Fault-tolerant control of spacecraft attitude with prescribed performance based on reinforcement learning
-
摘要:
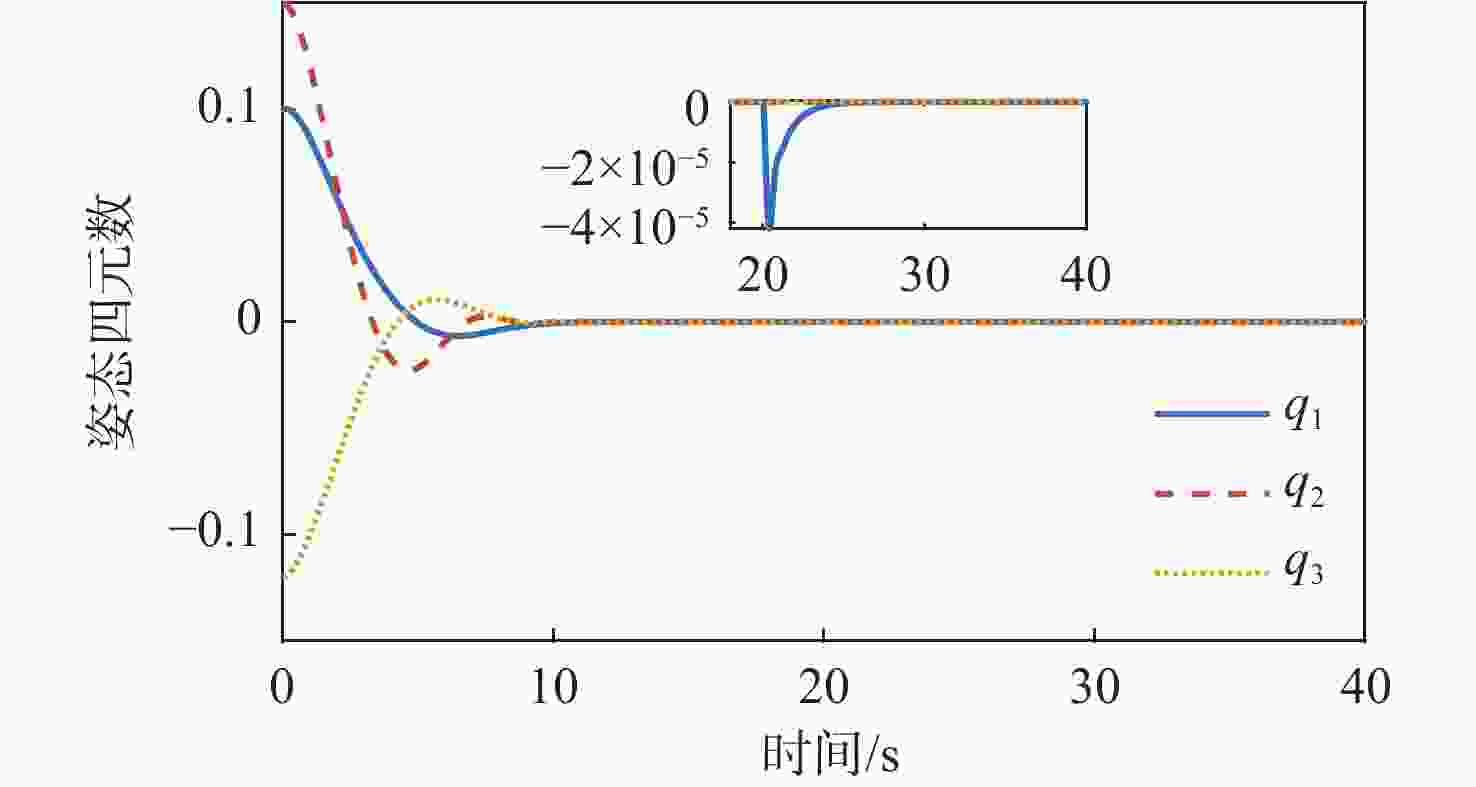
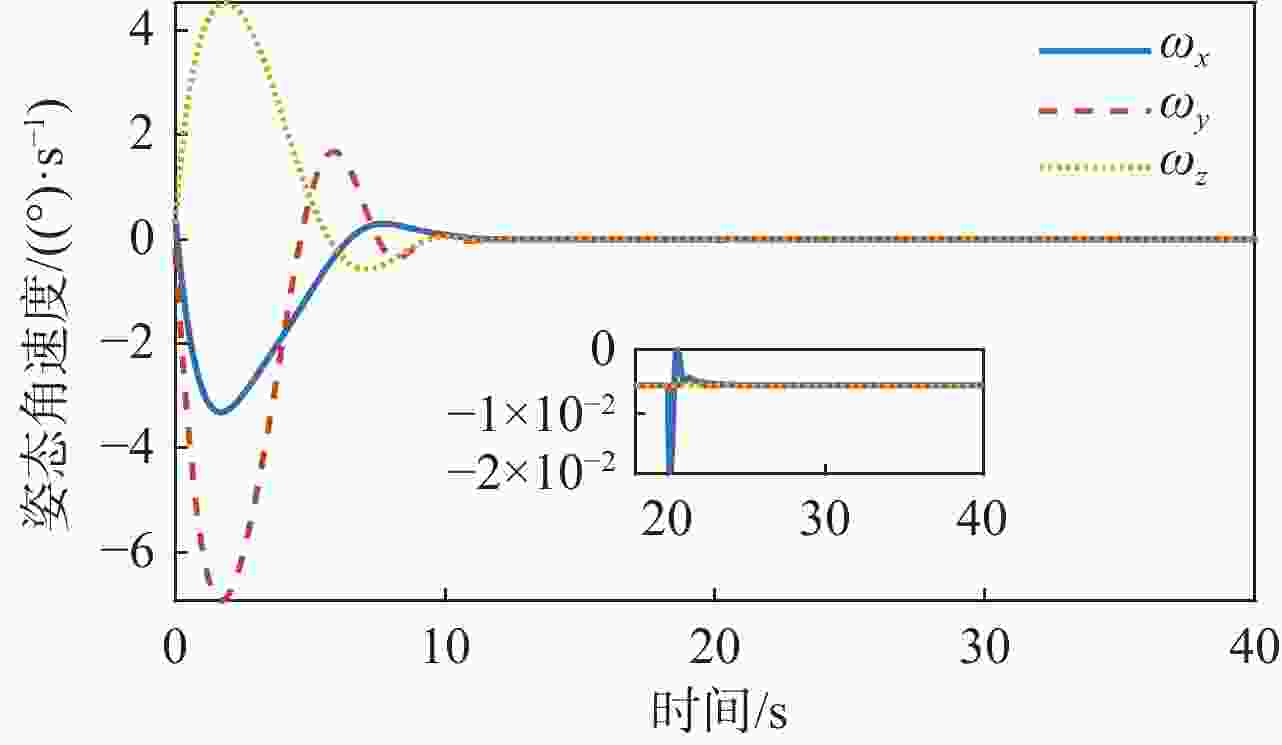
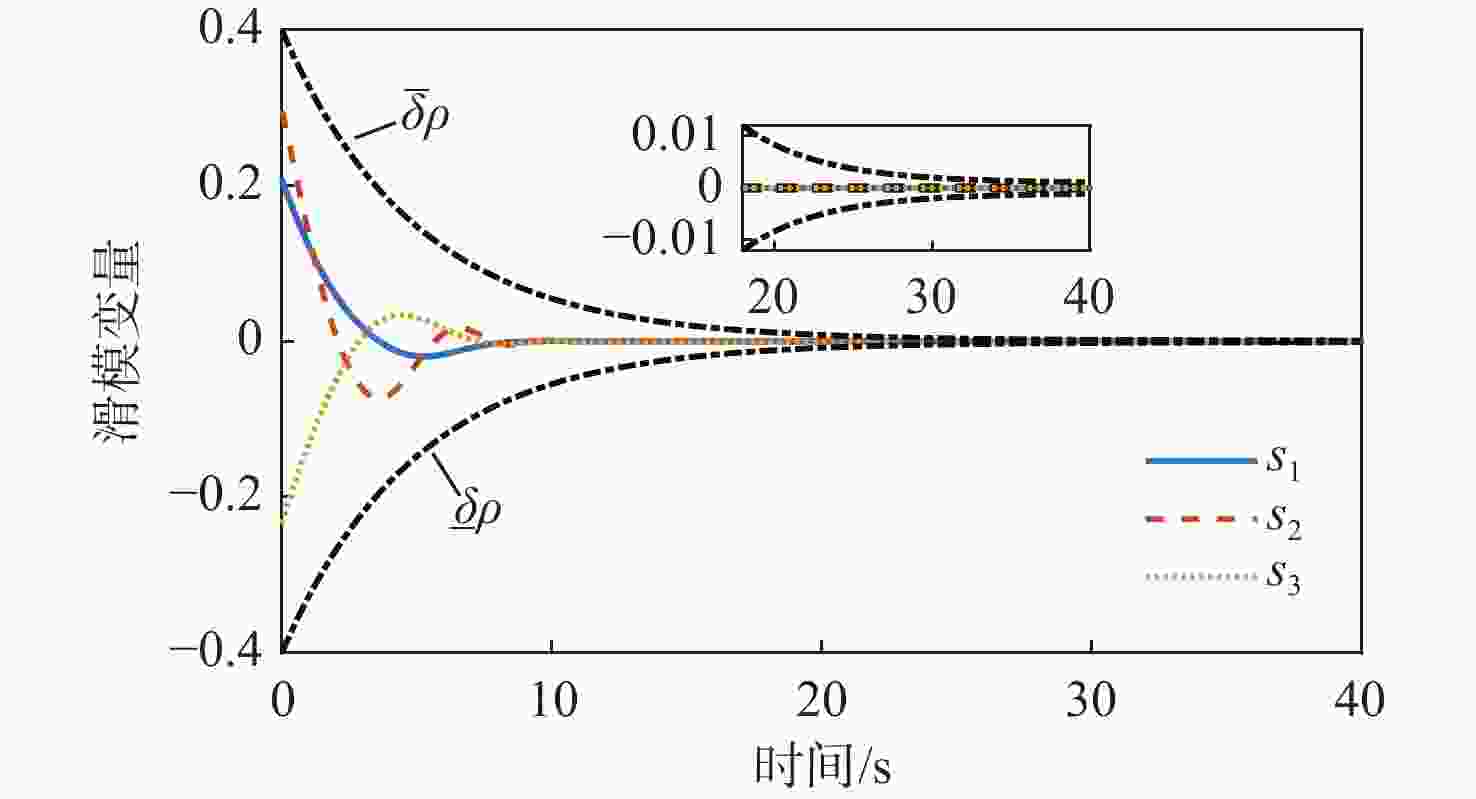
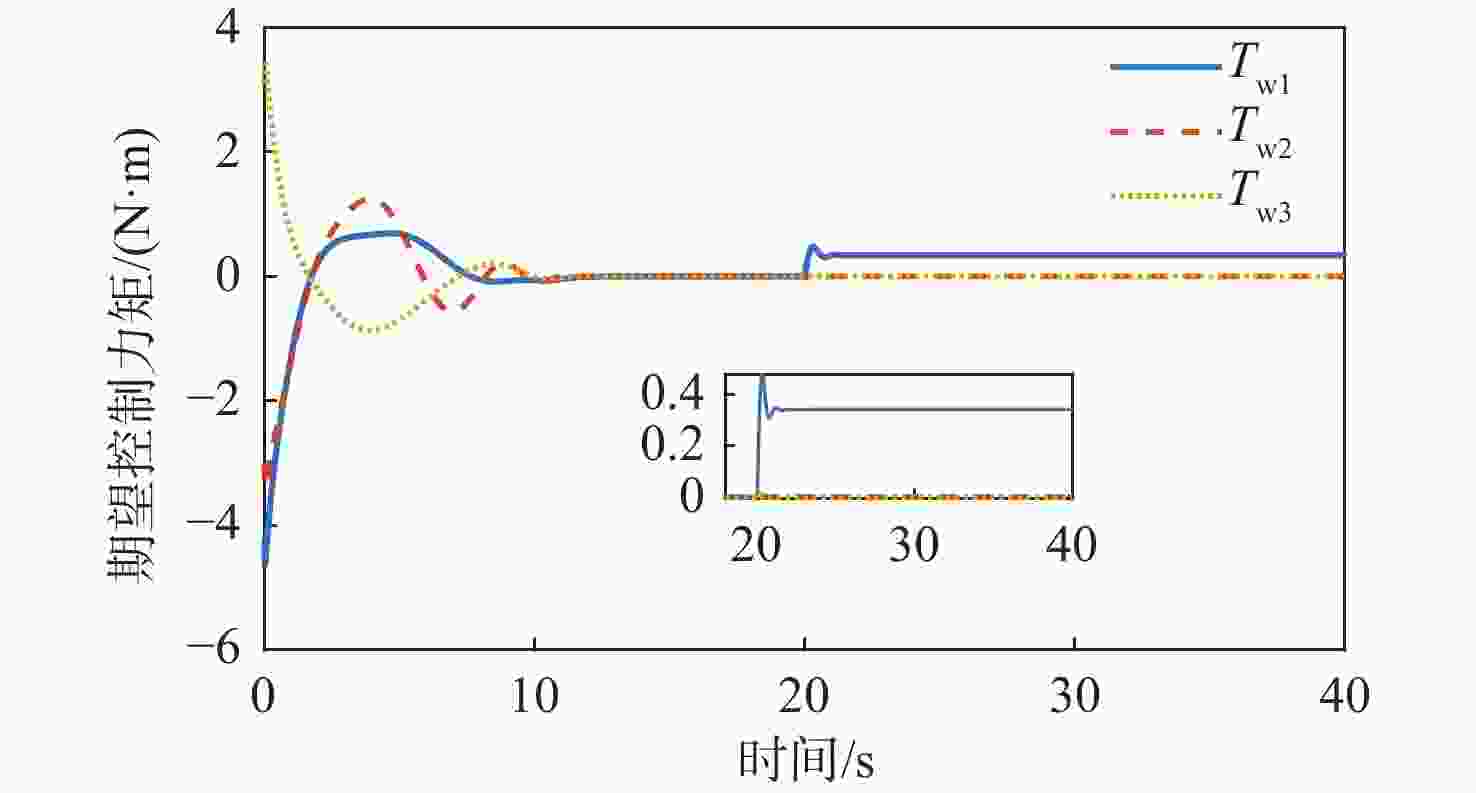
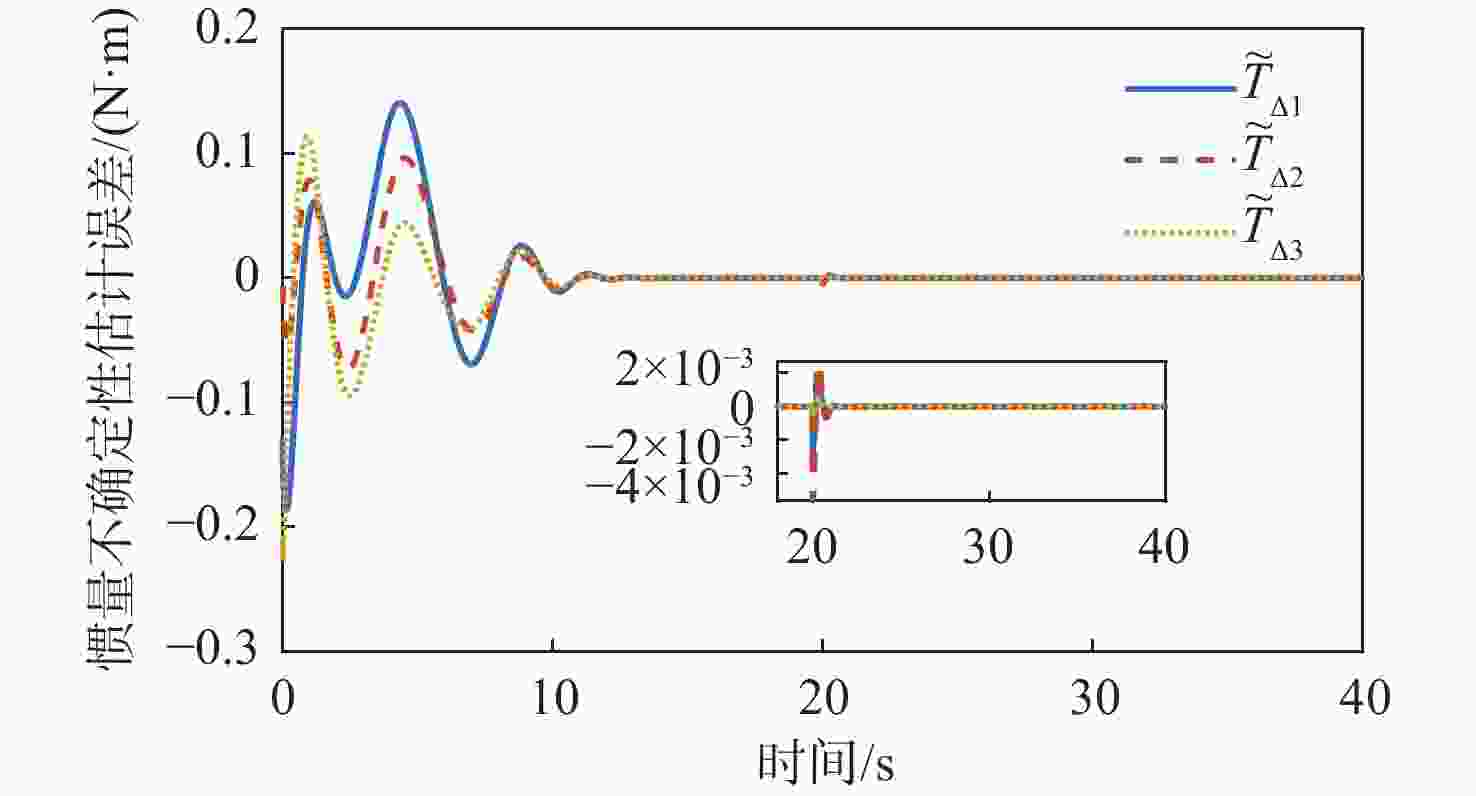
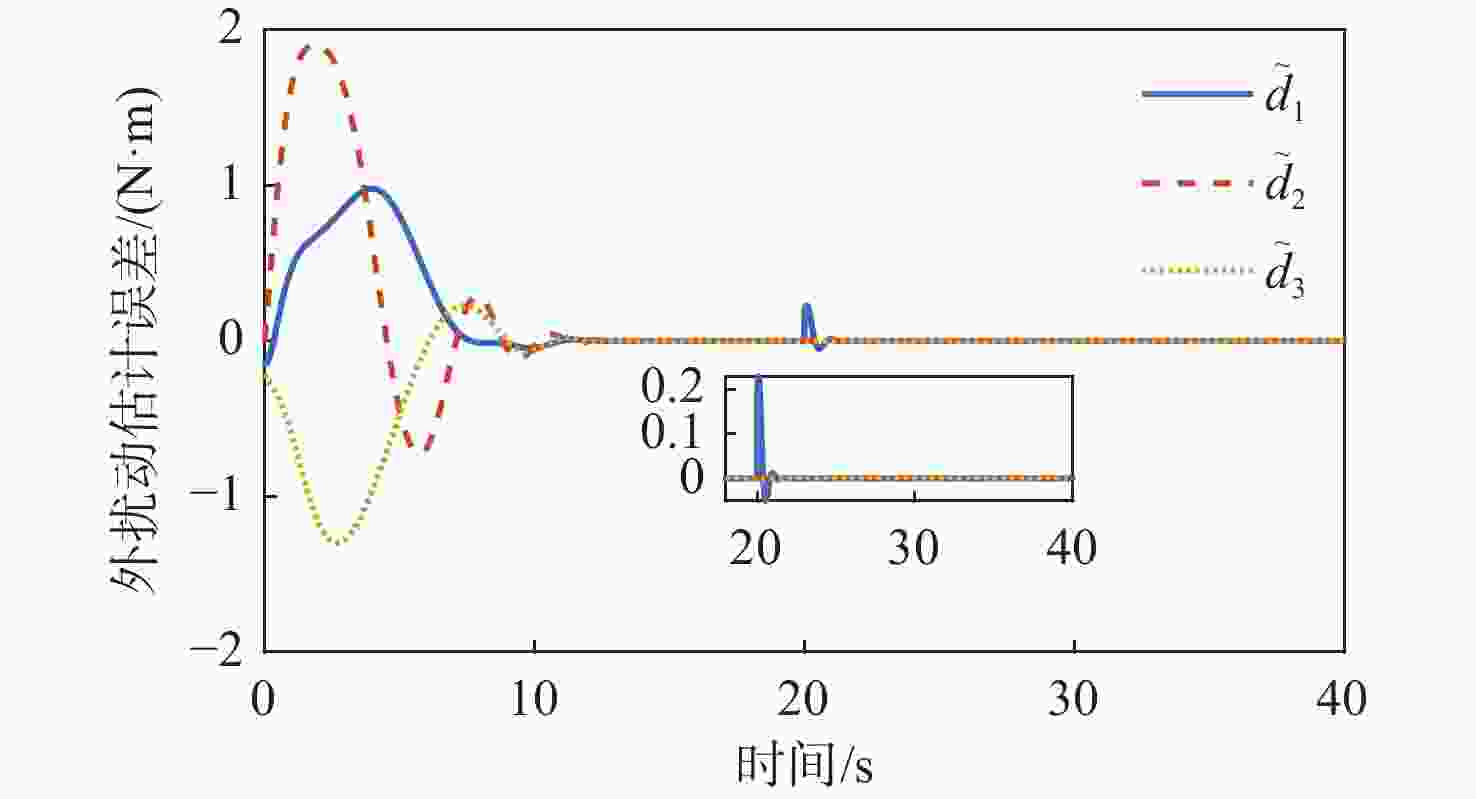
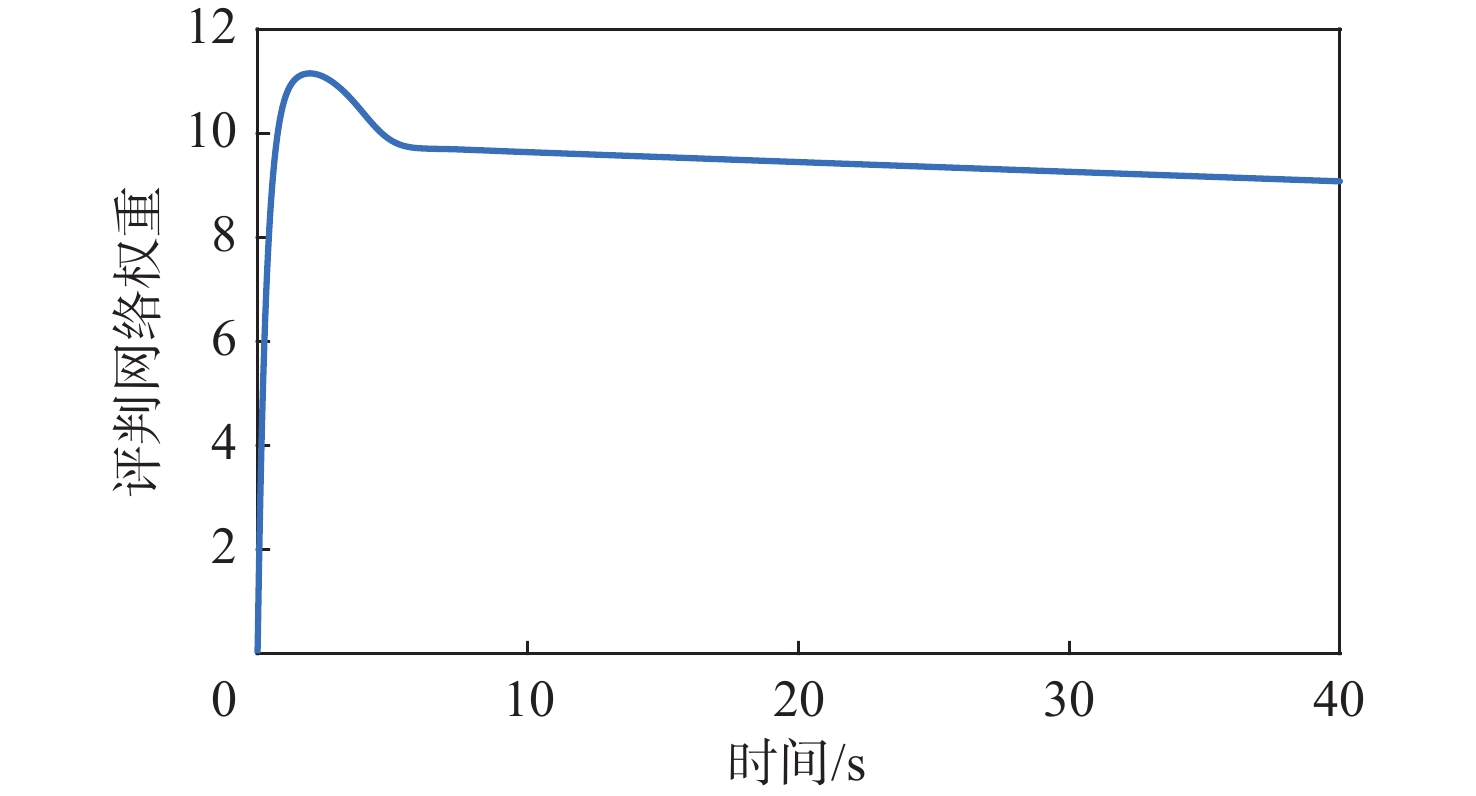
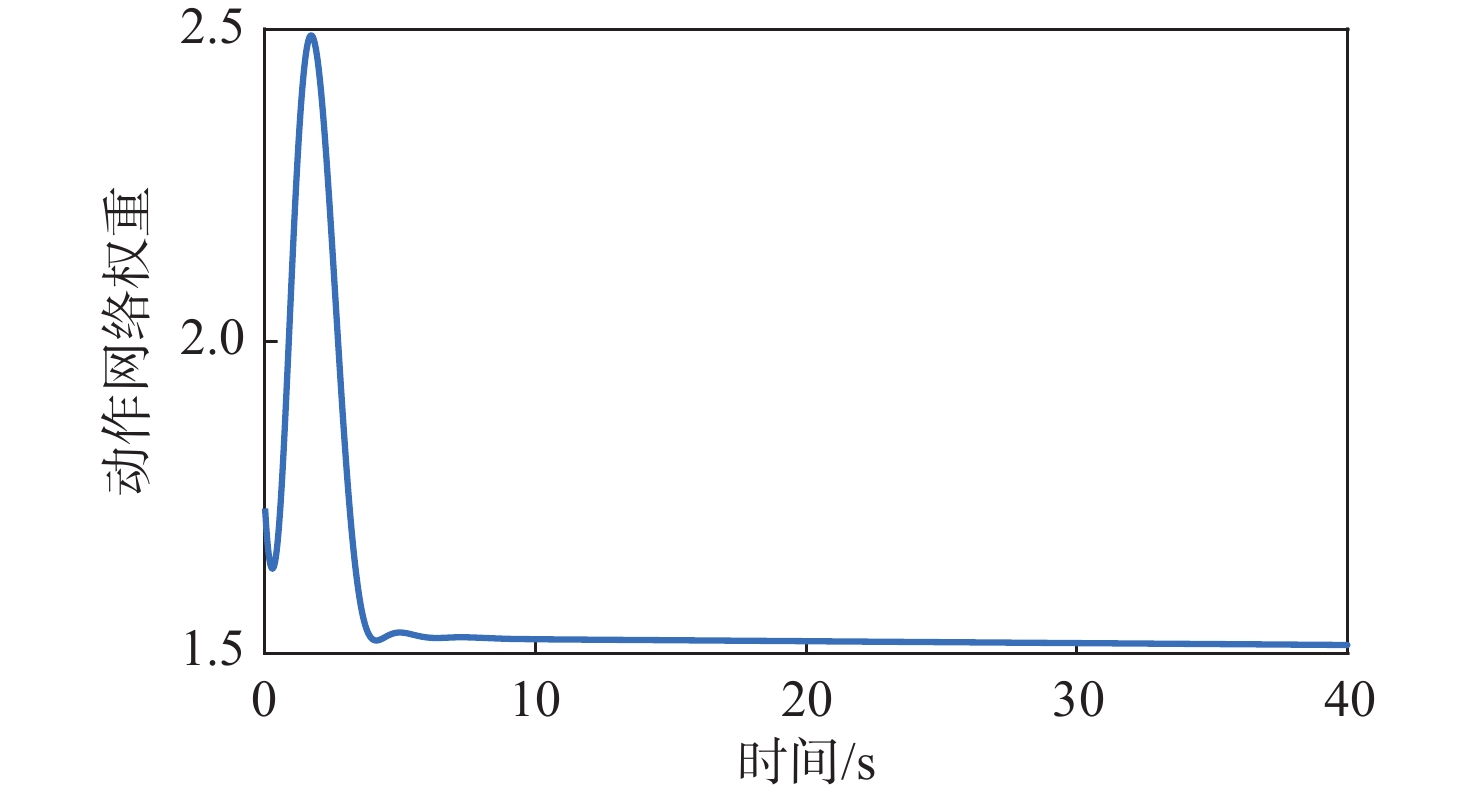
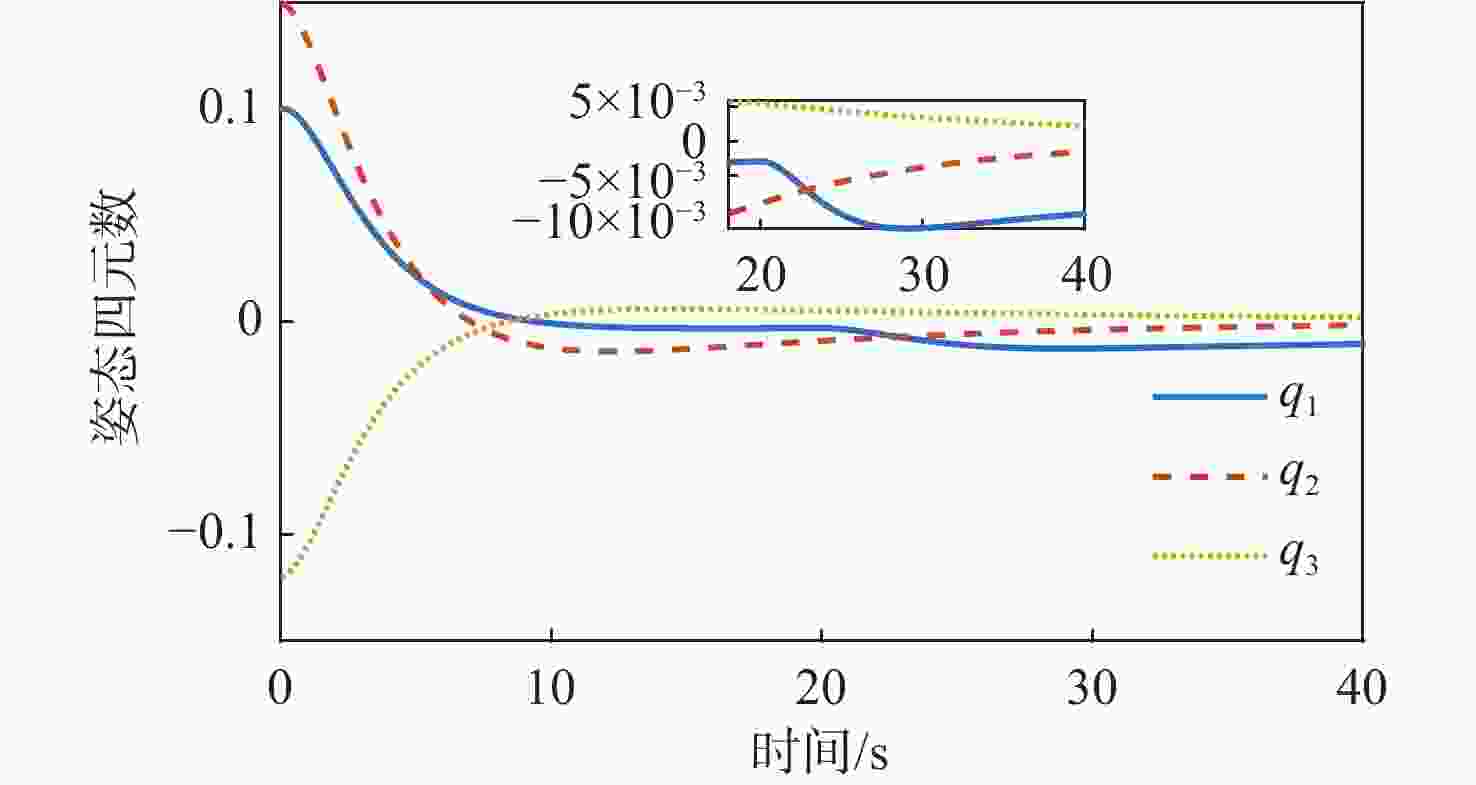
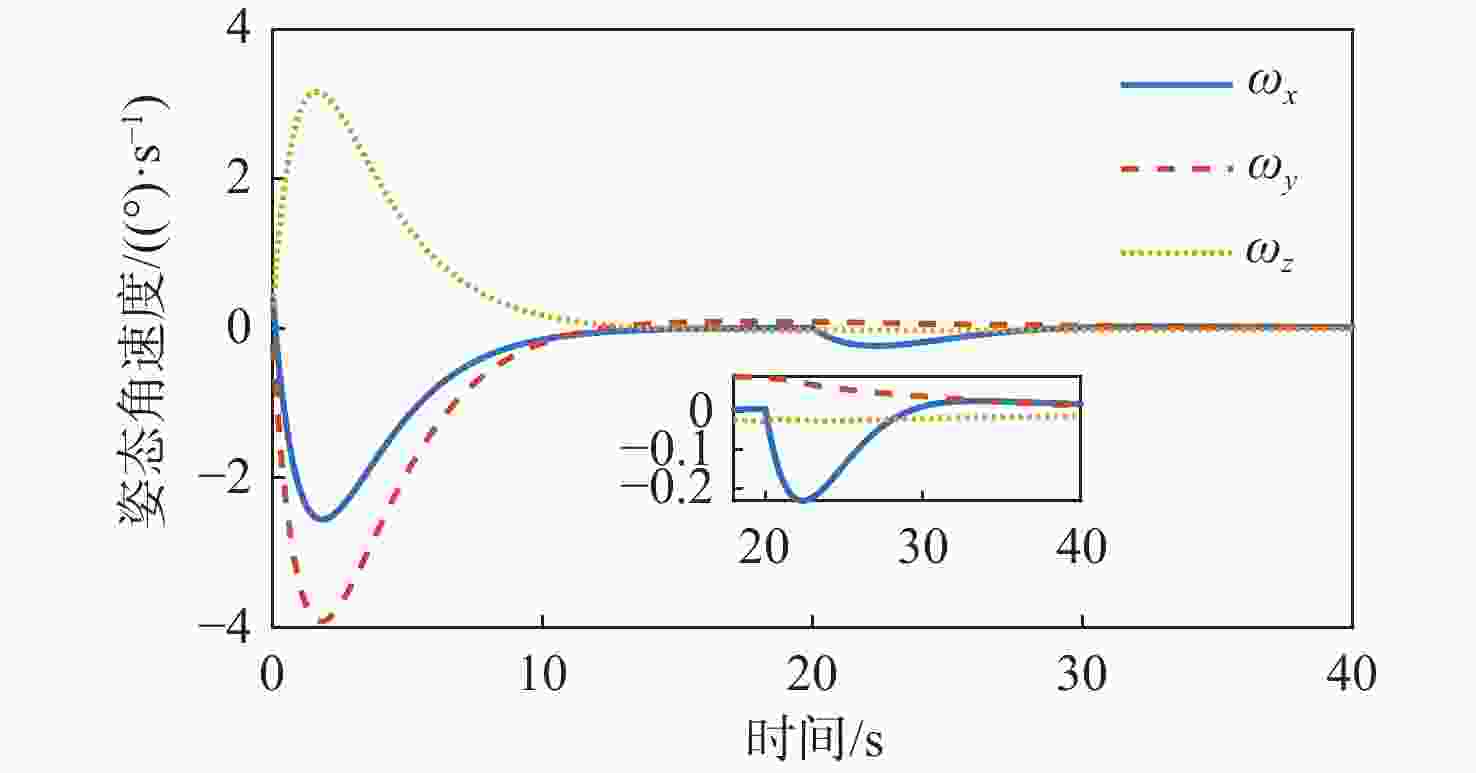
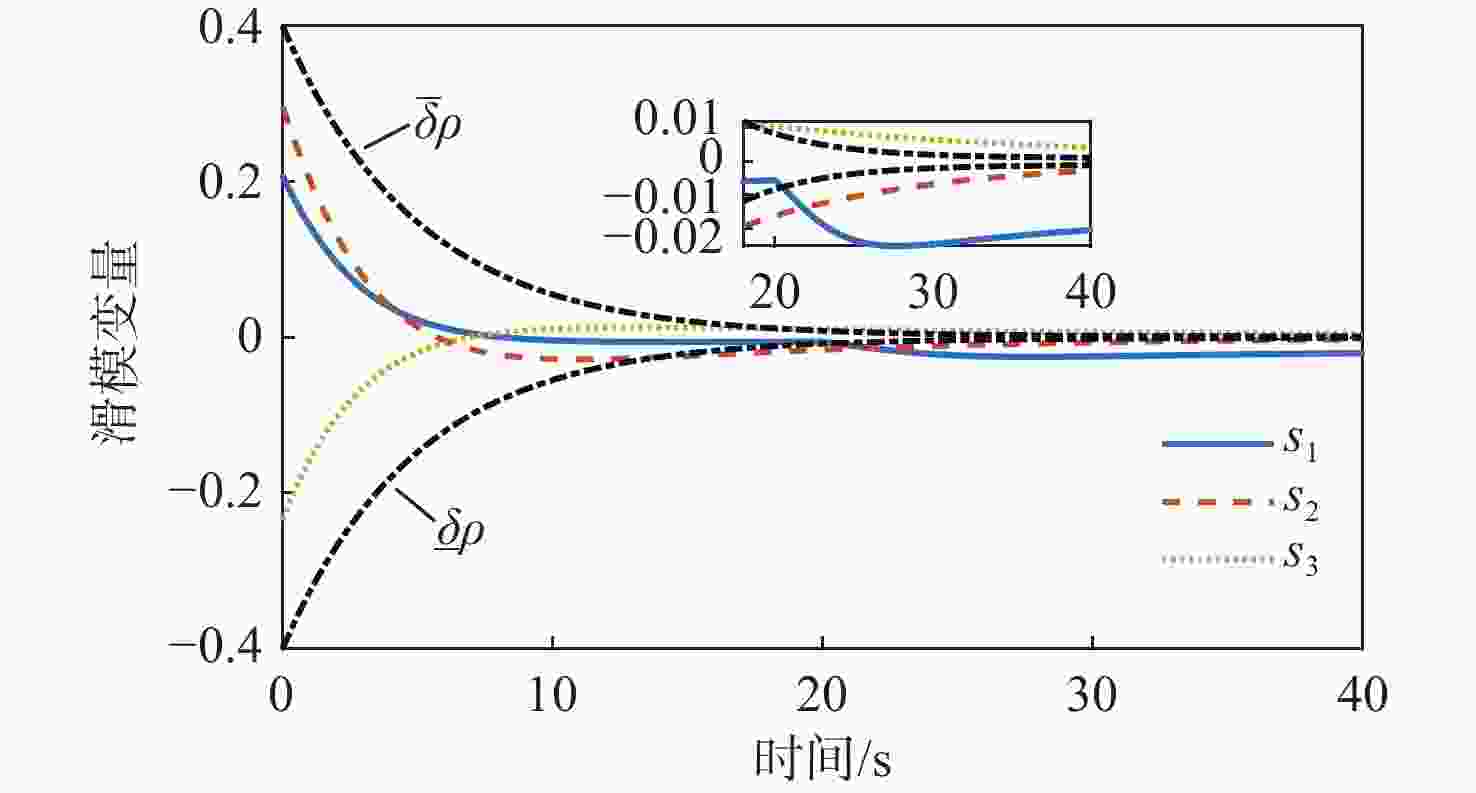
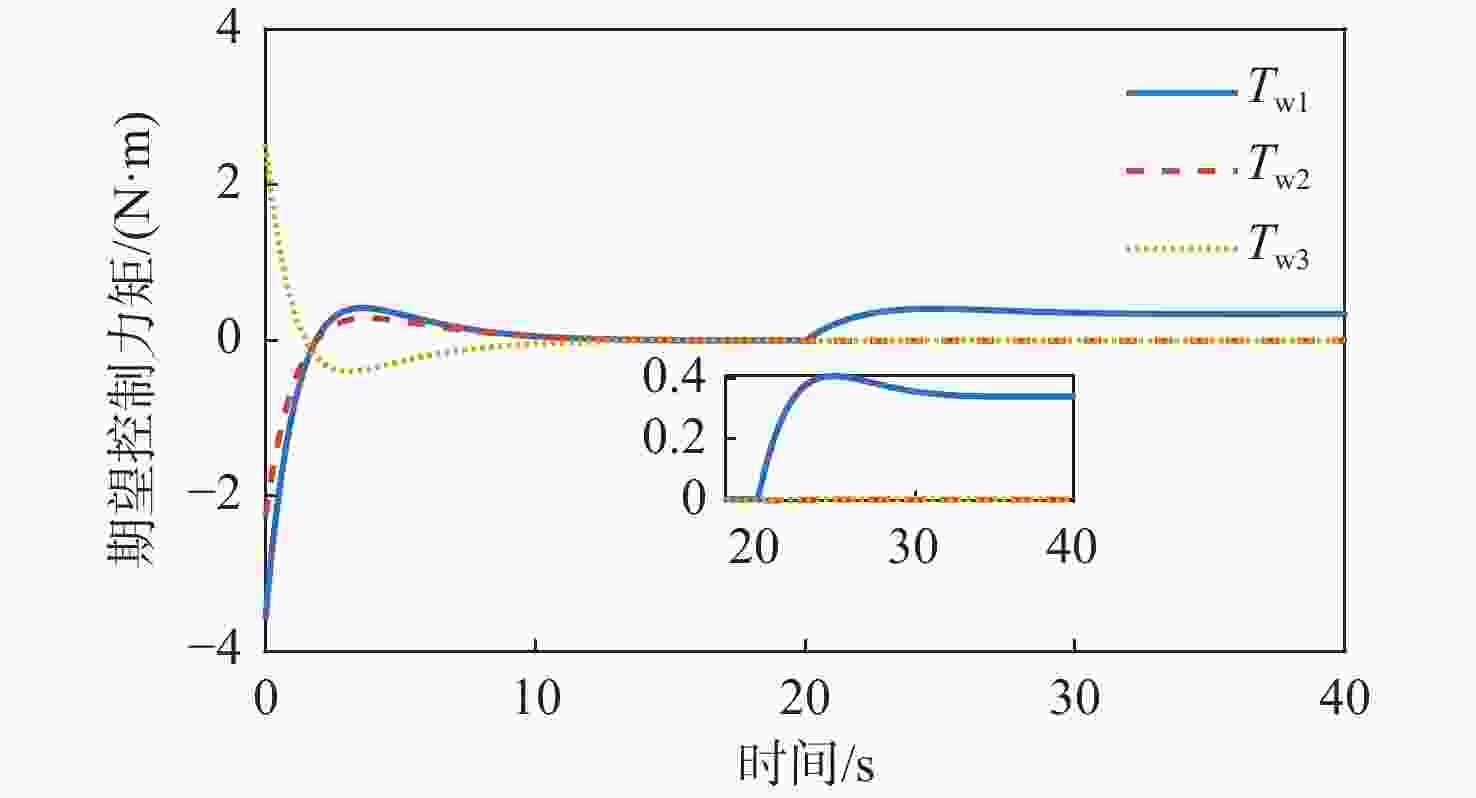
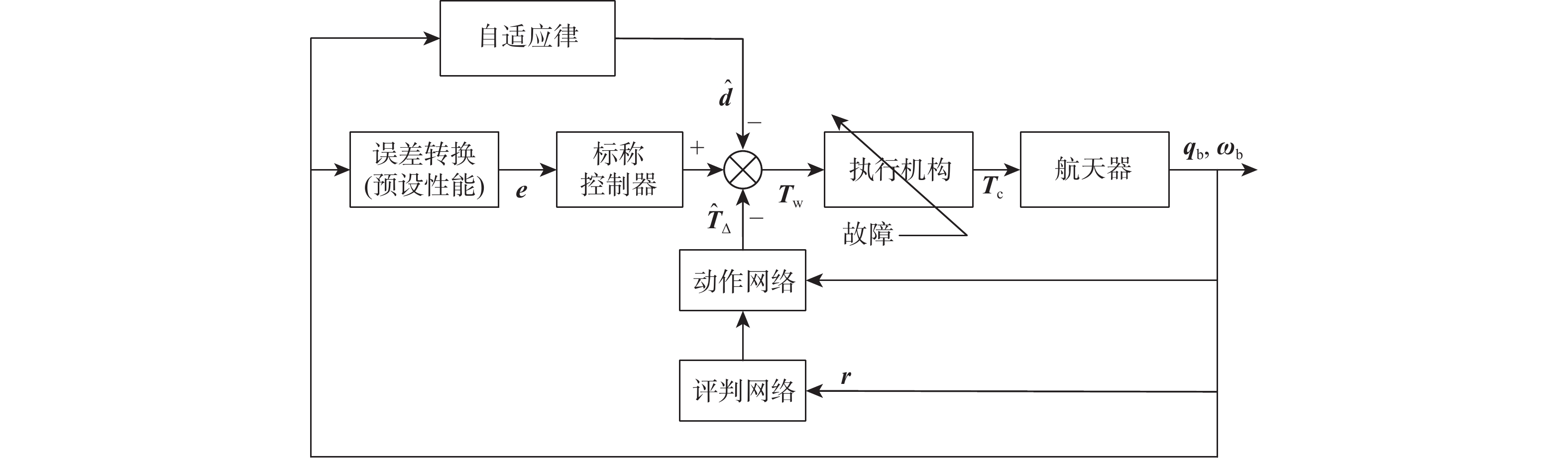
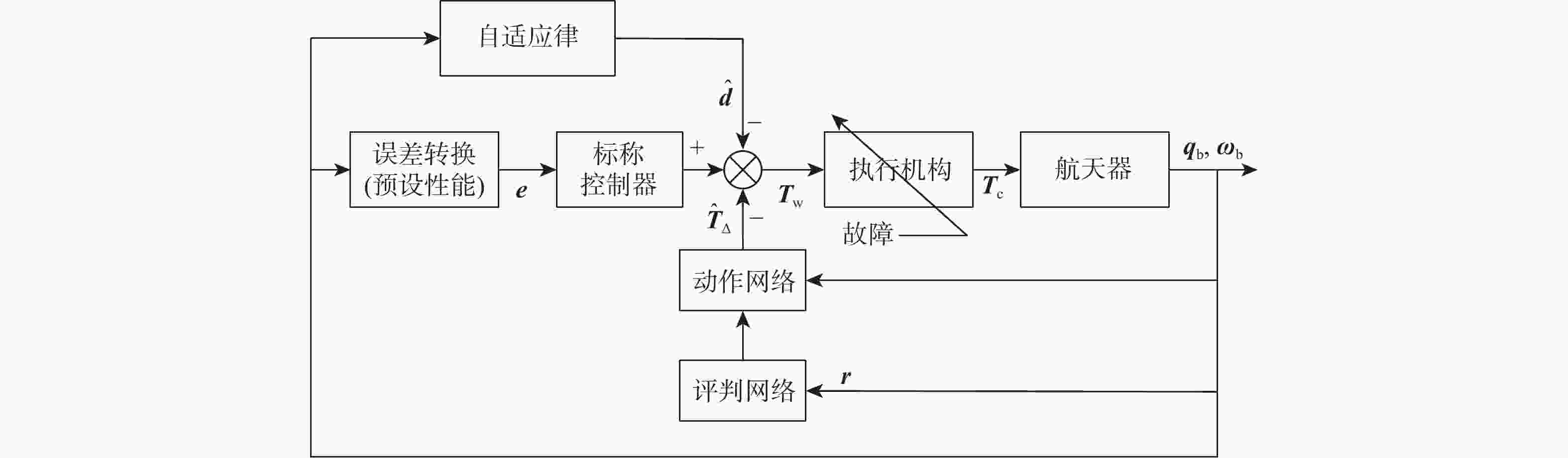
针对惯量不确定性和执行机构故障的航天器姿态控制问题,提出了一种基于强化学习的预设性能容错控制方法。采用预设性能方法设计航天器的姿态控制器,以保证控制过程的暂态响应。为在线补偿惯量不确定,在预设性能控制器的基础上引入强化学习算法,使用评判网络近似代价函数,用于评估系统性能,同时使用动作网络产生前馈补偿控制,用于处理惯量不确定;设计自适应补偿控制,补偿执行机构故障和外扰动对航天器姿态的影响。基于Lyapunov稳定性理论证明整个闭环系统的稳定性。仿真结果表明:所提容错控制方法能够实现航天器执行机构故障情况下的稳定控制。
Abstract:A fault-tolerant control method with prescribed performance based on reinforcement learning was proposed for spacecraft attitude control with inertia uncertainties and actuator faults. In order to ensure the transient response of the control process, the attitude controller of the spacecraft was designed by using the prescribed performance method. A reinforcement learning algorithm was introduced based on the prescribed performance controller to compensate for the inertia uncertainty online.The critic network was used to approximate the cost function to evaluate the performance of the system, and the actor network was used to generate feedforward compensation control and deal with the inertia uncertainty. Then, an adaptive compensation control law was designed to compensate for the effect of actuator faults and external disturbance on spacecraft attitude. According to Lyapunov stability theory, the stability of the whole closed-loop system was proved. The simulation results show that the proposed fault-tolerant control method can realize the stability control of spacecraft with actuator faults.
-
Key words:
- reinforcement learning /
- fault-tolerant control /
- prescribed performance /
- spacecraft /
- attitude control
-
-
[1] 王亚坤, 杨凯飞, 张婕, 等. 卫星在轨故障案例与人工智能故障诊断[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2022, 42(1): 16-29.WANG Y K, YANG K F, ZHANG J, et al. Case study of in-orbit satellite failures and artificial intelligence based failure detection[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2022, 42(1): 16-29(in Chinese). [2] 姜斌, 张柯, 杨浩, 等. 卫星姿态控制系统容错控制综述[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(11): 524662. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.24662JIANG B, ZHANG K, YANG H, et al. Fault-tolerant control of satellite attitude control systems: Review[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(11): 524662(in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.24662 [3] 沈毅, 李利亮, 王振华. 航天器故障诊断与容错控制技术研究综述[J]. 宇航学报, 2020, 41(6): 647-656.SHEN Y, LI L L, WANG Z H. A review of fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control techniques for spacecraft[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2020, 41(6): 647-656(in Chinese). [4] 陈雪芹, 孙瑞, 宋道喆, 等. 航天器姿态控制系统单机故障分析[C]//第三届中国指挥控制大会. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2015: 275-280.CHEN X Q, SUN R, SONG D Z, et al. Failure analysis of components in spacecraft attitude control system[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd China Conference on Command and Control. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2015: 275-280(in Chinese). [5] 林来兴. 最近十年航天器制导、导航与控制(GNC)系统故障分析研究[J]. 控制工程, 2004(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7848.2004.01.001LIN L X. Fault analysis of spacecraft guidance, navigation and control (GNC) systems in the last decade[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2004(1): 1-8(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7848.2004.01.001 [6] EDWARDS C, LOMBAERTS T, SMAILI H. Fault tolerant flight control: A benchmark challenge[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2010. [7] JIN J, KO S, RYOO C K. Fault tolerant control for satellites with four reaction wheels[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2008, 16(10): 1250-1258. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2008.02.001 [8] ZHOU J, LI X, LIU R, et al. Active fault-tolerant satellite attitude control based on fault effect classification[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2017, 231: 1917-1934. doi: 10.1177/0954410016662487 [9] SHEN Q, YUE C F, GOHC H, et al. Active fault-tolerant control system design for spacecraft attitude maneuvers with actuator saturation and faults[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(5): 3763-3772. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2854602 [10] 闫鑫. 基于滑模的航天器执行机构故障诊断与容错控制研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2012.YAN X. Research on sliding mode based spacecraft actuator fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2012(in Chinese). [11] 苏伟伟. 深空探测器高精度姿态容错控制研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2018.SU W W. Research on high precision fault-tolerant attitude control for deep space probe[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018(in Chinese). [12] WANG Z, LI Q, LI S R. Adaptive integral-type terminal sliding mode fault tolerant control for spacecraft attitude tracking[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 35195-35207. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2901966 [13] HUANG X W, DUAN G R. Fault-tolerant attitude tracking control of combined spacecraft with reaction wheels under prescribed performance[J]. ISA Transactions, 2020, 98: 161-172. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2019.08.041 [14] RICHARD S S, ANDREW G B. Reinforcement learning: An introduction[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2017: 1-18. [15] 李茹杨, 彭慧民, 李仁刚, 等. 强化学习算法与应用综述[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2020, 29(12): 13-25.LI R Y, PENG H M, LI R G, et al. Overview on algorithms and applications for reinforcement learning[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2020, 29(12): 13-25(in Chinese). [16] 孔松涛, 刘池池, 史勇, 等. 深度强化学习在智能制造中的应用展望综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(2): 49-59.KONG S T, LIU C C, SHI Y, et al. Review of application prospect of deep reinforcement learning in intelligent manufacturing[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2021, 57(2): 49-59(in Chinese). [17] 李铭浩, 张华, 刘满禄, 等. 基于深度强化学习的机械臂容错控制方法[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2020, 39(1): 53-55.LI M H, ZHANG H, LIU M L, et al. Fault tolerant control method of manipulator based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2020, 39(1): 53-55(in Chinese). [18] AHMED I, QUIÑONES-GRUEIRO M, BISWAS G. Fault-tolerant control of degrading systems with on-policy reinforcement learning[J]. IFAC-Papers OnLine, 2020, 53(2): 13733-13738. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2020.12.878 [19] ZHAO W B, LIU H, LEWIS F. Fault-tolerant control for the formation of multiple unknown nonlinear quadrotors via reinforcement learning[J]. IFAC-Papers OnLine, 2020, 53(2): 2465-2470. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2020.12.194 [20] ZHANG H G, ZHANG K, CAI Y L, et al. Adaptive fuzzy fault-tolerant tracking control for partially unknown systems with actuator faults via integral reinforcement learning method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 27(10): 1986-1998. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2893211 -






 下载:
下载: