Large-stroke microposition stage driven by reluctance actuator and its trajectory tracking control
-
摘要:
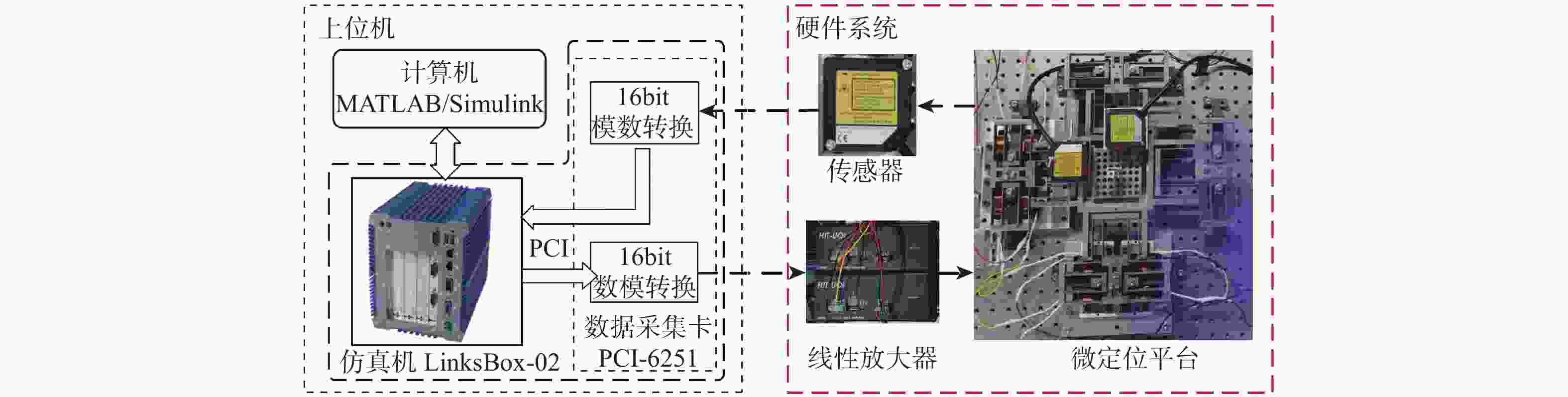
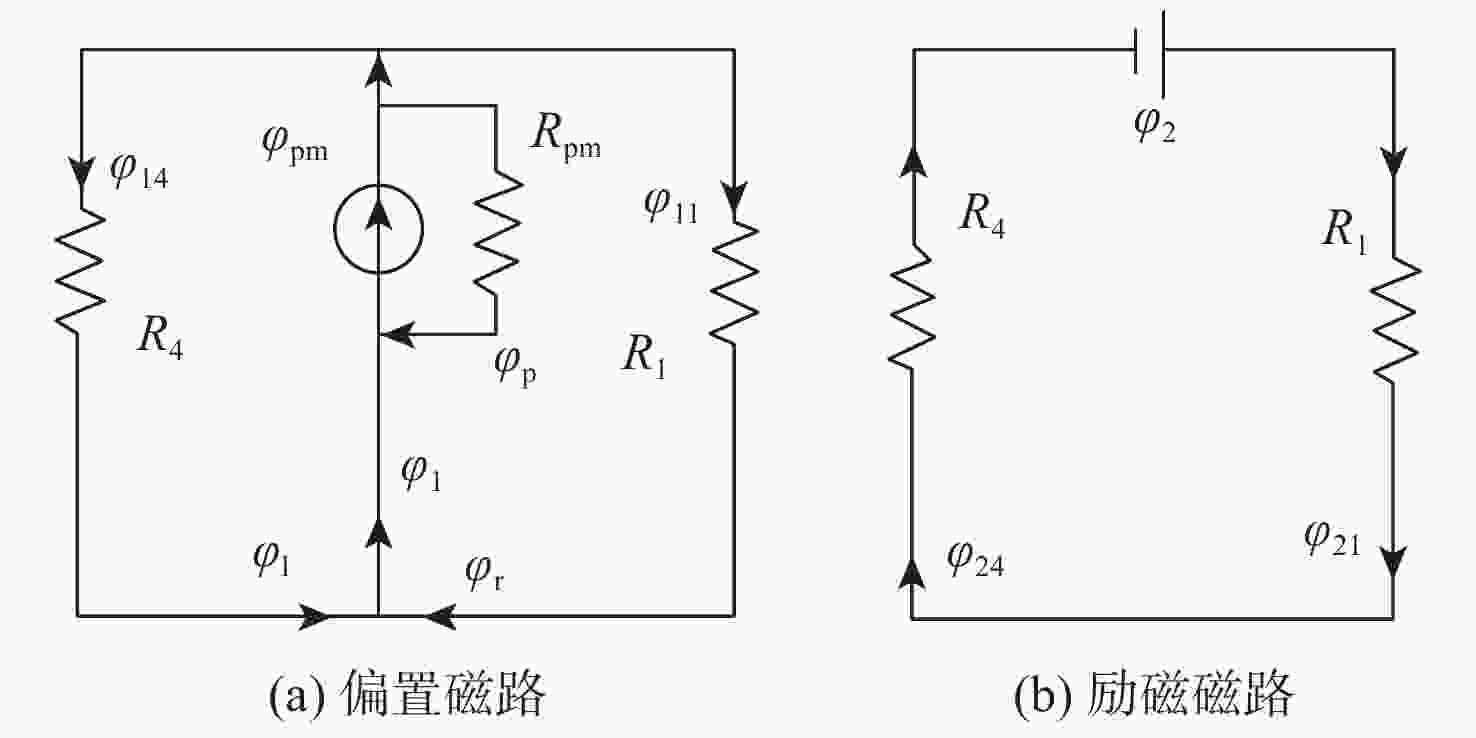
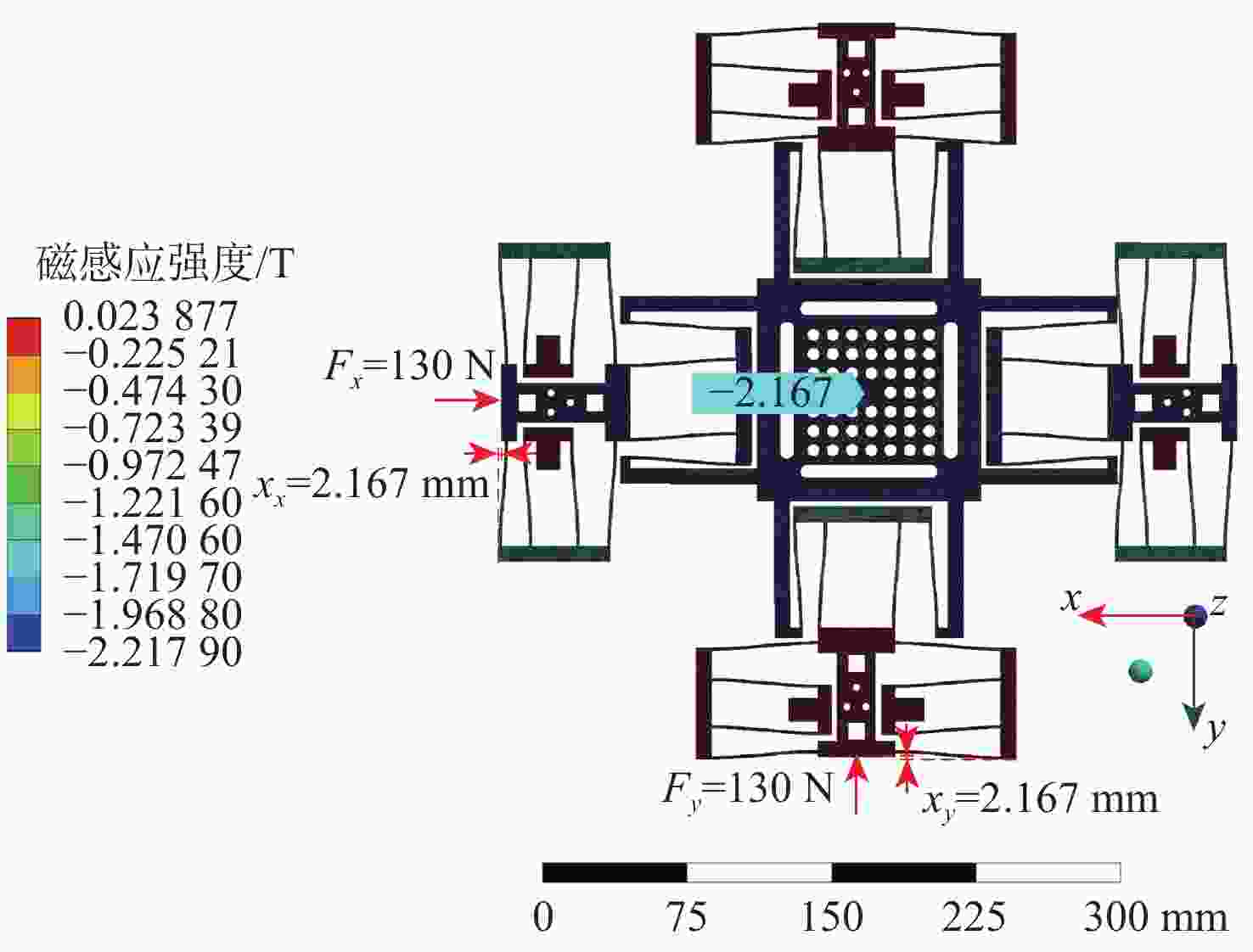
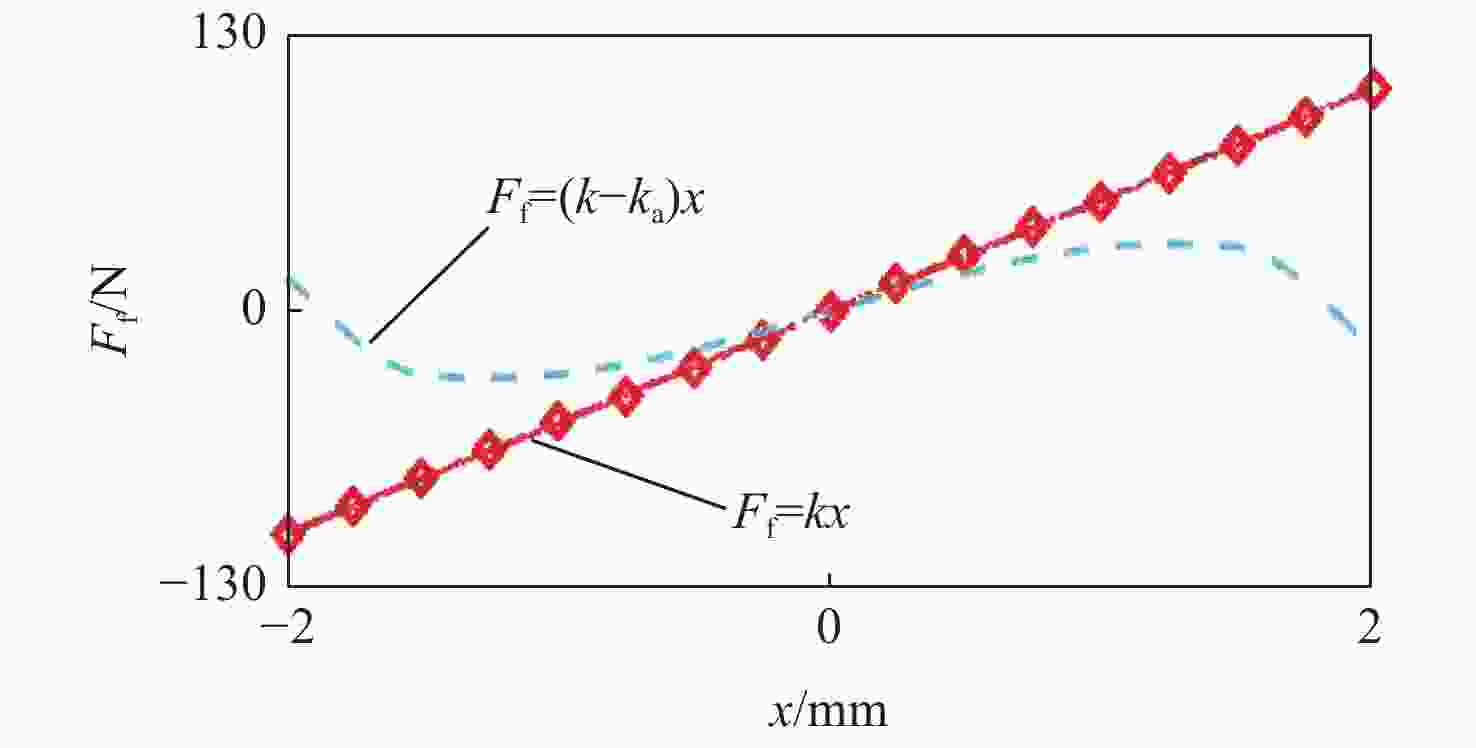
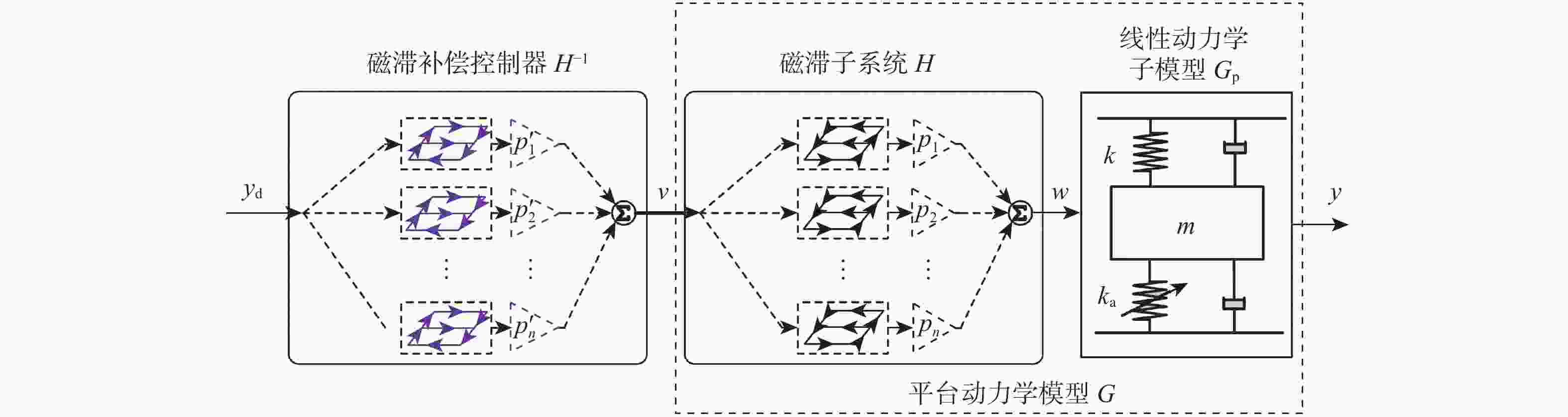
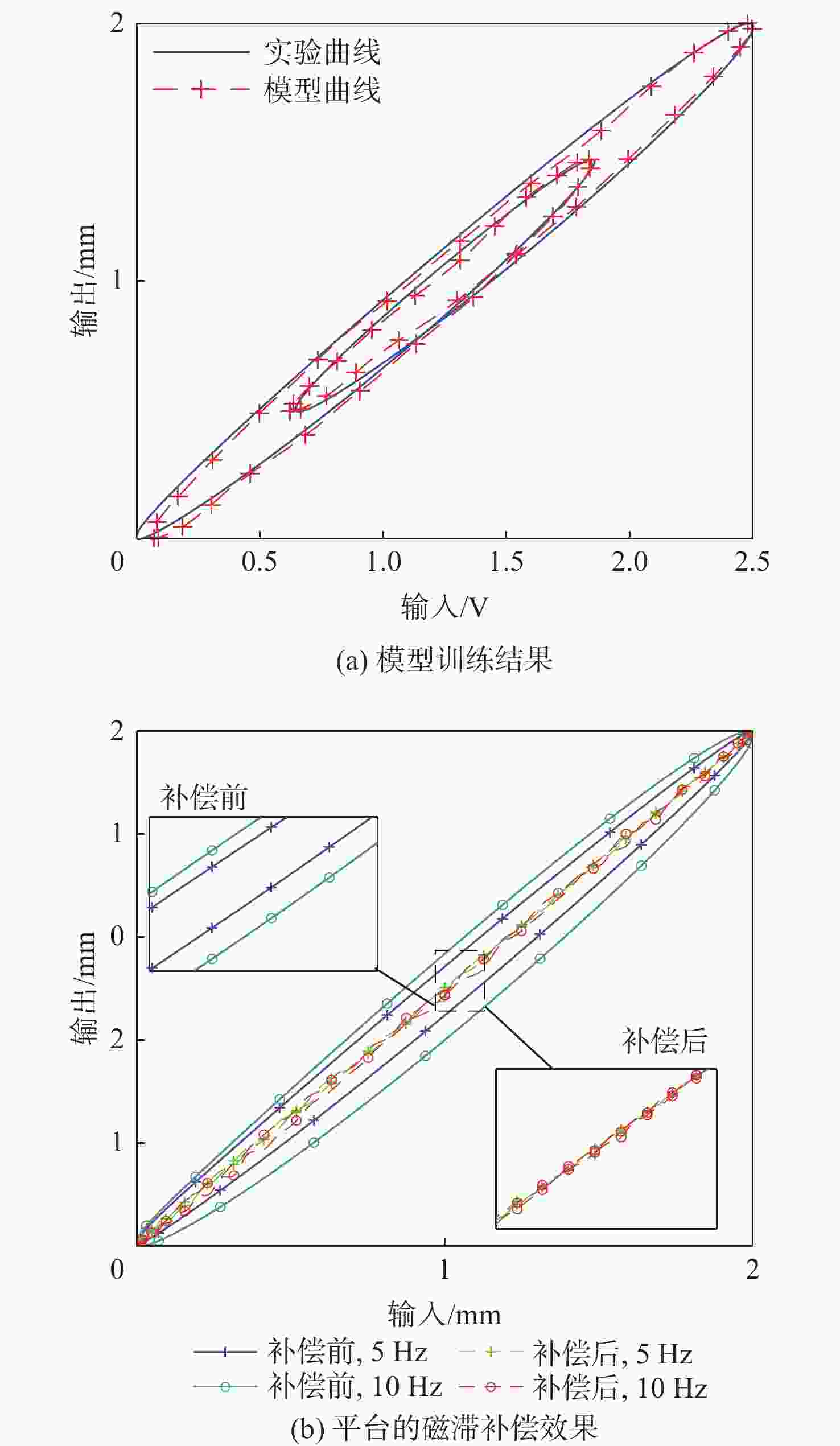
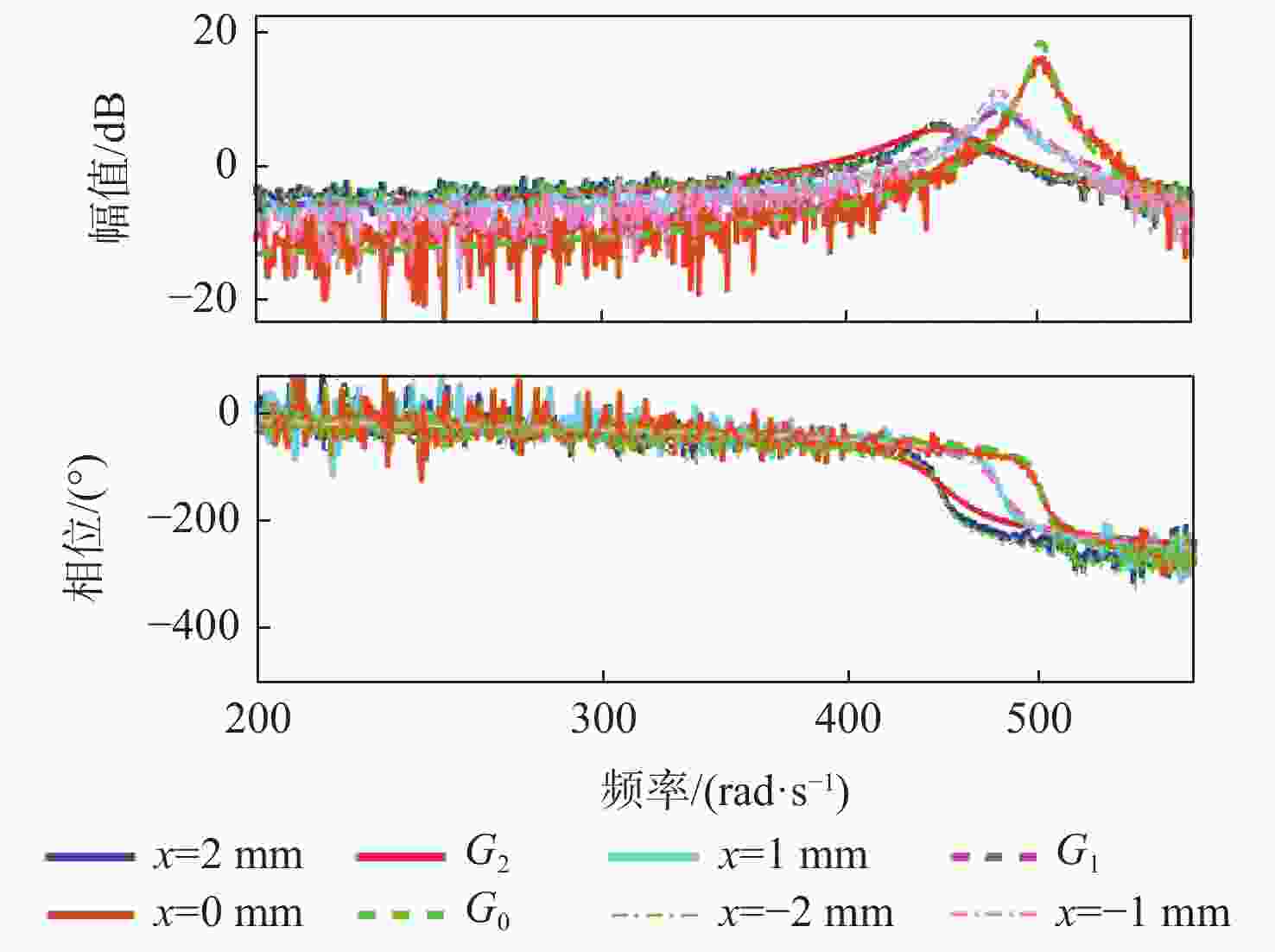
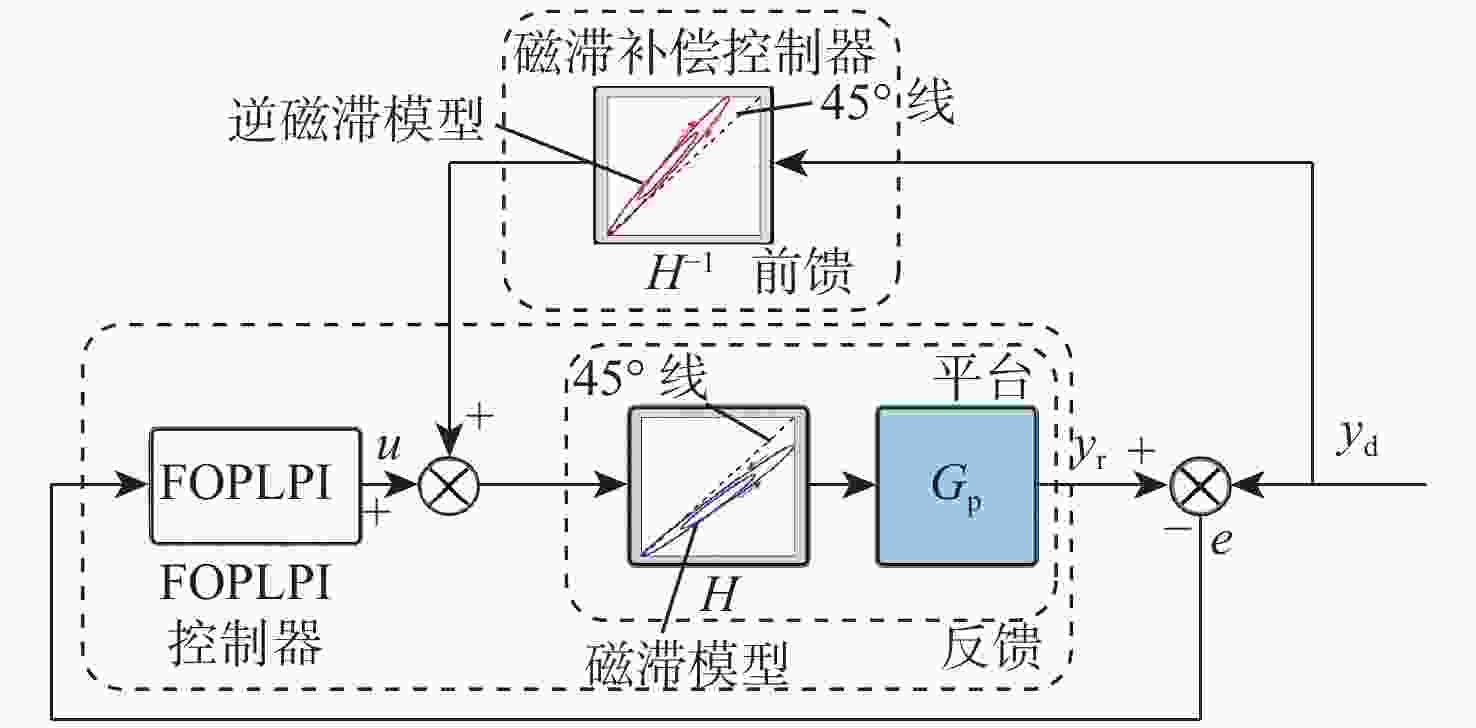
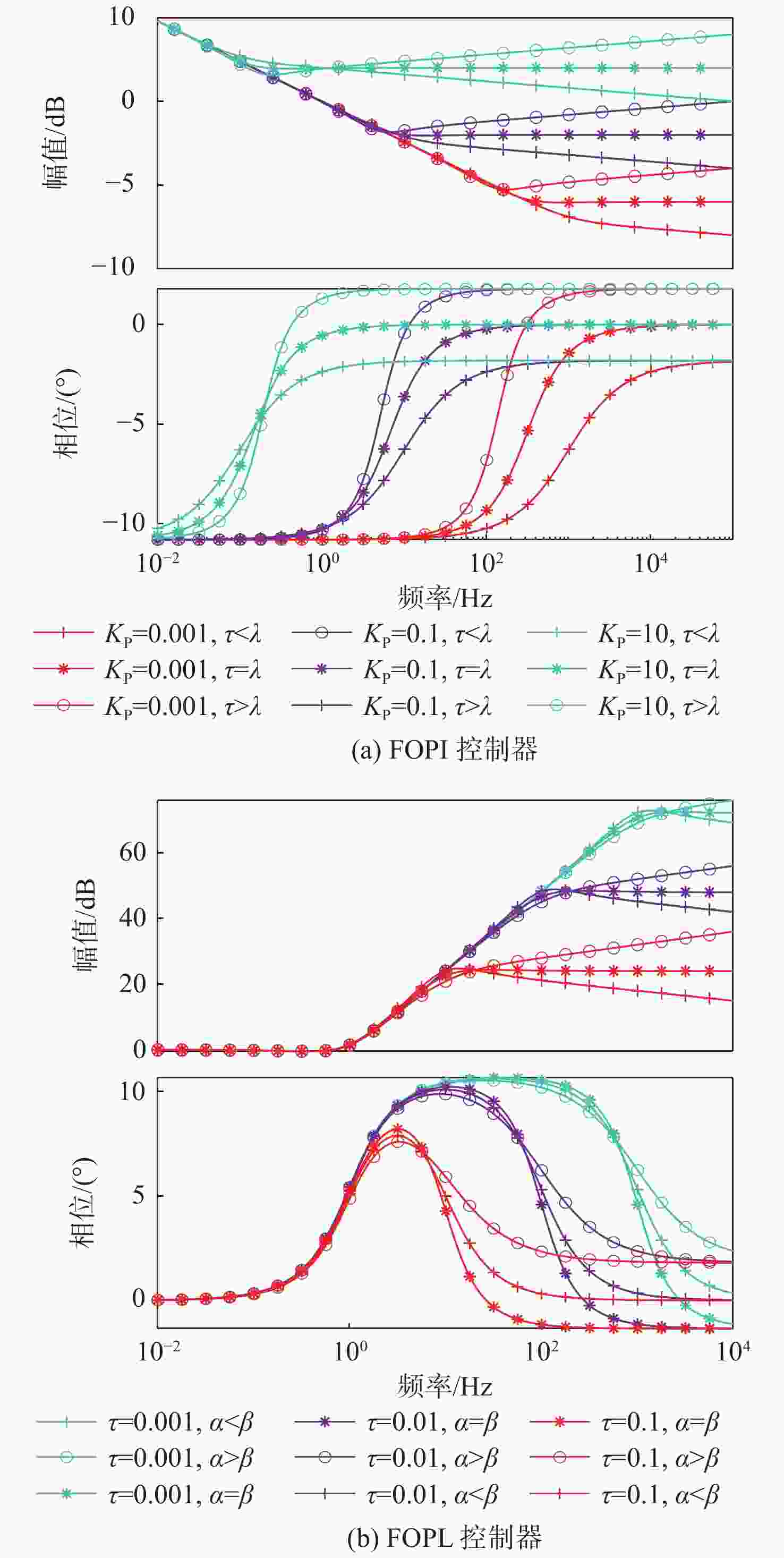
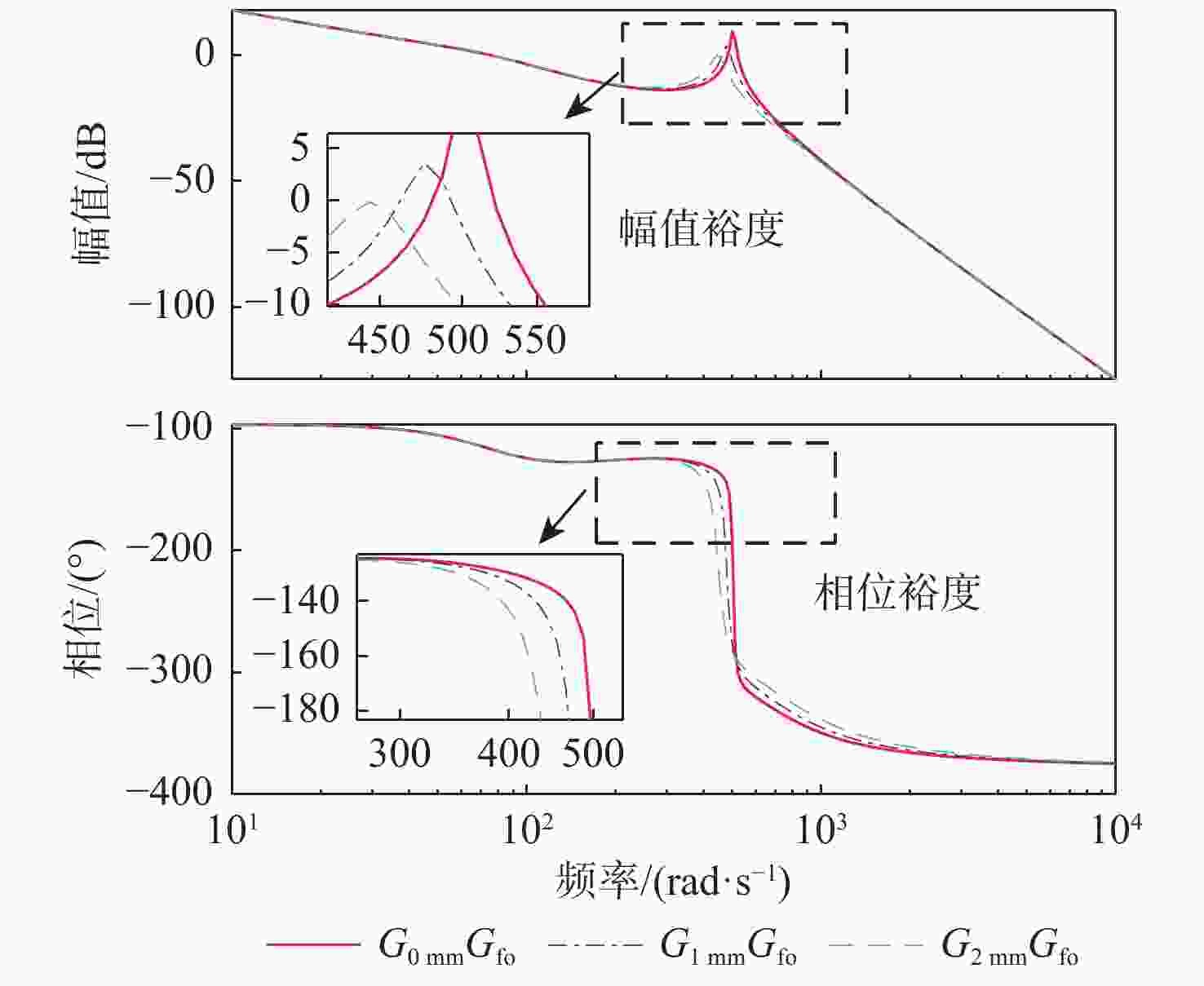
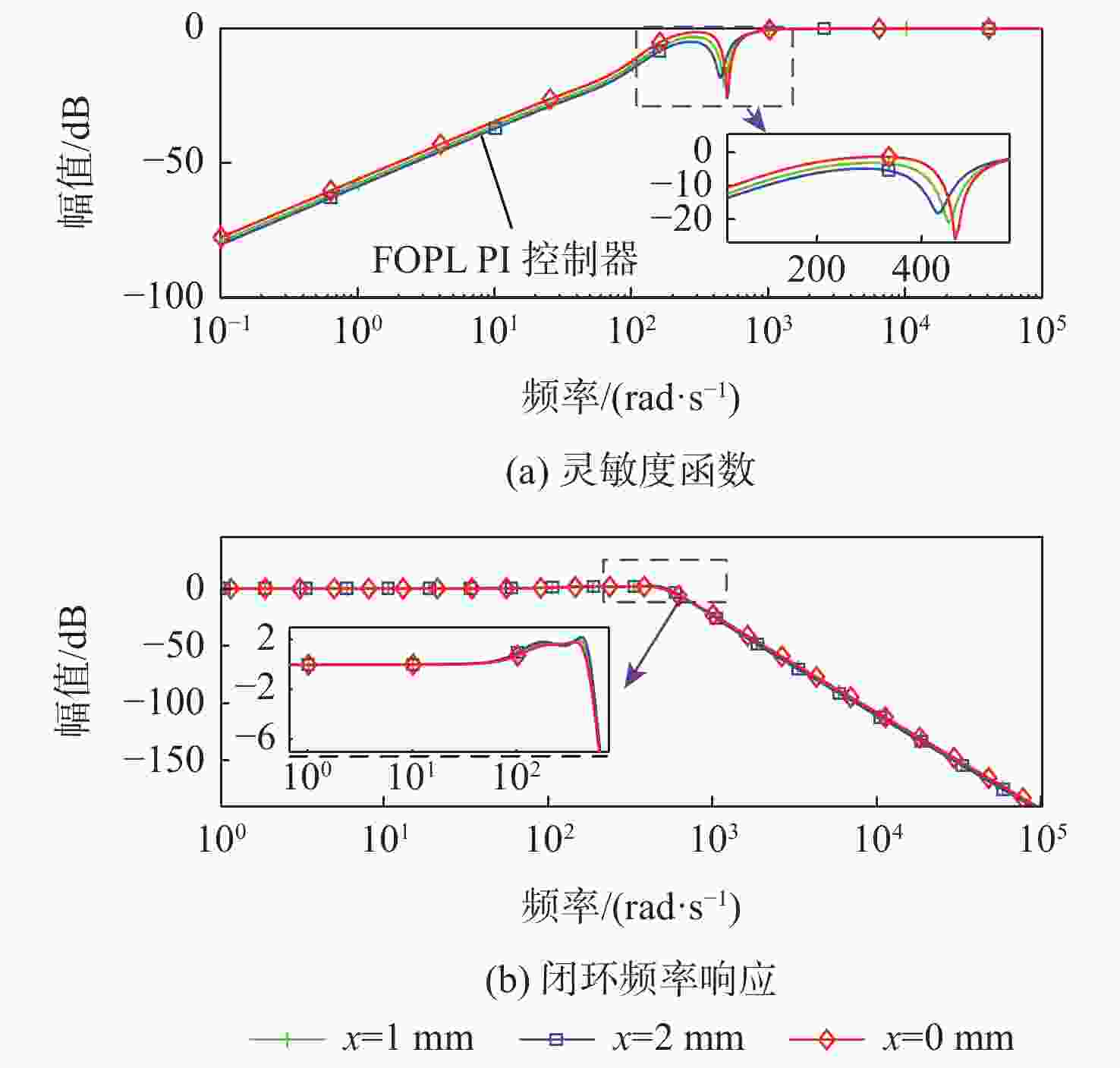
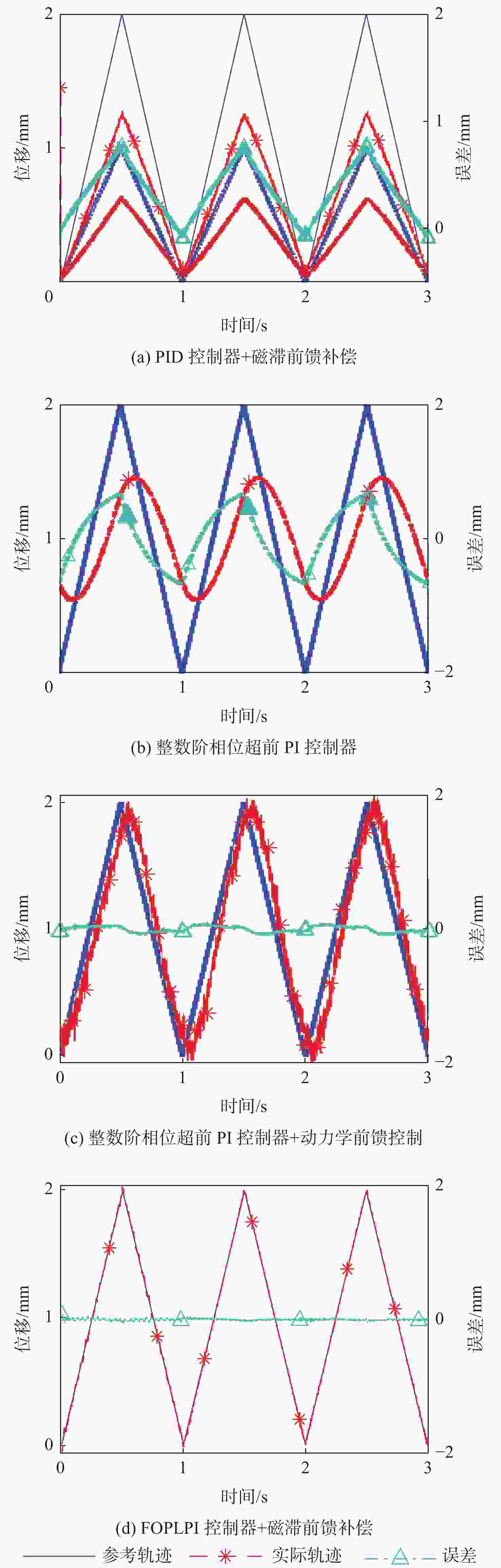
麦克斯韦磁阻驱动器克服了传统压电陶瓷驱动器行程小及音圈电机推力密度和效率低等难题,在大行程高速微纳米定位中具有极大的应用潜力。设计了一种基于麦克斯韦磁阻驱动的大行程二自由度柔顺微定位平台,并对其进行了高性能轨迹跟踪控制。该定位平台由2个永磁偏置的麦克斯韦磁阻驱动器和二自由度并联解耦柔性导向机构组成,平台利用磁阻驱动器的非线性负刚度来部分补偿柔性导向机构的弹性恢复力,有效提高了运动行程和能量传递效率,使其在±2 mm行程范围内的所需推力从±120 N减少至±24 N。轨迹跟踪控制方面,为补磁阻驱动器偿驱动器软磁材料冲磁带来的磁滞非线性,利用逆Prandtl-Ishlinskii磁滞模型构建了率相关磁滞补偿控制器并将其置于前馈回路中。为解决平台低阻尼谐振及动力学模型不一致等问题,设计了含分数阶相位超前环节的PI反馈控制器以完成对系统开环频率特性的灵活调整,实现了对平台的高精度轨迹跟踪控制,有效减小了系统的跟踪误差。对2 mm幅值、1 Hz和10 Hz频率的三角波信号进行轨迹跟踪所得到的均方根误差分别为0.013 mm和0.017 mm。
Abstract:Maxwell reluctance actuators overcome the problems of small strokes of traditional piezoelectric actuators and low thrust density and efficiency of voice coil motors and have great application potential in large-stroke and high-speed micro/nanoposition. In this paper, a large-stroke two-degree-of-freedom flexible microposition stage driven by a Maxwell reluctance actuator was designed, and its high-performance trajectory tracking control was carried out. The position stage was composed of two Maxwell reluctance actuators with permanent magnet bias and a two-degree-of-freedom decoupled and parallel flexible guiding mechanism. The stage made full use of the nonlinear negative stiffness of the reluctance actuator to partially compensate for the elastic restoring force of the flexible mechanism, which could effectively improve its motion range and energy transfer efficiency and reduce the required thrust of the stage within the range of ± 2 mm from ±120 N to ±24 N. In terms of trajectory tracking control, firstly, in order to compensate for the hysteresis nonlinearity caused by the impulse of soft magnetic material of the actuator, a rate-dependent hysteresis compensator was constructed by using the inverse Prandtl-ishlinskii hysteresis model and placed in the feedforward loop. In addition, in order to solve the low damping resonance and the inconsistency of the dynamic model of the stage, a PI feedback controller with a fractional order phase-lead link was designed to flexibly adjust the open-loop frequency characteristics of the system, realize the high-precision trajectory tracking control of the stage, and effectively reduce the tracking error of the system. The root mean square errors obtained by tracking the trajectory of triangular wave signals with amplitude of 2 mm and frequencies of 1 Hz and 10 Hz are 0.013 mm and 0.017 mm, respectively.
-
-
[1] LEE C, LEE J W, RYU S G, et al. Optimum design of a large area, flexure based XYθ mask alignment stage for a 12-inch wafer using grey relation analysis[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2019, 58: 109-119. doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2019.02.005 [2] 刘庆玲. 柔性对称微位移放大机构性能分析方法的研究[J]. 工程设计学报, 2013, 20(4): 344-347. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1006-754X.2013.04.015LIU Q L. Study on the performance analysis methods of the compliant symmetric micro-displacement magnifying mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Design, 2013, 20(4): 344-347(in Chinese). doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1006-754X.2013.04.015 [3] 王念峰, 张志远, 张宪民, 等. 三种两自由度柔顺精密定位平台的性能对比与分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(13): 102-109. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.13.102WANG N F, ZHANG Z Y, ZHANG X M, et al. Performance comparison and analysis of three 2-DOF compliant precision positioning stages[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(13): 102-109(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.13.102 [4] 李玄, 周双武, 路松, 等. 基于二级杠杆机构的二自由度微定位平台设计与分析[J]. 工程设计学报, 2020, 27(4): 533-540. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1006-754X.2020.00.063LI X, ZHOU S W, LU S, et al. Design and analysis of two-DOF micro-positioning platform based on two-level lever mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Design, 2020, 27(4): 533-540(in Chinese). doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1006-754X.2020.00.063 [5] KATALENIC A, DE BOEIJ J, BUTLER H, et al. Linearization of a current-driven reluctance actuator with hysteresis compensation[J]. Mechatronics, 2013, 23(2): 163-171. doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2013.01.004 [6] LU X D, TRUMPER D L. Ultrafast tool servos for diamond turning[J]. CIRP Annals, 2005, 54(1): 383-388. doi: 10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60128-0 [7] HIEMSTRA D B, PARMAR G, AWTAR S. Performance tradeoffs posed by moving magnet actuators in flexure-based nanopositioning[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2014, 19(1): 201-212. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2012.2226738 [8] ITO S, TROPPMAIR S, LINDNER B, et al. Long-range fast nanopositioner using nonlinearities of hybrid reluctance actuator for energy efficiency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(4): 3051-3059. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2842735 [9] ZHU Z W, CHEN L, TO S. A novel direct drive electromagnetic XY nanopositioning stage[J]. CIRP Annals, 2021, 70(1): 415-418. doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2021.04.064 [10] FANG Y N, PU X, TO S, et al. Normal-stressed electromagnetic triaxial fast tool servo for microcutting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(7): 7131-7140. [11] NIE Y H, FANG F Z, ZHANG X D. System design of Maxwell force driving fast tool servos based on model analysis[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2014, 72(1): 25-32. [12] FANG F Z, NIE Y H, ZHANG X D. Design of fast tool servo system based on magnetic field analysis[J]. Nanotechnology and Precision Engineering, 2011, 9(6): 539-544. [13] NASER M F M, AL-HDAIBAT B, GUMAH G, et al. On the consistency of local fractional semilinear Duhem model[J]. International Journal of Dynamics and Control, 2020, 8(3): 723-729. doi: 10.1007/s40435-019-00607-9 [14] RAKOTONDRABE M. Bouc-Wen modeling and inverse multiplicative structure to compensate hysteresis nonlinearity in piezoelectric actuators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2011, 8(2): 428-431. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2010.2081979 [15] AL JANAIDEH M, RAKHEJA S, SU C Y. An analytical generalized Prandtl-Ishlinskii model inversion for hysteresis compensation in micropositioning control[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2011, 16(4): 734-744. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2010.2052366 [16] CSENCSICS E, SCHLARP J, SCHITTER G. High-performance hybrid-reluctance-force-based tip/tilt system: Design, control, and evaluation[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2018, 23(5): 2494-2502. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2018.2866272 [17] XU Q S. New flexure parallel-kinematic micropositioning system with large workspace[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2012, 28(2): 478-491. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2011.2173853 [18] LAI L J, GU G Y, ZHU L M. Design and control of a decoupled two degree of freedom translational parallel micro-positioning stage[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2012, 83(4): 045105. doi: 10.1063/1.3700182 [19] JANOCHA H, KUHNEN K. Real-time compensation of hysteresis and creep in piezoelectric actuators[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2000, 79(2): 83-89. doi: 10.1016/S0924-4247(99)00215-0 [20] GU G Y, YANG M J, ZHU L M. Real-time inverse hysteresis compensation of piezoelectric actuators with a modified Prandtl-Ishlinskii model[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2012, 83(6): 065106. doi: 10.1063/1.4728575 [21] 薛定宇. 分数阶微积分学与分数阶控制[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018.XUE D Y. Fractional calculus and fractional-order control[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: