Integrated security control of industrial cyber-physical systems based on new type ADETCS
-
摘要:
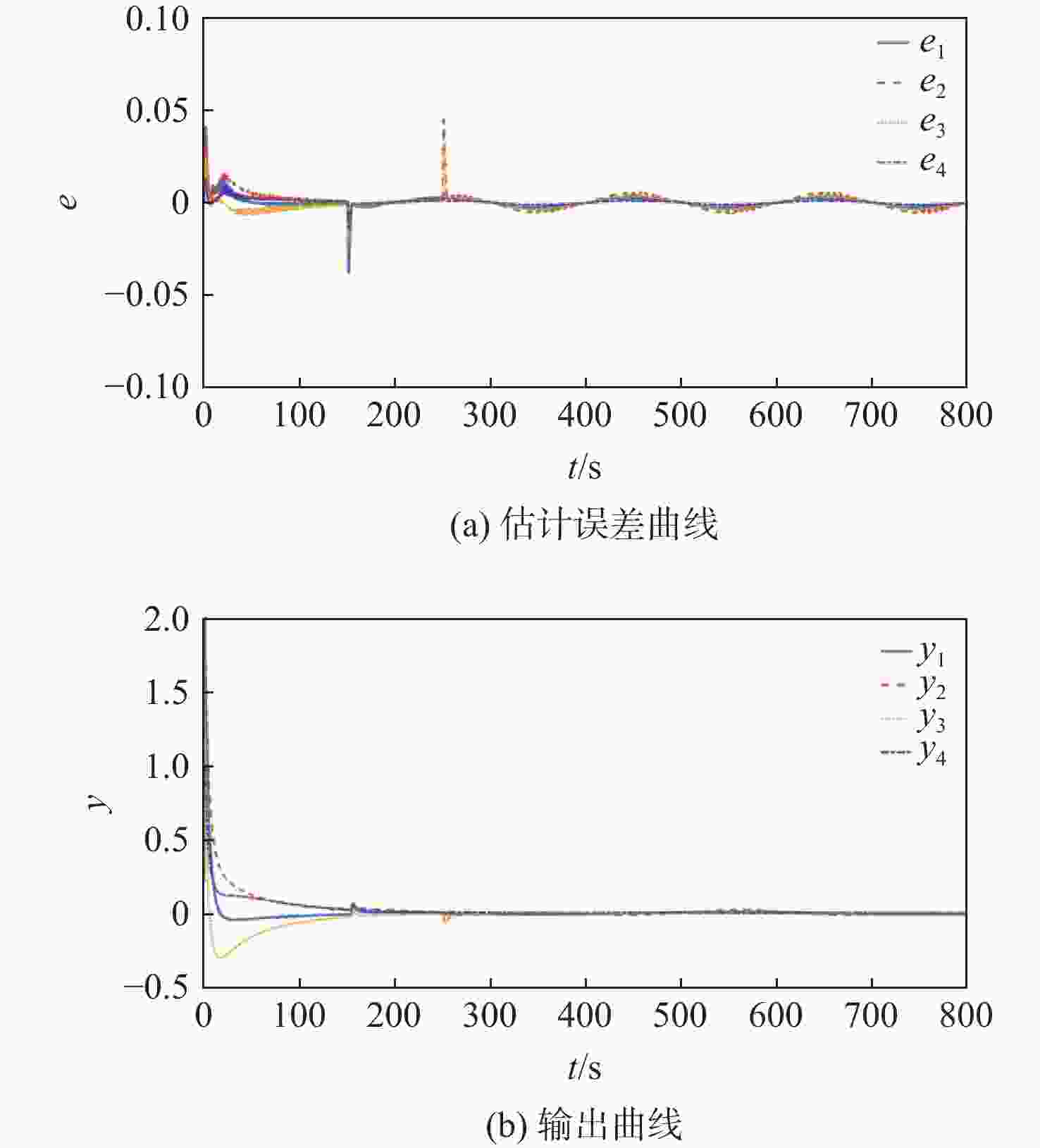
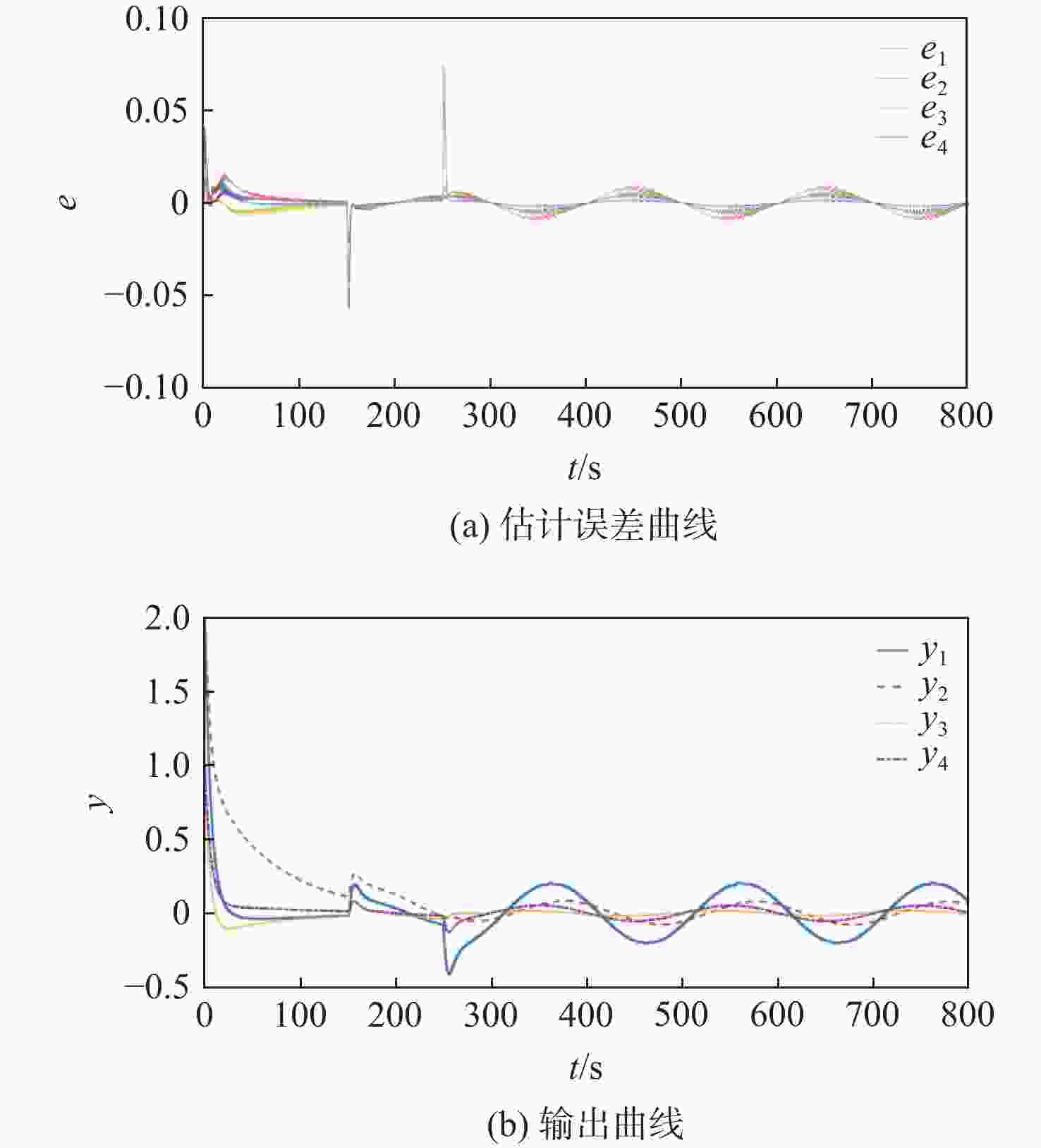
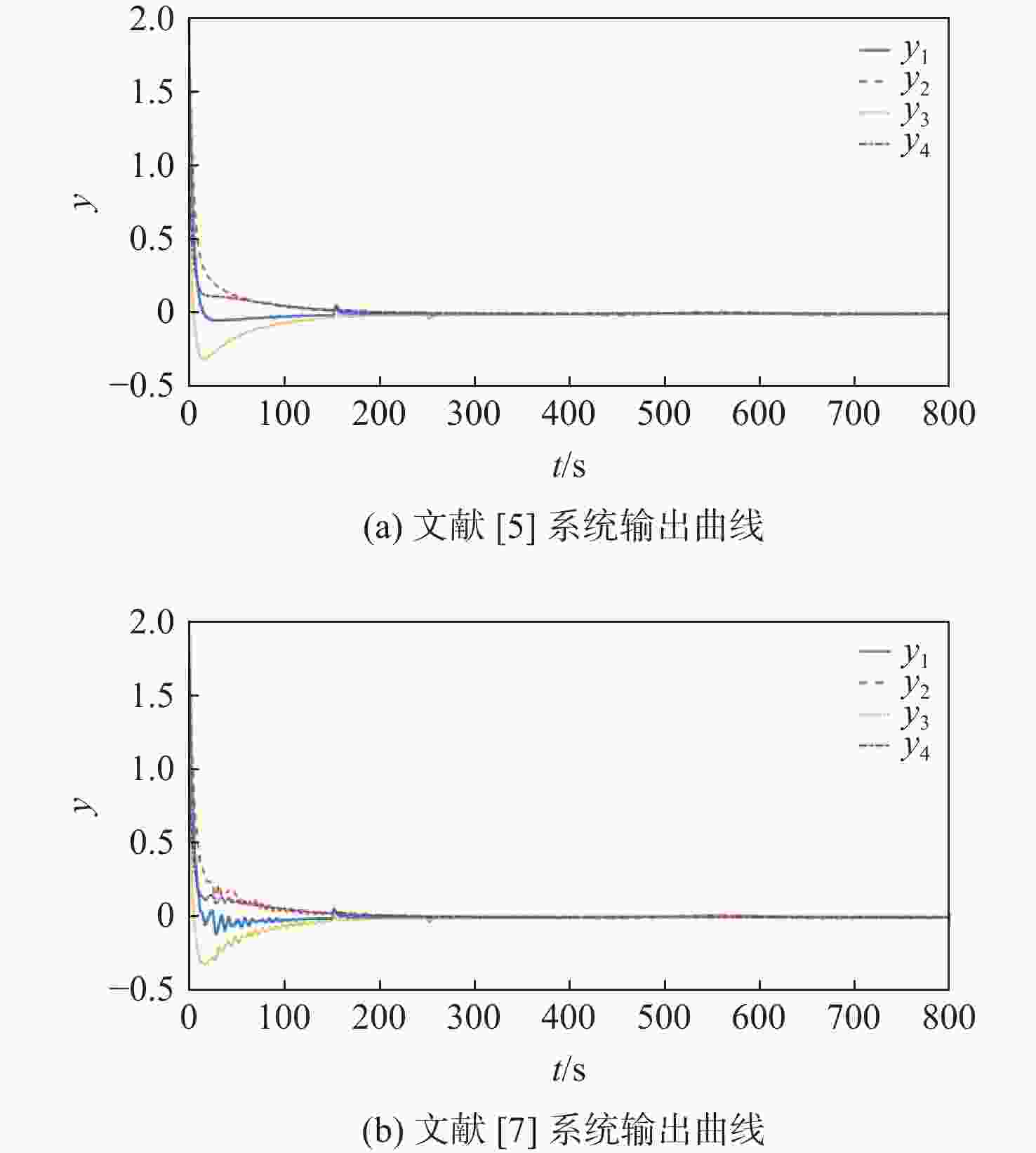
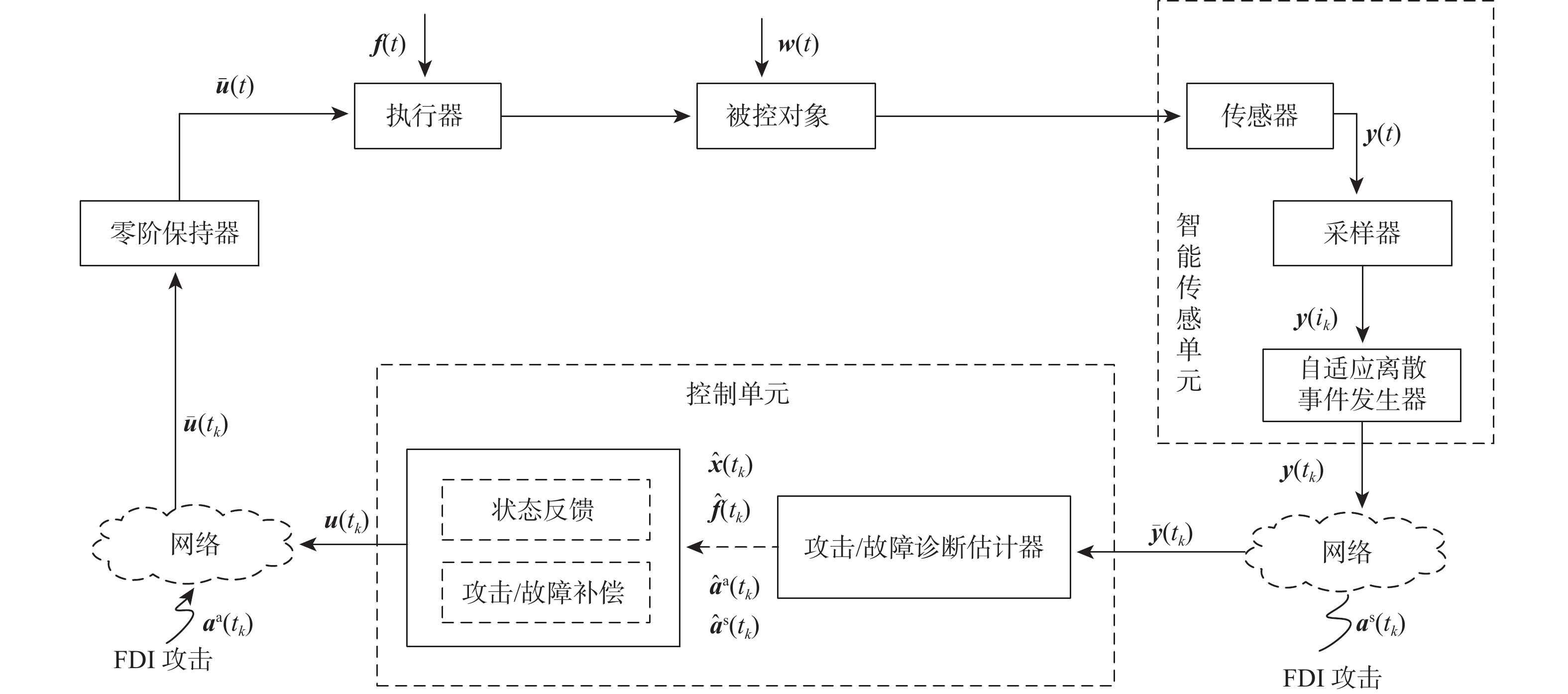
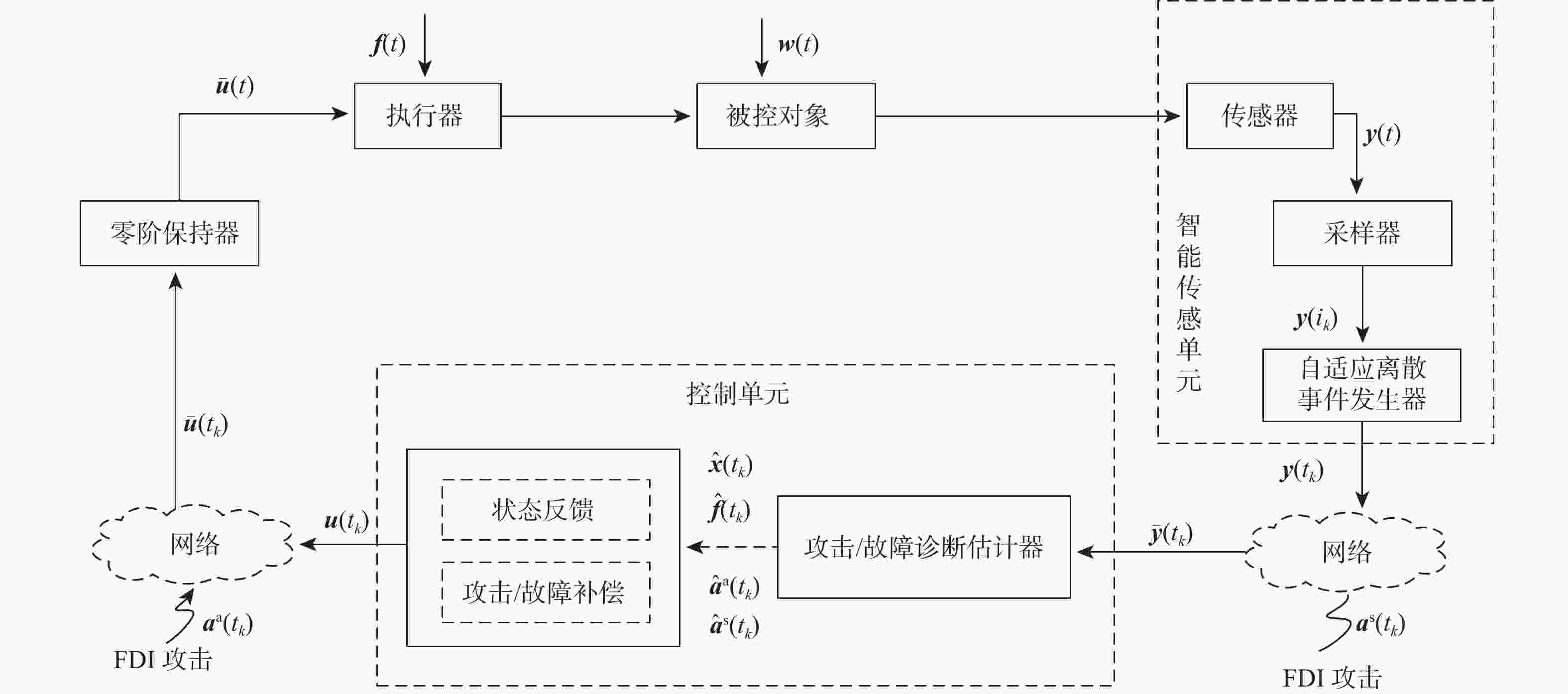
针对一类虚假数据注入(FDI)攻击与故障共存的工业信息物理系统(ICPS),在新型自适应离散事件触发通信机制(ADETCS)下,研究了综合安全控制与通信的协同设计问题。引入ADETCS取代传统离散事件触发通信机制,构建安全与通信可自适应协同优化运行的ICPS架构;通过对ADETCS中阈值函数的优化设计,获得一种可随系统动态行为双向连续变化的新型ADETCS;在该机制下,基于主动容侵和容错的思想,通过构造Lyapunov泛函,借助新型Bessel-Legebdre不等式、锥补线性化(CCL)等少保守性技术,在统一的自适应变采样框架下,推证出鲁棒估计器与综合安全控制器的求解方法,使ICPS可同时防御FDI攻击与故障,并具有更优的自适应通信调节能力。仿真结果表明:新型ADETCS中阈值函数的巧妙设计及 CCL的应用,相较现存通信机制和设计方法,可使ICPS的综合安全控制性能与资源节约获得更优的折中平衡。
-
关键词:
- 新型自适应离散事件触发通信机制 /
- 工业信息物理系统 /
- 综合安全控制 /
- 锥补线性化 /
- 动态优化平衡
Abstract:For industrial cyber-physical system (ICPS) with false data injection (FDI) attacks and faults, the collaborative design of integrated security control and communication in the new type adaptive discrete event-triggered communication scheme (ADETCS) was studied. Firstly, the ADETCS was introduced to replace the traditional discrete event-triggered communication scheme, and an ICPS architecture with adaptive collaborative optimization of security control and communication was constructed. Secondly, through the optimization design of the threshold function in ADETCS, a new type ADETCS was obtained, which could change continuously in both directions with the system’s dynamic behaviors. Then, based on the active attack-tolerant and active fault-tolerant ideas, the Lyapunov function was constructed, and less conservative techniques such as new Bessel-Legebdre inequality and cone complementarity linearization (CCL) were used. Under the unified adaptive variable sampling framework, the solution methods of the robust estimator and integrated security controller were derived so that ICPS could defend against FDI attacks and faults at the same time and have better adaptive communication regulation ability. The simulation results show that the ingenious design of threshold function in the new type ADETCS and the application of CCL can achieve a better compromise between the integrated security control performance and resource saving of ICPS.
-
-
[1] 刘烃, 田决, 王稼舟, 等. 信息物理融合系统综合安全威胁与防御研究[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(1): 5-24.LIU T, TIAN J, WANG J Z, et al. Integrated security threats and defense of cyber-physical systems[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(1): 5-24(in Chinese). [2] ANTA A, TABUADA P. To sample or not to sample: Self-triggered control for nonlinear systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2010, 55(9): 2030-2042. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2010.2042980 [3] WANG X F, LEMMON M D. Event-triggering in distributed networked control systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2011, 56(3): 586-601. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2010.2057951 [4] PENG C, HAN Q L, YUE D. To transmit or not to transmit: A discrete event-triggered communication scheme for networked Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2013, 21(1): 164-170. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2012.2199994 [5] PENG C, ZHANG J, YAN H. Adaptive event-triggering H∞ load frequency control for network-based power system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(8): 1685-1694. [6] YUAN S, YU C P, SUN J. Adaptive event-triggered consensus control of linear multi-agent systems with cyber attacks[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 442: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.02.040 [7] 乔伟豪, 朱凤增, 彭力. 基于自适应事件触发的时滞系统分布式l2-l∞滤波[J]. 控制与决策, 2022, 37(4): 1074-1080.QIAO W H, ZHU F Z, PENG L. Distributed l2-l∞ filtering based on adaptive event triggering for time-delay systems[J]. Control and Decision, 2022, 37(4): 1074-1080(in Chinese). [8] ZHANG J, PENG C, DU D J, et al. Adaptive event-triggered communication scheme for networked control systems with randomly occurring nonlinearities and uncertainties[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 174: 475-482. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.04.107 [9] PAN Y N, YANG G H. Novel event-triggered filter design for nonlinear networked control systems[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2018, 355(3): 1259-1277. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2017.12.019 [10] GU Z, SHI P, YUE D. An adaptive event-triggering scheme for networked interconnected control system with stochastic uncertainty[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2017, 27(2): 236-251. doi: 10.1002/rnc.3570 [11] GU Z, TIAN E G, LIU J L. Adaptive event-triggered control of a class of nonlinear networked systems[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2017, 354(9): 3854-3871. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2017.02.026 [12] HU L, WANG Z D, HAN Q L, et al. State estimation under false data injection attacks: Security analysis and system protection[J]. Automatica, 2018, 87: 176-183. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.09.028 [13] SUN Z W, XUE W F, LIU J L, et al. Adaptive event-triggered resilient control of industrial cyber physical systems under asynchronous data injection attack[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2022, 359(7): 3000-3023. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2022.02.009 [14] GU Y P, YU X, GUO K X, et al. Detection, estimation, and compensation of false data injection attack for UAVs[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 546: 723-741. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.08.055 [15] MAO Z H, JIANG B, SHI P. Observer-based fault-tolerant control for a class of networked control systems with transfer delays[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2011, 348(4): 763-776. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2011.02.004 [16] HUO Z H, ZHANG Z X, FANG H J. Research on fault-tolerant control of networked control systems based on information scheduling[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2008, 19(5): 1024-1028. doi: 10.1016/S1004-4132(08)60191-7 [17] HAN S Y, CHEN Y H, TANG G Y. Fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant tracking control for discrete-time systems with faults and delays in actuator and measurement[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2017, 354(12): 4719-4738. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2017.05.027 [18] YE D, LUO S P. A co-design methodology for cyber-physical systems under actuator fault and cyber attack[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 356(4): 1856-1879. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2019.01.009 [19] LI W, SHI Y, LI Y. Research on secure control and communication for cyber-physical systems under cyber attacks[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement & Control, 2019, 41(12): 3421-3437. [20] 李炜, 张建军. 攻击与故障共存的ICPS综合安全控制方法[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2021, 55(6): 1185-1198.LI W, ZHANG J J. Integrated security control method for industrial cyber-physical system with attack and fault[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2021, 55(6): 1185-1198(in Chinese). [21] FRIDMAN E. A refined input delay approach to sampled-data control[J]. Automatica, 2010, 46(2): 421-427. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.11.017 [22] ZHANG K, JIANG B, STAROSWIECKI M. Dynamic output feedback fault tolerant controller design for Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy systems with actuator faults[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2010, 18(1): 194-201. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2009.2036005 [23] 邱爱兵, 吉虹钢, 顾菊平. 非均匀采样数据系统时变故障估计与调节最优集成设计[J]. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(7): 1493-1504.QIU A B, JI H G, GU J P. Optimal integrated design of time-varying fault estimation and accommodation for nonuniformly sampled data systems[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(7): 1493-1504(in Chinese). [24] ZHANG X M, HAN Q L, SEURET A, et al. Overview of recent advances in stability of linear systems with time-varying delays[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2019, 13(1): 1-16. [25] EL GHAOUI L, OUSTRY F, AITRAMI M. A cone complementarity linearization algorithm for static output-feedback and related problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1997, 42(8): 1171-1176. doi: 10.1109/9.618250 [26] JOHANSSON K H. The quadruple-tank process: A multivariable laboratory process with an adjustable zero[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2000, 8(3): 456-465. doi: 10.1109/87.845876 -






 下载:
下载: