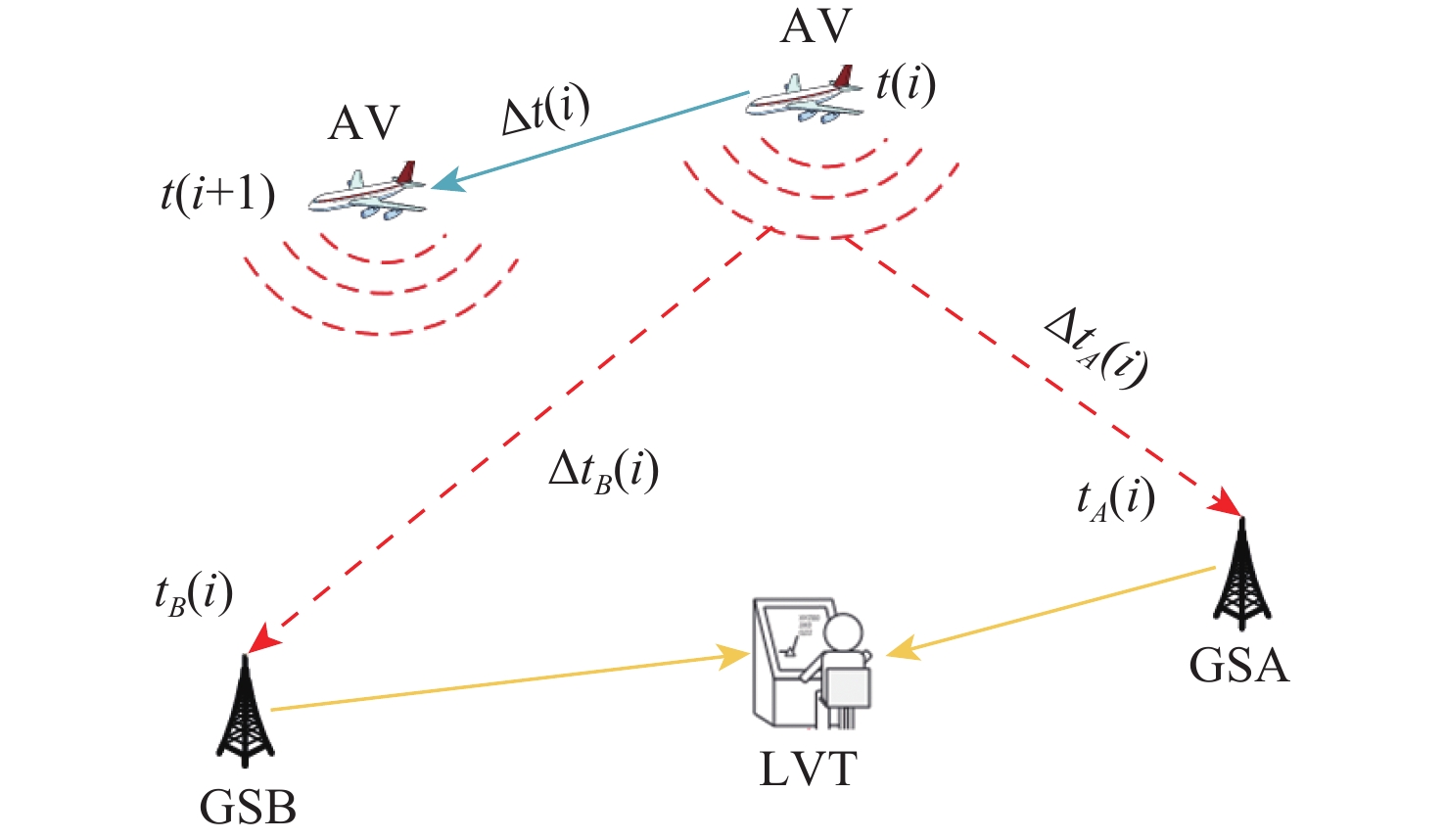
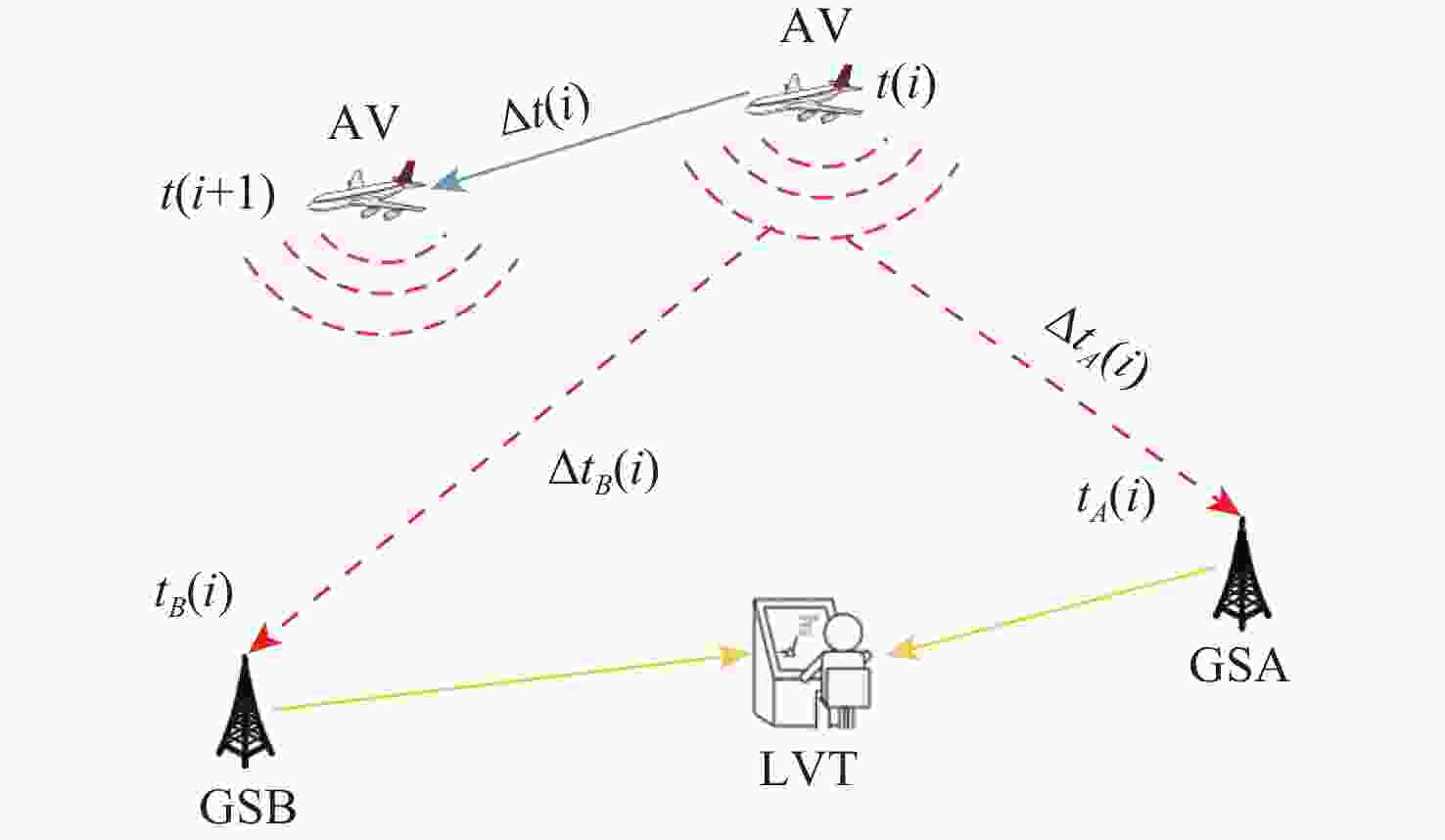
Verification scheme of position message for automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast system based on interval difference of arrival
-
摘要:
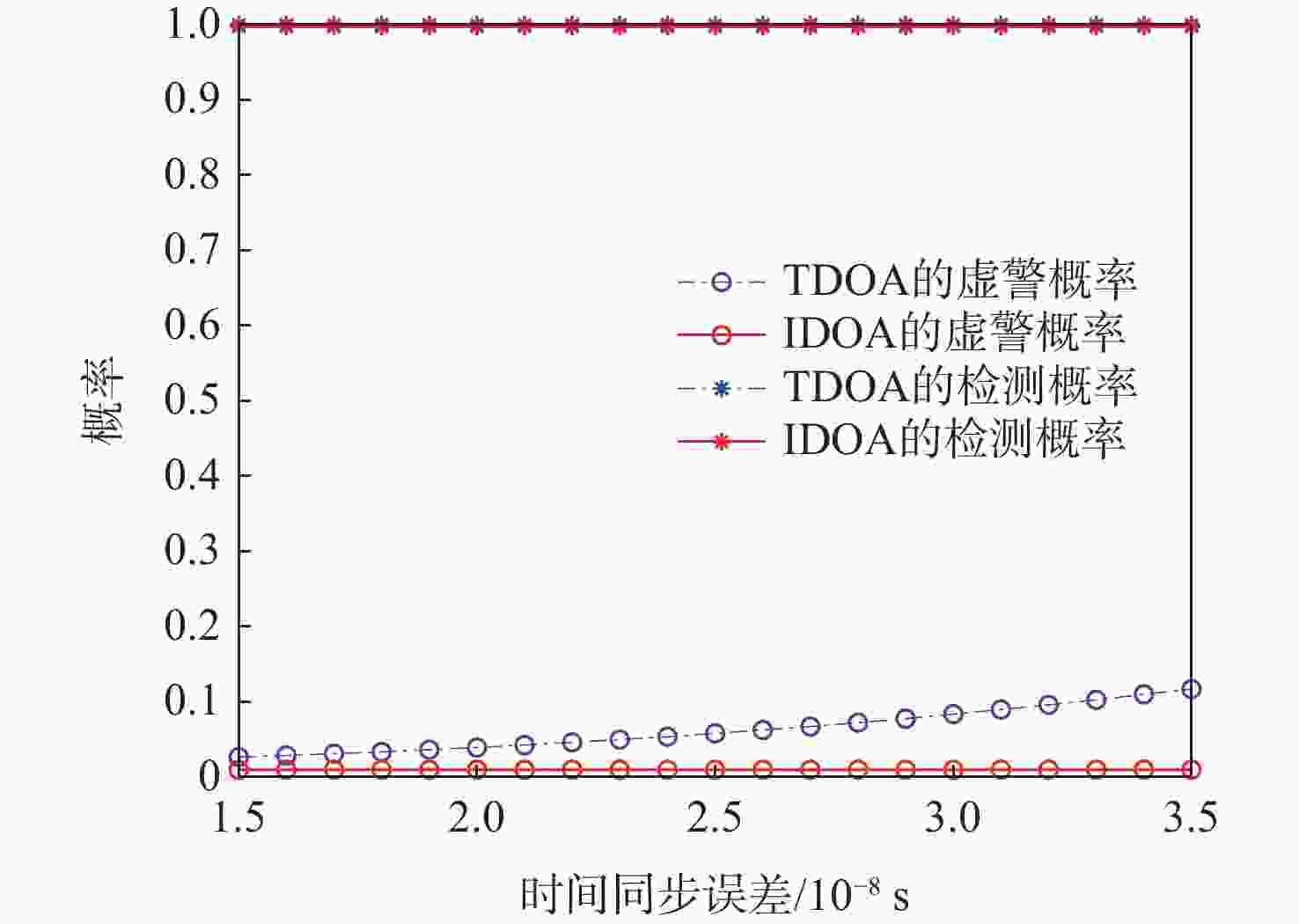
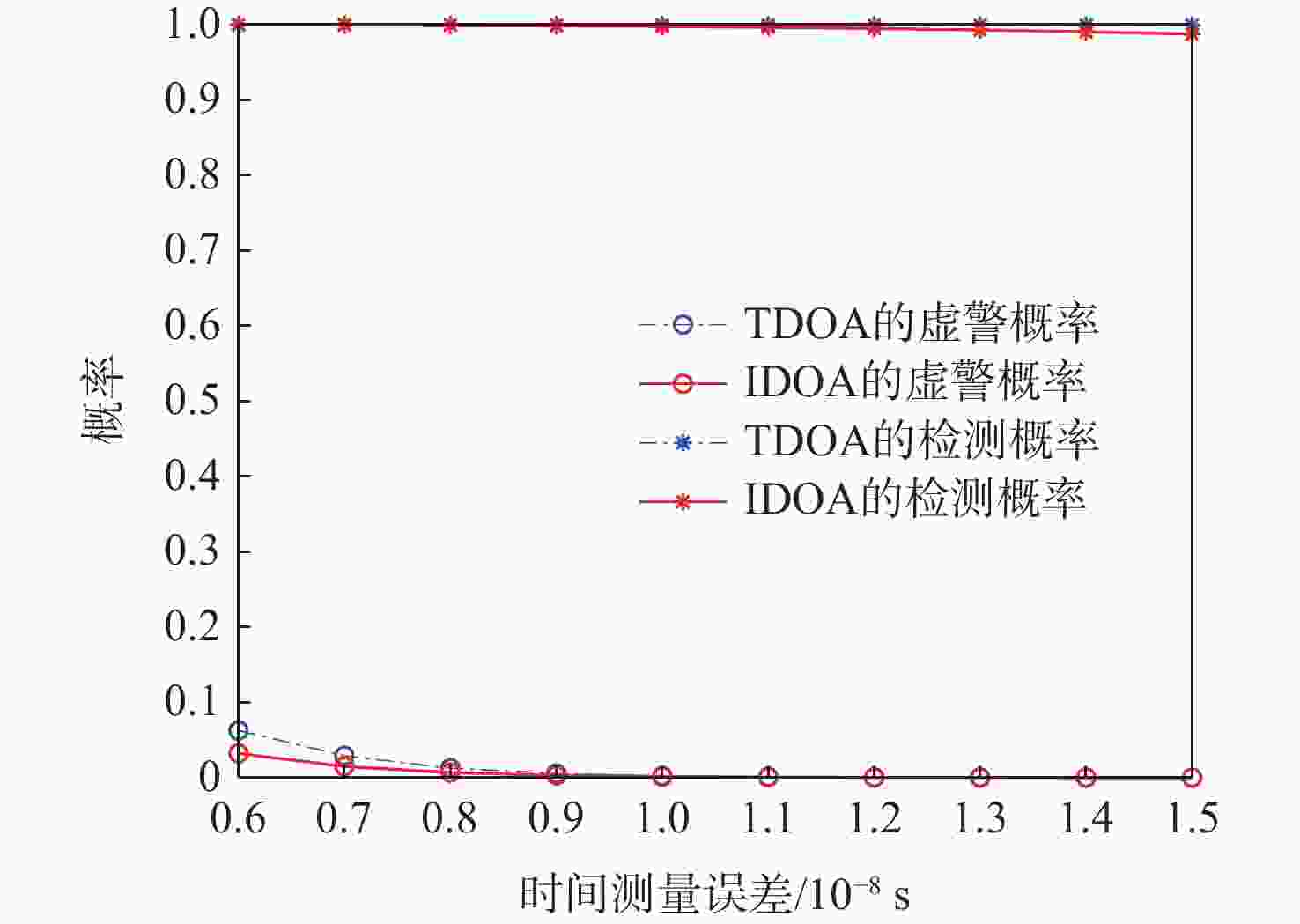
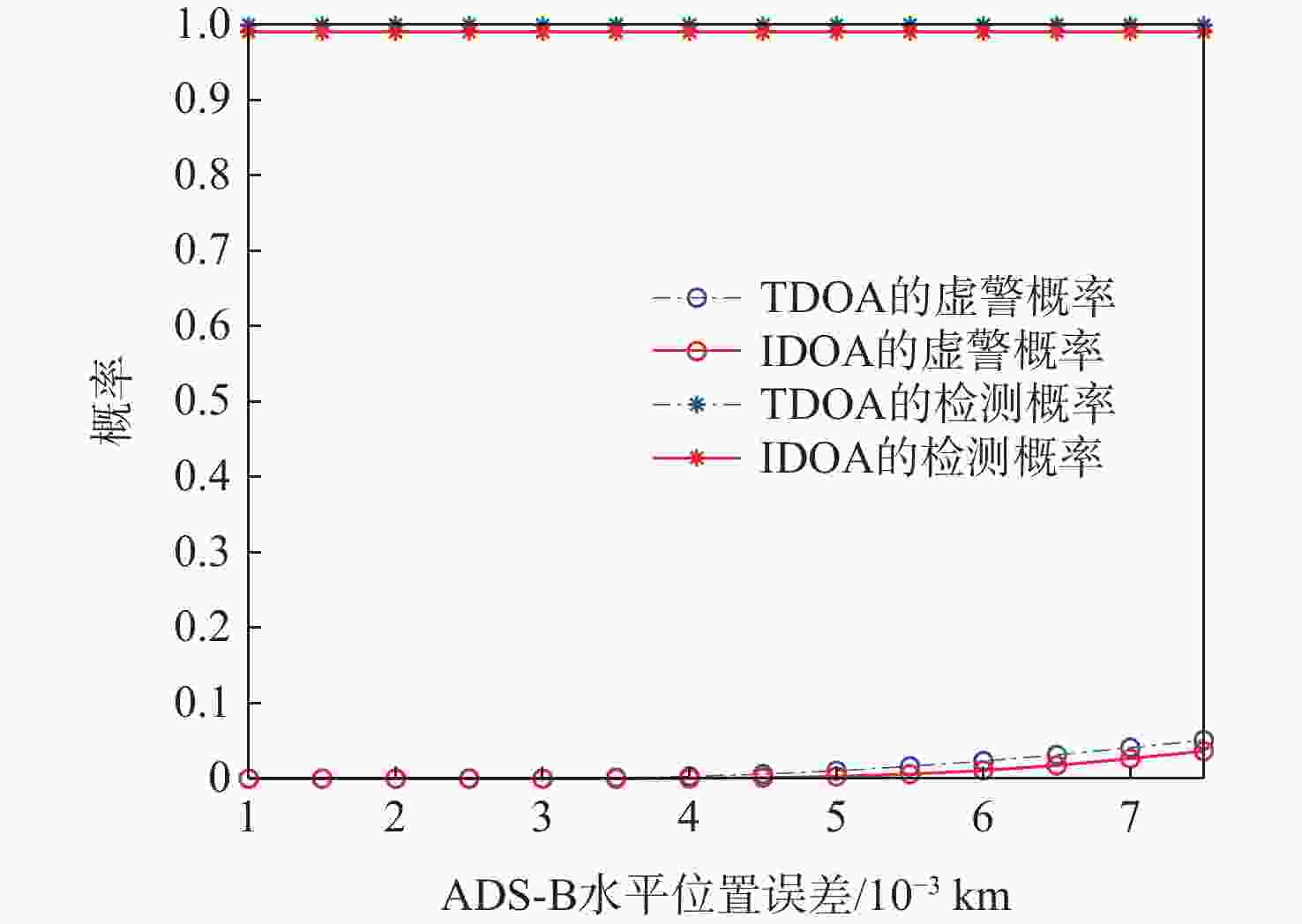
广播式自动相关监视(ADS-B)是一种新型的航空器监视技术,具有定位精度高、更新速度快及覆盖范围广等优势,在民用航空监视领域获得广泛应用。由于ADS-B消息以广播方式传输,未采用加密与认证机制,ADS-B系统易受外部欺骗源的干扰。为解决该问题,提出了一种基于到达时间间隔差(IDOA)的ADS-B位置消息验证方法。建立基于IDOA的ADS-B位置消息验证系统模型,理论分析给出检验统计量的表达式及其统计特性,进一步分析给出检测门限的确定方法,通过仿真验证所提方法的正确性与有效性。结果表明:所提方法与基于到达时间差(TDOA)的验证方法具有相同的检测性能,且对时间测量误差和ADS-B位置误差不敏感,但所提方法可克服基于TDOA的验证方法存在的对地面站时间同步误差敏感的缺点。
Abstract:Because of its precise aircraft position, quick update interval, and broad surveillance coverage, automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) is a rapidly developing aeronautical surveillance system that has been extensively utilized in civil aviation surveillance. Nevertheless, since ADS-B communications are transmitted without cryptographic security protections, ADS-B is susceptible to spoofing sources. To detect spoofing, a verification scheme of ADS-B position messagesbased on interval difference of arrival (IDOA) is proposed. Firstly, the system model of ADS-B position message verification based on IDOA is presented.Then, the expression of the test statistic for ADS-B position message verification is derived. In addition, the detection threshold is given by the derived statistical property of the test statistic. Finally, computer simulation is used to confirm the accuracy and efficacy of the suggested strategy.The simulation results show that the probability of detection and probability of false of the IDOA scheme is equivalent to that of the time difference of arrival (TDOA) scheme,and IDOA is not sensitive to time measurement error and ADS-B position error. However, the benefit of IDOA is that it is not affected by time synchronization errors.
-
表 1 仿真参数设置
Table 1. Simulation parameter setting
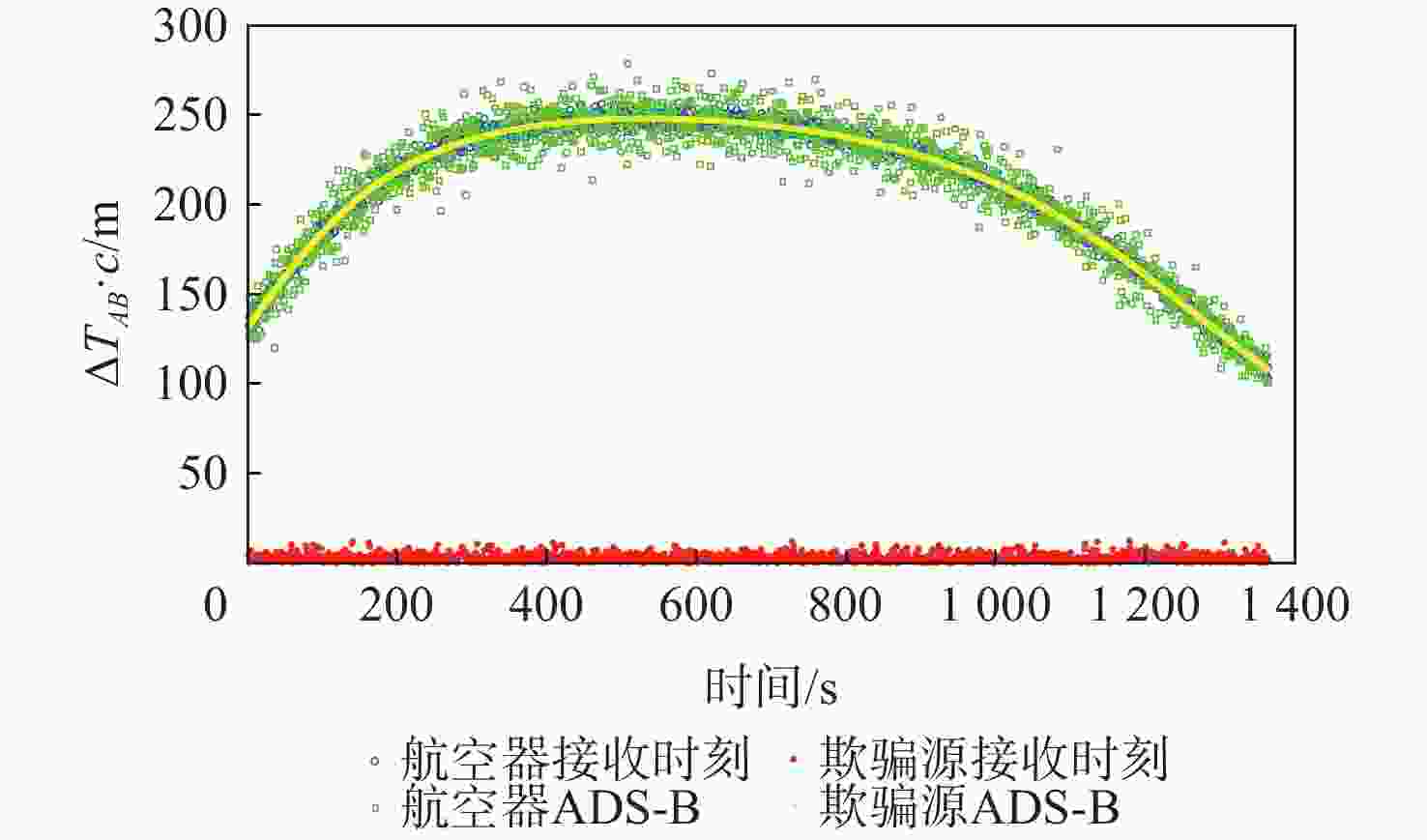
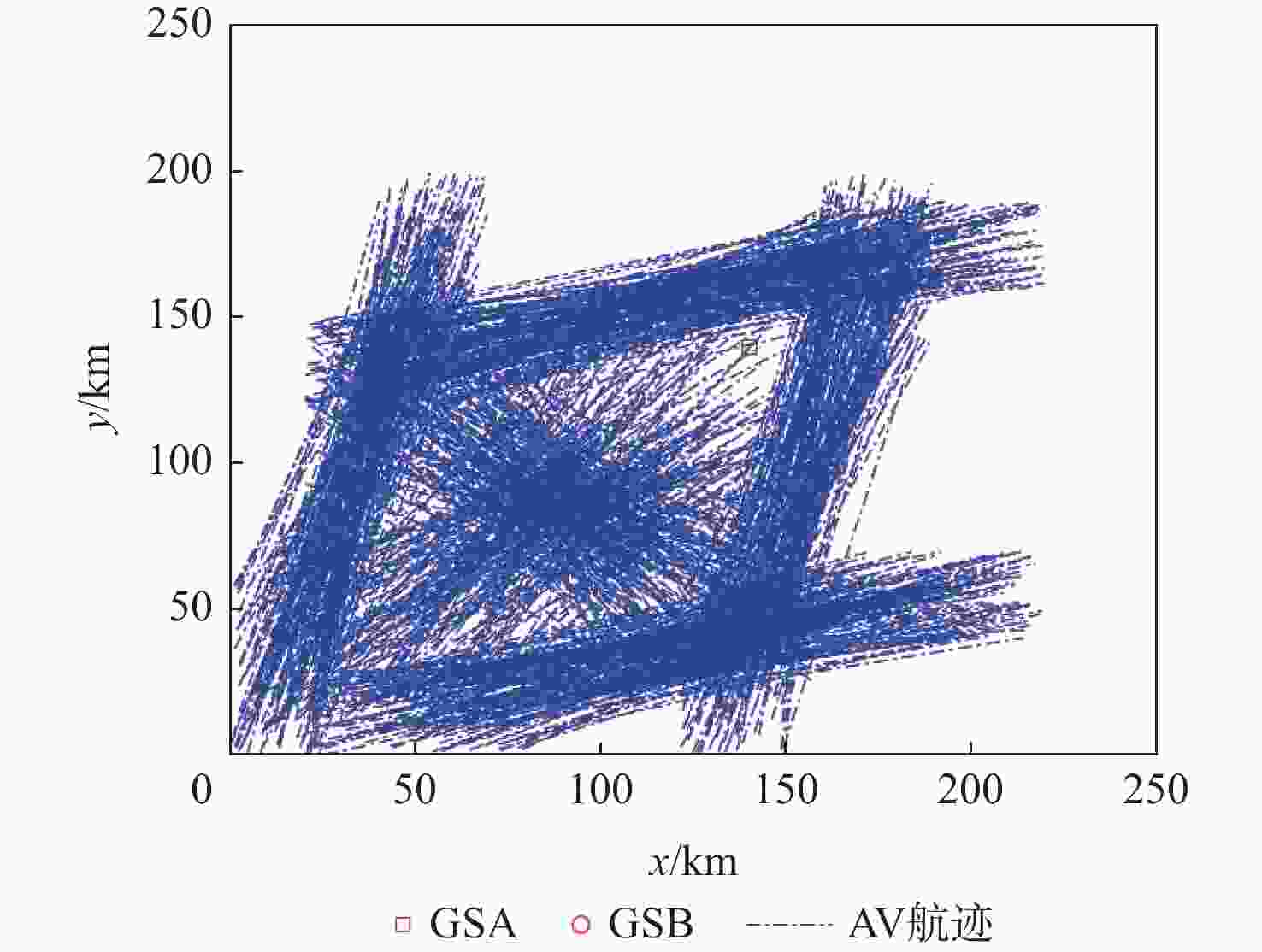
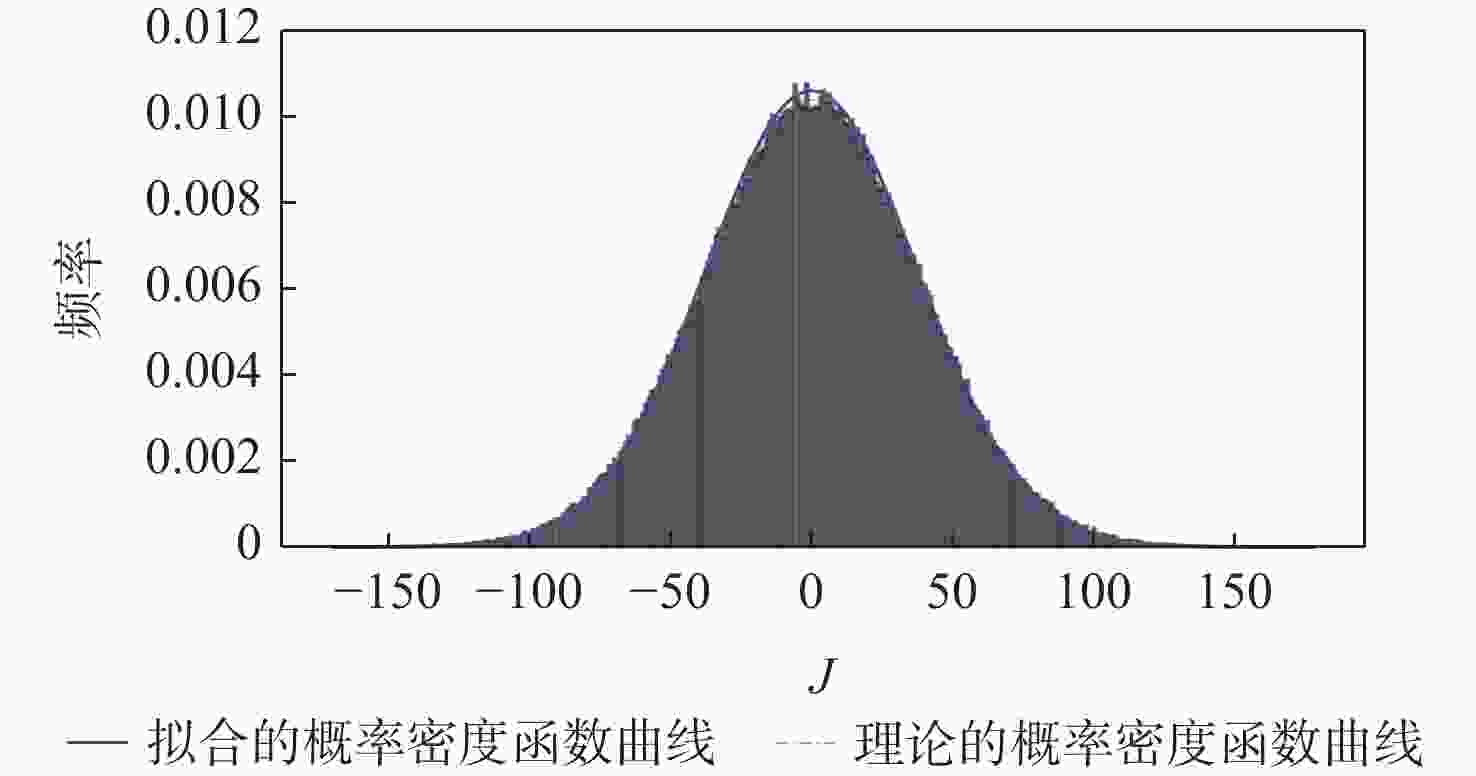
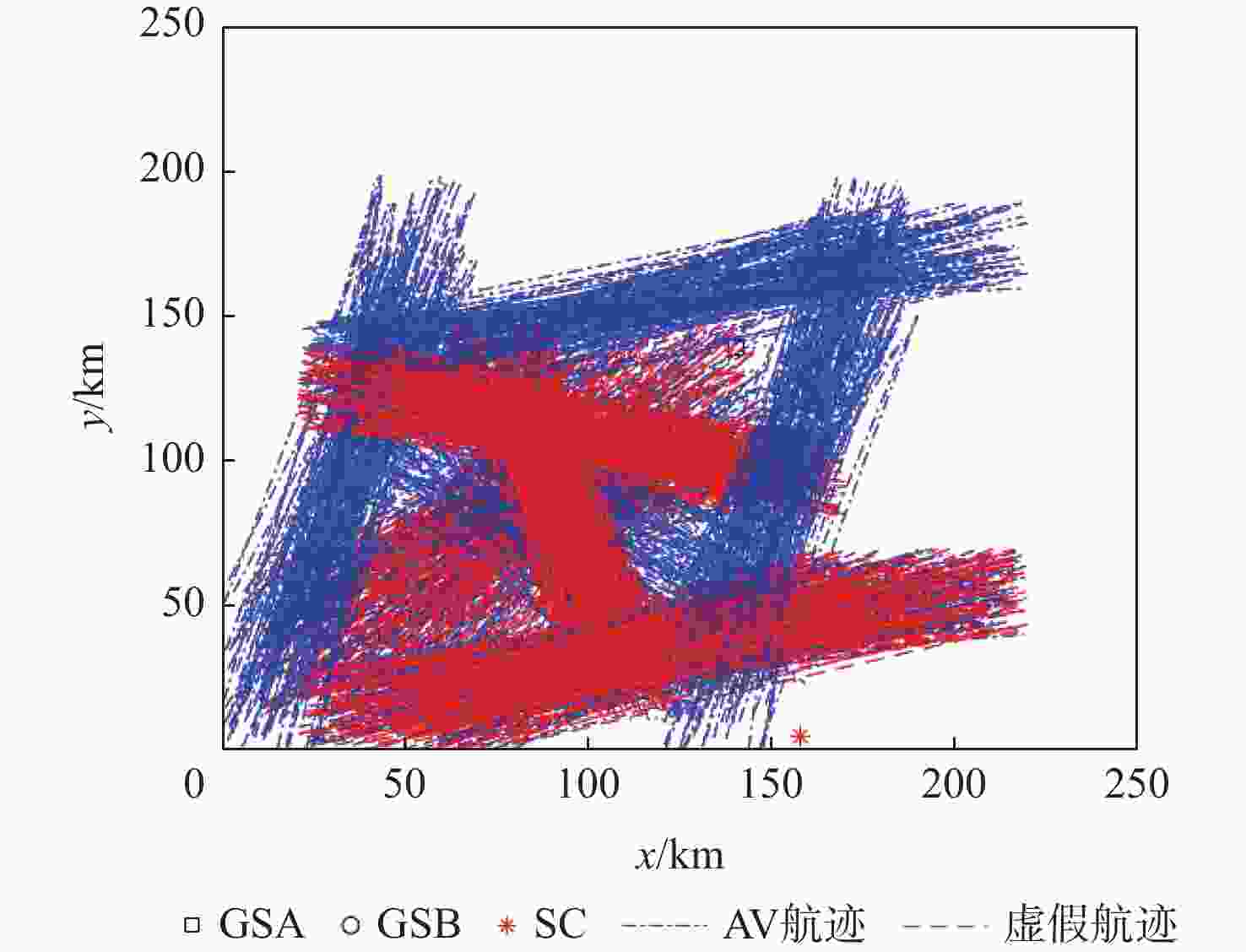
参数 数值 地面站A的位置坐标/km (140,140,0) 地面站B的位置坐标/km (40,40,0) 静止欺骗源SC的位置坐标/km (157.68,4.67,0) 航空器AV的航迹 随机生成900条航迹 时间测量误差的标准差/s 6.4×10−9 地面站时间同步误差/s 2×10−8 ADS-B水平位置误差的标准差/km 4×10−3 ADS-B垂直位置误差的标准差/km 6.6×10−3 虚警概率 0.01 表 2 TDOA与IDOA的检测性能比较
Table 2. Comparison of detection performance between TDOA and IDOA
方法 虚警概率 检测概率 TDOA 0.0325 0.9998 IDOA 0.0158 0.9986 -
[1] 张军. 空域监视技术的新进展及应用[J]. 航空学报, 2011, 32(1): 1-14.ZHANG J. New development and application of airspace surveillance technology[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2011, 32(1): 1-14(in Chinese). [2] ICAO. Technical provisions for mode S services and extended squitter: ICAO 9871[S]. Montreal: ICAO, 2012. [3] RTCA DO-260B. Minimum operational performance standards for 1090 MHz extended squitter automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) and traffic information services-broadcast (TIS-B): ED-102A[S]. Washington, D. C. : RTCA, 2009.[4] International Civil Aviation Organization Asia and Pacific Office. Guidance material on comparison of surveillance technologies (GMST)[R]. Montreal: ICAO, 2007. [5] STROHMEIER M, SCHAFER M, LENDERS V, et al. Realities and challenges of nextgen air traffic management: The case of ADS-B[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(5): 111-118. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2014.6815901 [6] STROHMEIER M, LENDERS V, MARTINOVIC I. On the security of the automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast protocol[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2015, 17(2): 1066-1087. [7] SCHÄFER M, LENDERS V, MARTINOVIC I. Experimental analysis of attacks on nextgeneration air traffic communication[M]//ABDALLA M, POINTCHEVAL D, FOUQUE P A, et al. Applied cryptography and network security. Berlin: Springer, 2013: 253-271. [8] FINKE C, BUTTS J, MILLS R, et al. Enhancing the security of aircraft surveillance in the next generation air traffic control system[J]. International Journal of Critical Infrastructure Protection, 2013, 6(1): 3-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcip.2013.02.001 [9] HABLEEL E, BAEK J, BYON Y J, et al. How to protect ADS-B: Confidentiality framework for future air traffic communication[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 155-160. [10] AMIN S, CLARK T, OFFUTT R, et al. Design of a cyber security framework for ADS-B based surveillance systems[C]//Proceedings of the Systems and Information Engineering Design Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 304-309. [11] LI W, KAMAL P. Integrated aviation security for defense-in-depth of next generation air transportation system[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Technologies for Homeland Security. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 136-142. [12] BAEK J, BYON Y J, HABLEEL E, et al. Making air traffic surveillance more reliable: A new authentication framework for automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) based on online/offline identity-based signature[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2015, 8(5): 740-750. doi: 10.1002/sec.1021 [13] 丁建立, 邹云开, 王静, 等. 基于深度学习的ADS-B异常数据检测模型[J]. 航空学报, 2019, 40(12): 323220. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2019.23220DING J L, ZOU Y K, WANG J, et al. ADS-B anomaly data detection model based on deep learning[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2019, 40(12): 323220(in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2019.23220 [14] WANG W Y, CHEN G, WU R B, et al. A low-complexity spoofing detection and suppression approach for ADS-B[C]//Proceedings of the Integrated Communication, Navigation and Surveillance Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-8. [15] 王文益, 陈庚, 吴仁彪, 等. 基于十字阵列的ADS-B欺骗式干扰抑制方法: CN104360323A[P]. 2015-02-18.WANG W Y, CHEN G, WU R B, et al. ADS-B deception jamming restraining method based on cross array: CN104360323A[P]. 2015-02-18(in Chinese). [16] STROHMEIER M, LENDERS V, MARTINOVIC I. Intrusion detection for airborne communication using PHY-layer information[M]//JULISCH K, KRUEGEL C. Detection of intrusions and malware, and vulnerability assessment. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 67-77. [17] SCHÄFER M, LEU P, LENDERS V, et al. Secure motion verification using the Doppler effect[C]//Proceedings of the 9th ACM Conference on Security & Privacy in Wireless and Mobile Networks. New York: ACM, 2016: 135-145. [18] GHOSE N, LAZOS L. Verifying ADS-B navigation information through Doppler shift measurements[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/AIAA 34th Digital Avionics Systems Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-27. [19] LI T Y, WANG B H, SHANG F T, et al. Dynamic temporal ADS-B data attack detection based on sHDP-HMM[J]. Computers & Security, 2020, 93: 101789. [20] YING X H, MAZER J, BERNIERI G, et al. Detecting ADS-B spoofing attacks using deep neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 187-195. [21] HABLER E, SHABTAI A. Using LSTM encoder-decoder algorithm for detecting anomalous ADS-B messages[J]. Computers & Security, 2018, 78: 155-173. [22] NUSEIBEH B, HALEY C B, FOSTER C. Securing the skies: Inrequirements we trust[J]. Computer, 2009, 42(9): 64-72. doi: 10.1109/MC.2009.299 [23] STROHMEIER M, MARTINOVIC I, LENDERS V. A k-NN-based localization approach for crowdsourced air traffic communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(3): 1519-1529. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2797760 [24] SCHAFER M, LENDERS V, SCHMITT J. Secure track verification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 199-213. [25] NAGANAWA J, MIYAZAKI H. A theory of aircraft position verification using TDOA[C]//Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 833-835. [26] US Department of Defense. Global positioning system standard positioning service performance standard[S]. Washington, D. C. : US Department of Defense, 2008. -






 下载:
下载: