3D SLAM algorithm based on geometric constraints of feature points in dynamic scenarios
-
摘要:
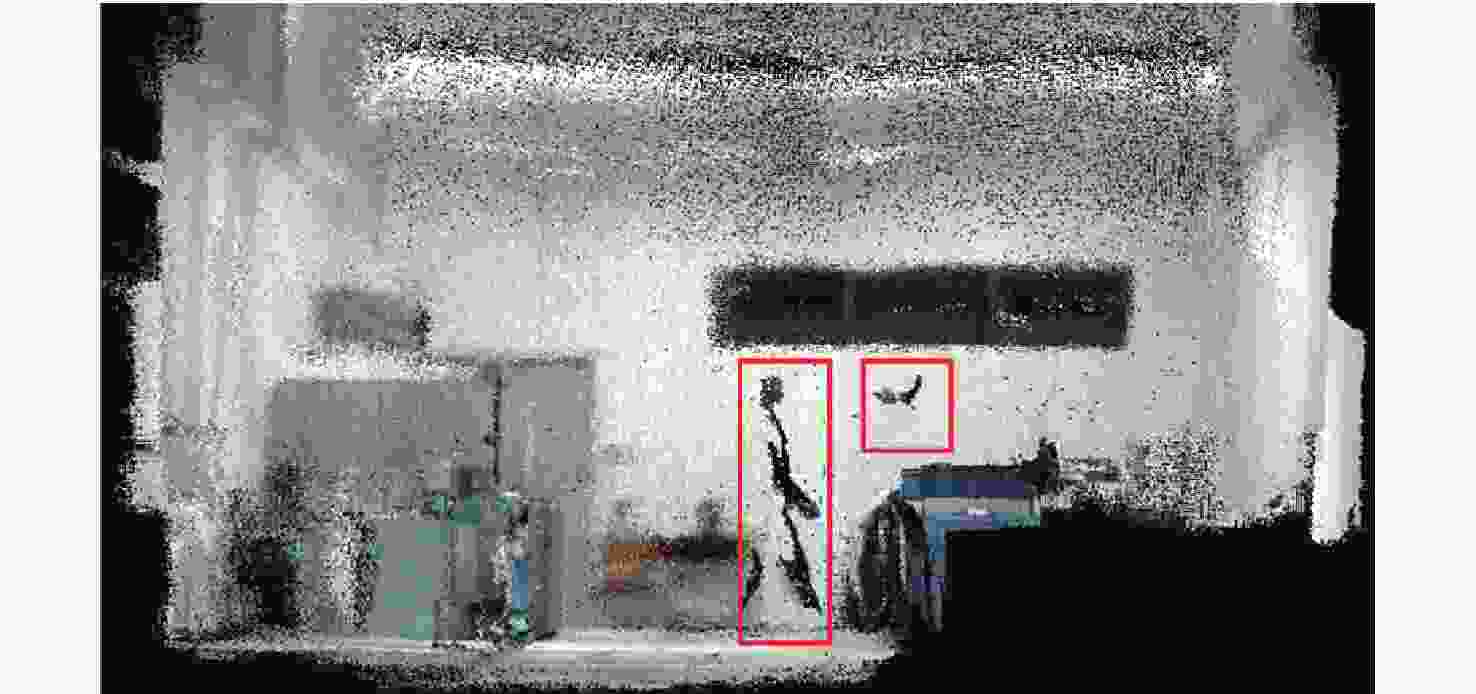
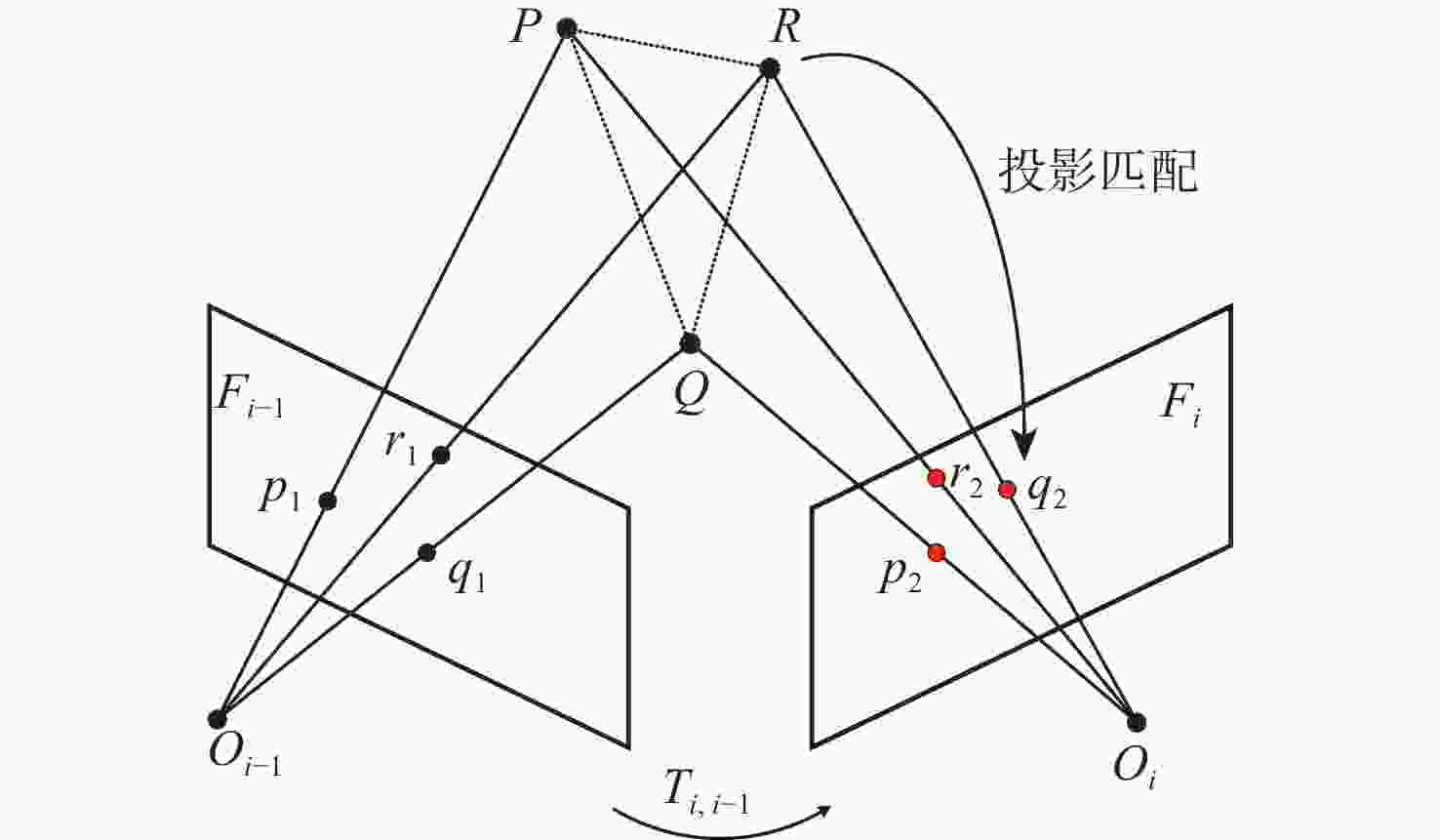
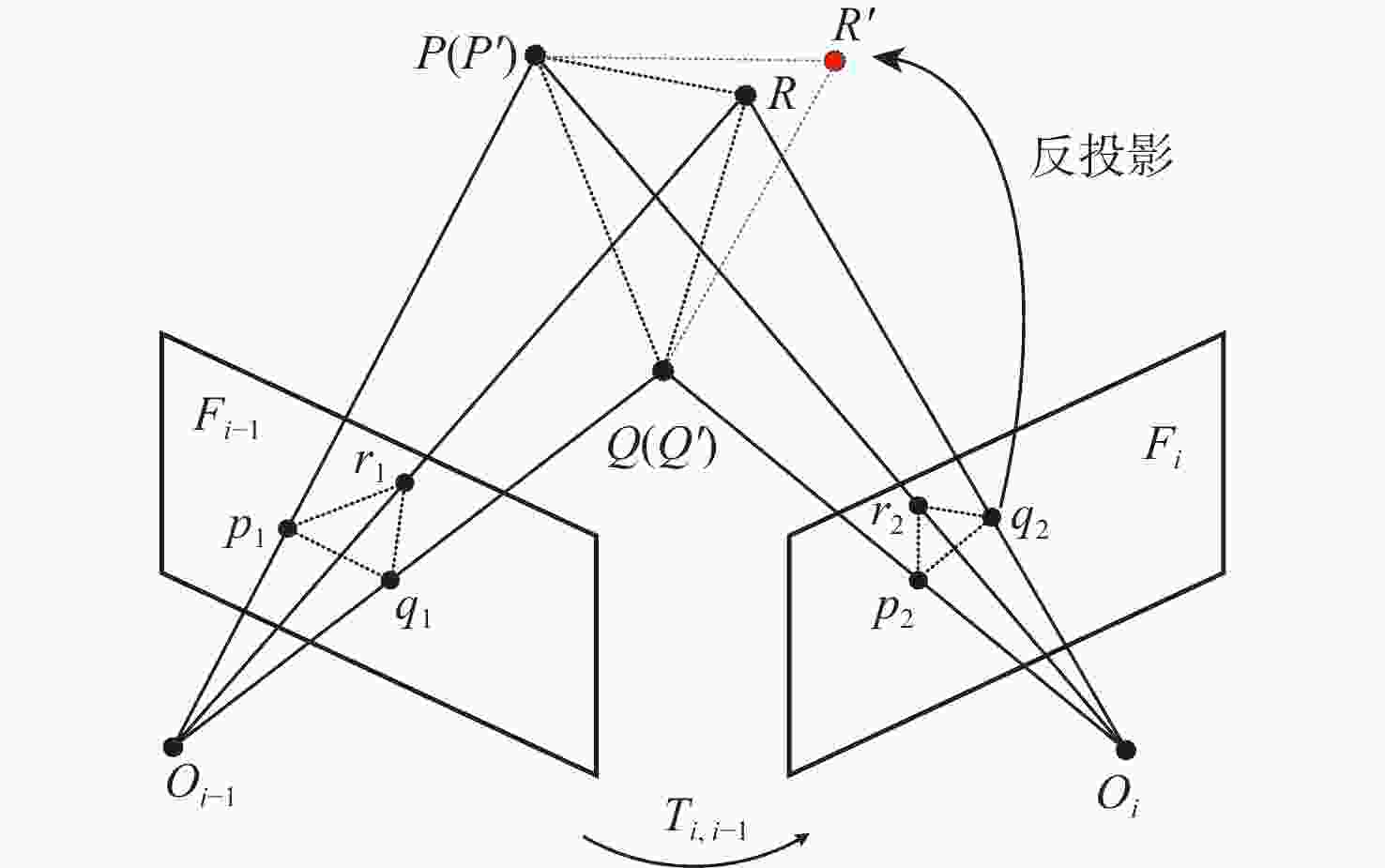
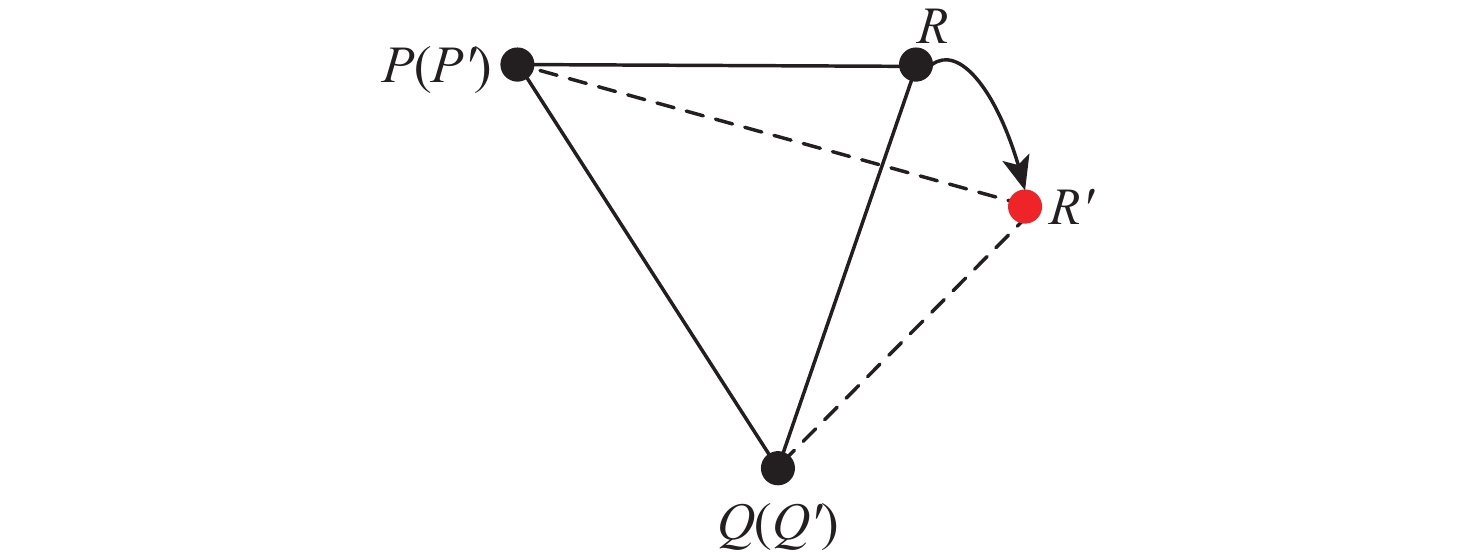
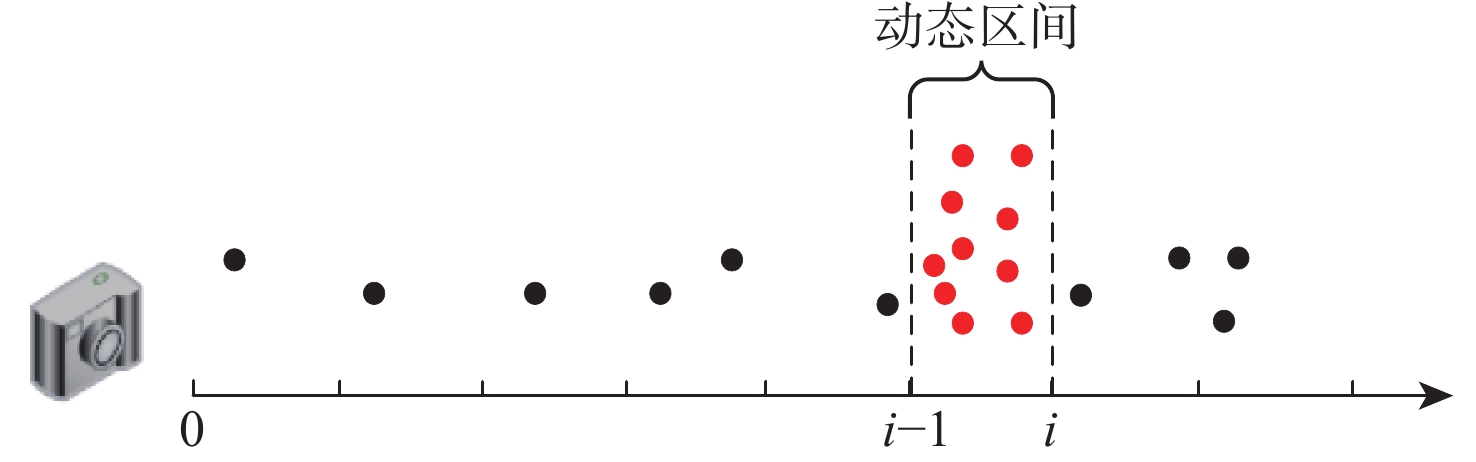
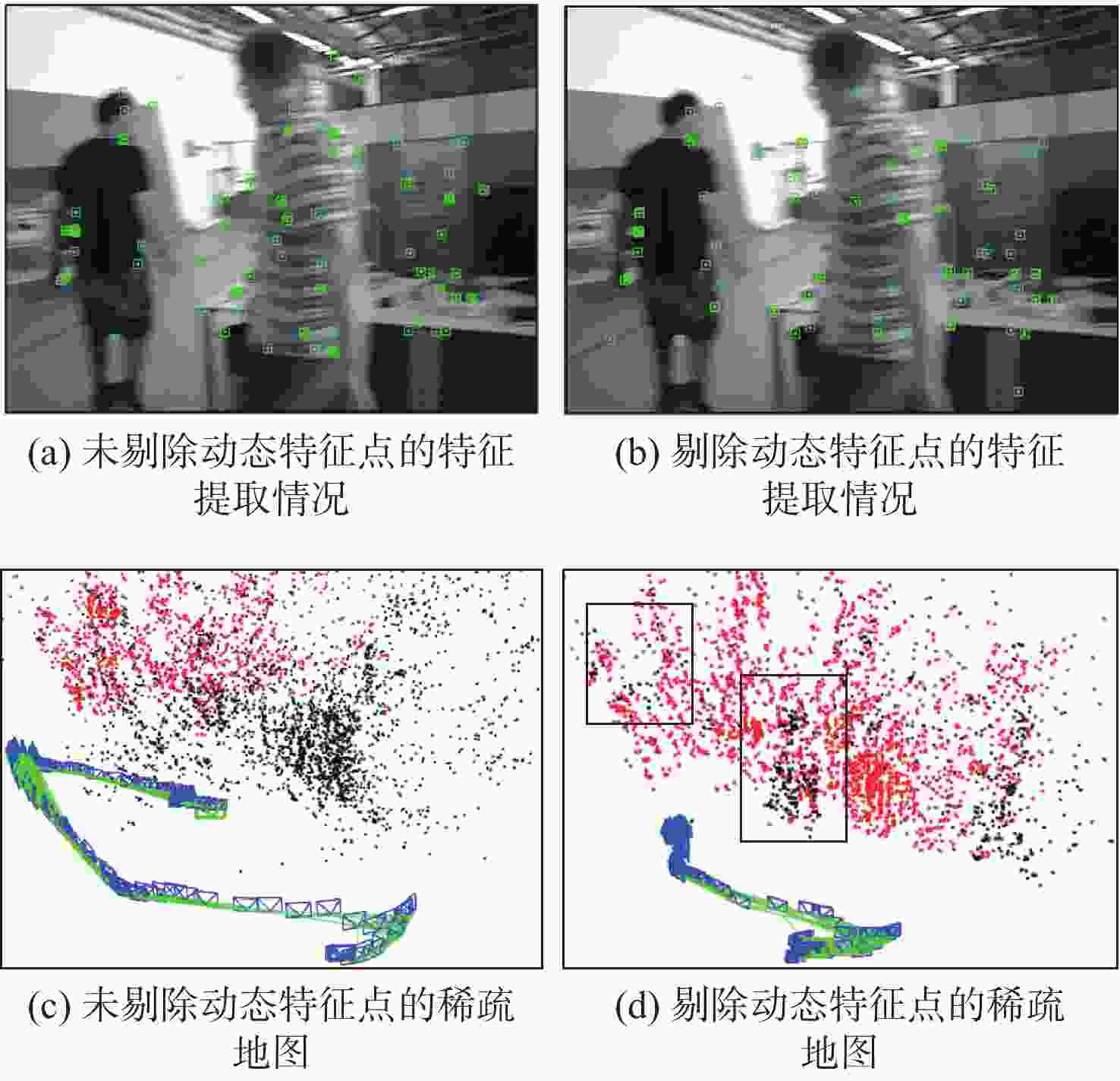
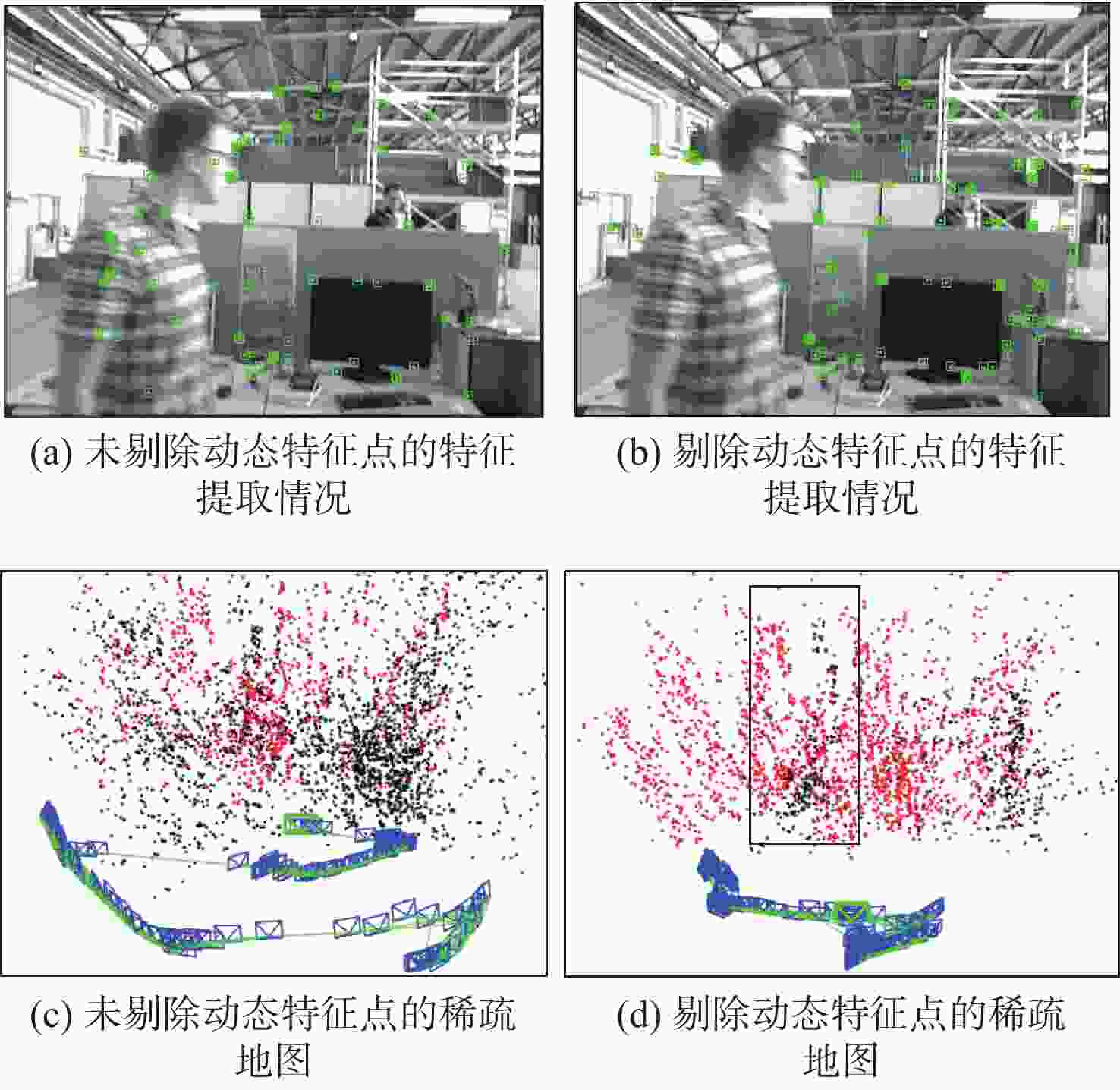
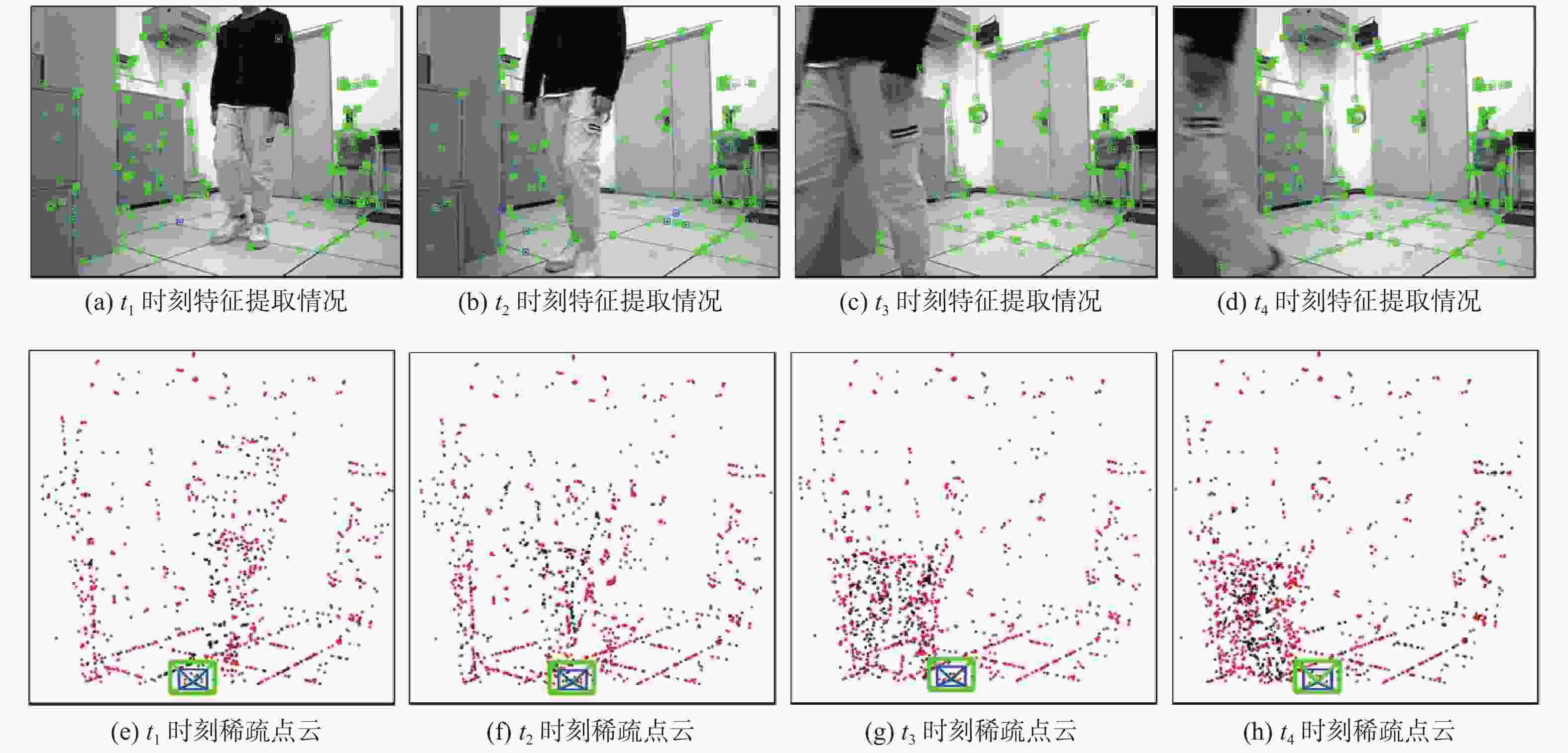
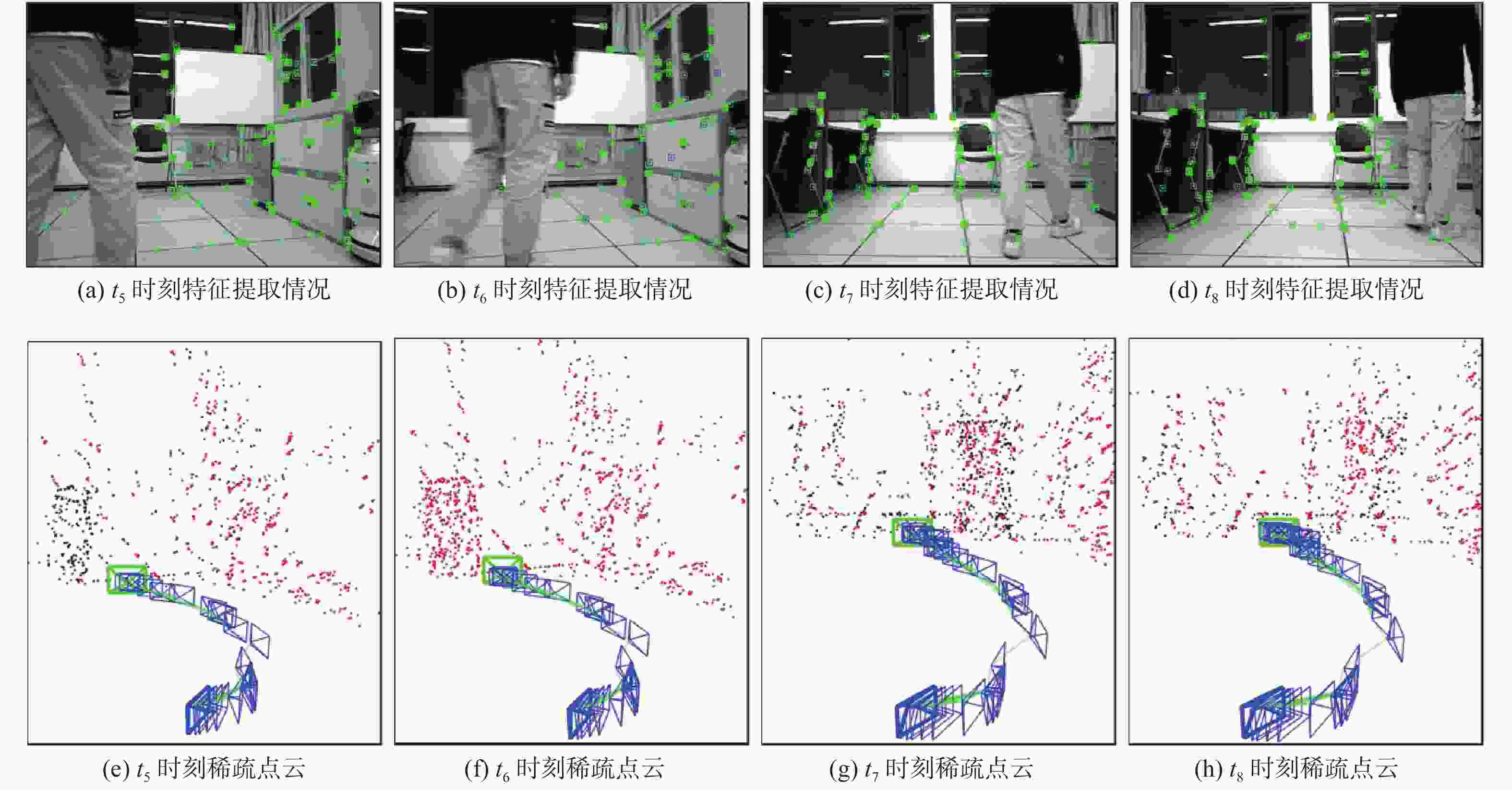
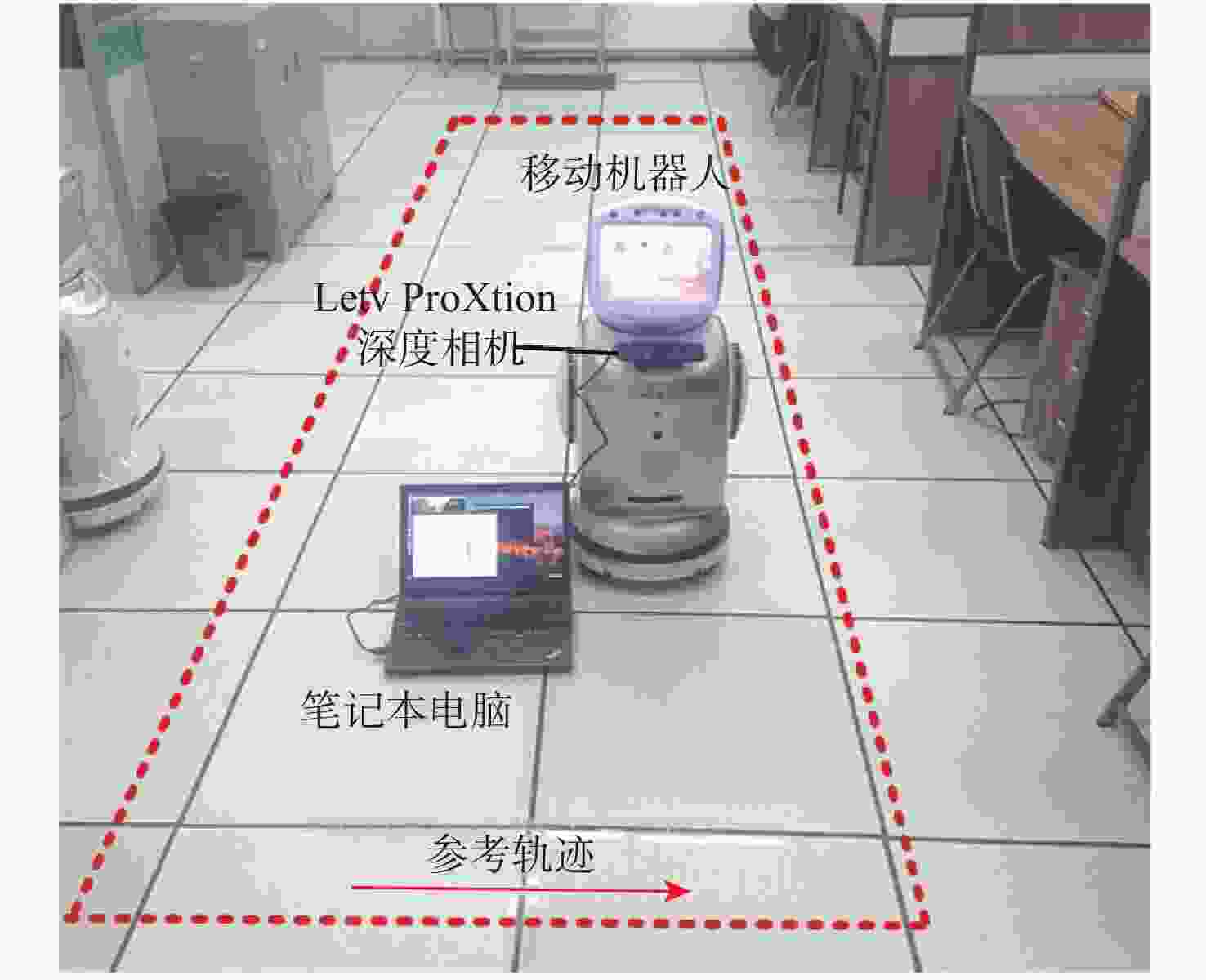
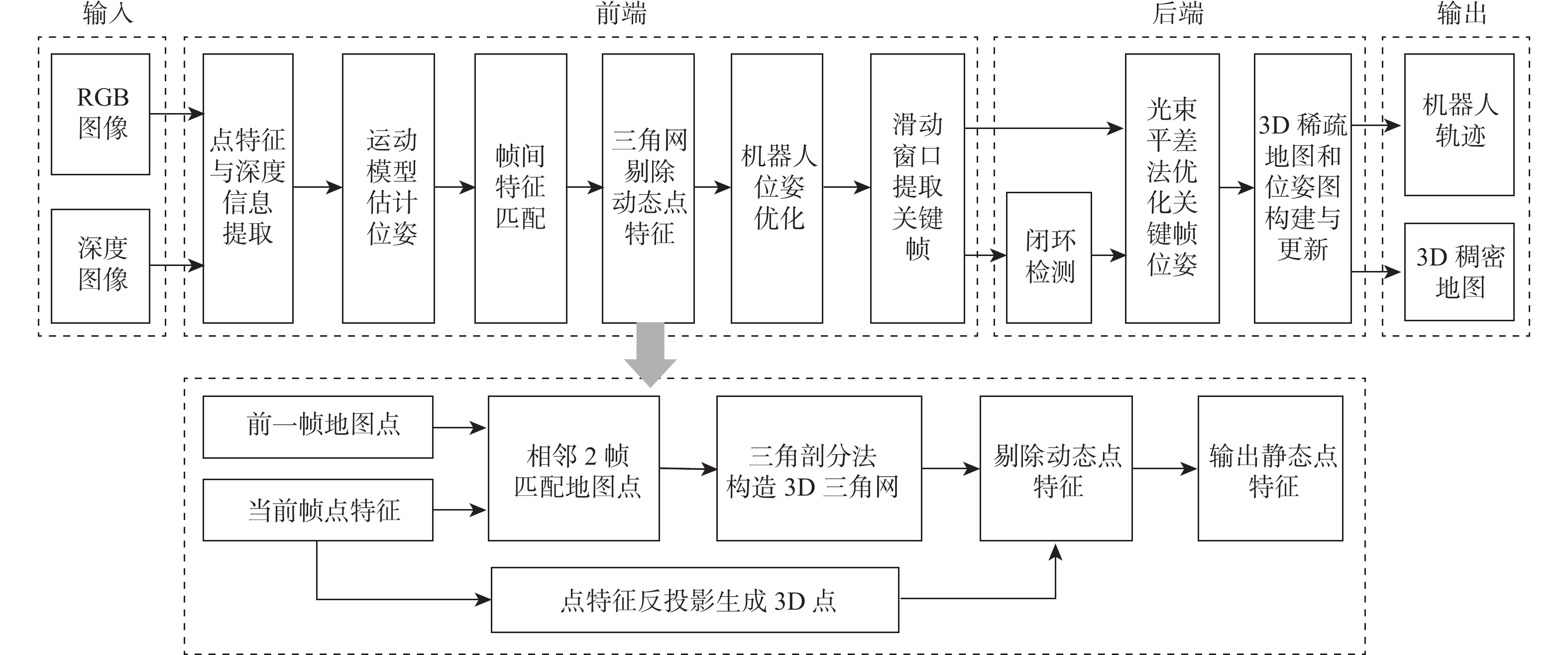
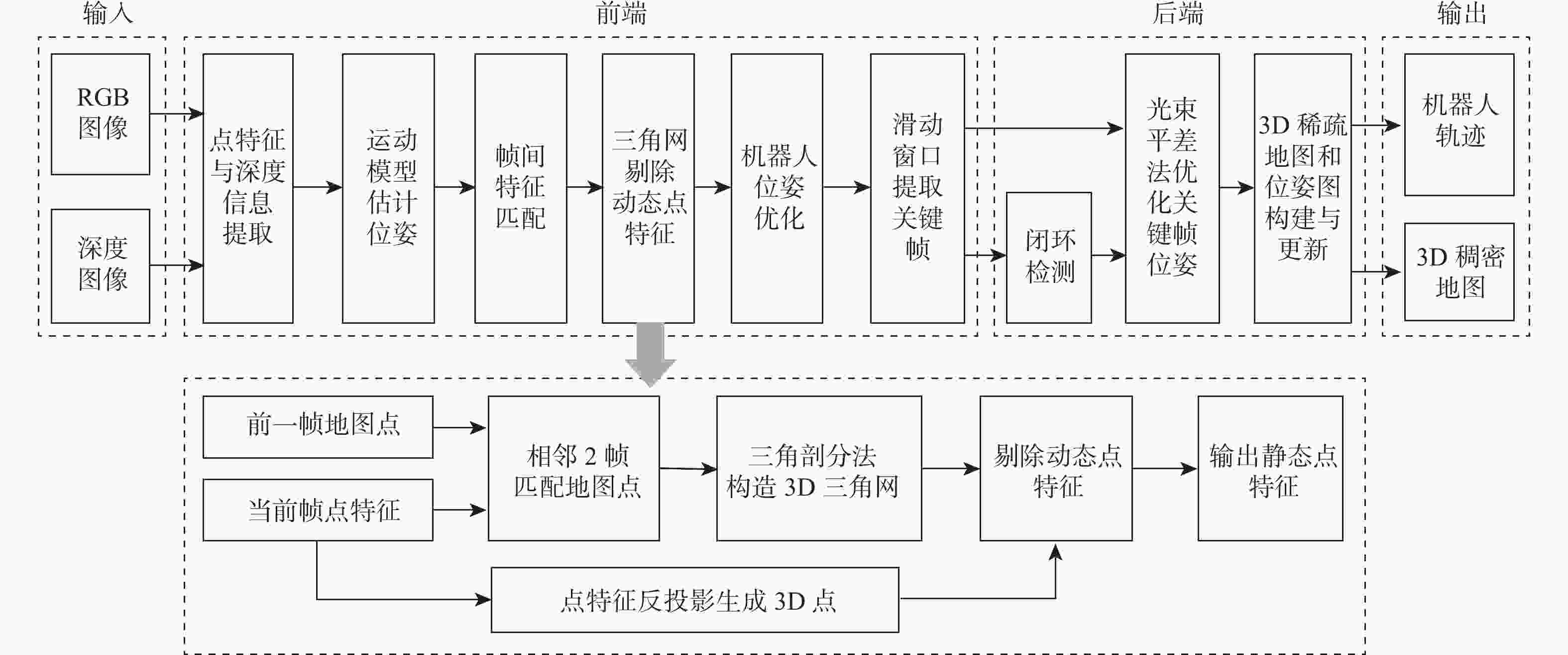
针对动态场景中动态物体会导致机器人在进行位姿估计时引入大量动态误差的问题,提出一种利用特征点间几何约束来剔除动态特征点的移动机器人3D 同步定位与地图构建(SLAM)算法。利用当前帧的ORB特征点与上一帧特征点生成的地图点进行投影匹配,通过引入Delaunay三角剖分法构建能够表示2帧间、匹配地图点间几何关系的三角网。利用相邻2帧地图点的几何关系变化检测出动态特征点,考虑到静态特征点可能被误检测为动态特征点而导致特征点缺失的情况,在相邻2帧匹配时提取更多的特征点以实现静态特征点的补偿,进而剔除动态特征点,实现对移动机器人位姿的精确估计。在此基础上,通过引入滑动窗口提取关键帧并完成闭环检测,从而构建出精确的3D稠密地图。在多组公开数据集上进行仿真实验及室内动态场景下的实验,结果表明,所提算法能够有效剔除动态特征点,提高移动机器人在动态场景中位姿估计的精度和地图的一致性。
Abstract:The dynamic objects will cause a large number of dynamic errors in the pose estimation of robots in dynamic scenarios. To address this issue, a 3D simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithm for mobile robots was presented by using geometric constraints between feature points to eliminate dynamic feature points. First, the ORB feature points of the current frame and the map points generated by feature points of the previous frame were used for projection matching, and the Delaunay triangulation method was introduced to construct a triangle net that could represent the geometric relationship between the matching map points of the two frames. Then, the dynamic feature points were detected according to the geometric relationship changes of the map points in the adjacent two frames. Since the static feature points may be incorrectly detected as dynamic feature points, which thus brings about the loss of feature points, more feature points were extracted during the matching of the adjacent two frames, so as to compensate for static feature points. Then, the dynamic feature points were eliminated, and the pose of the mobile robots was estimated accurately. On this basis, a sliding window was introduced to extract key frames and complete closed-loop detection, and thus an accurate 3D dense map was constructed. The results of simulation experiments on multiple sets of public datasets and the experiments in the indoor dynamic scenarios show that the proposed algorithm in this paper can effectively eliminate the dynamic feature points and improve the accuracy of the pose estimation of mobile robots in dynamic scenarios and the consistency of the map.
-
表 1 不同算法的相对平移轨迹误差对比
Table 1. Comparison of relative translation trajectory error among different algorithms
m 图像序列 平移RMSE DVO BaMVO 线特征法 半直接法 DVO+MR 本文算法 walking_static 0.3818 0.1339 0.0234 0.0102 0.0842 0.0424 walking_xyz 0.4360 0.2326 0.2433 0.0320 0.1214 0.0426 walking_rpy 0.4308 0.3584 0.1560 0.1751 0.1717 walking_halfsphere 0.2628 0.1738 0.1351 0.0476 0.1672 表 2 不同算法的相对旋转轨迹误差对比
Table 2. Comparison of relative rotation trajectory error among different algorithms
(°) 图像序列 旋转RMSE DVO BaMVO 线特征法 半直接法 DVO+MR 本文算法 walking_static 6.3502 2.0833 1.8547 0.2525 2.0487 0.6005 walking_xyz 7.6669 4.3911 6.9116 0.6869 3.2346 0.8566 walking_rpy 7.0662 6.3398 5.5809 4.3755 3.6021 walking_halfsphere 5.2179 4.2863 4.6412 1.045 5.0108 表 3 不同算法的绝对轨迹误差对比
Table 3. Comparison of absolute trajectory error among different algorithms
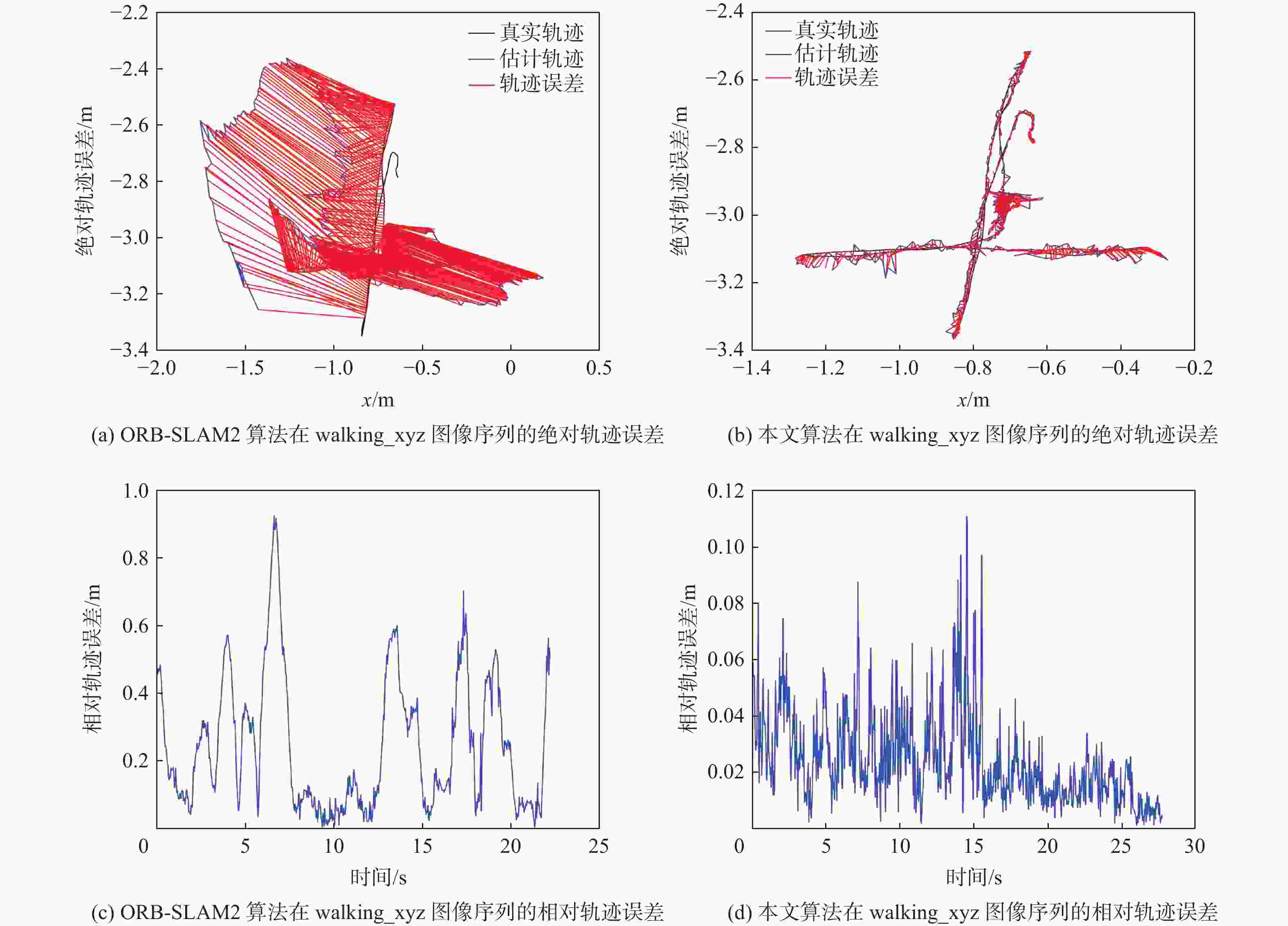
m 图像序列 绝对轨迹误差 ORB-SLAM2 半直接法 DVO+MR Detect-SLAM 本文算法 walking_static 0.4300 0.0080 0.0656 0.0079 walking_xyz 0.6202 0.0371 0.0932 0.0241 0.0231 walking_rpy 0.6689 0.1333 0.2959 0.3174 walking_halfsphere 0.3231 0.0409 0.1252 0.0514 -
[1] FISCHLER M A, BOLLES R C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography[M]//FISCHLER M A, FIRSCHEIN O. Readings in computer vision. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1987: 726-740. [2] STRASDAT H, MONTIEL J M M, DAVISON A J. Visual SLAM: Why filter?[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2012, 30(2): 65-77. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2012.02.009 [3] ZOU D P, TAN P. CoSLAM: Collaborative visual SLAM in dynamic environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(2): 354-366. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.104 [4] 张慧娟, 方灶军, 杨桂林. 动态环境下基于线特征的RGB-D视觉里程计[J]. 机器人, 2019, 41(1): 75-82.ZHANG H J, FANG Z J, YANG G L. RGB-D visual odometry in dynamic environments using line features[J]. Robot, 2019, 41(1): 75-82(in Chinese). [5] RUBLEE E, RABAUD V, KONOLIGE K, et al. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 2564-2571. [6] VON GIOI R G, JAKUBOWICZ J, MOREL J M, et al. LSD: A line segment detector[J]. Image Processing On Line, 2012, 2: 35-55. doi: 10.5201/ipol.2012.gjmr-lsd [7] SUN Y X, LIU M, MENG M Q H. Improving RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments: A motion removal approach[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2017, 89: 110-122. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2016.11.012 [8] 艾青林, 刘刚江, 徐巧宁. 动态环境下基于改进几何与运动约束的机器人RGB-D SLAM算法[J]. 机器人, 2021, 43(2): 167-176.AI Q L, LIU G J, XU Q N. An RGB-D SLAM algorithm for robot based on the improved geometric and motion constraints in dynamic environment[J]. Robot, 2021, 43(2): 167-176(in Chinese). [9] LI S L, LEE D. RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments using static point weighting[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2017, 2(4): 2263-2270. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2017.2724759 [10] 高成强, 张云洲, 王晓哲, 等. 面向室内动态环境的半直接法RGB-D SLAM算法[J]. 机器人, 2019, 41(3): 372-383.GAO C Q, ZHANG Y Z, WANG X Z, et al. Semi-direct RGB-D SLAM algorithm for dynamic indoor environments[J]. Robot, 2019, 41(3): 372-383(in Chinese). [11] DEROME M, PLYER A, SANFOURCHE M, et al. Real-time mobile object detection using stereo[C]//Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Control Automation Robotics & Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 1021-1026. [12] LI X Z, XU C L. Moving object detection in dynamic scenes based on optical flow and superpixels[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 84-89. [13] JAIMEZ M, KERL C, GONZALEZ-JIMENEZ J, et al. Fast odometry and scene flow from RGB-D cameras based on geometric clustering[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 3992-3999. [14] DAI W C, ZHANG Y, LI P, et al. RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments using point correlations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(1): 373-389. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3010942 [15] BARBER C B, DOBKIN D P, HUHDANPAA H. The quickhull algorithm for convex hulls[J]. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 1996, 22(4): 469-483. doi: 10.1145/235815.235821 [16] STURM J, ENGELHARD N, ENDRES F, et al. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 573-580. [17] MUR-ARTAL R, TARDÓS J D. ORB-SLAM2: An open-source SLAM system for monocular, stereo, and RGB-D cameras[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2017, 33(5): 1255-1262. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103 [18] GRUPP M. EVO: Python package for the evaluation of odometry and SLAM[EB/OL]. (2017-09-14)[2022-04-28]. https://michaelgrupp.github.io/evo/. [19] KERL C, STURM J, CREMERS D. Robust odometry estimation for RGB-D cameras[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 3748-3754. [20] KIM D H, KIM J H. Effective background model-based RGB-D dense visual odometry in a dynamic environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2016, 32(6): 1565-1573. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2016.2609395 [21] ZHONG F W, WANG S, ZHANG Z Q, et al. Detect-SLAM: Making object detection and SLAM mutually beneficial[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1001-1010. -






 下载:
下载: