Influence of unloading groove opening of port plate of plunger pumps on transient flow field characteristics
-
摘要:
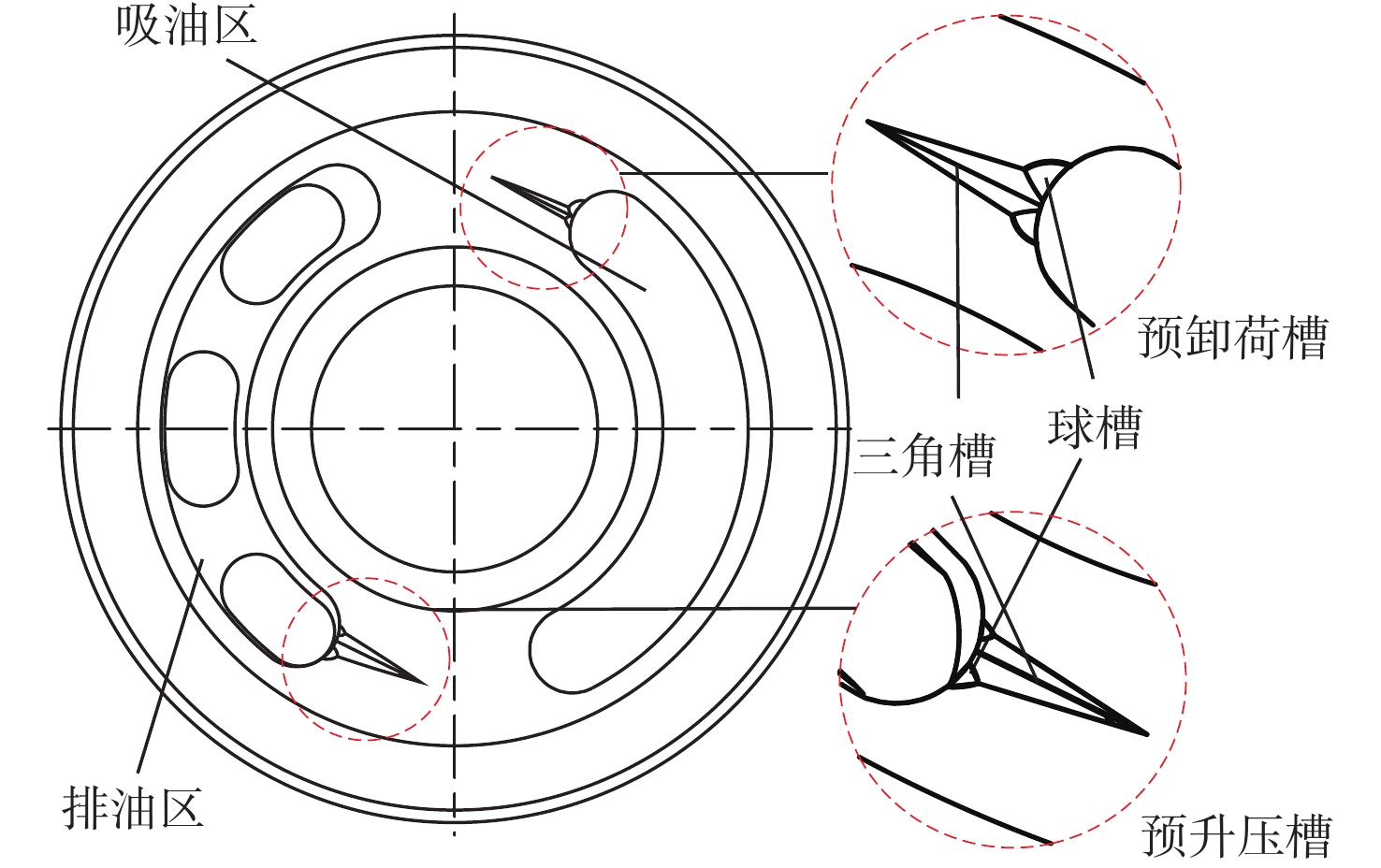
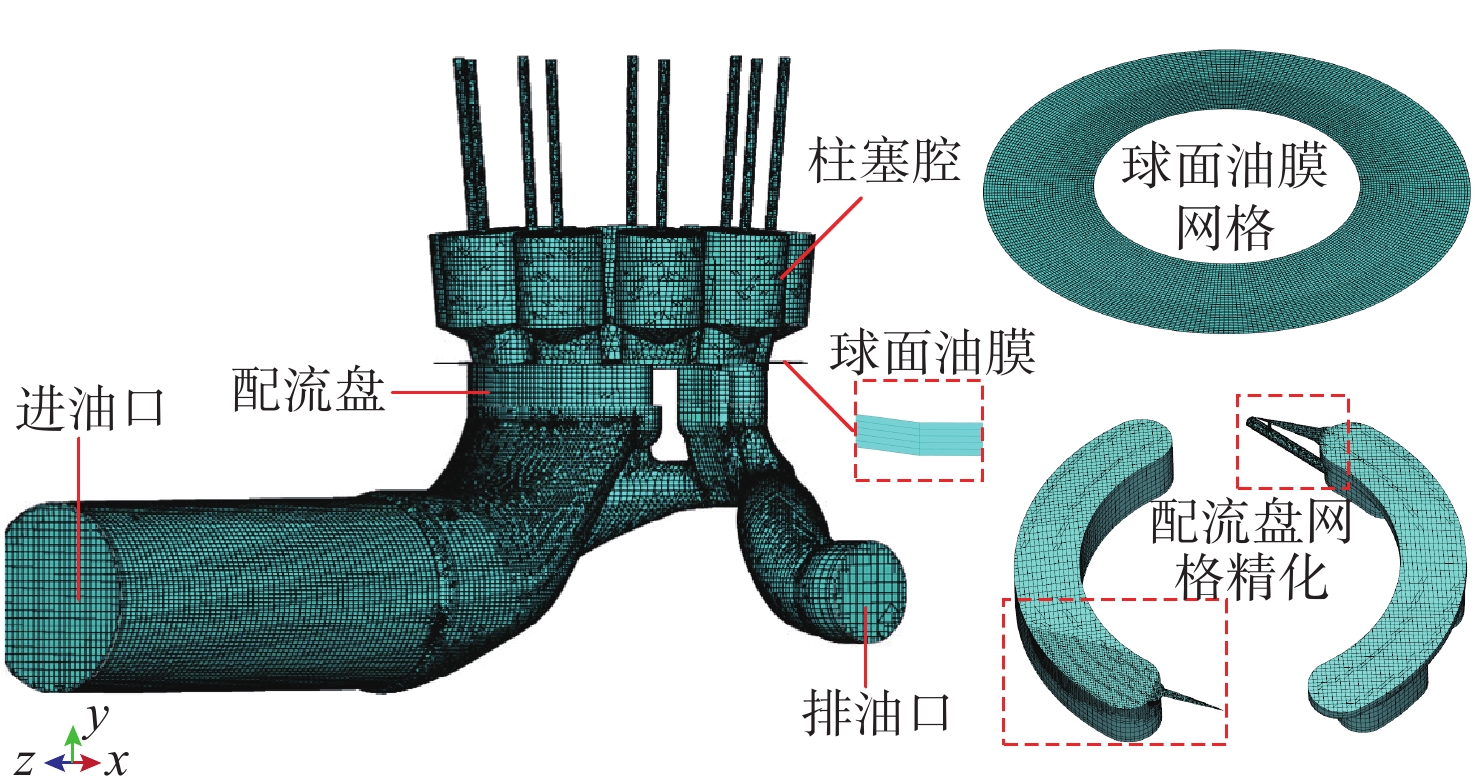
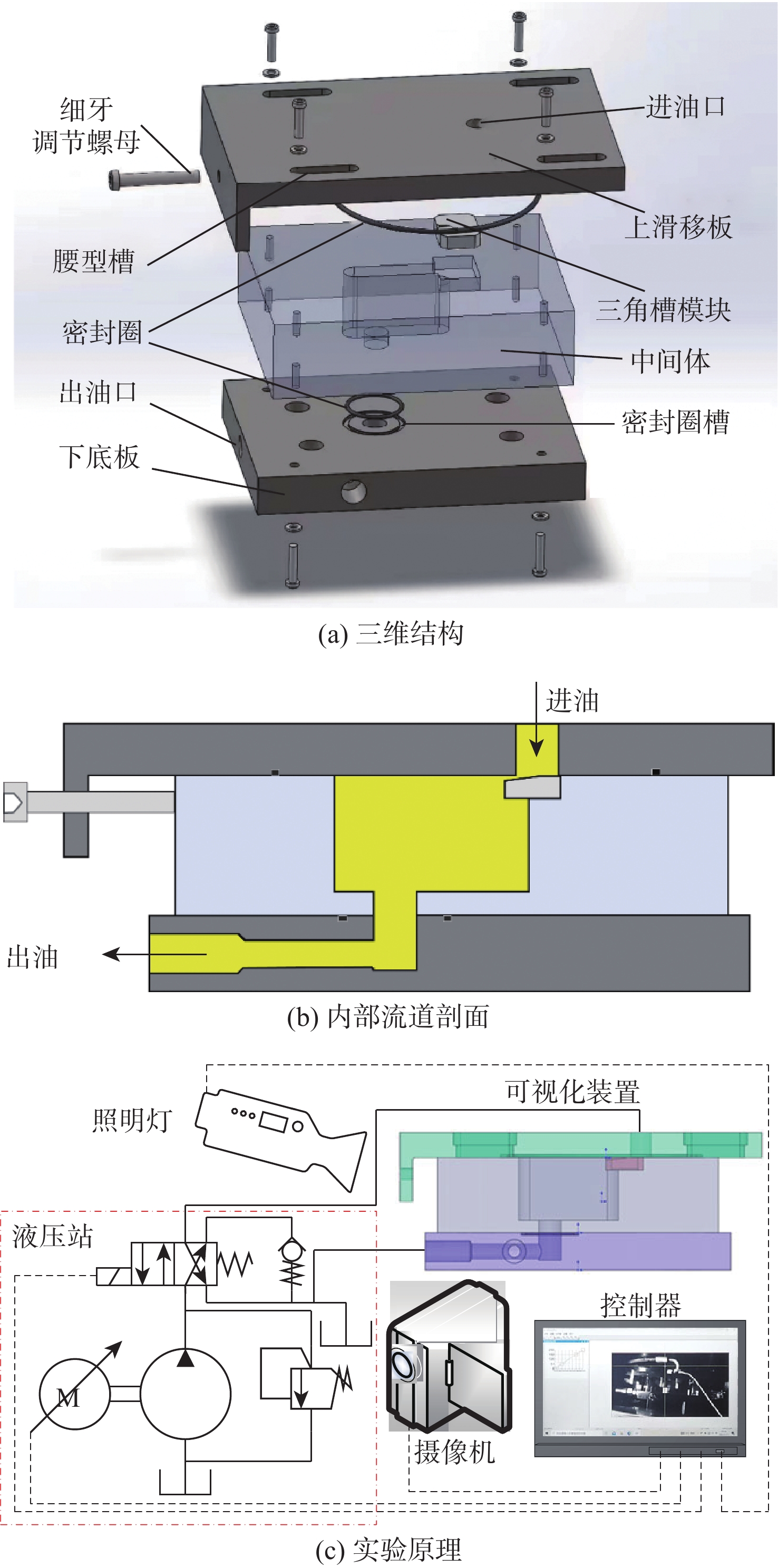
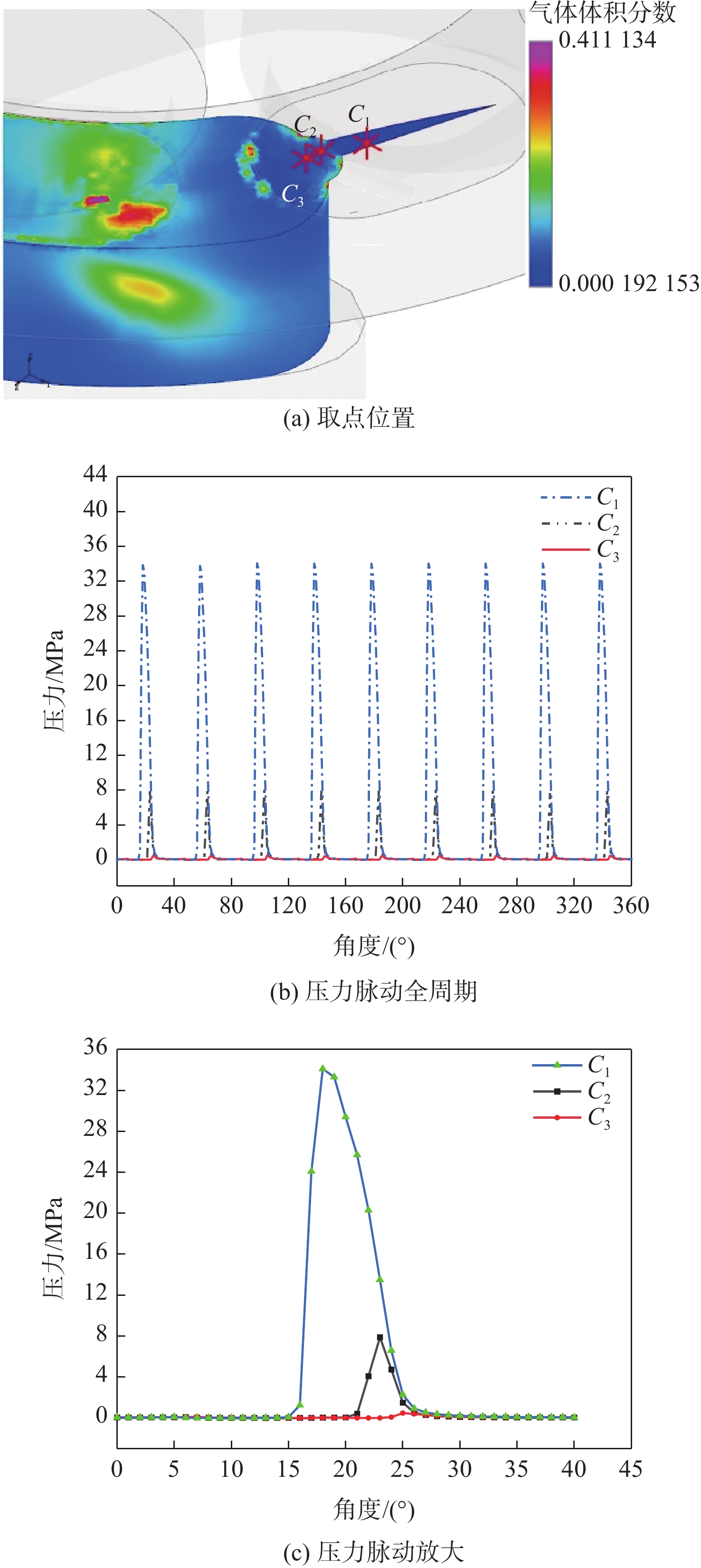
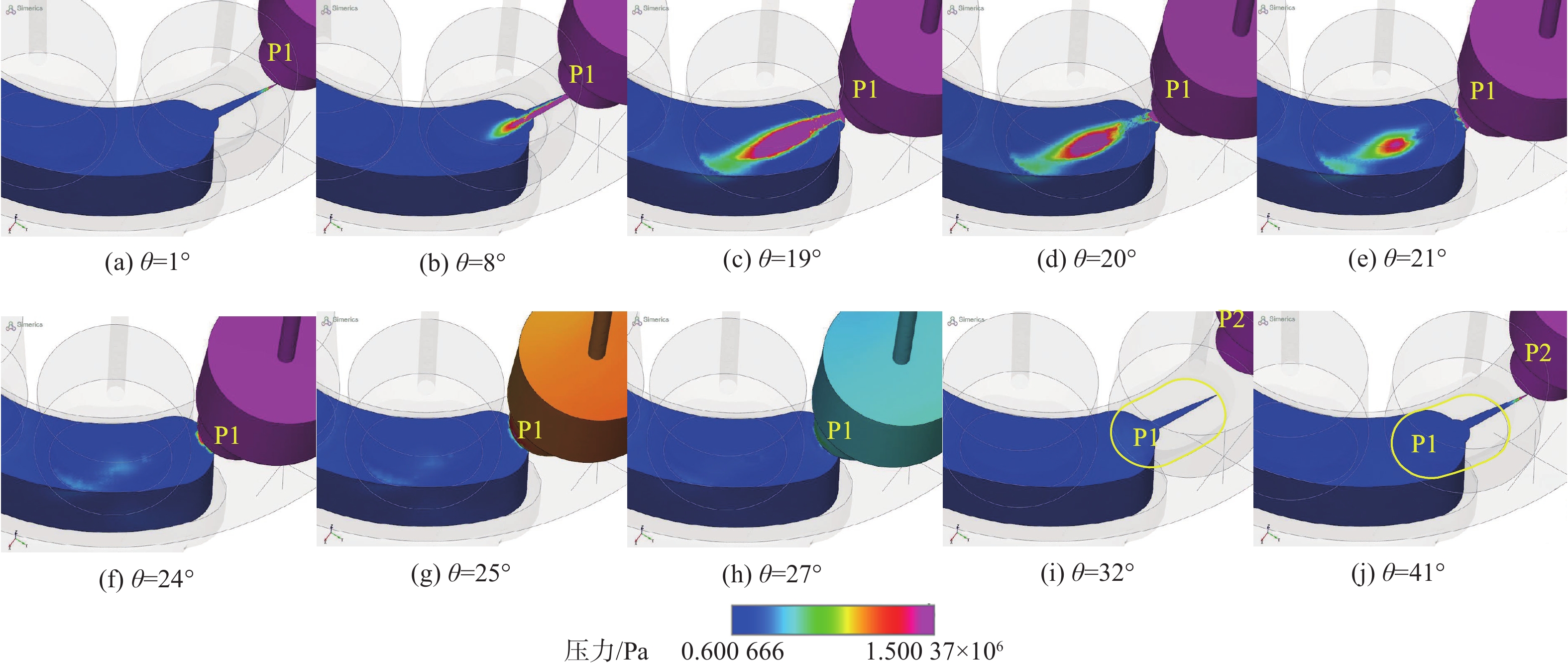
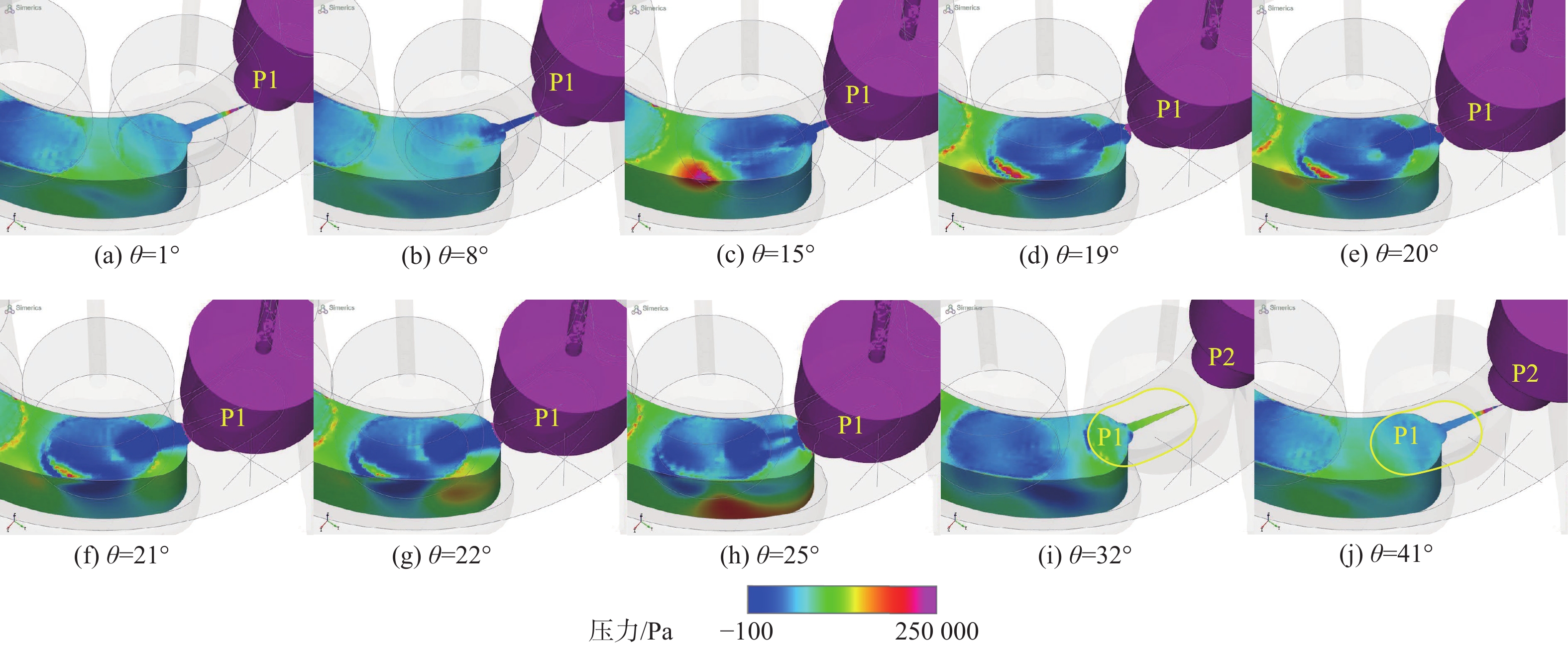
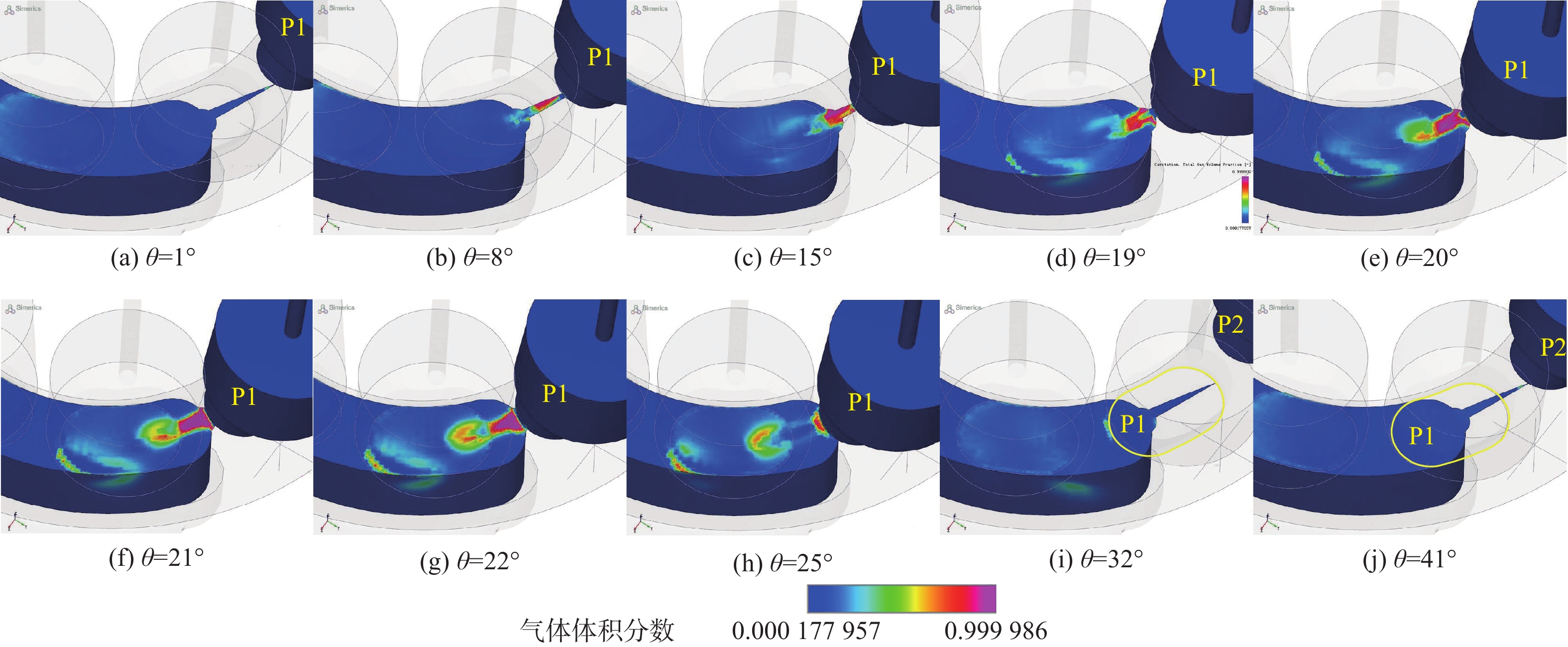
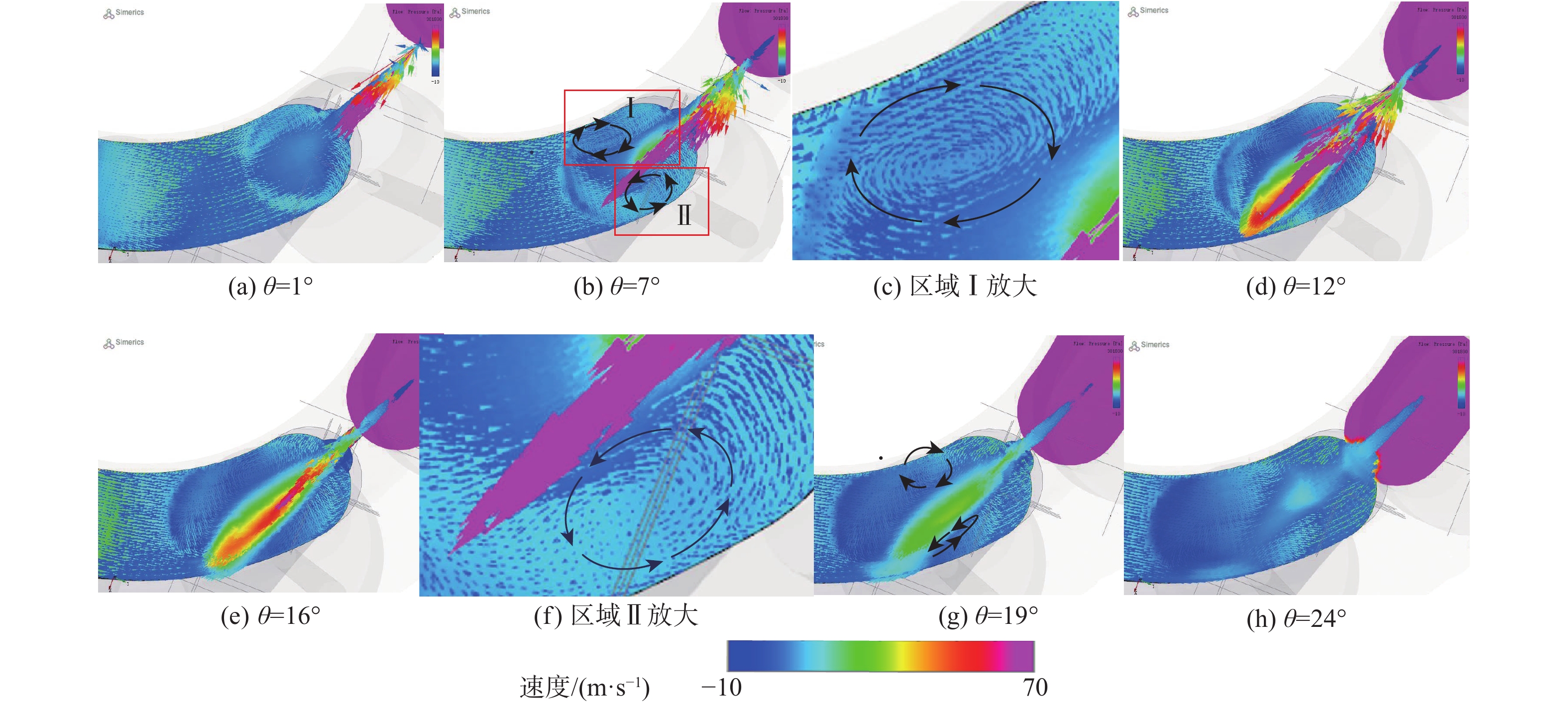
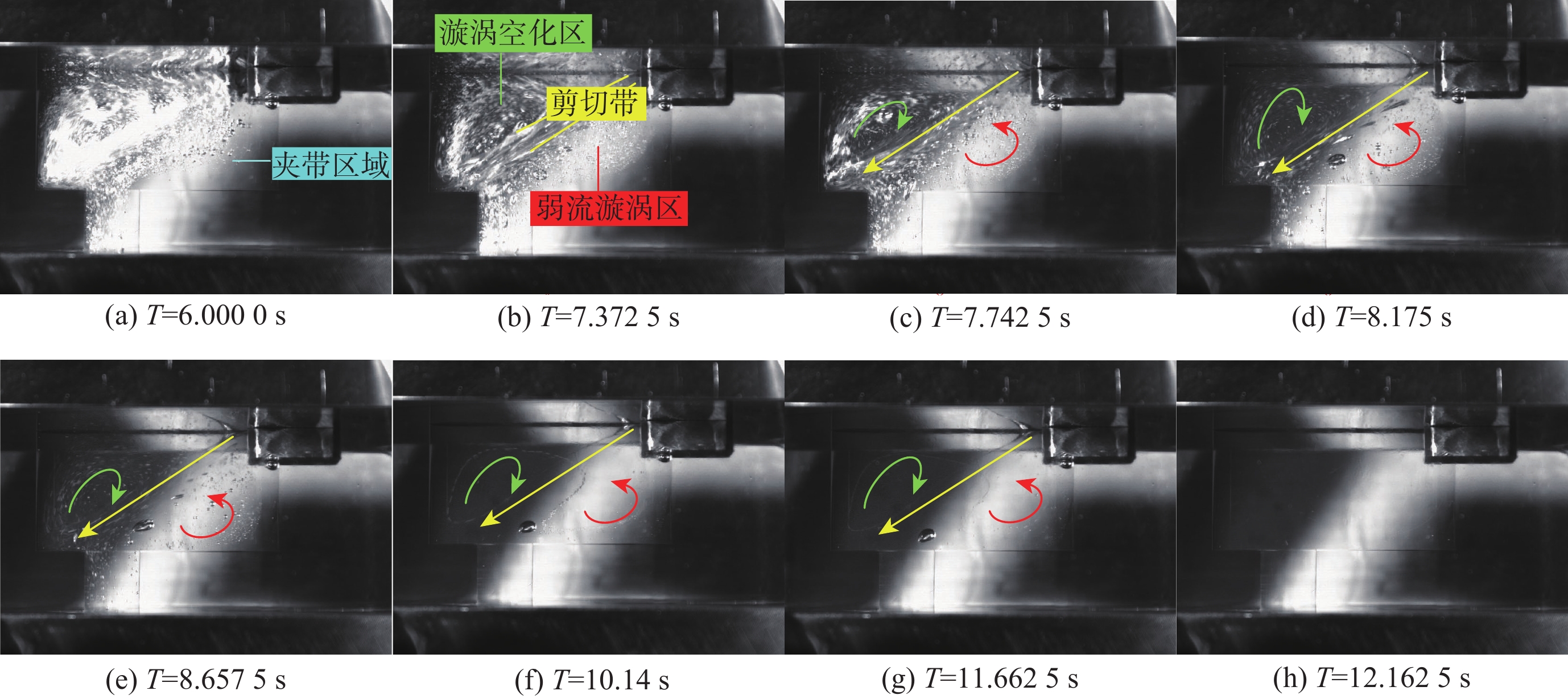
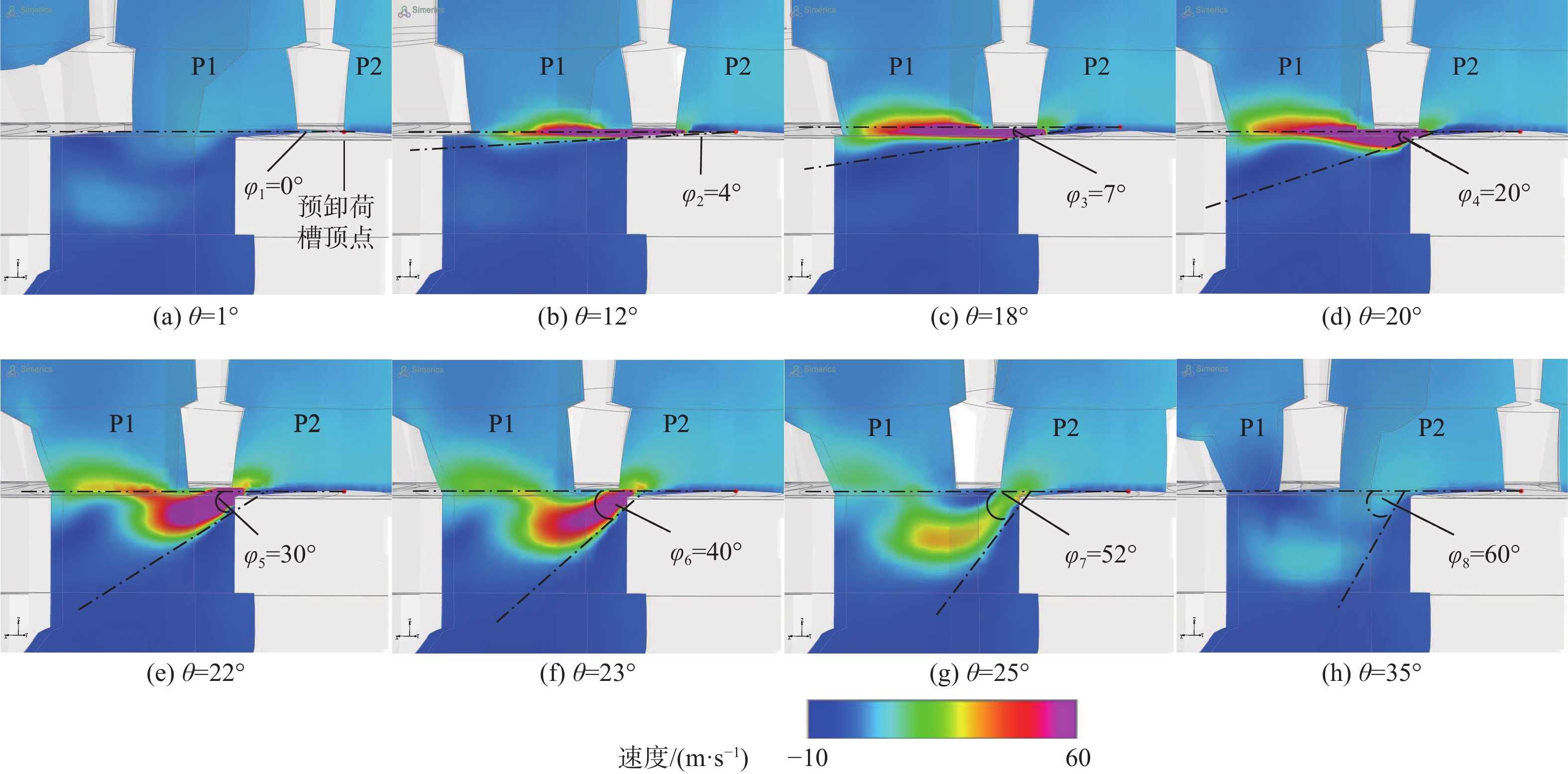
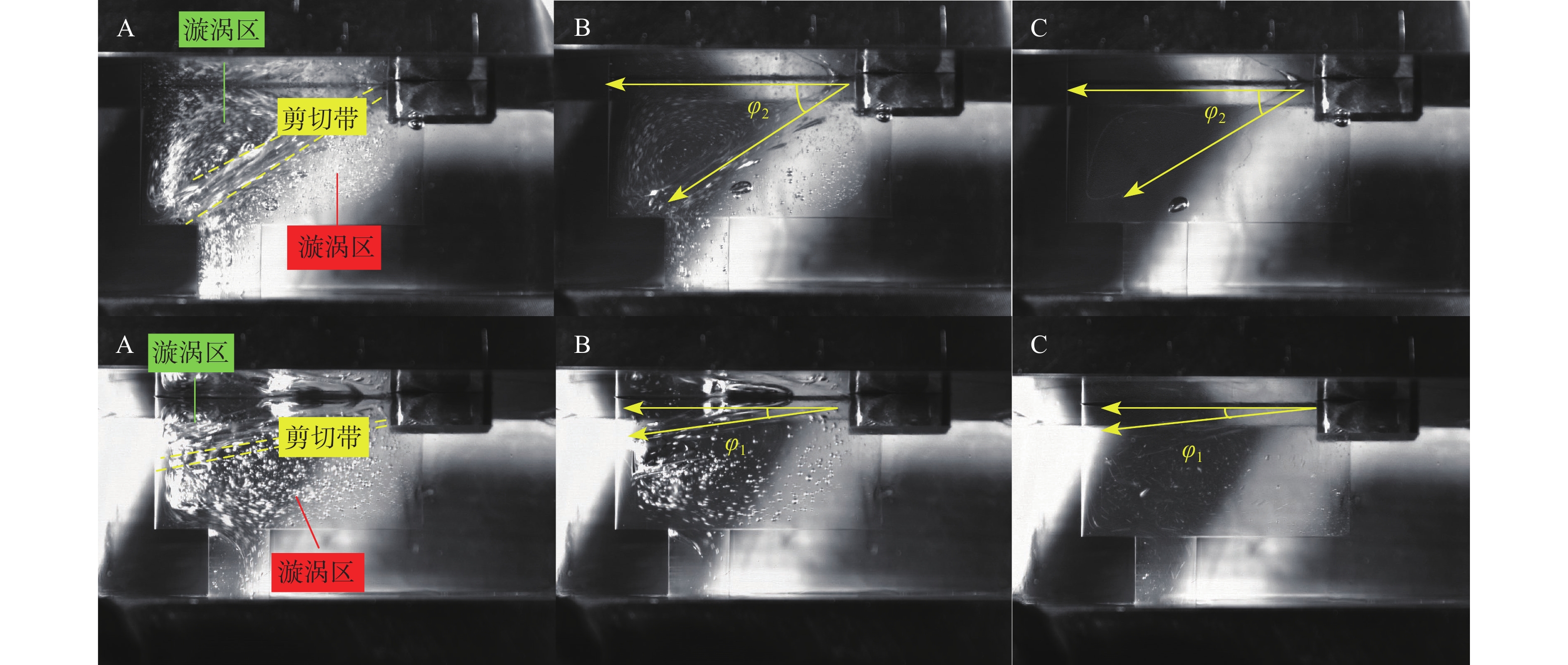
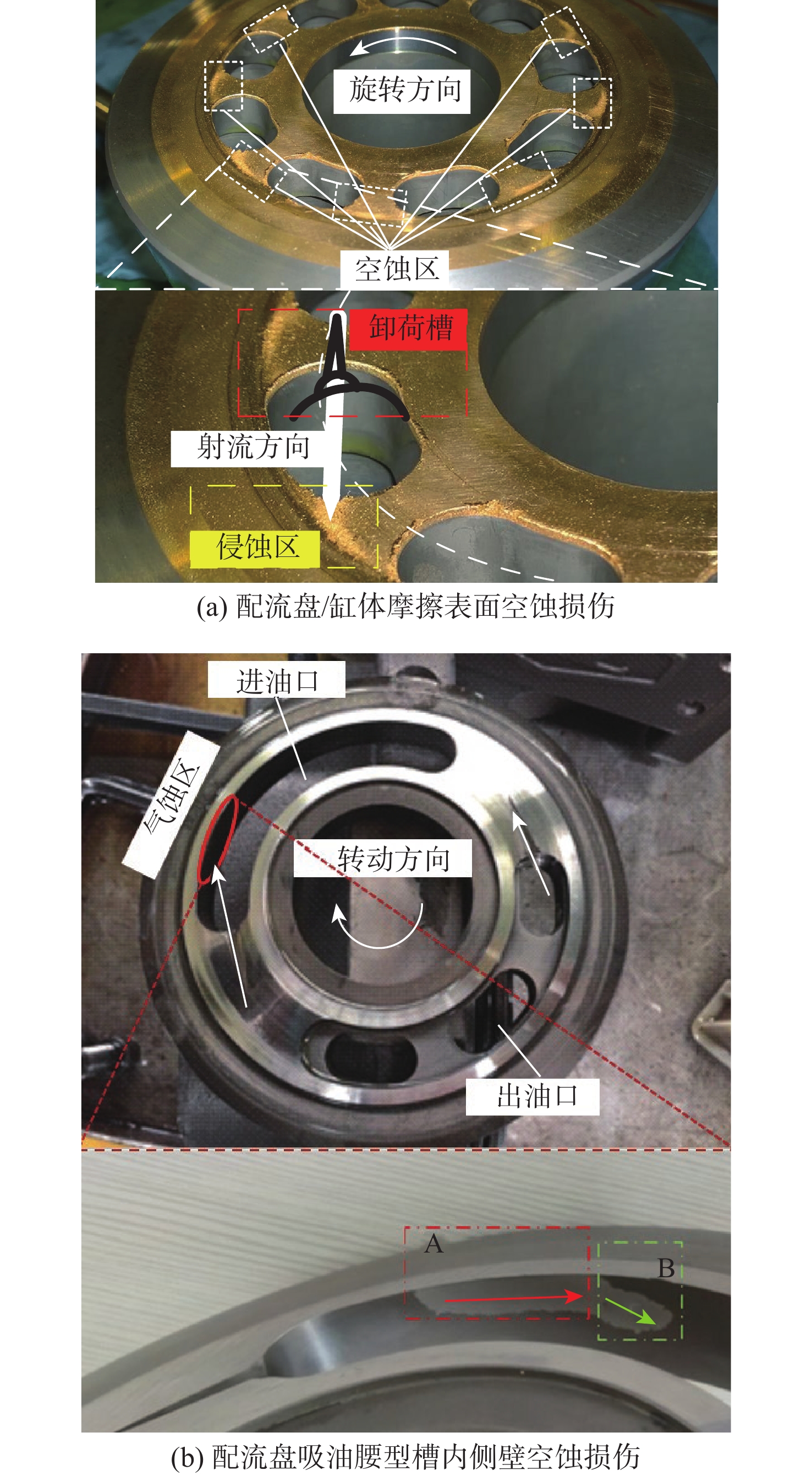
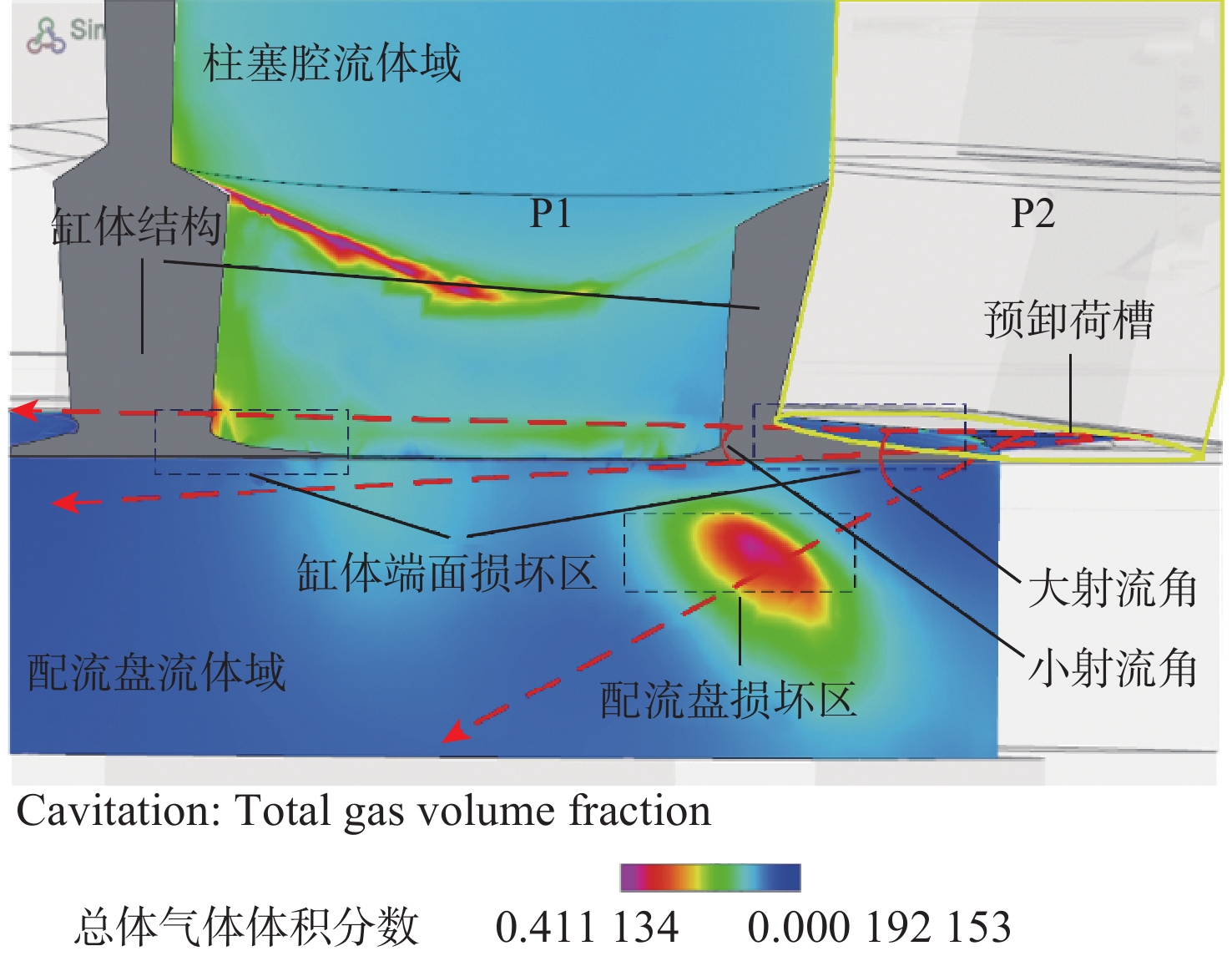
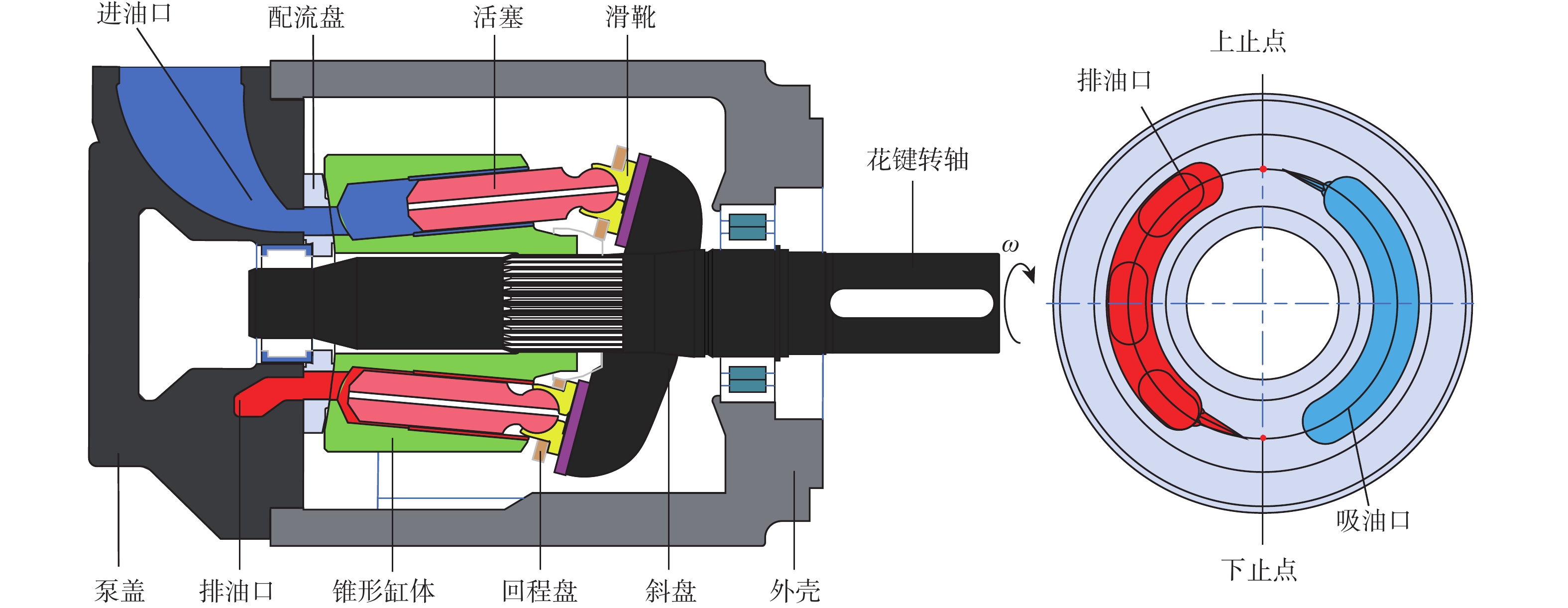
空化是影响轴向柱塞泵性能的关键因素,柱塞缸体表面损坏是一种常见的失效形式,但目前成因尚不清晰。建立柱塞泵三维流场仿真模型,设计可观察单个柱塞腔与卸荷槽导通状态下流场特征的实验装置,并采用流体仿真和流场可视化测量的方法揭示了其成因。研究结果表明:射流角随卸荷槽开度的增大而增大,并伴随漩涡的产生与消失,射流中心速度大于20 m/s时漩涡产生;柱塞腔与卸荷槽由导通至完全截止的转变过程中,射流角由0°逐渐增大至60°,当射流角由0°向20°变化时,射流方向主要集中于柱塞缸体与配流盘腰型槽接触的表面处,导致柱塞缸体表面和配流盘吸油腰型槽上部产生射流破坏和气蚀破坏;当射流角由20°向60°变化时,射流方向将向配流盘腰型槽内部扩展,导致配流盘破坏区域由上部移向内部。上述研究结果有助于厘清柱塞缸体摩擦表面气蚀成因,为配流盘结构优化设计提供了约束条件,对提升柱塞泵的综合性能也有重要意义。
Abstract:Cavitation in axial plunger pumps is a main factor affecting its comprehensive performance. The damage in the surface of plunger cylinder is a common failure mode, but the cause is not clear. In view of this damage reason, a three-dimensional CFD model of the pump was established, and a visualization device was designed to observe the flow field characteristics of single plunger cavity and unloading groove on state, so the cause relationship was revealed by simulation and visual measurement of the flow field. The results show that the jet angle increases with the increase in unloading groove opening, accompanied by the generation and disappearance of the vortex, the vortex is generated when the central velocity of the jet is greater than 20 m/s. The simulation results further show that during the transition of the plunger and unloading groove from on state to complete cut-off, the jet angle increases from 0° to 60° gradually. When the jet angle changes from 0° to 20°, the jet direction mainly concentrates on the contact surface between the plunger type cylinder and the waistband groove of the port plate, which leads to jet damage and cavitation damage on the friction surface of the plunger type cylinder and the upper part of the oil absorption waistband groove of the port plate. When the jet angle changes from 20° to 60°, the jet angle expands to the inside of the waistband groove of the port plate, which causes the damaged area of the port plate to move from the upper part to the inside. The formation and disappearance of the vortex are related to the central velocity of the jet. The above research results are helpful in clarifying the causes of cavitation damage on the friction surface of plunger type cylinders, and they provide constraints for the optimization design of port plate structure and have important significance for improving the comprehensive performance of plunger pumps.
-
Key words:
- axial plunger pump /
- cavitation /
- valve plate /
- cylinder block /
- unloading trough /
- cavitation damage
-
表 1 网格敏感性
Table 1. Grid sensitivity
组别 关键边界
角度曲率
分辨率最大
单元格边界单元格
尺寸网格数目 ΔQ/% 1 30 35 0.03 0.015 188105 7.13 2 30 35 0.025 0.0125 214750 4.76 3 30 35 0.02 0.01 225204 2.26 4 25 30 0.02 0.01 232352 1.42 5 15 20 0.02 0.01 367691 1.12 6 15 20 0.02 0.005 518554 0.97 7 15 20 0.01 0.005 897371 0.98 表 2 柱塞泵内流态情况
Table 2. Flow pattern in plunger pump
位置 雷诺数 流态 柱塞泵吸油口 Re=vdinυ=1.415×10−3×7546×10−6≈2307<2320 层流 柱塞泵排油口 Re=vdoutυ=3.4×10−3×4046×10−6≈2957>2320 湍流 三角槽处 Re=4vRHυ=4×186×10−3×0.48146×10−6≈7780>2320 湍流 柱塞腔内 Re=vdpisυ=10×10−3×3146×10−6≈6739>2320 湍流 表 3 仿真参数的设置
Table 3. Settings of simulation parameters
斜盘
倾角/(°)工作
压力/MPa油膜泄漏
压力/MPa球面副
曲率
半径/mm液压油密
度/(kg·m−3)空气分
离压/
MPa饱和
蒸汽压/
MPa动力
黏度/(Pa·s)额定转速/
(r·min−1)体积
弹性
模量/MPa入口
压力/MPa饱和
压力/MPa空化蒸汽
系数冷凝
系数工作
温度/K15 35 2 396±0.3 865 0.004 0.0035 0.03979 1500 1.5×103 0.1 0.04 0.02 0.01 313 -
[1] CHAO Q, XU Z, TAO J F, et al. Cavitation in a high-speed aviation axial piston pump over a wide range of fluid temperatures[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part A: Journal of Power and Energy, 2022, 236(4): 727-737. doi: 10.1177/09576509211046998 [2] CHAO Q, ZHANG J H, XU B, et al. Effects of inclined cylinder ports on gaseous cavitation of high-speed electro-hydrostatic actuator pumps: a numerical study[J]. Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 13(1): 245-253. doi: 10.1080/19942060.2019.1576545 [3] GULLAPALLI S, MICHAEL P, KENSLER J, et al. An investigation of hydraulic fluid composition and aeration in an axial piston pump[C]//Proceedings of the ASME/BATH Symposium on Fluid Power and Motion Control. Sarasota: American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2017: 4259. [4] ZHAO B, GUO W W, QUAN L. Cavitation of a submerged jet at the spherical valve plate/cylinder block interface for axial piston pump[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 33(1): 67. doi: 10.1186/s10033-020-00486-8 [5] HARRIS R M, EDGE K A, TILLEY D G. The suction dynamics of positive displacement axial piston pumps[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 1994, 116(2): 281-287. doi: 10.1115/1.2899221 [6] SINGHAL A K, ATHAVALE M M, LI H Y, et al. Mathematical basis and validation of the full cavitation model[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2002, 124(3): 617-624. doi: 10.1115/1.1486223 [7] 苑士华, 周俊杰, 罗先伟, 等. 轴向柱塞泵空化时气相动态演进过程及影响[J]. 兵工学报, 2015, 36(3): 559-565. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.03.026YUAN S H, ZHOU J J, LUO X W, et al. Dynamic evolution and effects of gas phase in cavitation of axial piston pump[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2015, 36(3): 559-565(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.03.026 [8] 潮群. EHA轴向柱塞泵高速化若干关键技术研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019.CHAO Q. Research on some key technologies of EHA axial piston pump with high speed[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019(in Chinese). [9] PENG K W, TIAN S C, LI G S, et al. Bubble dynamics characteristics and influencing factors on the cavitation collapse intensity for self-resonating cavitating jets[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(2): 343-350. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(18)30038-7 [10] LIANG J, LUO X H, LIU Y S, et al. A numerical investigation in effects of inlet pressure fluctuations on the flow and cavitation characteristics inside water hydraulic poppet valves[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2016, 103: 684-700. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.07.112 [11] SHEN X, ZHANG D S, XU B, et al. Comparative study of tip leakage vortex trajectory and cavitation in an axial flow pump with various tip clearances[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2022, 36(3): 1289-1302. doi: 10.1007/s12206-022-0219-2 [12] CHO I S. A study on the optimum design for the valve plate of a swash plate-type oil hydraulic piston pump[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2015, 29(6): 2409-2413. doi: 10.1007/s12206-015-0533-z [13] GIOVANNESCHI P, DUFRESNE D. Experimental study of laser-induced cavitation bubbles[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1985, 58(2): 651-652. doi: 10.1063/1.336204 [14] AKHATOV I, LINDAU O, TOPOLNIKOV A, et al. Collapse and rebound of a laser-induced cavitation bubble[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2001, 13(10): 2805-2819. doi: 10.1063/1.1401810 [15] BRUJAN E A, KEEN G S, VOGEL A, et al. The final stage of the collapse of a cavitation bubble close to a rigid boundary[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2002, 14(1): 85-92. doi: 10.1063/1.1421102 [16] ROBINSON P B, BLAKE J R, KODAMA T, et al. Interaction of cavitation bubbles with a free surface[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 89(12): 8225-8237. doi: 10.1063/1.1368163 [17] ZHANG Y, DONG Z, HU X. Cavitation limiting strategies for pumping system: US, 20180040226A1[P]. 2018-02-08. [18] 郭伟伟. 轴向柱塞泵淹没空化射流特征研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2020.GUO W W. Study on characteristics of submerged cavitation jet in axial piston pump[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2020(in Chinese). [19] 築地徹浩, 陈卓, 陈晶晶. 轴向柱塞泵内部空化流的可视化分析[J]. 液压与气动, 2015(2): 1-7. doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2015.02.001Tetsuhiro T, CHEN Z, CHEN J J. Visualized analysis of cavitation inside axial piston pump[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2015(2): 1-7(in Chinese). doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2015.02.001 [20] YAMAGUCHI A, TAKABE T. Cavitation in an axial piston pump[J]. Bulletin of JSME, 1983, 26(211): 72-78. doi: 10.1299/jsme1958.26.72 [21] ITO K, INOUE K, SAITO K. Visualization and detection of cavitation in v-shaped groove type valve plate of an axial piston pump[J]. Proceedings of the JFPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, 1996, 1996(3): 67-72. doi: 10.5739/isfp.1996.67 [22] QI G N, TIAN T, HE Z Q, et al. Cavitation phenomenon of high-pressure piston pump and control[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2021, 49(9): 187-191. [23] LIU W, WANG A L, SHAN X W, et al. Valve plate for piston pump cavitation problem with the damp groove structural optimization[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 543-547: 154-157. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.543-547.154 [24] KOLLEK W, KUDŹMA Z, STOSIAK M, et al. Possibilities of diagnosing cavitation in hydraulic systems[J]. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 2007, 7(1): 61-73. doi: 10.1016/S1644-9665(12)60005-3 [25] GB/T 265-1988,石油产品运动粘度测定法和动力粘度计算法[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,1990.GB/T 265-1988, Petroleum products-determination of kinematic viscosity and calculation of dynamic viscosity[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1990(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: