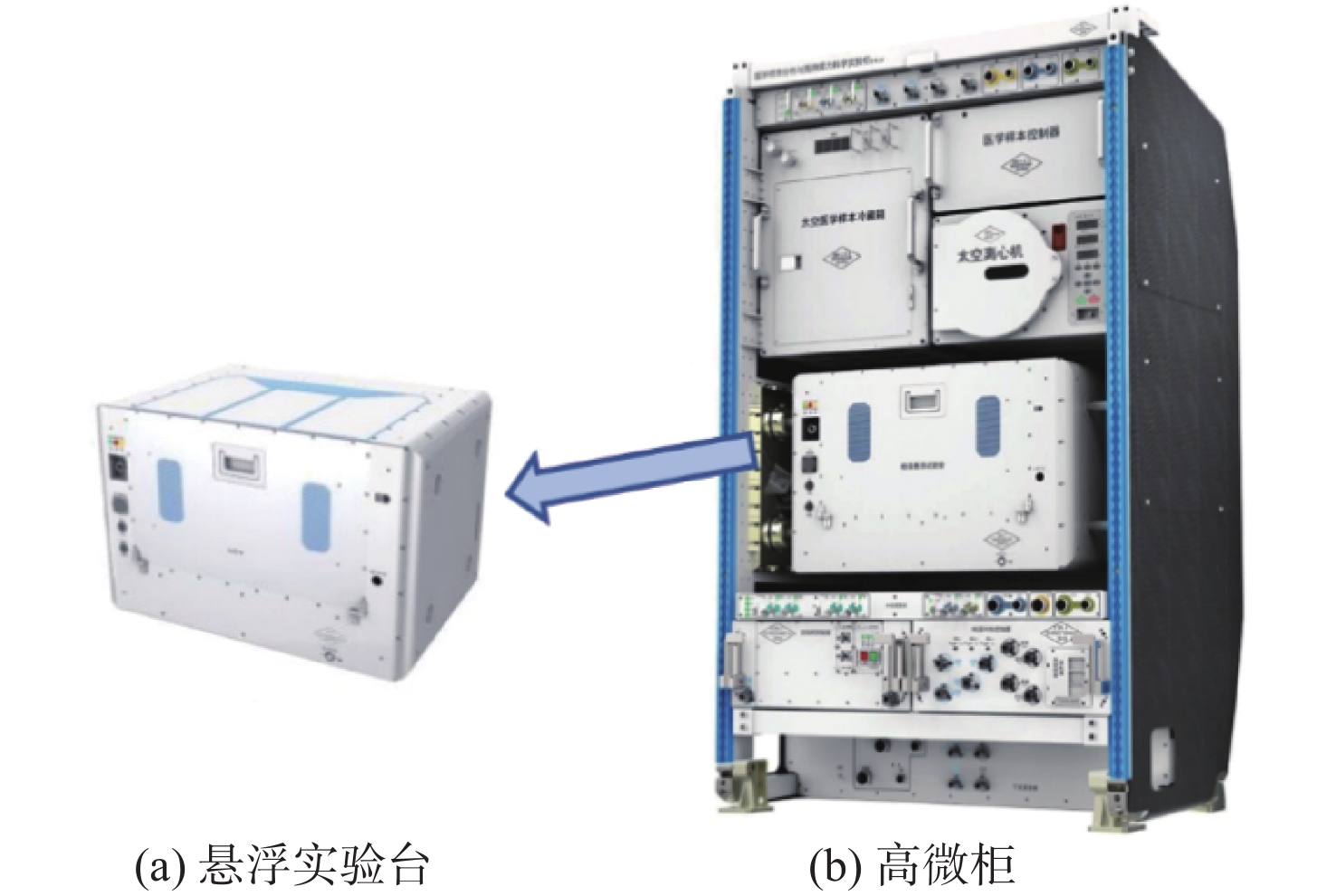
Guidance and control method of levitation experiment facility inside China’s Space Station
-
摘要:
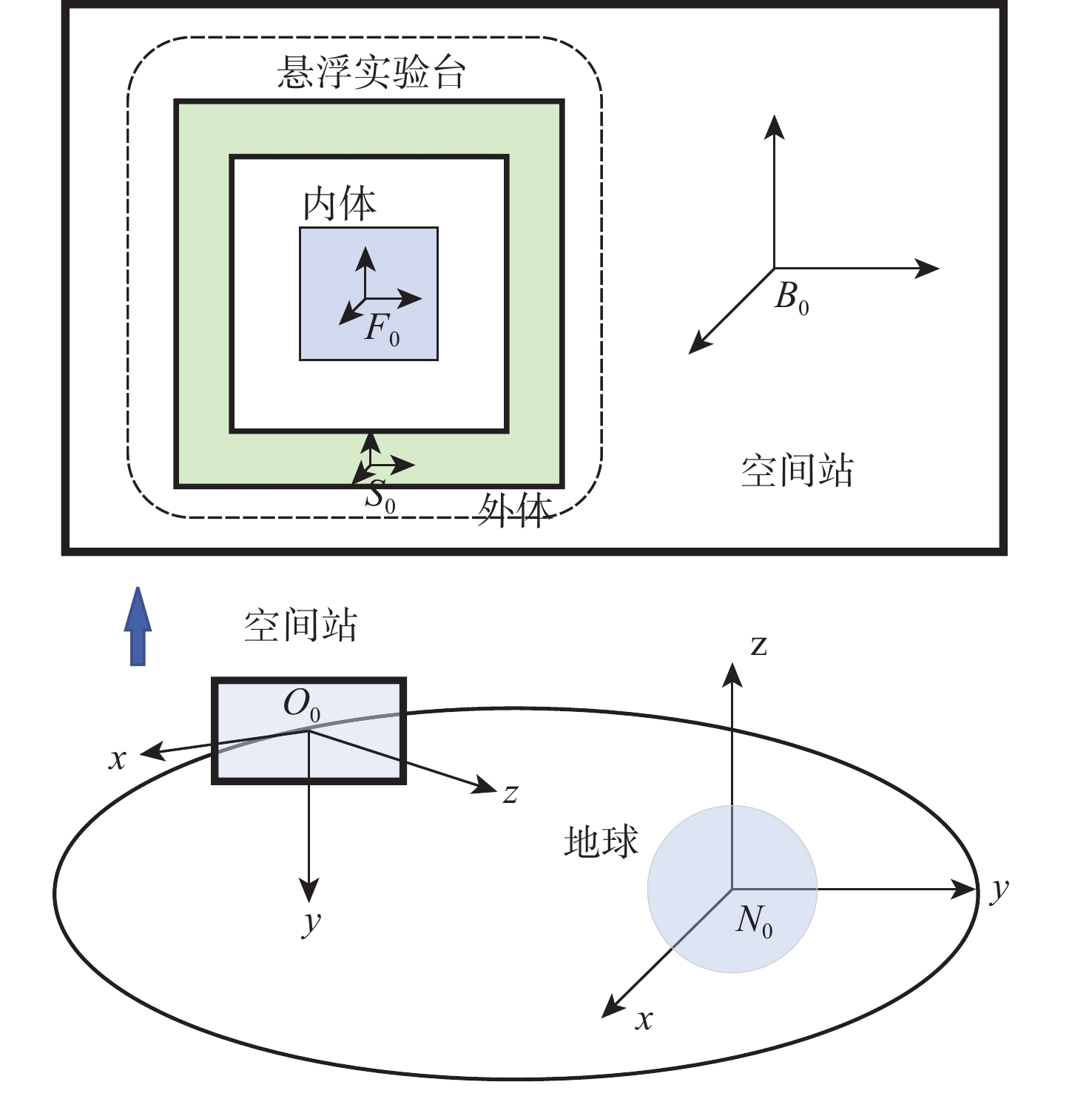
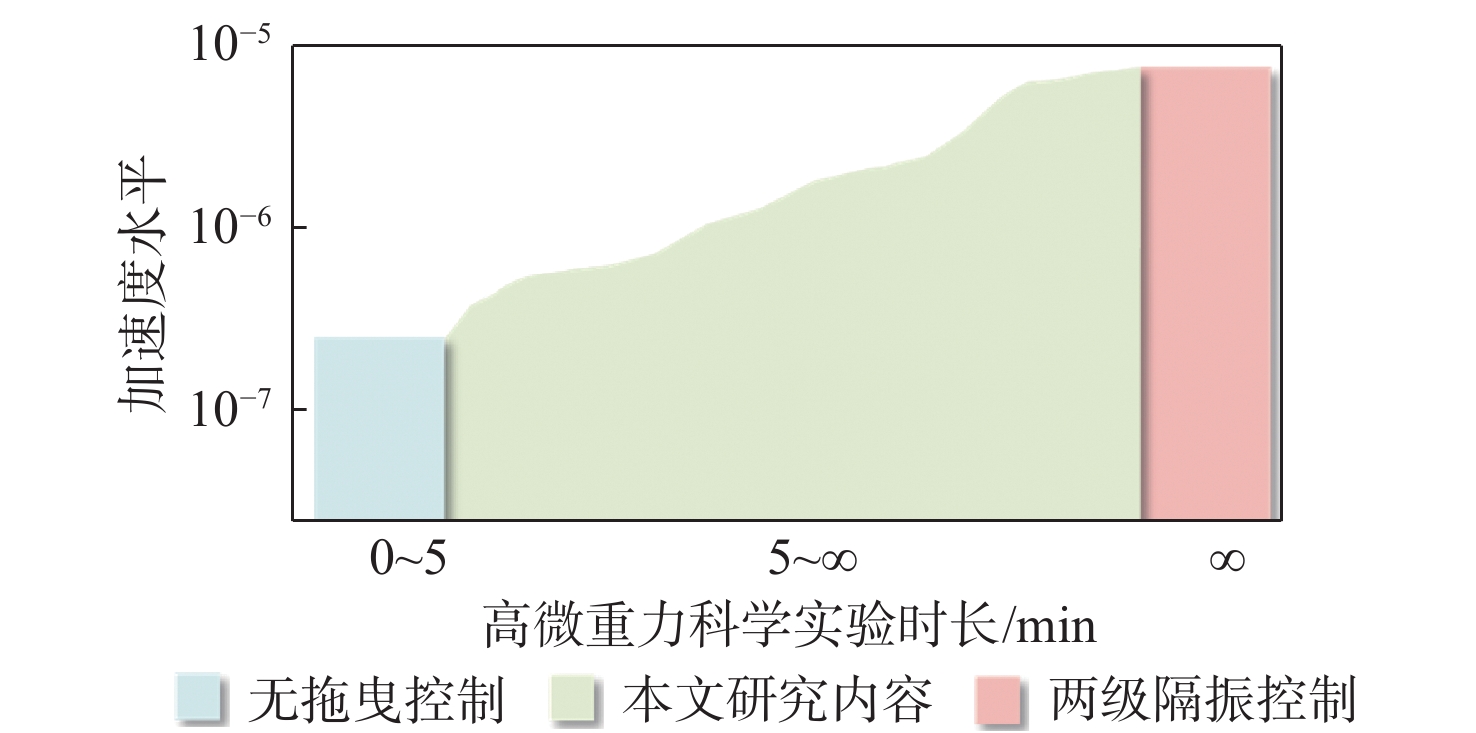
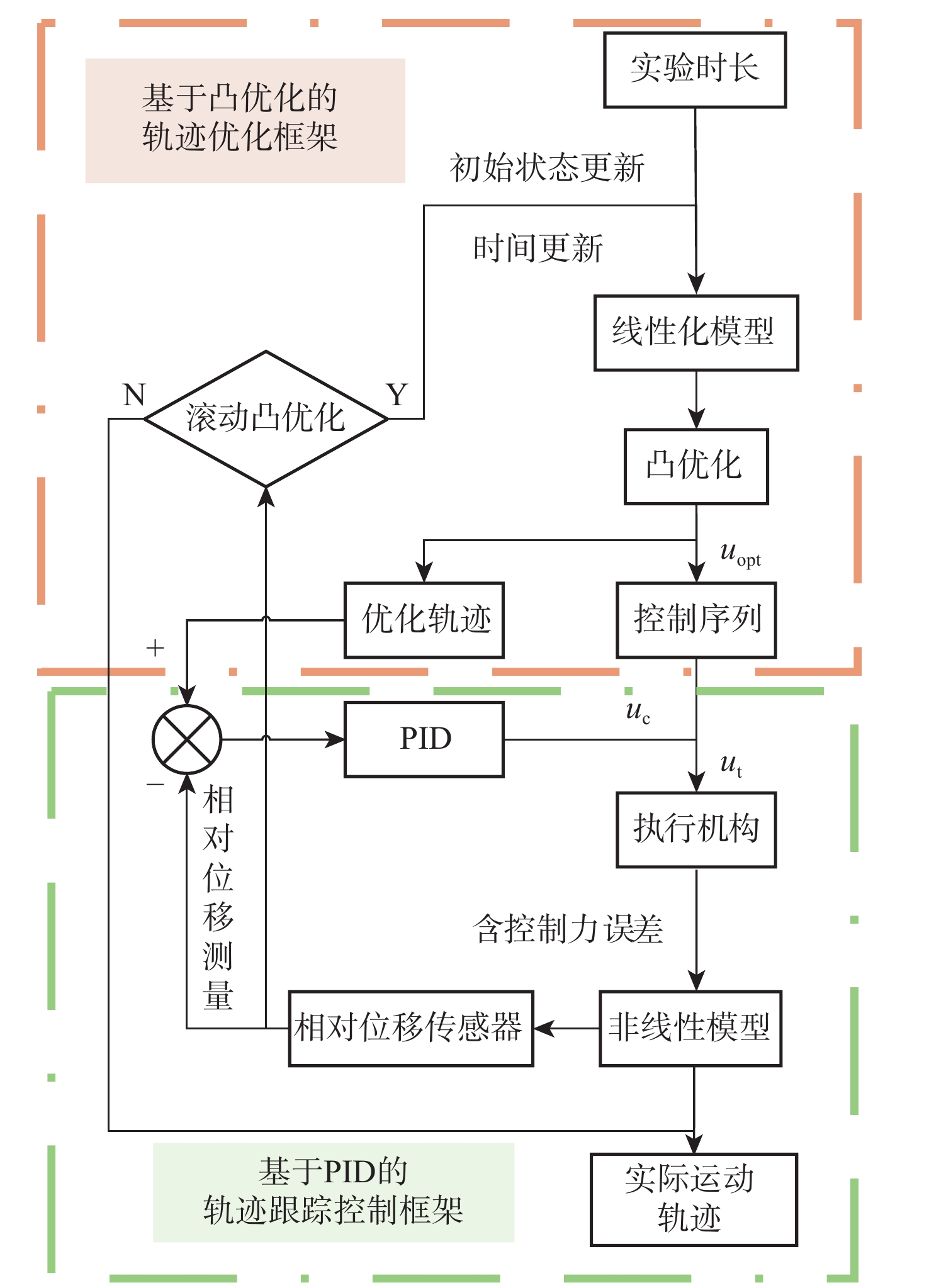
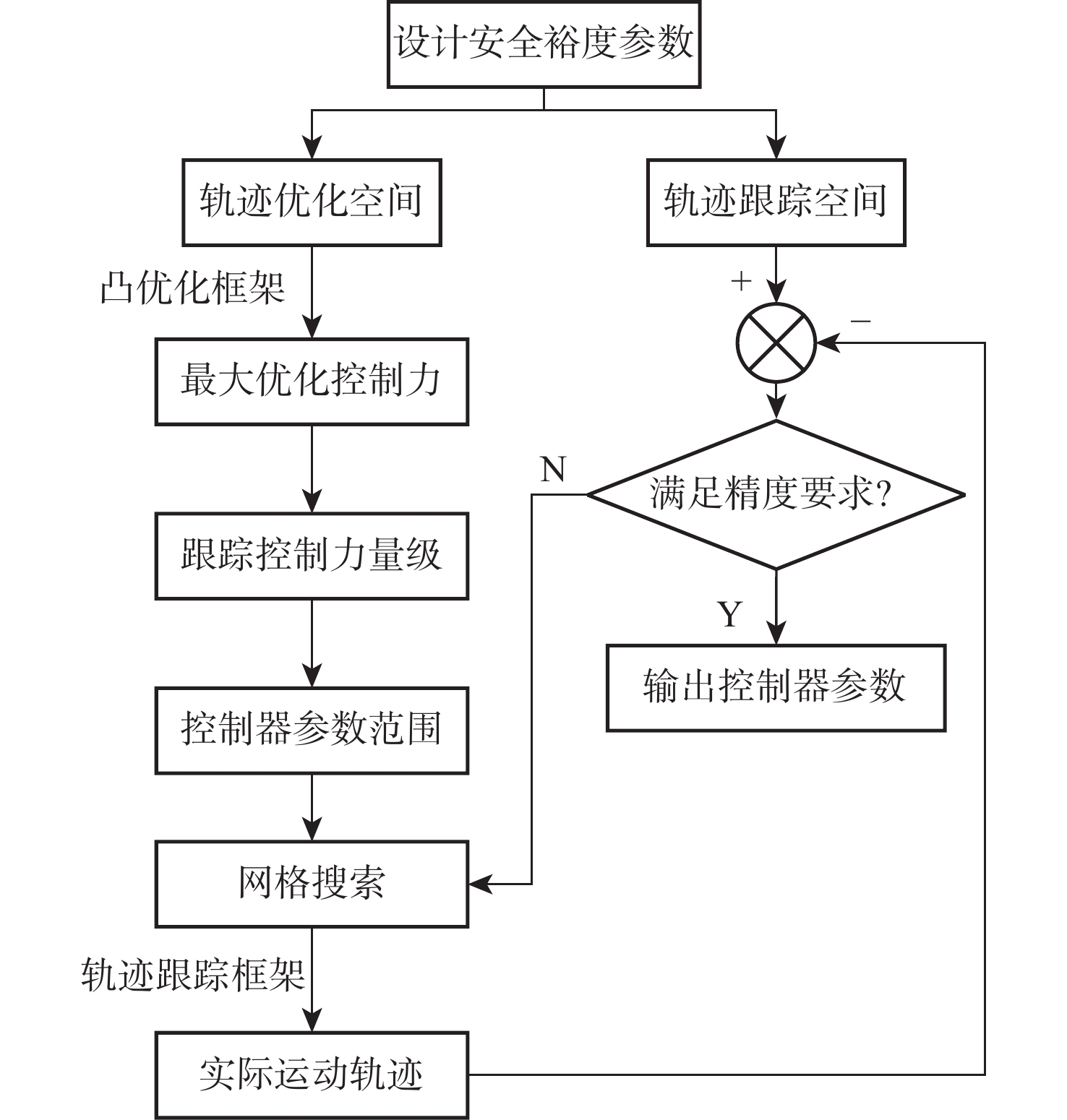
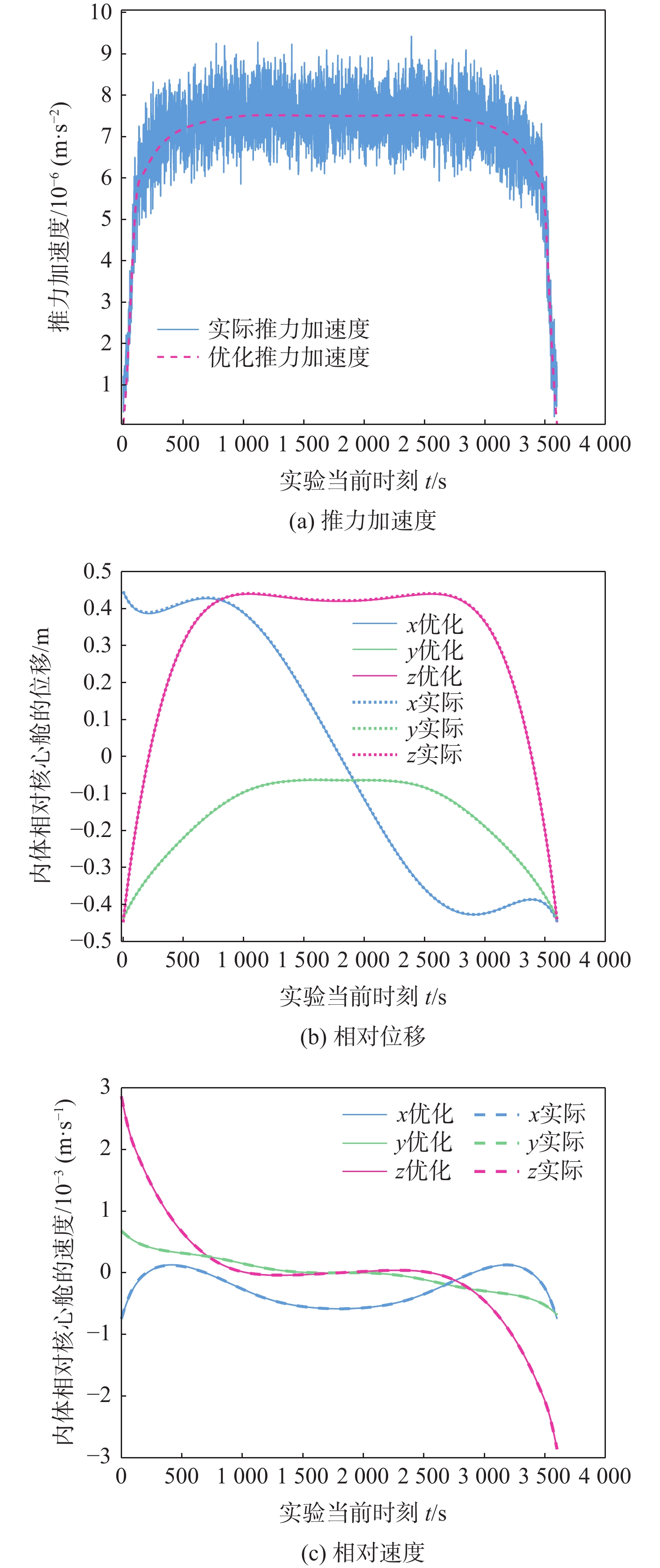
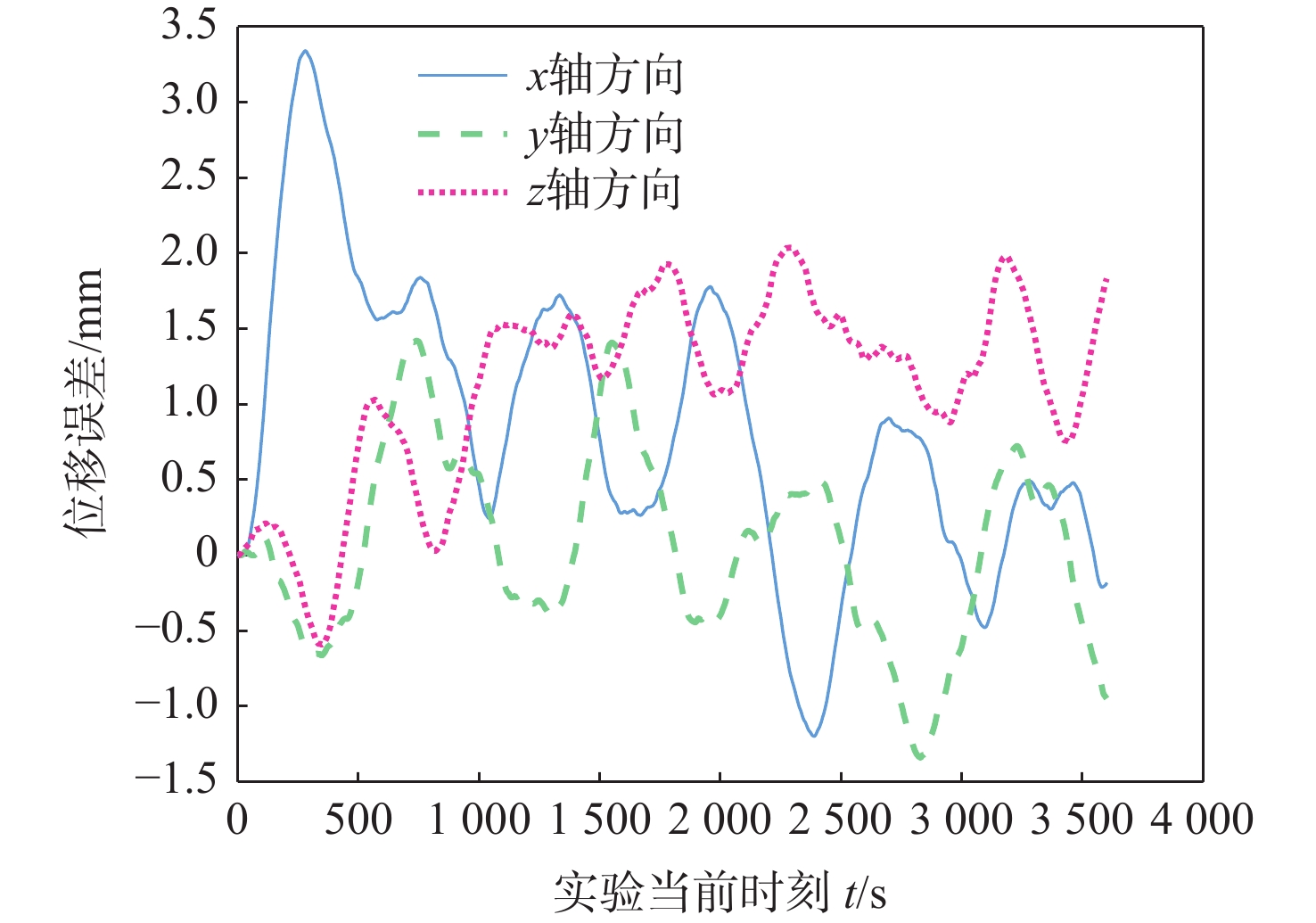
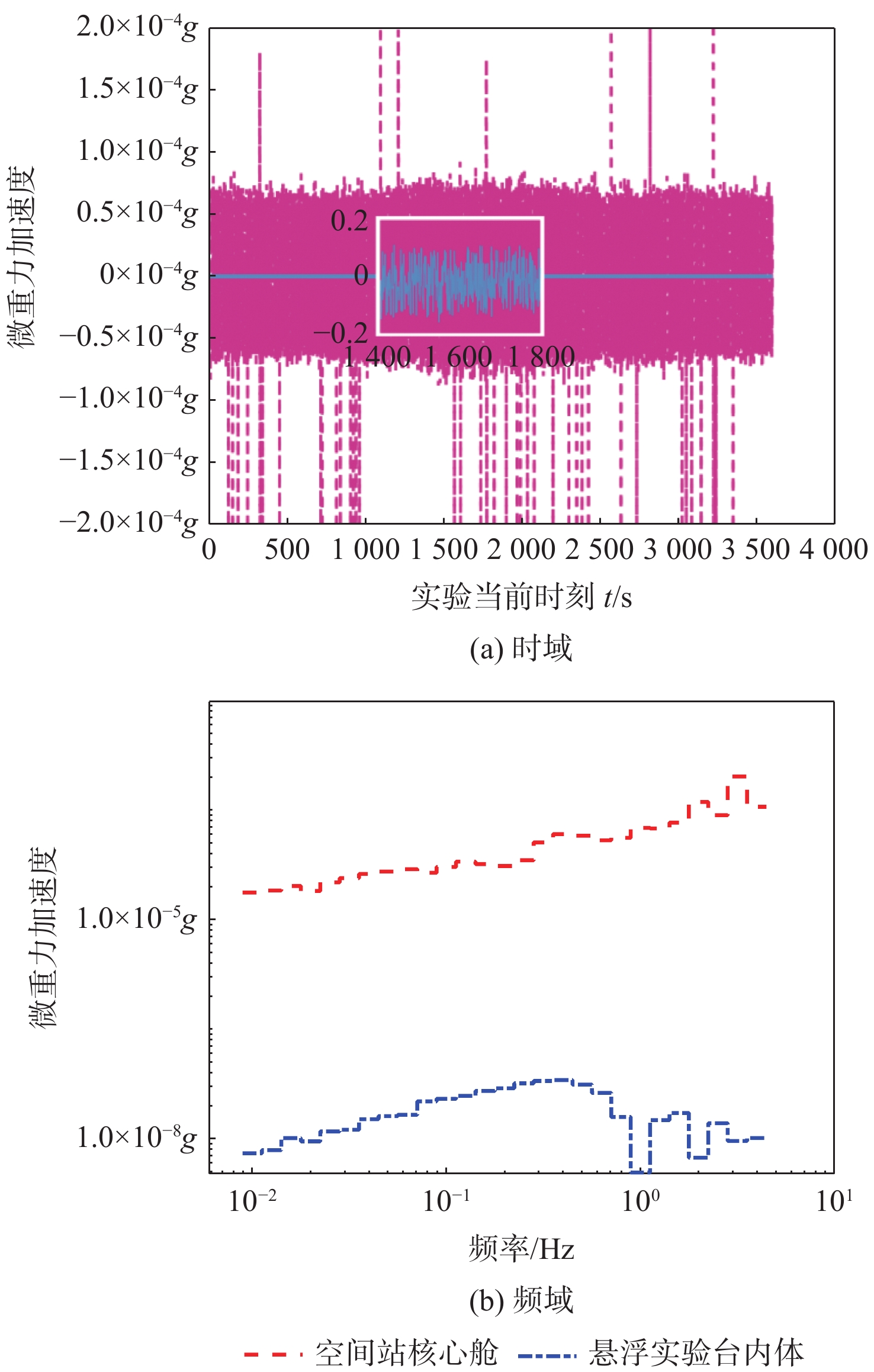
针对中国空间站舱内悬浮实验台微重力水平最优的控制问题,考虑舱内运动行程空间约束及各类不确定性因素的影响,以不同时长下的最优微重力水平为目标,提出基于凸优化的空间站舱内悬浮实验台自主轨迹规划方法和基于误差反馈控制的轨迹跟踪方案。介绍悬浮实验台的结构,建立空间相对运动动力学模型,并将其线性化;通过凸优化的方法求解微重力水平最优的运动轨迹及相应的控制力序列;设计基于误差反馈的PID跟踪控制律,兼顾微重力水平的同时实现对优化轨迹的快速跟踪控制。数值仿真结果表明:当微重力科学实验时长需求为1 h时,最优微重力水平可达9.121×10−6 m/s2。基于凸优化的空间站舱内悬浮实验台自主轨迹规划方法和基于误差反馈控制的轨迹跟踪方案,能够实现指定时长需求的最优微重力水平,给当前中等时长(1 h)最优微重力水平问题提供了解决思路,提升了中国空间站舱内悬浮实验台的应用价值。
Abstract:To optimize the microgravity level of the levitation experiment facility (LEF) inside China’s Space Station (CSS), the limited intra-vehicular travel distance and various uncertainties were considered, so as to achieve the optimal microgravity level under different time scales. An autonomous trajectory planning method based on convex optimization and a trajectory tracking scheme based on error feedback control were proposed. Firstly, the structure of the LEF was introduced, and a spatial relative motion model was provided and linearized. Secondly, the motion trajectory and corresponding controlling force sequence with the optimal microgravity level were solved by convex optimization. Finally, the proportion-integration-differentiation (PID) tracking control law based on error feedback was designed to realize the fast tracking control of the optimized trajectory while guaranteeing the microgravity level. Numerical simulation results show that the optimal microgravity level can be 9.121×10−6m/s2 when the microgravity science experiment lasts for one hour. The autonomous trajectory planning method based on convex optimization and the trajectory tracking scheme based on error feedback control can achieve the optimal microgravity level for the specified duration. It provides a new solution to the current problem of the optimal microgravity level for a medium duration (such as one hour) and enhances the application value of the LEF in the CSS.
-
表 1 空间站和悬浮实验台内质心受力分析
Table 1. Centroid force analysis of CSS and LEF inner body
类型 符号 说明 空间站 {{\boldsymbol{f}}_{{\rm{graE}}\_{\rm{B}}}} 空间站所受地球球形引力加速度 {{\boldsymbol{f}}_{{\rm{gra}}\_{\rm{B}}}} 空间站所受地球非球形引力摄动加速度和其他天体引力加速度,包括日、地、月三体引力摄动加速度等 {{\boldsymbol{f}}_{{\rm{env}}\_{\rm{B}}}} 环境摄动加速度,包括大气阻力、太阳辐射光压等引起的摄动加速度 {{\boldsymbol{f}}_{{\rm{ctr}}\_{\rm{B}}}} 对空间站施加的控制加速度 {{\boldsymbol{f}}_{{\rm{oth}}\_{\rm{B}}}} 其他扰动加速度,包括载荷动作、风扇转动等引起的振动加速度 悬浮实验台 {{\boldsymbol{f}}_{{\rm{graE}}\_{\rm{F}}}} 悬浮实验台所受地球球形引力加速度 {{\boldsymbol{f}}_{{\rm{gra}}\_{\rm{F}}}} 悬浮实验台所受地球非球形引力摄动加速度和其他天体引力加速度,包括日、地、月三体引力摄动加速度等 {{\boldsymbol{f}}_{{\rm{env}}\_{\rm{F}}}} 环境摄动加速度,包括空气流动、温度波动等引起的摄动加速度 {{\boldsymbol{f}}_{{\rm{ctr}}\_{\rm{F}}}} 对悬浮实验台内体施加的控制加速度 {{\boldsymbol{f}}_{{\rm{oth}}\_{\rm{F}}}} 其他扰动加速度,包括测量扰动、电磁扰动等与外体耦合的扰动加速度 表 2 航天器运动仿真参数
Table 2. Simulation parameters of spacecraft motion
参数 数值 太阳帆板面积/ {\rm m^2} 230 核心舱行程中心位置 {}^{({\mathrm{B}})}{{\boldsymbol{r}}_{{\rm B}P}} / \rm m {\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} { - 8.5}&{1.8}&{ - 2.6} \end{array}} \right]^{\mathrm{T}}} 悬浮实验台内体质量/ \rm kg 30 轨道偏心率 e 0 轨道高度 h / \rm km 400 轨道倾角 i /(^\circ ) 42 升交点赤经 \varOmega /(^\circ ) 120 近地点幅角 \omega /(^\circ ) 30 过近地点时刻 {t_{\rm p}} /s 25 航天器大气阻力系数 {C_{\rm d}} 3 大气密度 NRLMSISE 2000 航天器太阳光压反射系数 {C_{\rm P}} 1.5 大气阻力偏心矢量 {}^{(B)}{{\boldsymbol{L}}_{{\rm drag}}} / \rm m {[ \begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&{ - 3}&2 \end{array} ]^{\text{T}}} 太阳辐射光压偏心矢量 {}^{(B)}{{\boldsymbol{L}}_{{\rm spr}}} / \rm m {[ \begin{array}{*{20}{c}} { - 2}&1&3 \end{array} ]^{\text{T}}} 表 3 PID控制器仿真参数
Table 3. Simulation parameters of PID controller
参数 数值 比例项系数 {{\boldsymbol{K}}_{\rm p} } \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {2.7 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}&{2.7 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}&{2.7 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}} \end{array}} \right] 积分项系数 {{\boldsymbol{K}}_{\rm i}} \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {6.0 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}&{6.0 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}&{6.0 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}} \end{array}} \right] 微分项系数 {{\boldsymbol{K}}_{\rm d}} \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {2.4 \times {{10}^{ - 1}}}&{2.4 \times {{10}^{ - 1}}}&{2.4 \times {{10}^{ - 1}}} \end{array}} \right] 控制器频率/Hz 1 表 4 不确定性参数
Table 4. Uncertain parameters
参数 数值 \Delta {m_{{{\mathrm{const}}\_{\mathrm{error}}}}} 不确定性/ {\mathrm{kg}} 0.1 \Delta {{\boldsymbol{r}}_{{{\mathrm{PF}}\_{\mathrm{nosie}}\_{\mathrm{error}}}}} 不确定性/mm ±1 \Delta {{\boldsymbol{v}}_{{{\mathrm{PF}}\_{\mathrm{noise}}\_{\mathrm{error}}}}} 不确定性/( {\mathrm{mm}} \cdot {{\mathrm{s}}^{ - 1}} ) ±0.1 \Delta {{\boldsymbol{F}}_{{{\mathrm{ctr}}\_{\mathrm{noise}}\_{\mathrm{error}}}}} 不确定性/(m·N) ±0.01 -
[1] 胡文瑞. 微重力科学概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010.HU W R. Introduction to microgravity science[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010(in Chinese). [2] 吴季, 孙丽琳, 尤亮, 等. 2016—2030年中国空间科学发展规划建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2015, 30(6): 707-720.WU J, SUN L L, YOU L, et al. Prospect for Chinese space science in 2016—2030[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015, 30(6): 707-720(in Chinese). [3] 陈善广, 陈金盾, 姜国华, 等. 我国载人航天成就与空间站建设[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2012, 25(6): 391-396.CHEN S G, CHEN J D, JIANG G H, et al. Achievements of manned space program and construction of space station in China[J]. Space Medicine & Medical Engineering, 2012, 25(6): 391-396(in Chinese). [4] 胡文瑞, 龙勉, 康琦, 等. 中国微重力流体科学的空间实验研究[J]. 科学通报, 2009, 54(18): 2615-2626. doi: 10.1360/csb2009-54-18-2615HU W R, LONG M, KANG Q, et al. Research on space experiment of microgravity fluid science in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(18): 2615-2626(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2009-54-18-2615 [5] DELOMBARD R, HROVAT K, KELLY E, et al. Interpreting the international space station microgravity environment[C]// Proceedings of the 43rd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2005. [6] LIU W, GAO Y, DONG W B, et al. Flight test results of the microgravity active vibration isolation system in China’s Tianzhou-1 mission[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2018, 30(6): 995-1009. doi: 10.1007/s12217-018-9659-9 [7] KLUMPP A R. Apollo lunar descent guidance[J]. Automatica (Journal of IFAC), 1974, 10(2): 133-146. doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(74)90019-3 [8] 孙军伟, 崔平远. 月球软着陆多项式制导控制方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2007, 28(5): 1171-1174,1218. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2007.05.019SUN J W, CUI P Y. Polynomial guidance law for lunar soft landing[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2007, 28(5): 1171-1174,1218(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2007.05.019 [9] ACıKMESE B, CARSON J M, BLACKMORE L. Lossless convexification of nonconvex control bound and pointing constraints of the soft landing optimal control problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2013, 21(6): 2104-2113. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2012.2237346 [10] ACIKMESE B, PLOEN S R. Convex programming approach to powered descent guidance for Mars landing[J]. Journal of Guidance Control Dynamics, 2007, 30(5): 1353-1366. doi: 10.2514/1.27553 [11] GERALDINK K T. People in control: Lars Blackmore[J]. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2016, 36(6): 24-26. [12] 邓云山, 夏元清, 孙中奇, 等. 扰动环境下火星精确着陆自主轨迹规划方法[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(11): 524834. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2021.24834DENG Y S, XIA Y Q, SUN Z Q, et al. Autonomous trajectory planning method for Mars precise landing in disturbed environment[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(11): 524834(in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2021.24834 [13] 王劲博, 崔乃刚, 郭继峰, 等. 火箭返回着陆问题高精度快速轨迹优化算法[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2018, 35(3): 389-398. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2017.70730WANG J B, CUI N G, GUO J F, et al. High precision rapid trajectory optimization algorithm for launch vehicle landing[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 35(3): 389-398(in Chinese). doi: 10.7641/CTA.2017.70730 [14] 中国载人航天办公室. 中国空间站科学实验资源手册[M]. 北京: 中国载人航天办公室, 2019.China Manned Space Office. China's Space Station science experiment resource manual[M]. Beijing: China Manned Space Office, 2019(in Chinese). [15] 刘伟. 空间高微重力悬浮平台控制技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2019.LIU W. Research on control technology of space high microgravity suspension platform[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019(in Chinese). -








 下载:
下载: