-
摘要:
针对飞蛾火焰优化算法容易出现局部最优解、接近全局最优时开发能力不足等问题,提出一种多策略融合改进的飞蛾火焰优化 (RGMFO) 算法。在每次迭代开始时,使用随机反向学习策略获得高质量飞蛾种群;利用高斯变异将较差的火焰个体替换为优秀个体;使用阿基米德螺线、权重因子和围绕最优火焰飞行3种方式改进飞蛾更新机制。为验证所提算法的有效性,与11个不同类型的基准函数进行寻优测试,基准函数实验结果与秩和检验表明:相较于其他优化算法及其他MFO改进算法,所提算法具有更好的全局搜索能力与更高的寻优精度。将所提算法应用于减速器设计和槽形舱壁设计的实际工程场景中,以进一步验证算法的实用性与可行性。
Abstract:An enhanced moth-flame optimization algorithm with multi-strategy integration (RGMFO) was proposed in order to address the issues that the moth-flame optimization algorithm was prone to falling into the local optimum and that its exploitation ability was insufficient while it was approaching the global optimum. To generate high-quality moth populations, a random opposition-based learning strategy was applied at the start of each iteration. To generate high-quality moth populations, a random opposition-based learning strategy was applied at the start of each iteration. Gaussian mutation was then used to swap out subpar flame individuals with superior ones. Archimedes spirals, weighting factors, and the surrounding of a small number of optimal flames were employed to enhance the moth update mechanism. The proposed algorithm was tested on 11 benchmark functions of different types. The test results and rank sum test show that RGMFO has better global search ability and higher search accuracy. Lastly, RGMFO is applied to the engineering scenarios of reducer design and trough bulkhead design, which further verifies the practicability and feasibility of the algorithm.
-
表 1 各算法参数设置
Table 1. Parameter setting of each algorithms
算法 参数 RGMFO b=1,e1=0.5,e2=1,β=10 IMFO b=1,A=0.5,B=0.6,crmin=0.55,crmax=0.65
σmin=0.1,σmax=0.15CGMFO b=2,β=8 ODSFMFO m=6,γ=5,Pc=0.5,aalpha=1,
bbeta=1.5,l=10,b=1MFO b=1 GWO a从2线性递减至0,r1、r2∈[0,1] SCA a=2,r1从a线性递减至0 PSO Vmax=8,Vmin=−8,w=0.2,c1=3,c2=3 DE pc=0.5 GA pc=0.7,pm=0.1 表 2 基准测试函数
Table 2. Benchmark functions
函数类型 基准测试函数 维度 搜索区间 最优值 高维单峰 F1(x)=d∑i=1x2i 30 [−100,100]d 0 F2(x)=d∑i=1|xi|+d∏i=1|xi| 30 [−10,10]d 0 F3(x)=d∑i=1(i∑j=1xj)2 30 [−100,100]d 0 F4(x)=maxi{|xi|,1⩽i⩽d} 30 [−100,100]d 0 F5(x)=d−1∑i=1[100(xi+1−xi)2+(xi−1)2] 30 [−30,30]d 0 F6(x)=d∑i=1i⋅x4i+random[0,1) 30 [−1.28,1.28]d 0 高维多峰 F7(x)=d∑i=1[x2i−10cos(2πxi+10)] 30 [−5.12,5.12]d 0 F8(x)=−20exp(−0.2√1dd∑i=1x2i)−exp(1dd∑i=1cos(2πxi))+20+e 30 [−32,32]d 0 F9(x)=14000d∑i=1x2i−d∏i=1cos(xi√i)+1 30 [−600,600]d 0 F10(x)=0.1{sin2(3πx1)+d∑i=1(xi−1)2[1+sin2(3πx1+1)]+(xd−1)2[1+sin2(2πxd)]}+d∑i=1u(xi,5,100,4) 30 [−50,50]d 0 低维多峰 {F_{11}}(x) = - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^{10} {{{[(X - {{\boldsymbol{a}}_{{\mathrm{SHi}}}}){{(X - {{\boldsymbol{a}}_{{\mathrm{SHi}}}})}^{\text{T}}} + {{\boldsymbol{c}}_{{\mathrm{SHi}}}}]}^{ - 1}}} 4 [0,10]4 −10.536 表 3 RGMFO算法及其他算法高维单峰函数寻优结果
Table 3. High-dimensional single-peak function optimization results of RGMFO algorithm and other algorithms
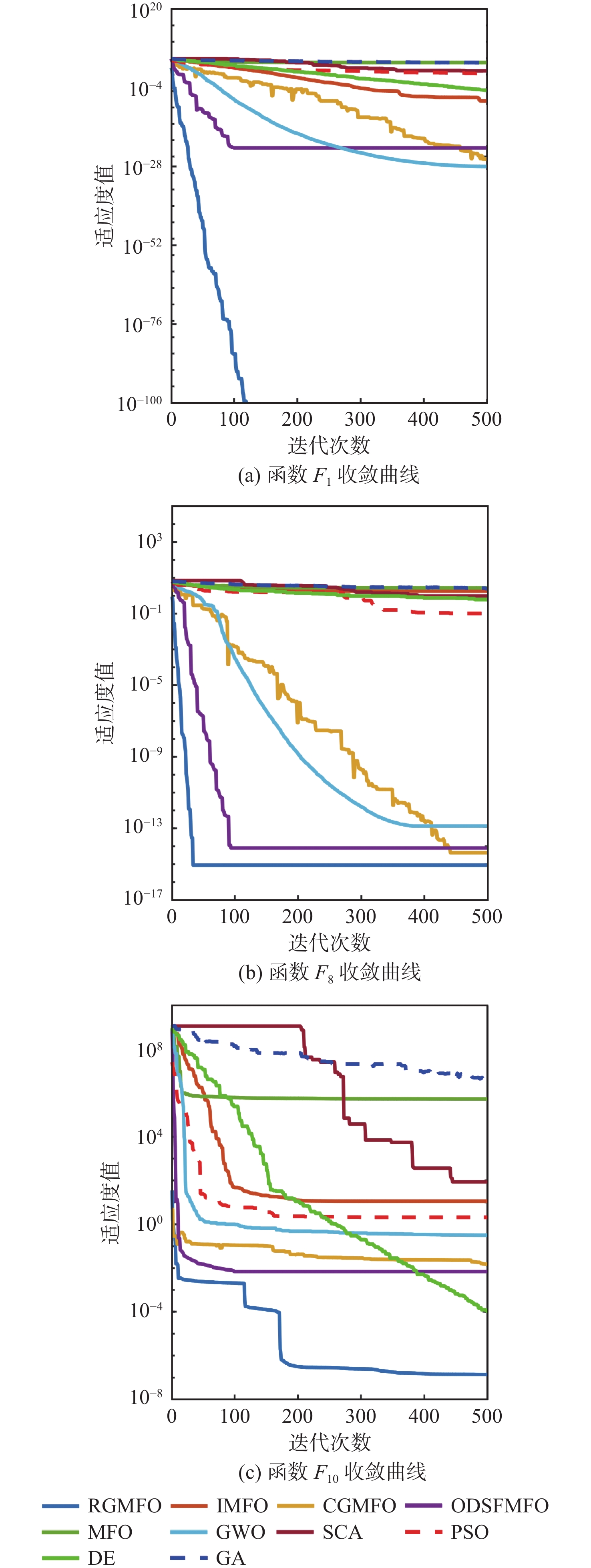
算法 平均值 标准差 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 RGMFO 0 1.68×10−208 0 4.19×10−208 1.98×10−5 1.07×10−4 0 0 0 0 3.07×10−5 1.2×10−4 IMFO 2.68×10−7 5.13×10−4 5850 17.6 15700 0.117 5.15×10−7 6.74×10−4 3440 4.85 11000 0.0447 CGMFO 1.66×10−23 7.32×10−14 1.81×10−17 7.50×10−15 1.46×10−3 0.0268 7.45×10−23 2.92×10−13 9.93×10−17 1.66×10−14 2.92×10−3 0.0218 ODSFMFO 1.96×10−24 4.98×10−13 1.40×10−14 8.87×10−14 0.017 0.0563 8.54×10−24 1.55×10−12 6.08×10−14 2.12×10−13 0.0459 0.0403 MFO 4970 20.3 59600 22.6 494 0.824 2350 4.54 58600 6.94 2690 0.439 GWO 9.68×10−28 1.01×10−16 2.09×10−5 5.60×10−7 27.9 2.18×10−3 1.65×10−27 1.19×10−16 4.99×10−5 4.36×10−7 0.851 1.48×10−3 PSO 12.2 0.0269 10500 37.2 7480 0.1 17.8 0.041 8450 9.88 26100 0.0839 DE 0.399 0.402 1120 0.179 36.2 7.43×10−3 0.344 0.312 2940 0.124 7.33 3.91×10−3 GA 2.12×10−5 2.61×10−4 18500 14.1 752 0.314 1.31×10−5 6.69×10−5 3530 4.79 460 0.0679 表 4 RGMFO算法及其他算法高维多峰函数寻优结果
Table 4. High-dimensional multi-peak function optimization results of RGMFO algorithm and other algorithms
算法 平均值 标准差 F7 F8 F9 F10 F7 F8 F9 F10 RGMFO 0 8.88×10−16 0 7.58×10−6 0 0 0 1.10×10−5 IMFO 69.9 1.16 8.86×10−3 7.16 19.5 0.246 9.33×10−3 5.34 CGMFO 0 1.60×10−14 0 0.0226 0 4.58×10−14 0 0.0309 ODSFMFO 0 1.92×10−14 0 0.0231 0 4.16×10−14 0 0.0214 MFO 113 2.58 36.2 3.87×106 25 0.321 13.8 3.51×106 GWO 4.09 0.0215 3.73×10−3 0.653 6.06 0.0562 8.01×10−3 0.26 PSO 39.9 1.07 0.876 1.90×105 30.6 0.529 0.357 8.09×105 DE 33.2 0.395 0.591 2.78 35.6 0.387 0.296 0.639 GA 27.4 0.631 1.33×10−4 0.358 6.85 0.0874 3.17×10−4 0.965 表 5 RGMFO算法及其他算法低维多峰函数寻优结果
Table 5. Low-dimensional multi-peak function optimization results of RGMFO algorithm and other algorithms
算法 平均值 标准差 RGMFO −10.5 4.47×10−9 IMFO −8.2 3.43 CGMFO −10.5 4.34×10−4 ODSFMFO −8.19 2.72 MFO −8.72 2.88 GWO −9.99 2.06 PSO −3.89 1.65 DE −10.5 6.09×10−3 GA −10.4 0.987 表 6 Wilcoxon秩和检验p值
Table 6. P-value for Wilcoxon rank sum test
函数 RGMFO-IMFO RGMFO-CGMFO RGMFO-ODSFMFO RGMFO-MFO RGMFO-GWO RGMFO-SCA RGMFO-PSO RGMFO-DE RGMFO-GA F1 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 F2 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 F3 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 F4 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 F5 3.02×10−11 2.44×10−9 3.69×10−11 5.57×10−10 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 F6 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 F7 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.94×10−9 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 F8 1.21×10−12 2.82×10−5 2.16×10−6 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 F9 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 0.011 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 F10 3.02×10−11 3.34×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.01×10−7 3.02×10−11 F11 0.0254 3.47×10−10 2.30×10−7 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 2.20×10−10 3.02×10−11 表 7 RGMFO算法及其他算法寻优运算时间
Table 7. Optimization operation time of RGMFO algorithm and other algorithms
s 函数 RGMFO IMFO CGMFO ODSFMFO MFO GWO SCA PSO DE GA F1 0.257 9 0.163 1 0.084 2 0.785 5 0.0675 0.2406 0.1729 0.0579 0.1858 0.0850 F2 0.469 5 0.363 9 0.193 7 1.020 6 0.0716 0.2331 0.1767 0.0606 0.1223 0.0750 F3 0.503 8 0.389 3 0.222 8 1.036 6 0.0905 0.2476 0.1948 0.0761 0.1404 0.0839 F4 0.535 0 0.373 7 0.198 1 1.023 0 0.0702 0.2257 0.1815 0.1136 0.1206 0.0729 F5 0.567 6 0.357 8 0.183 3 1.012 7 0.0648 0.2369 0.1685 0.0569 0.1455 0.0656 F6 0.980 2 0.747 9 0.366 2 1.608 0 0.2153 0.3963 0.3933 0.2093 0.2361 0.1320 F7 0.718 6 0.426 6 0.200 4 1.324 6 0.0961 0.2395 0.1878 0.0901 0.1378 0.0779 F8 0.732 1 0.466 9 0.230 5 1.494 8 0.1001 0.2531 0.2131 0.0924 0.1401 0.0800 F9 0.727 0 0.605 8 0.320 0 1.995 9 0.1672 0.3148 0.2644 0.1271 0.2096 0.1371 F10 1.172 2 0.740 3 0.415 1 1.930 5 0.3277 0.4571 0.4770 0.3205 0.6867 0.4184 F11 0.809 2 0.473 8 0.346 4 1.463 1 0.1527 0.1711 0.1607 0.1379 0.3427 0.2041 表 8 高维单峰函数消融实验结果
Table 8. High-dimensional single-peak function experimental results of model ablation
算法 平均值 标准差 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 RGMFO 0 1.68×10−208 0 4.19×10−208 1.98×10−5 1.07×10−4 0 0 0 0 3.07×10−5 1.20×10−4 GMFO 2.00×10−210 6.63×10−115 2.59×10−165 3.66×10−110 2.66 0.0225 0 3.16×10−114 0 1.86×10−109 3.23 0.0164 RMFO 0.263 1.66 7.38 0.178 5.72×10−5 0.62 0.144 0.823 5.47 0.0888 2.15×10−4 1.02 MFO 4970 20.3 59600 22.6 494 0.824 2350 4.54 58600 6.94 2690 0.439 表 9 高维多峰函数消融实验结果
Table 9. High-dimensional multi-peak function experimental results of model ablation
算法 平均值 标准差 F7 F8 F9 F10 F7 F8 F9 F10 RGMFO 0 8.88×10−16 0 7.58×10−6 0 0 0 1.10×10−5 GMFO 0 8.88×10−16 0 0.145 0 0 0 0.0615 RMFO 0.477 0.0147 0.0103 2.37×10−5 0.947 0.016 6.74×10−3 4.97×10−5 MFO 113 2.58 36.2 3.87×106 25 0.321 13.8 3.51×106 表 10 低维多峰函数消融实验结果
Table 10. Low-dimensional multi-peak function experimental results of model ablation
算法 平均值 标准差 RGMFO −10.5 4.47×10−9 GMFO −7.72 2.66 RMFO −5.13 1.83×10−12 MFO −8.72 2.88 表 11 减速器设计变量边界约束
Table 11. Reducer design variable boundary constraints
变量 下界 上界 x1 2.6 3.6 x2 0.7 0.8 x3 17 28 x4 7.3 8.3 x5 7.8 8.3 x6 2.9 3.9 x7 5.0 5.5 表 12 减速器设计结果
Table 12. Reducer design results
算法 x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 x6 x7 适应度值 RGMFO 3.50 0.70 17.00 7.30 7.80 3.35 5.29 2996.41 IMFO 3.50 0.70 17.00 7.30 7.80 3.35 5.29 2996.41 CGMFO 3.50 0.70 17.00 7.60 7.80 3.80 5.29 3130.09 ODSFMFO 3.50 0.70 17.00 7.30 7.80 3.35 5.29 2996.41 MFO 3.50 0.70 17.00 7.30 7.80 3.35 5.37 3047.56 GWO 3.50 0.70 17.00 7.39 7.85 3.36 5.29 3003.19 SCA 3.60 0.70 17.00 8.30 8.30 3.45 5.37 3133.94 PSO 3.60 0.70 17.00 7.30 8.28 3.35 5.29 3046.37 DE 3.50 0.70 17.00 7.30 7.80 3.35 5.29 2996.41 GA 3.57 0.70 17.16 7.67 7.82 3.43 5.30 3096.49 表 13 槽形舱壁设计结果
Table 13. Trough bulkhead design results
算法 x1 x2 x3 x4 适应度值 RGMFO 37.51 33.11 37.51 0.74 5.89 IMFO 37.83 33.19 37.83 0.74 5.89 CGMFO 31.34 32.48 37.88 0.78 6.23 ODSFMFO 38.89 33.46 38.89 0.76 5.90 MFO 37.28 33.23 38.13 0.74 5.90 GWO 37.69 33.20 37.85 0.74 5.90 SCA 32.71 35.53 46.11 0.90 6.70 PSO 40.91 33.30 39.36 0.79 6.02 DE 37.49 33.11 37.49 0.73 5.89 GA 90.70 33.53 75.91 1.67 10.29 -
[1] MIRJALILI S. Moth-flame optimization algorithm: A novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2015, 89: 228-249. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2015.07.006 [2] 张淑清, 段晓宁, 张立国, 等. Tsne降维可视化分析及飞蛾火焰优化ELM算法在电力负荷预测中应用[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41(9): 3120-3130.ZHANG S Q, DUAN X N, ZHANG L G, et al. Tsne dimension reduction visualization analysis and moth flame optimized ELM algorithm applied in power load forecasting[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41(9): 3120-3130(in Chinese). [3] 安许锋, 田洲, 钱锋. 基于多策略扰动机制的飞蛾火焰算法及在乙烯聚合过程动力学参数估计中的应用[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2018, 32(4): 918-925. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2018.04.023AN X F, TIAN Z, QIAN F. Moth-flame optimization algorithm based on multi-strategy disturbance and its application in kinetic parameter estimation of ethylene polymerization[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2018, 32(4): 918-925(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2018.04.023 [4] 田鸿, 陈国彬, 刘超. 新型飞蛾火焰优化算法的研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2019, 55(16): 138-143. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1805-0027TIAN H, CHEN G B, LIU C. Research on new moth-flame optimization algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2019, 55(16): 138-143(in Chinese). doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1805-0027 [5] 黄鹤, 吴琨, 王会峰, 等. 基于改进飞蛾扑火算法的无人机低空突防路径规划[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2021, 29(2): 256-263.HUANG H, WU K, WANG H F, et al. Path planning of UAV low altitude penetration based on improved moth-flame optimization[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2021, 29(2): 256-263(in Chinese). [6] 刘倩, 冯艳红, 陈嶷瑛. 基于混沌初始化和高斯变异的飞蛾火焰优化算法[J]. 郑州大学学报(工学版), 2021, 42(3): 53-58.LIU Q, FENG Y H, CHEN Y Y. Moth-flame optimization algorithm based on chaotic initialization and Gaussian mutation[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Engineering Science), 2021, 42(3): 53-58(in Chinese). [7] PELUSI D, MASCELLA R, TALLINI L, et al. An improved moth-flame optimization algorithm with hybrid search phase[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 191: 105277. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.105277 [8] LI Z F, ZENG J H, CHEN Y Q, et al. Death mechanism-based moth-flame optimization with improved flame generation mechanism for global optimization tasks[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 183: 115436. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115436 [9] 刘宝宁, 章卫国, 李广文, 等. 一种改进的多目标粒子群优化算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2013, 39(4): 458-462.LIU B N, ZHANG W G, LI G W, et al. Improved multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013, 39(4): 458-462(in Chinese). [10] MIRJALILI S. SCA: A sine cosine algorithm for solving optimization problems[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2016, 96: 120-133. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2015.12.022 [11] MIRJALILI S, MIRJALILI S M, LEWIS A. Grey wolf optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 69: 46-61. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007 [12] TIZHOOSH H R. Opposition-based learning: a new scheme for machine intelligence[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Modelling, Control and Automation and International Conference on Intelligent Agents, Web Technologies and Internet Commerce. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2006, 1: 695-701. [13] LONG W, JIAO J J, LIANG X M, et al. A random opposition-based learning grey wolf optimizer[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 113810-113825. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2934994 [14] XU Y T, CHEN H L, LUO J, et al. Enhanced moth-flame optimizer with mutation strategy for global optimization[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 492: 181-203. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.04.022 [15] HEIDARI A A, MIRJALILI S, FARIS H, et al. Harris Hawks optimization: algorithm and applications[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 97: 849-872. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.02.028 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李君恩,丁天明,韩喜红,刘虎. 基于改进麻雀搜索算法的USV路径规划. 舰船科学技术. 2025(05): 153-158 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-







 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术

