-
摘要:
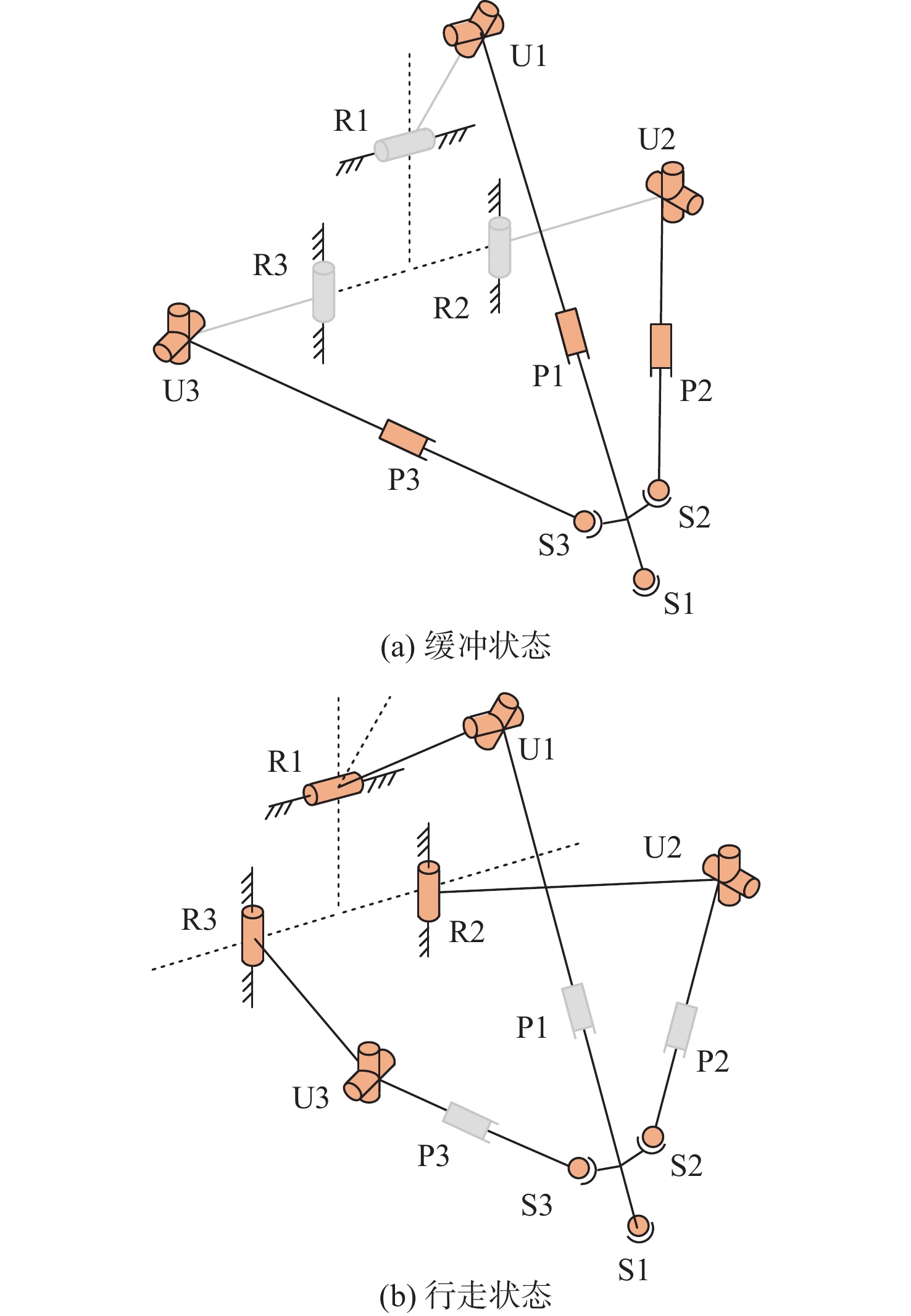
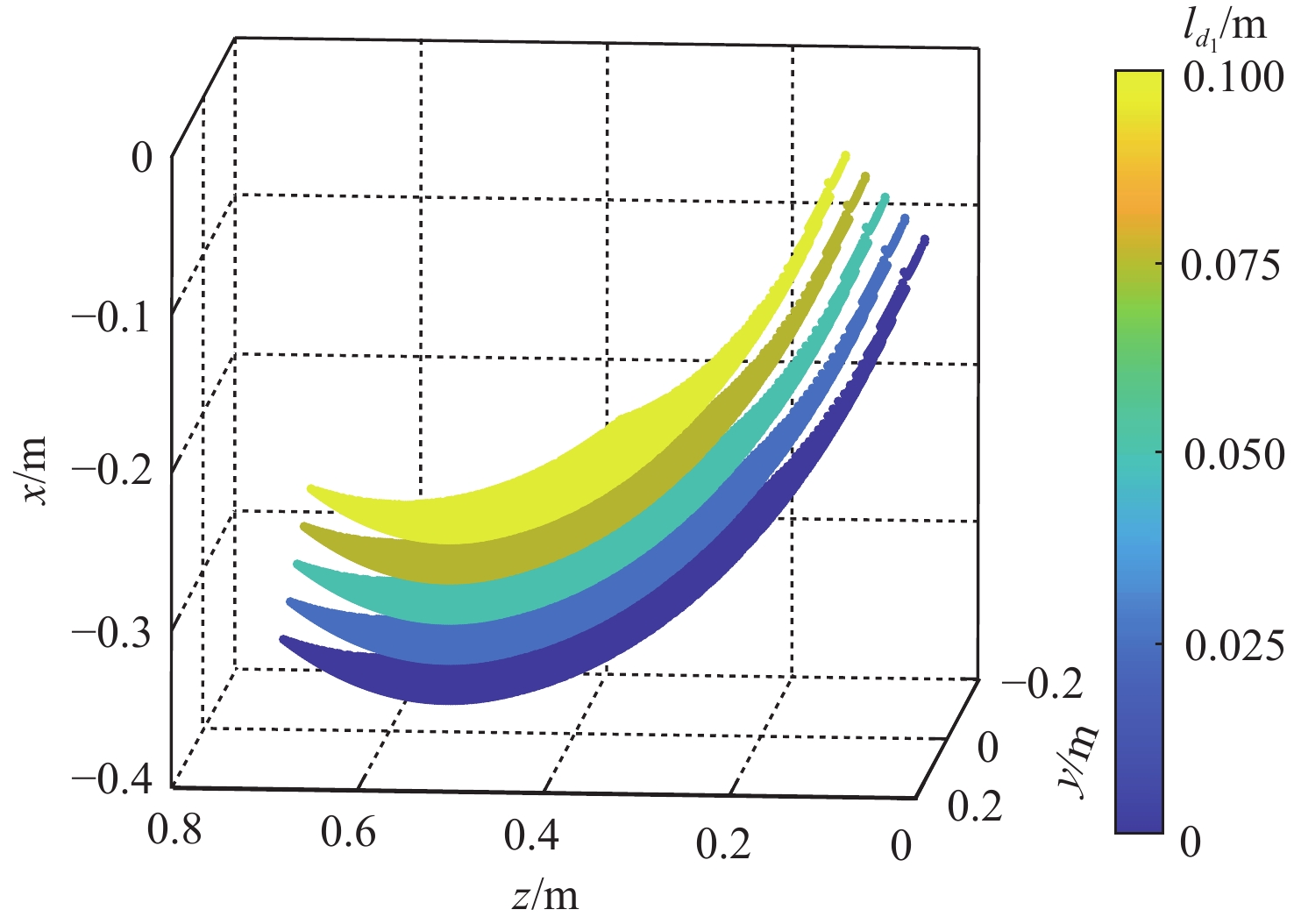
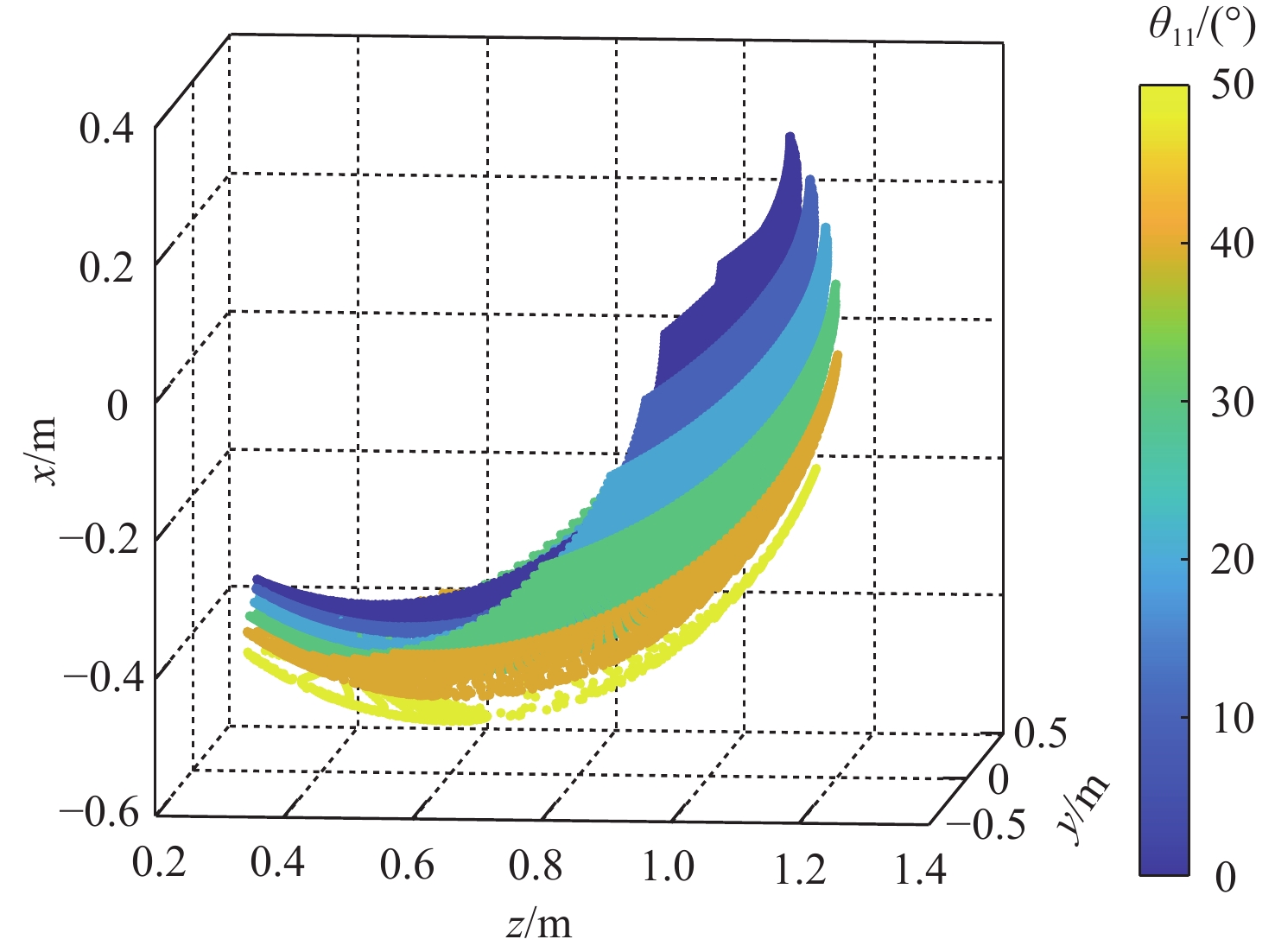
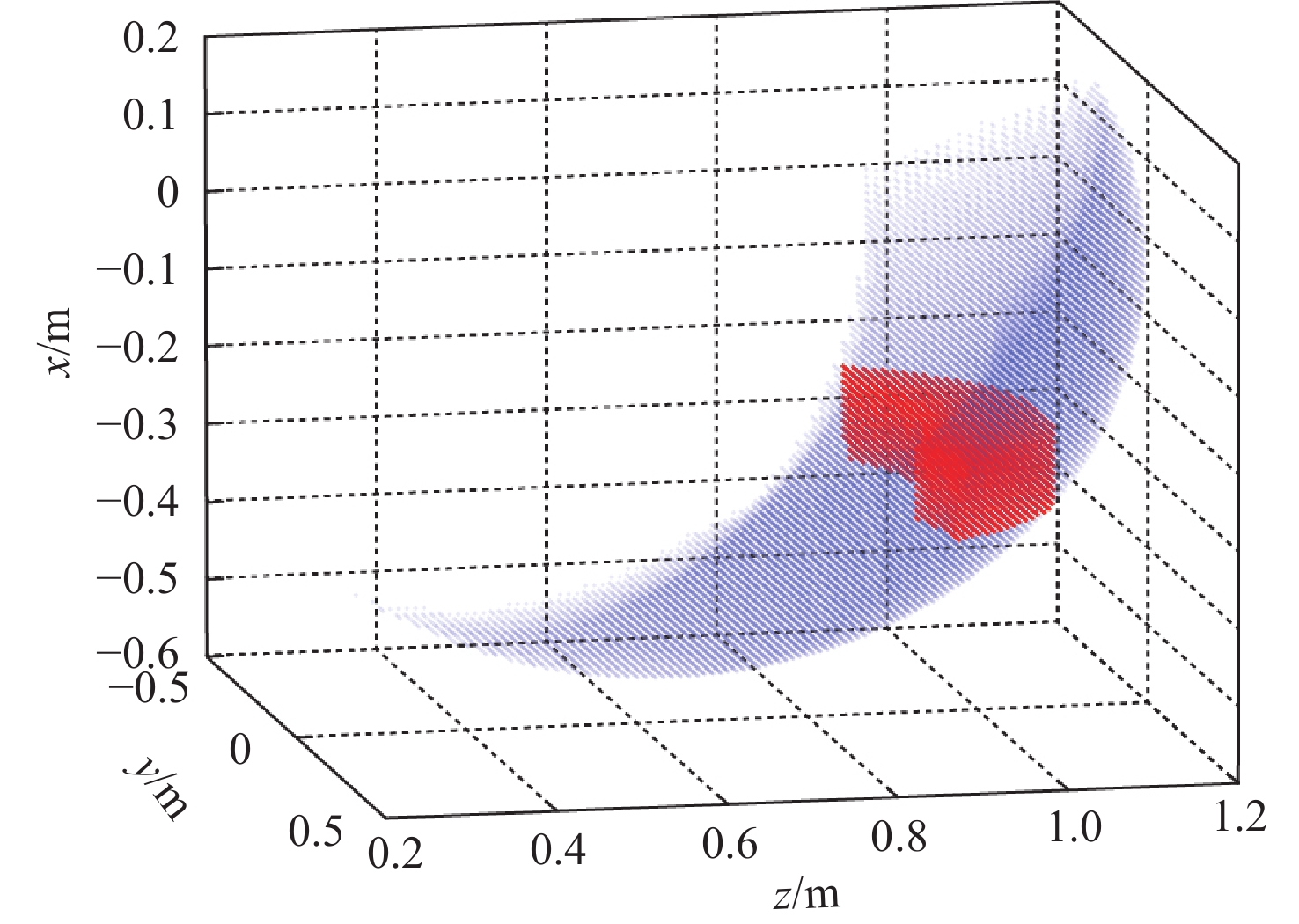
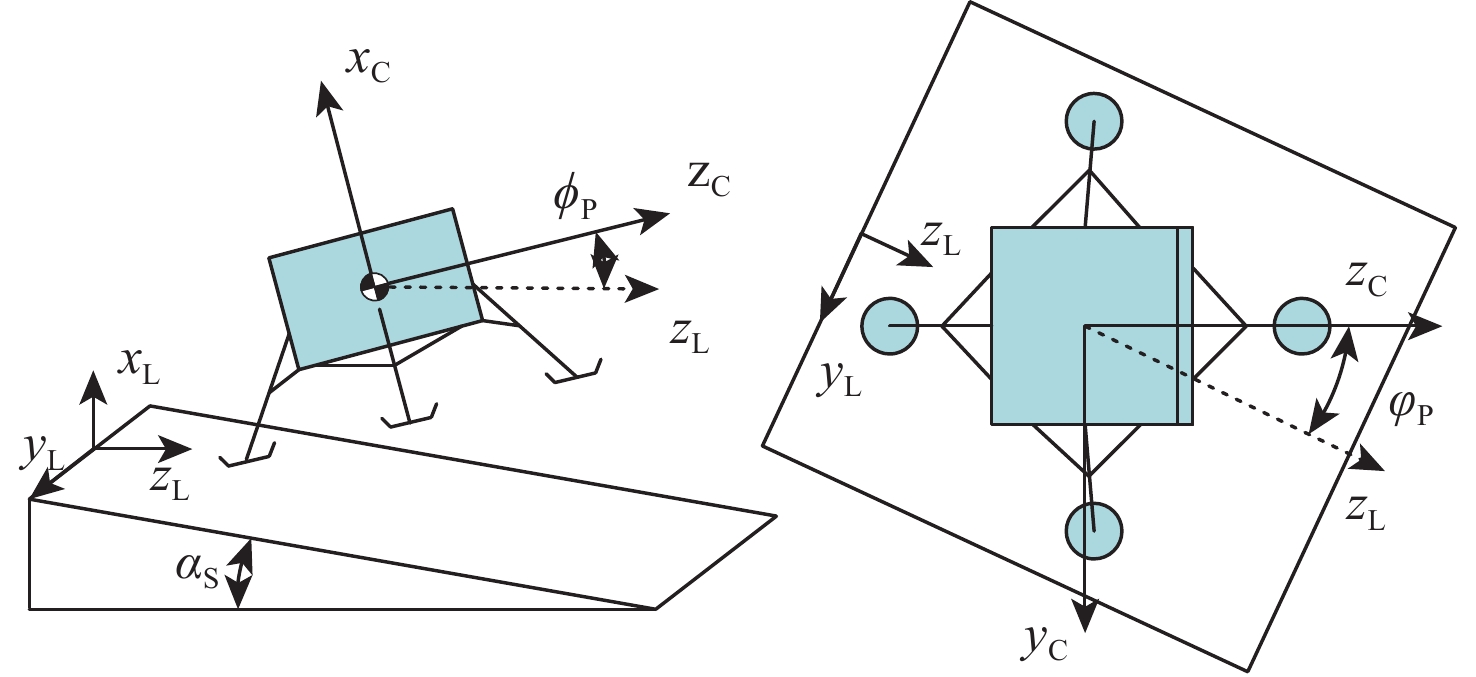
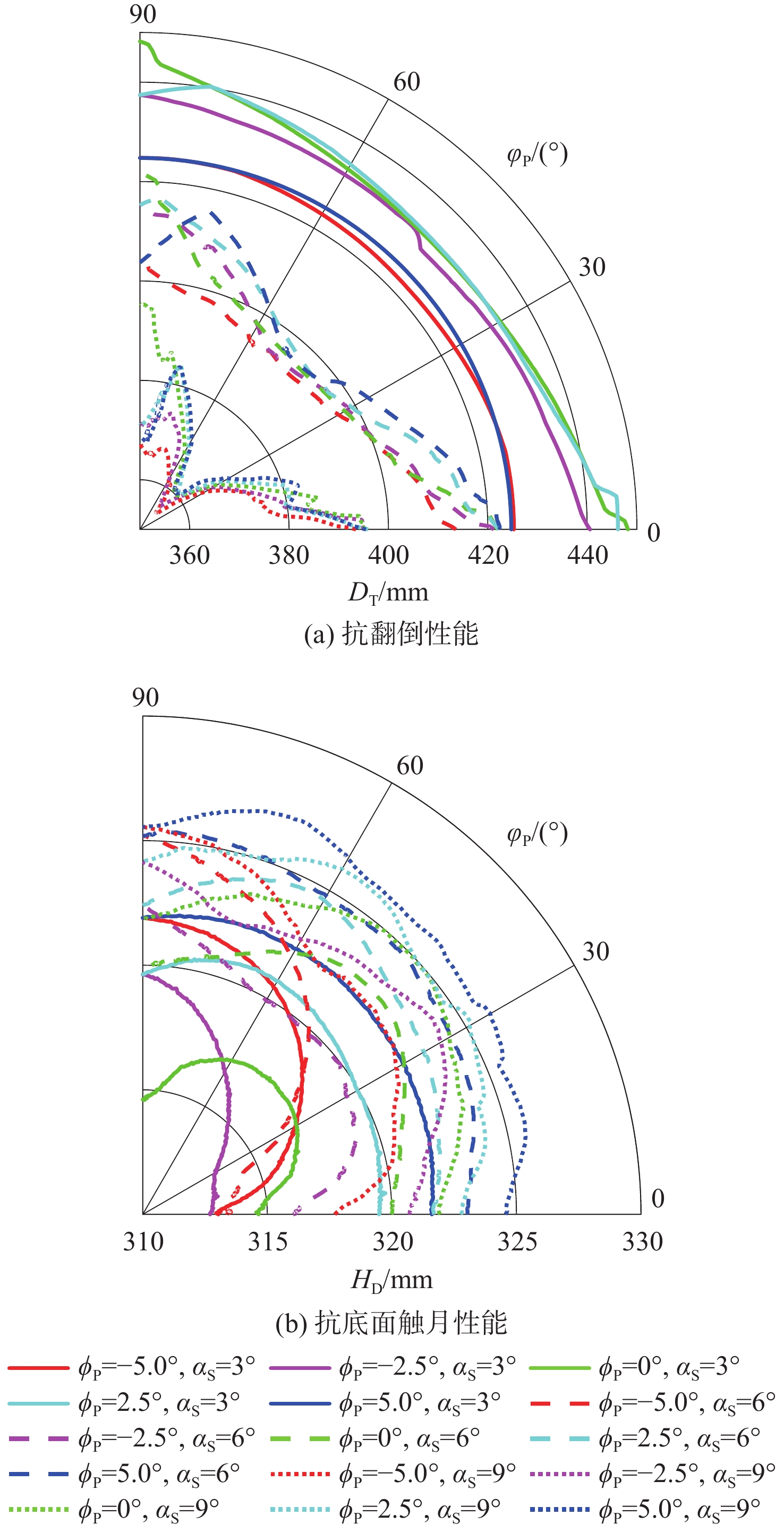
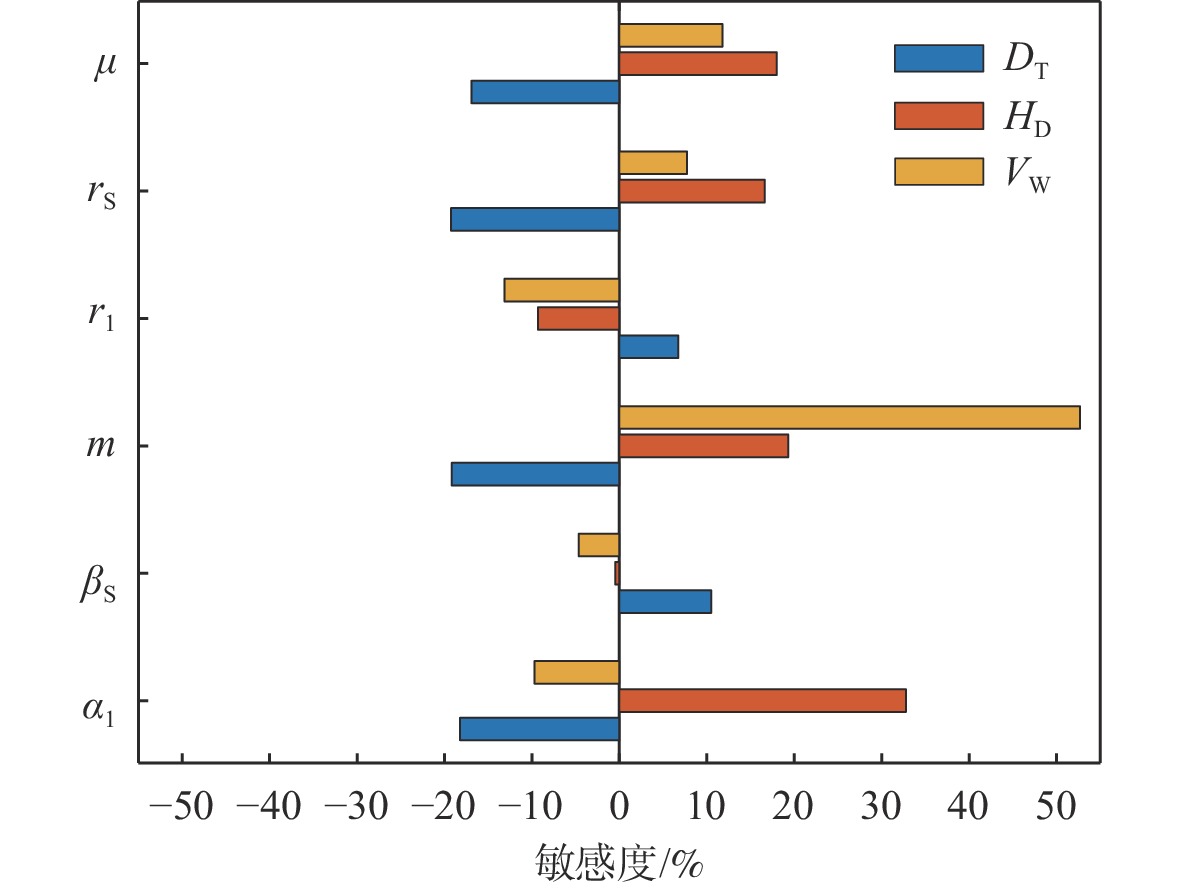
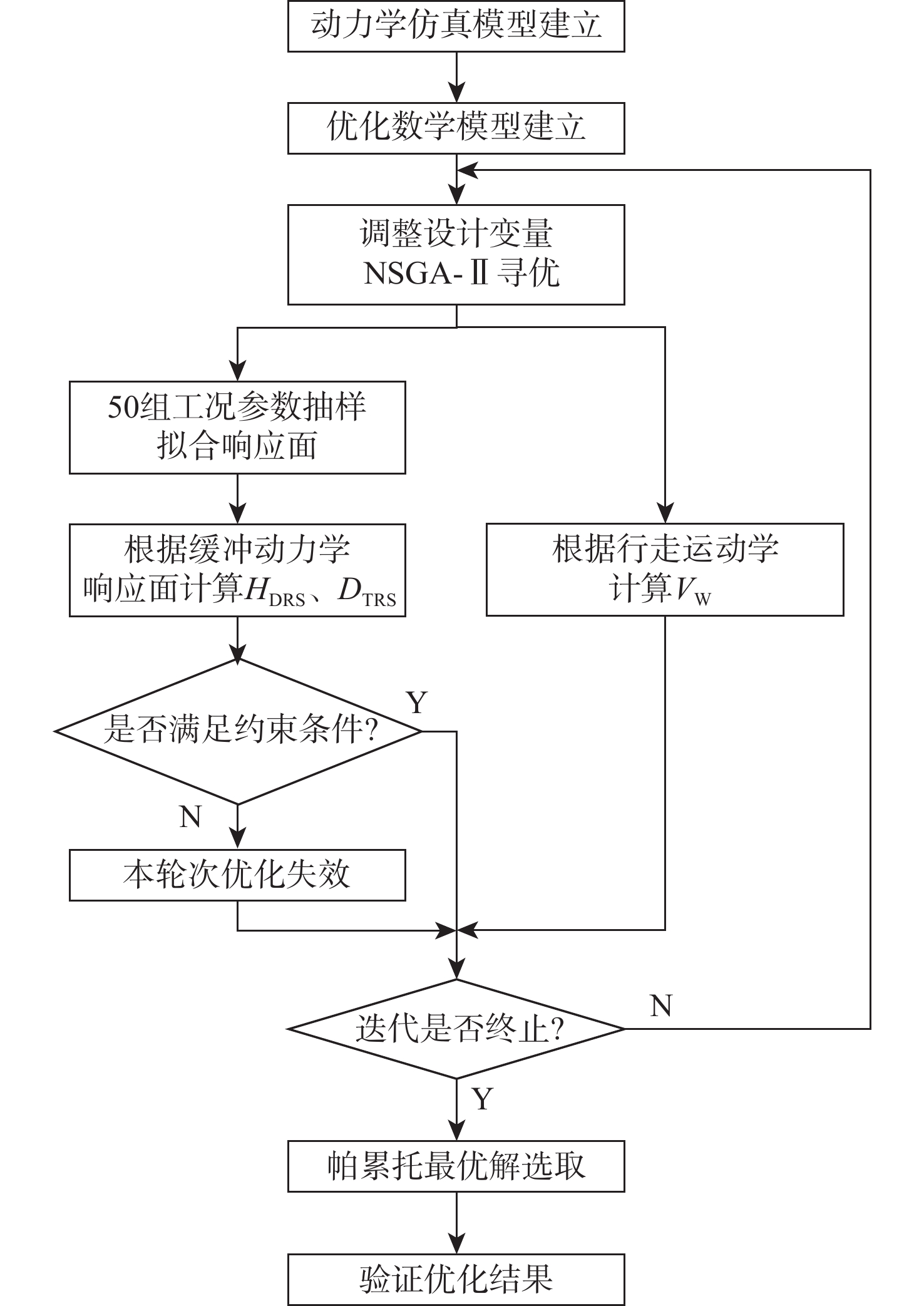
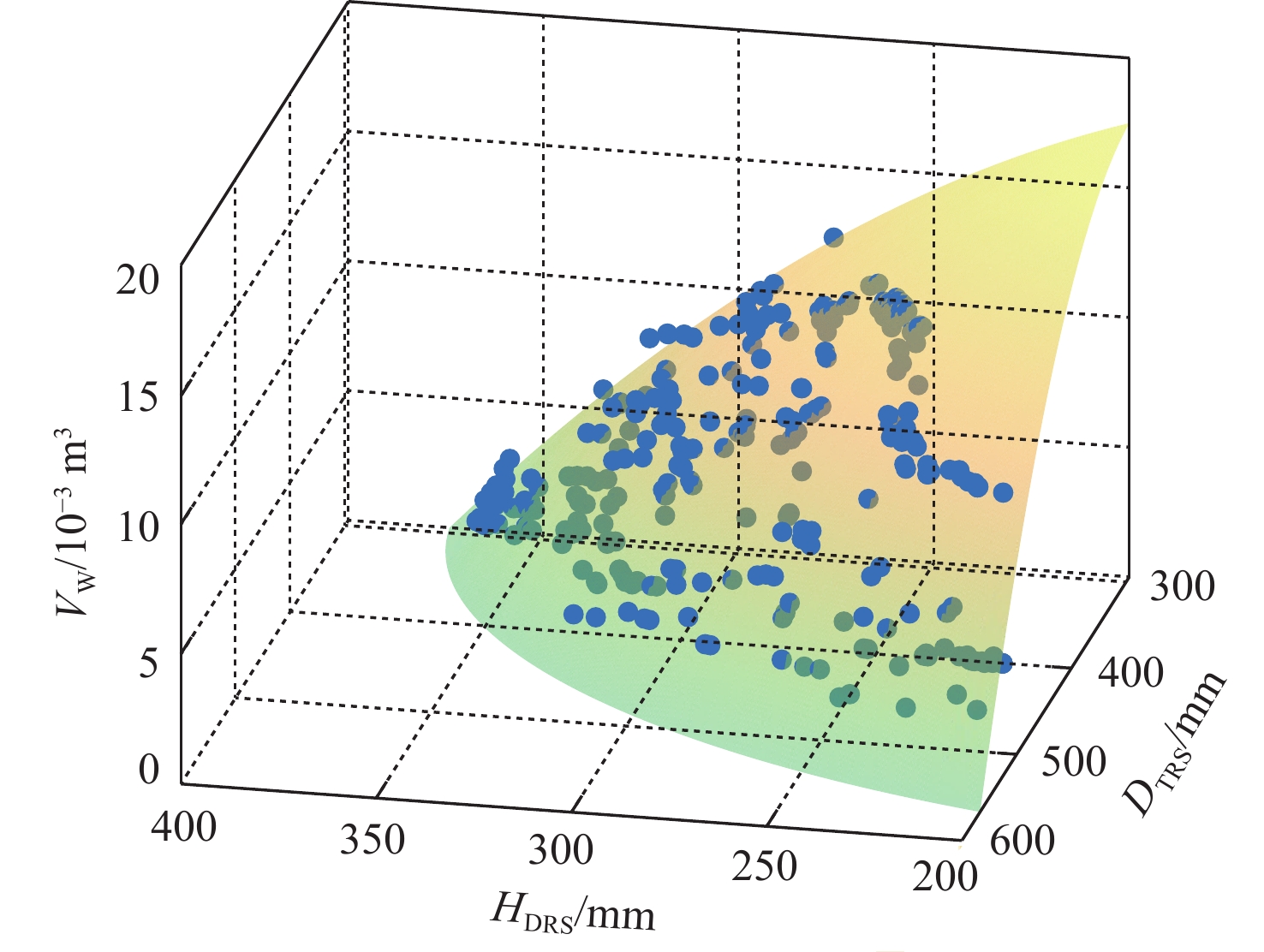
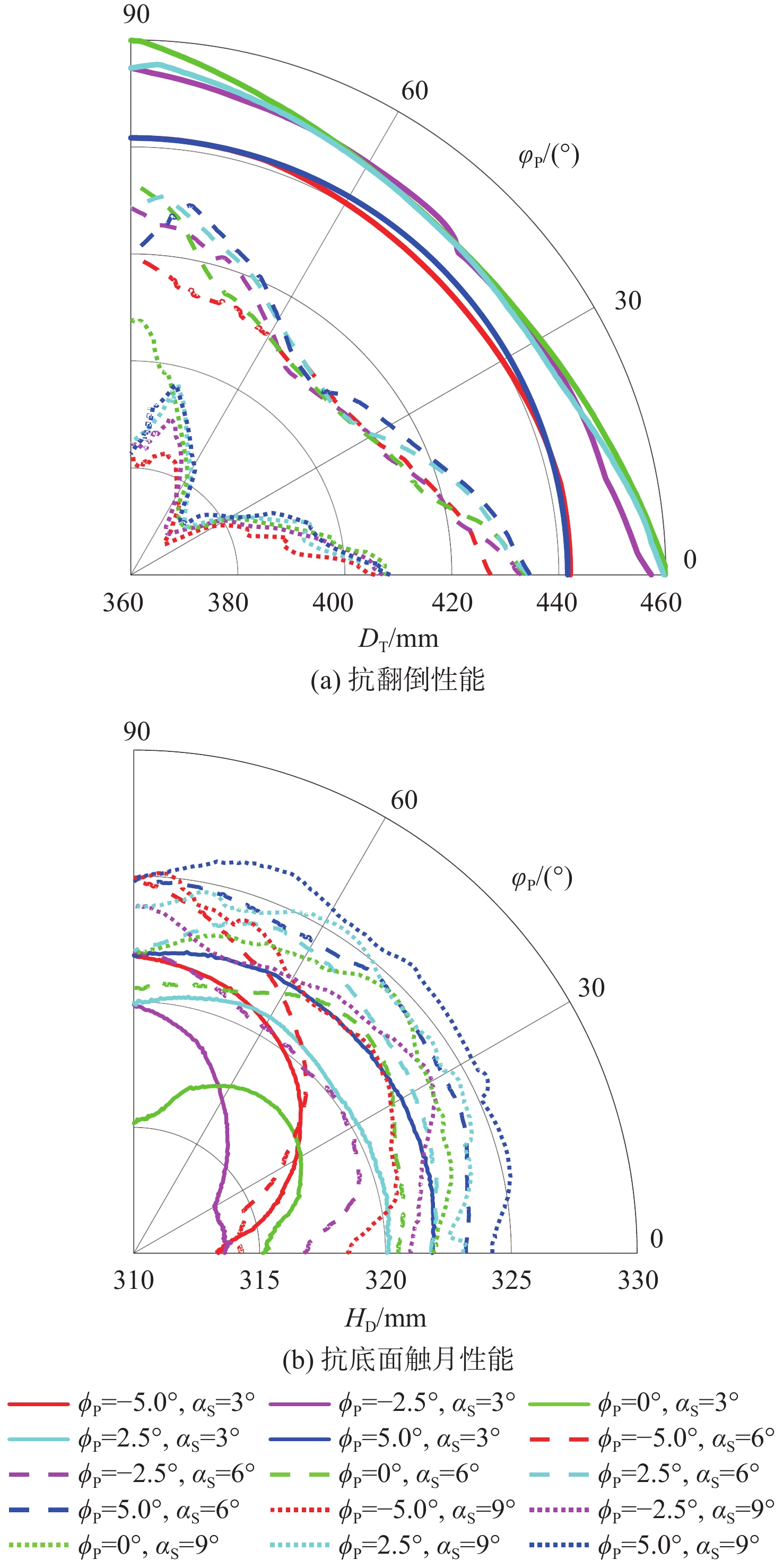
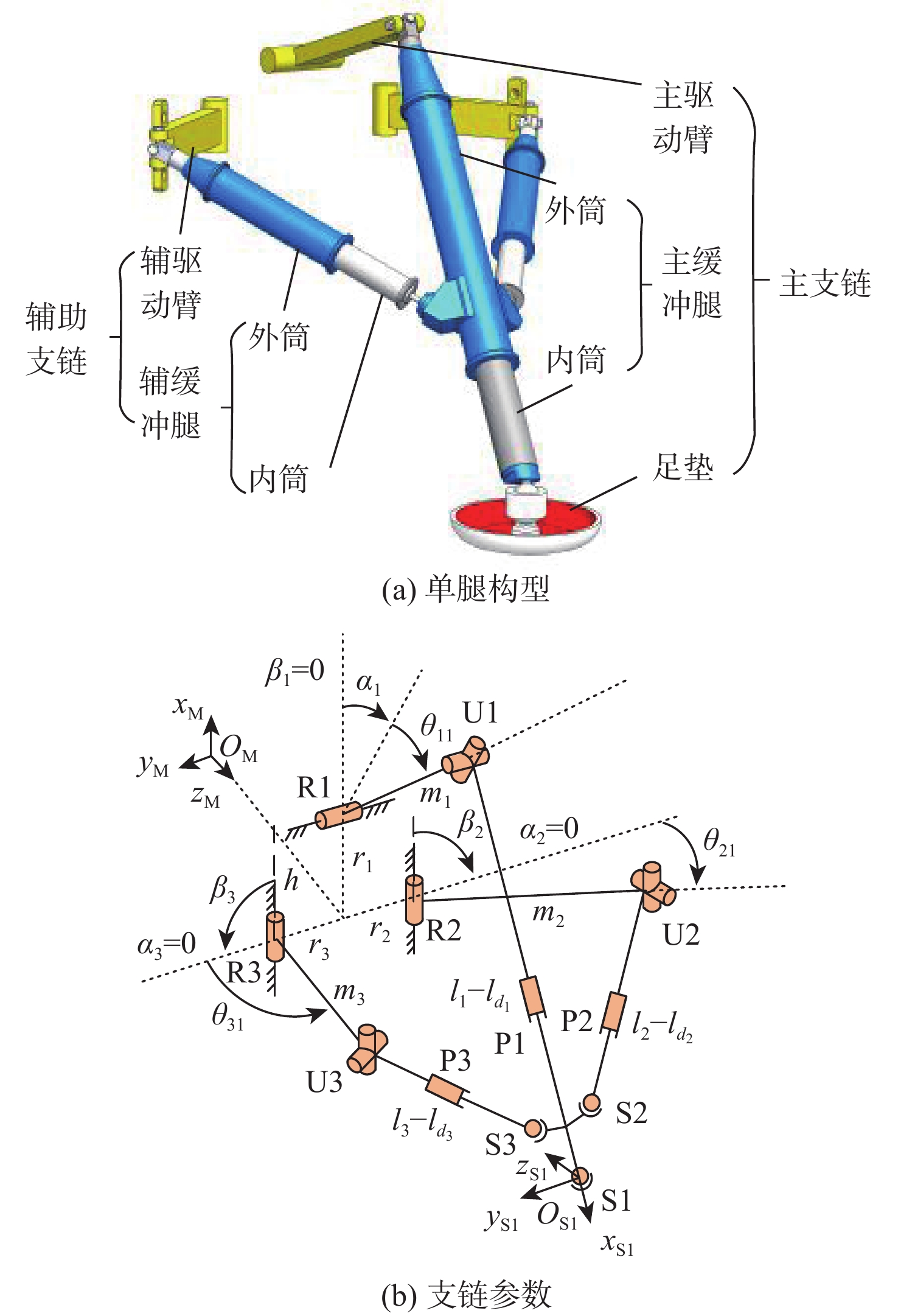
针对缓冲行走一体式月面探测器将着陆缓冲与月面行走功能融为一体,导致设计优化困难的问题,提出一种综合考虑缓冲特性和行走特性的性能分析与优化方法。根据月面探测器着陆腿的功能需求,设计了构型为RUP-2RUPS的冗余自由度并联机构,并建立其参数化模型,该构型可通过运动副生效或失效实现缓冲和行走2种功能的构型切换。结合全因子实验方法分析月面探测器的两功能运动学特性与动力学特性,依据月面复杂着陆和行走工况,给出综合优化的目标函数和约束条件。在敏感度分析的基础上,利用随优化过程更新的全工况响应面模型与非劣排序遗传算法,完成月面探测器着陆腿构型参数的优化。所提方法在提高运算效率的同时,保证了每轮优化均能筛选出当前构型的最恶劣着陆工况,并计算其极限值。优化后,最大有效工作空间增加了8.7%,抗翻倒性能最小值提高了4.0%,抗底面触月性能最小值提高了0.2%,整体性能更优。
Abstract:Taking into account the buffering and walking characteristics, a performance analysis and landing leg configuration optimization method is proposed to address the issue of the lunar probe integrating landing buffer and lunar walking functions, which causes challenges in its design optimization. According to the functional requirements of the landing legs of the lunar probe, a redundant DOF parallel mechanism with RUP-2RUPS configuration is proposed, and its parametric model is constructed. The mechanism can realize the configuration switching of buffering and walking functions by activating and deactivating the kinematic pairs. Combined with the full factor experimental method, the kinematic and dynamic characteristics of the lunar probe with two functions are analyzed. The objective function and constraint conditions of comprehensive optimization are given based on the intricate landing and walking conditions on the lunar surface. Based on the sensitivity analysis, the configuration parameters of the landing leg of the lunar probe are optimized by using the full-condition response surface model updated with the optimization process and the non-inferior sorting genetic algorithm. This optimization method not only improves the operation efficiency, but also ensures that each round of optimization can select the limit value of the worst working condition of the current configuration. After optimization, the maximum effective working space is increased by 8.7%, the minimum anti-overturning performance is increased by 4.0%, and the minimum anti-bottom-touchdown performance is increased by 0.2%. The overall performance is better.
-
Key words:
- lunar probe /
- kinematic analysis /
- dynamic analysis /
- response surface model /
- optimal design
-
表 1 支链构型参数
Table 1. Configuration parameters of chain
支链 α/(°) β/(°) r/m h/ m m/m l/m 主支链 36.87 0 0.07 0.415 0.2 0.6 左支链 0 90 0.125 0.415 0.2 0.35 右支链 0 90 0.125 0.415 0.2 0.35 表 2 月面探测器单腿单支链改进DH参数
Table 2. Improved DH parameter of single chain of single leg
连杆k 转角ϕk−1 偏置αk−1 转角φk 偏置dk 1 0 0 βi 0 2 0 ri 0 hi 3 π/2 0 αi+θi1 0 4 0 mi θi2 0 5 −π/2 0 θi3 0 6 0 li-ldi 0 0 表 3 工况参数取值
Table 3. Values for landing conditions parameters
(°) φP ϕP αS 取值范围 增量 取值范围 增量 取值范围 增量 0~90 0.5 −5~5 2.5 3~9 3 表 4 设计变量取值范围及初始值
Table 4. Design variable range and initial value
α1/(°) m/m rS/m 取值范围 初始值 取值范围 初始值 取值范围 初始值 [25,45] 36.87 [0.125,0.225] 0.2 [0.05,0.15] 0.125 表 5 优化前后对比
Table 5. Comparison before and after optimization
α1/(°) m/m rS/m VW/10−3 m3 DTmin/mm HDmin/mm 初始值 最优解 初始值 最优解 初始值 最优解 初始值 最优解 初始值 最优解 初始值 最优解 36.87 41.73 0.200 0.214 0.125 0.095 7.28 7.91 354.34 368.50 312.70 313.30 -
[1] 曾福明, 杨建中, 满剑锋, 等. 月球着陆器着陆缓冲机构设计方法研究[J]. 航天器工程, 2011, 20(2): 46-51.ZENG F M, YANG J Z, MAN J F, et al. Study on design method of landing gear for lunar lander[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2011, 20(2): 46-51(in Chinese). [2] 王永滨, 蒋万松, 王磊, 等. 载人登月月面软着陆缓冲装置设计与分析[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2015, 36(6): 22-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2015.06.004WANG Y B, JIANG W S, WANG L, et al. Research of landing gear technology of human lunar landing[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(6): 22-28(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2015.06.004 [3] WANG C, NIE H, CHEN J B, et al. The design and dynamic analysis of a lunar lander with semi-active control[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2019, 157: 145-156. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2018.12.037 [4] 陈金宝, 万峻麟, 李立春, 等. 月球探测器着陆性能若干影响因素分析[J]. 宇航学报, 2010, 31(3): 669-673.CHEN J B, WAN J L, LI L C, et al. Analysis on the influencing factors of performance in lunar lander[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2010, 31(3): 669-673(in Chinese). [5] 丁建中, 王春洁, 王家俊, 等. 着陆工况对月球着陆器着陆缓冲性能影响分析[J]. 载人航天, 2016, 22(1): 132-137.DING J Z, WANG C J, WANG J J, et al. Effects of touchdown conditions on the buffering performance of the lunar lander[J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2016, 22(1): 132-137(in Chinese). [6] 董洋, 王春洁, 吴宏宇, 等. 触地关机模式下的着陆器软着陆稳定性研究[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(2): 317-324.DONG Y, WANG C J, WU H Y, et al. Soft landing stability of lander in mode of shutdown at touchdown[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(2): 317-324(in Chinese). [7] MAEDA T, OTSUKI M, HASHIMOTO T, et al. Attitude stabilization for lunar and planetary lander with variable damper[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2016, 39(8): 1790-1804. doi: 10.2514/1.G000325 [8] 宋顺广, 王春洁. 基于蒙特卡罗法的月球探测器着陆稳定性分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2013, 39(9): 1192-1196.SONG S G, WANG C J. Landing stability analysis of the lunar lander based on Monte Carlo approach[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013, 39(9): 1192-1196(in Chinese). [9] 丁宗茂, 王春洁, 吴宏宇, 等. 探测器触地关机软着陆稳定性分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(3): 614-620.DING Z M, WANG C J, WU H Y, et al. Stability analysis of explorer in soft landing mode of engine shutdown at touchdown[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(3): 614-620(in Chinese). [10] DING J Z, LIU X A, DONG Y, et al. Stability analysis of Mars soft landing under uncertain landing conditions and two landing strategies[J]. Aircraft Engineering and Aerospace Technology, 2022, 94(10): 1883-1891. doi: 10.1108/AEAT-12-2021-0377 [11] 王家俊, 王春洁, 宋顺广. 基于响应面法的月球着陆器软着陆性能优化[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2014, 40(5): 707-711.WANG J J, WANG C J, SONG S G. Performance optimization of lunar lander based on response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014, 40(5): 707-711(in Chinese). [12] 吴宏宇, 王春洁, 丁宗茂, 等. 两种着陆模式下的着陆器缓冲机构构型优化[J]. 宇航学报, 2017, 38(10): 1032-1040.WU H Y, WANG C J, DING Z M, et al. Configuration optimization of landing gear under two kinds of landing modes[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2017, 38(10): 1032-1040(in Chinese). [13] 吴宏宇, 王春洁, 丁宗茂, 等. 着陆姿态不确定下的着陆器缓冲机构优化设计[J]. 宇航学报, 2018, 39(12): 1323-1331.WU H Y, WANG C J, DING Z M, et al. Optimization design of a landing gear under uncertain landing attitude[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2018, 39(12): 1323-1331(in Chinese). [14] HOWE A S. A modular habitation system for human planetary and space exploration[C]//Proceedings of the 45th International Conference Environmental Systems. Washington, D. C.: NASA, 2015: 1-24. [15] 梁鲁, 张志贤, 果琳丽, 等. 可移动式月球着陆器在载人月球探测活动中的任务分析[J]. 载人航天, 2015, 21(5): 472-478.LIANG L, ZHANG Z X, GUO L L, et al. Task analysis of mobile lunar lander in crewed lunar exploration missions[J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2015, 21(5): 472-478(in Chinese). [16] LIN R F, GUO W Z, CHEN X B, et al. Type synthesis of legged mobile landers with one passive limb using the singularity property[J]. Robotica, 2018, 36(12): 1836-1856. doi: 10.1017/S0263574718000760 [17] LIN R F, GUO W Z. Novel design of a family of legged mobile landers based on decoupled landing and walking functions[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2020, 34(9): 3815-3822. doi: 10.1007/s12206-020-0832-x [18] HAN Y C, GUO W Z, PENG Z K, et al. Dimensional synthesis of the reconfigurable legged mobile lander with multi-mode and complex mechanism topology[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2021, 155: 104097. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2020.104097 [19] HAN Y C, GUO W Z, ZHAO D H, et al. Multi-mode unified modeling and operation capability synergistic evaluation for the reconfigurable legged mobile lander[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2022, 171: 104714. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2021.104714 [20] 贾山, 周向华, 陈金宝, 等. 可移动月球着陆器系统设计与实验验证[J]. 深空探测学报, 2022, 9(1): 29-41.JIA S, ZHOU X H, CHEN J B, et al. System design and experimental verification of mobile lunar lander[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2022, 9(1): 29-41(in Chinese). [21] 佟振鸣. 移动式着陆探测机器人构型设计与行走规划研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2016: 15-49.TONG Z M. On configuration design and gait planning of mobile exploration lander[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2016: 15-49(in Chinese). [22] 贾山, 周向华, 陈金宝, 等. 缓冲/行走一体化着陆器运动学研究与步态规划[J]. 宇航学报, 2021, 42(4): 467-476.JIA S, ZHOU X H, CHEN J B, et al. Kinematics research and gait planning of buffering/walking integrated lander[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2021, 42(4): 467-476(in Chinese). [23] 赵辰尧, 郭为忠, 林荣富. 基于尺度互异的腿式移动着陆器步态规划[J]. 机械设计与研究, 2021, 37(5): 68-72.ZHAO C Y, GUO W Z, LIN R F. Gait planning of legged mobile lander based on different leg-length scales[J]. Machine Design & Research, 2021, 37(5): 68-72(in Chinese). [24] 何天宇, 董洋, 檀傈锰, 等. 月基装备行走运动学分析与连续步态规划[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(1): 308-316.HE T Y, DONG Y, TAN L M, et al. Kinematic analysis and continuous gait planning of lunar-based equipment in walking state[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(1): 308-316(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: