-
摘要:
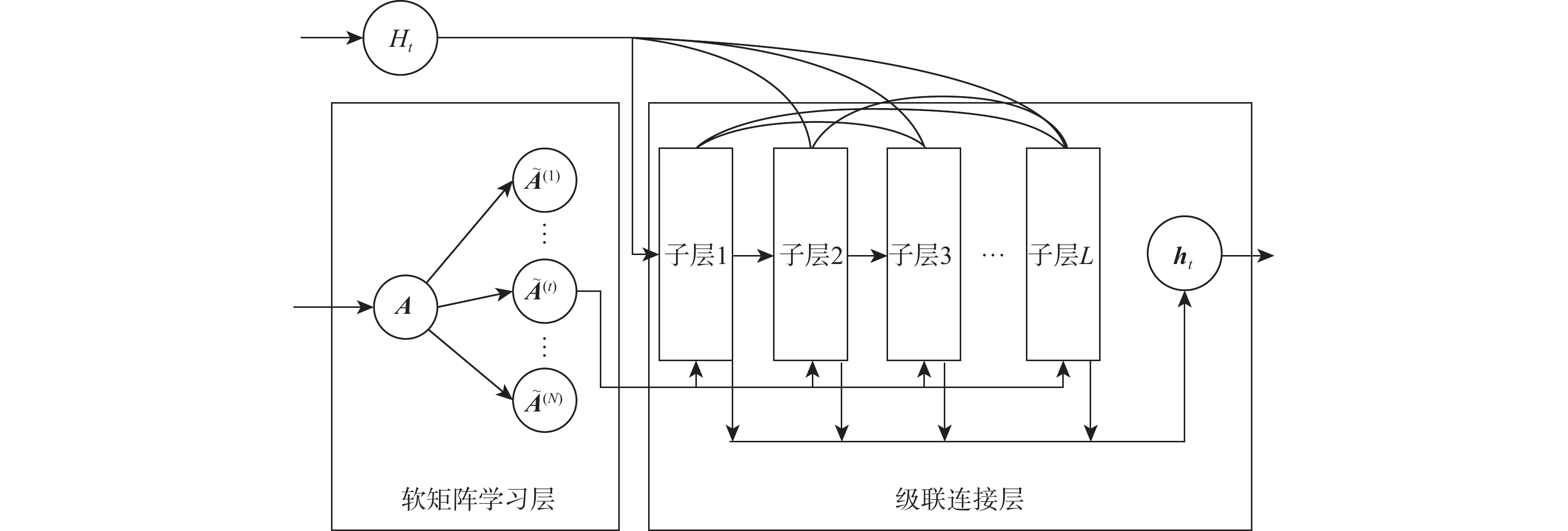
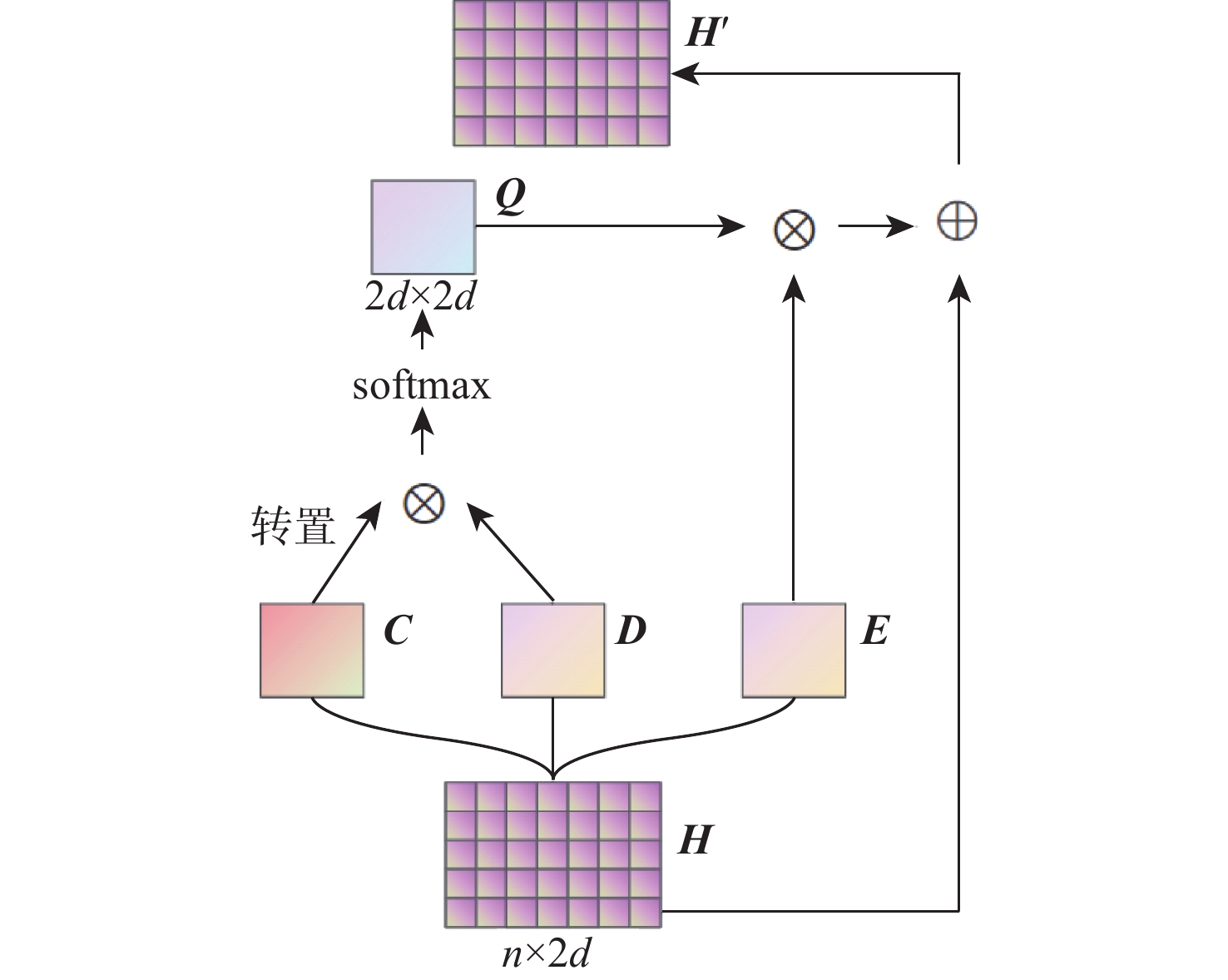
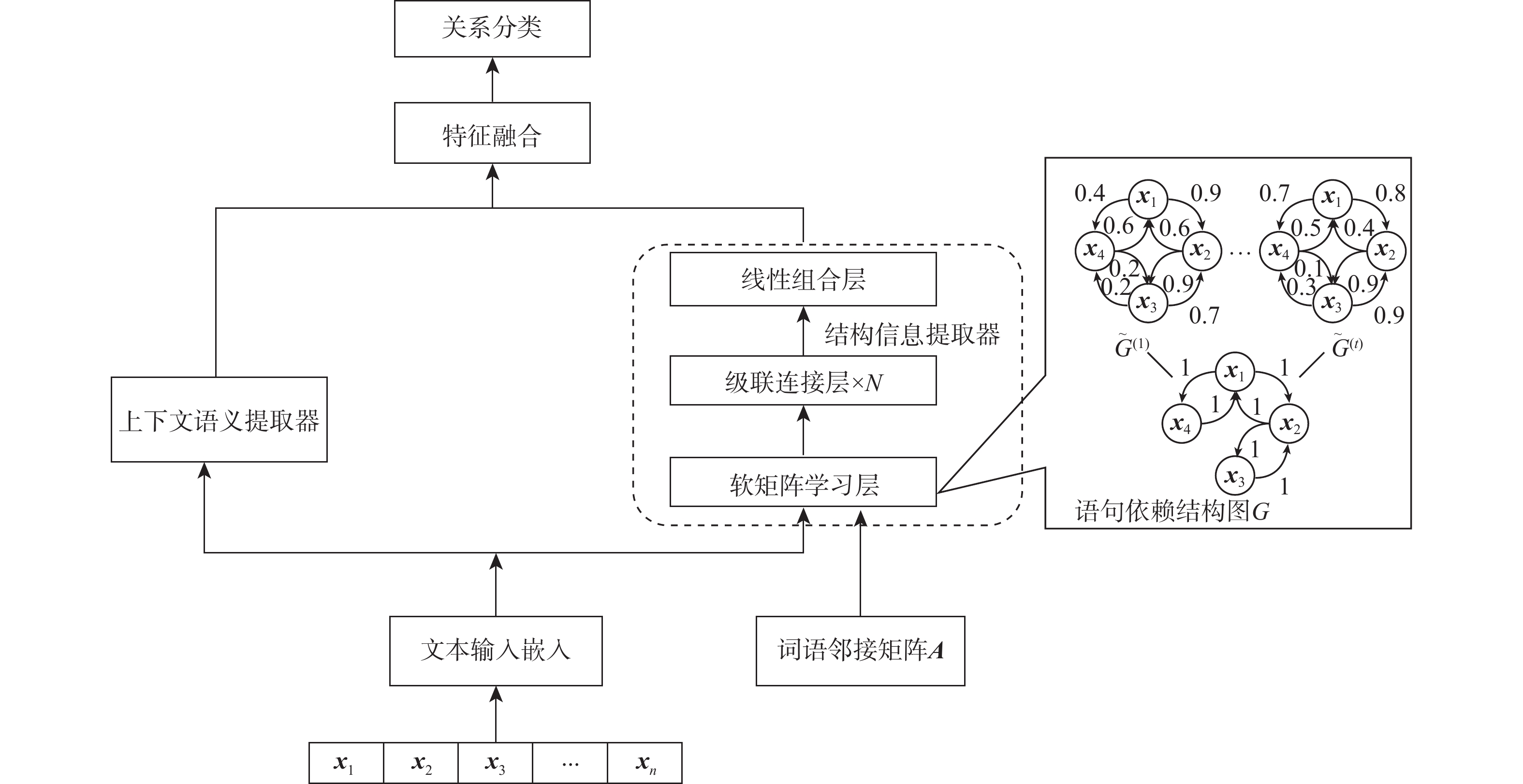
关系抽取是自然语言处理应用中的一项重要任务。现有的关系抽取方法主要基于语言序列特征或句子结构信息来预测关系,并不能有效地反映实体间关系的内在结构和特征。为此,提出一种融合句子中图结构和序列特征信息的关系抽取模型。该模型利用基于注意力的图卷积网络(GCN)学习语句中的结构信息,利用双向长短期记忆(BiLSTM)网络学习语句的序列语义特征,通过注意力机制结合句子结构特征和序列语义对关系进行分类。在公共数据集和手工构建的数据集上进行了大量实验,验证了所提模型的优越性。
Abstract:Relation extraction is an important task for natural language processing applications. Most of the existing relation extraction methods mainly predict the relation based on language sequence features or structure information of sentences, which fails to effectively reflect the internal structure and features of the relation between entities. In this paper, a relation extraction model fusing graph structure and sequence feature information in sentences was proposed. The model used an attention-based graph convolutional neural network (GCN) to learn the structure information of sentences and utilized bi-directional long short-term memory (BiLSTM) to learn the sequence semantics. The relation was classified by considering the two features through the attention mechanism. Extensive experiments were conducted on a public dataset and a manually constructed dataset, which demonstrated the priority of the proposed model.
-
Key words:
- information extraction /
- relation extraction /
- graph neural network /
- sequence model /
- feature fusion
-
表 1 CSGC-3数据子集中不同关系的数量
Table 1. Number of relations in CSGC-3 subdatasets
子集 从属/个 缺陷/个 原因/个 训练集 1796 860 930 验证集 143 64 83 测试集 151 62 105 表 3 在 CSGC-3数据集上的句级关系抽取性能表现
Table 3. Sentence-level relation extraction performance on CSGC-3 dataset
% 表 5 在 CSGC-3数据集上的跨句关系抽取性能
Table 5. Cross-sentence relation extraction performance on CSGC-3 dataset
% 模型 精确率 召回率 F1 CaStr-NO-BiLSTM 65.35 56.78 60.76 CaStr-NO-ATT 68.41 59.01 63.36 CaStr 71.03 61.76 66.07 表 7 在 CSGC-3 数据集上的消融实验
Table 7. Ablation experiments on CSGC-3 dataset
% 模型 精确率 召回率 F1 CaStr-NO-BiLSTM 93.12 84.91 88.82 CaStr-NO-ATT 96.03 86.85 91.21 CaStr 98.22 90.27 94.08 表 8 不同模型从CSGC-3数据集中抽取出的关系实例
Table 8. Examples of relation extracted by different models from CSGC-3 dataset
-
[1] BOLLACKER K, EVANS C, PARITOSH P, et al. Freebase: A collaboratively created graph database for structuring human knowledge[C]//Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data. New York: ACM, 2008: 1247-1250. [2] YU M, YIN W P, HASAN K S, et al. Improved neural relation detection for knowledge base question answering[EB/OL]. (2017-04-20)[2022-04-10]. [3] 宁康, 陈挺. 生物医学大数据的现状与展望[J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60(5): 534-546.NING K, CHEN T. Big Data for biomedical research: Current status and prospects[J]. Chin Sci Bull, 2015, 60(5): 534-546(in Chinese). [4] 王群弼. 电力领域实体关系抽取及知识图谱构建研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020: 23-70.WANG Q B. Research on relation extraction and knowledge graph construction in the filed of electric power[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020: 23-70(in Chinese). [5] BEKOULIS G, DELEU J, DEMEESTER T, et al. Adversarial training for multi-context joint entity and relation extraction[EB/OL]. (2018-08-21)[2022-04-12]. [6] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [7] LIU C Y, SUN W B, CHAO W H, et al. Convolution neural network for relation extraction[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Data Mining and Applications. Berlin: Springer, 2013: 231-242. [8] CHENG J P, DONG L, LAPATA M. Long short-term memory-networks for machine reading[EB/OL]. (2016-01-25)[2022-04-12]. [9] TAI K S, SOCHER R, MANNING C D. Improved semantic representations from tree-structured long short-term memory networks[EB/OL]. (2015-02-28)[2022-04-12]. [10] GUO Z J, ZHANG Y, LU W. Attention guided graph convolutional networks for relation extraction[EB/OL]. (2019-06-18)[2022-04-13]. [11] KIPF T N, WELLING M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks[EB/OL]. (2016-09-09)[2022-04-13]. [12] SHI M Y, HUANG J Y, LI C F. Entity relationship extraction based on BLSTM model[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/ACIS International Conference on Computer and Information Science. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 266-269. [13] LI J, WANG X, TU Z P, et al. On the diversity of multi-head attention[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 454: 14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.04.038 [14] ZENG D J, LIU K, LAI S W, et al. Relation classification via convolutional deep neural network[C]//Proceedings of the COLING International Conference on Computational Linguistics: Technical Papers. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014: 2335-2344. [15] JIANG X T, WANG Q, LI P, et al. Relation extraction with multi-instance multi-label convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the COLING International Conference on Computational Linguistics: Technical Papers. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016: 1471-1480. [16] LIN Y K, SHEN S Q, LIU Z Y, et al. Neural relation extraction with selective attention over instances[C]//Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016: 2124-2133. [17] NGUYEN T H, GRISHMAN R. Relation extraction: Perspective from convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the Workshop on Vector Space Modeling for Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2015: 39-48. [18] ZHOU P, SHI W, TIAN J, et al. Attention-based bidirectional long short-term memory networks for relation classification[C]//Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016: 207-212. [19] ZHANG Y H, ZHONG V, CHEN D Q, et al. Position-aware attention and supervised data improve slot filling[C]//Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2017: 35-45. [20] HUANG Z H, XU W, YU K. Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging[EB/OL]. (2015-08-09)[2022-04-15] [21] SCARSELLI F, GORI M, TSOI A C, et al. The graph neural network model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2009, 20(1): 61-80. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2008.2005605 [22] FU T J, LI P H, MA W Y. GraphRel: Modeling text as relational graphs for joint entity and relation extraction[C]//Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2019: 1409-1418. [23] ZHANG Y H, QI P, MANNING C D. Graph convolution over pruned dependency trees improves relation extraction[EB/OL]. (2018-09-26)[2022-04-16]. [24] GENG Z Q, CHEN G F, HAN Y M, et al. Semantic relation extraction using sequential and tree-structured LSTM with attention[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 509: 183-192. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.09.006 [25] MIWA M, BANSAL M. End-to-end relation extraction using LSTMs on sequences and tree structures[EB/OL]. (2016-01-05)[2022-04-16]. [26] VERGA P, STRUBELL E, MCCALLUM A. Simultaneously self-attending to all mentions for full-abstract biological relation extraction[EB/OL]. (2018-02-28)[2022-04-17]. [27] YAO Y, YE D M, LI P, et al. DocRED: A large-scale document-level relation extraction dataset[EB/OL]. (2019-06-14)[2022-04-17]. [28] QUIRK C, POON H. Distant supervision for relation extraction beyond the sentence boundary[EB/OL]. (2019-09-15)[2022-04-17]. [29] NAN G S, GUO Z J, SEKULIĆ I, et al. Reasoning with latent structure refinement for document-level relation extraction[EB/OL]. (2020-05-13)[2022-04-18]. [30] CHRISTOPOULOU F, MIWA M, ANANIADOU S. Connecting the dots: Document-level neural relation extraction with edge-oriented graphs[EB/OL]. (2019-08-31)[2022-04-18]. [31] JIA R, WONG C, POON H. Document-level N-ary relation extraction with multiscale representation learning[EB/OL]. (2019-04-04)[2022-04-18]. [32] GUPTA P, RAJARAM S, SCHÜTZE H, et al. Neural relation extraction within and across sentence boundaries[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Washton, D. C. : AAAI, 2019, 33(1): 6513-6520. [33] CHRISTOPOULOU F, MIWA M, ANANIADOU S. A walk-based model on entity graphs for relation extraction[C]//Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: Association for Computional Linguistics, 2018: 81-88. [34] LIU Y, LAPATA M. Learning structured text representations[J]. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2018, 6: 63-75. doi: 10.1162/tacl_a_00005 [35] PENNINGTON J, SOCHER R, MANNING C. Glove: Global vectors for word representation[C]//Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014: 1532-1543. [36] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: ACM, 2017: 6000–6010. [37] HUANG G, LIU Z, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2261-2269. [38] HENDRICKX I, KIM S N, KOZAREVA Z, et al. SemEval-2010 task 8: Multi-way classification of semantic relations between pairs of nominals[EB/OL]. (2019-11-23)[2022-04-20]. [39] PENG N Y, POON H, QUIRK C, et al. Cross-sentence N-ary relation extraction with graph LSTMs[J]. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2017, 5: 101-115. doi: 10.1162/tacl_a_00049 [40] MANNING C, SURDEANU M, BAUER J, et al. The stanford CoreNLP natural language processing toolkit[C]//Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014: 55-60. [41] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[EB/OL]. (2014-12-22)[2022-04-20]. -







 下载:
下载: