. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2020.04.023CAI Y F, ZHANG T T, WANG H, et al. Multi-lane detection based on instance segmentation and adaptive perspective transformation[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 50(4): 775-781(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2020.04.023 [6] KIM J, LEE M. Robust lane detection based on convolutional neural network and random sample consensus[C]//Proceeding of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 454-461. [7] LI J,MEI X,PROKHOROV D,et al. Deep neural network for structural prediction and lane detection in traffic scene[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(3): 690-703. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2522428 [8] PAN X G, SHI J P, LUO P, et al. Spatial as deep: Spatial CNN for traffic scene understanding[C]//Proceeding of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alco: AAAI, 2018: 7276-7283. [9] HOU Y N, MA Z, LIU C X, et al. Learning lightweight lane detection CNNs by self attention distillation[C]//Proceeding of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1013-1021. [10] NEVEN D, DE BRABANDERE B, GEORGOULIS S, et al. Towards end-to-end lane detection: An instance segmentation approach[C]//Proceeding of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 286-291. [11] TABELINI L, BERRIEL R, PAIXÃO T M, et al. PolyLaneNet: Lane estimation via deep polynomial regression[C]//Proceeding of the 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 6150-6156. [12] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceeding of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 3-19. [13] DAI J F, QI H Z, XIONG Y W, et al. Deformable convolutional networks[C]/Proceeding of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 764-773. [14] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [15] ZHU X Z, HU H, LIN S, et al. Deformable ConvNets V2: More deformable, better results[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 9300-9308. [16] QIN Z Q, WANG H Y, LI X. Ultra fast structure-aware deep lane detection[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 276-291. [17] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834-848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [18] PHILION J. FastDraw: Addressing the long tail of lane detection by adapting a sequential prediction network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 11574-11583. [19] KO Y, LEE Y, AZAM S, et al. Key points estimation and point instance segmentation approach for lane detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 8949-8958. [20] GHAFOORIAN M, NUGTEREN C, BAKA N, et al. EL-GAN: Embedding loss driven generative adversarial networks for lane detection[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2019: 256-272. -







 下载:
下载: